Promising Therapeutic Efficacy of GC1118, an Anti-EGFR Antibody, against KRAS Mutation-Driven Colorectal Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
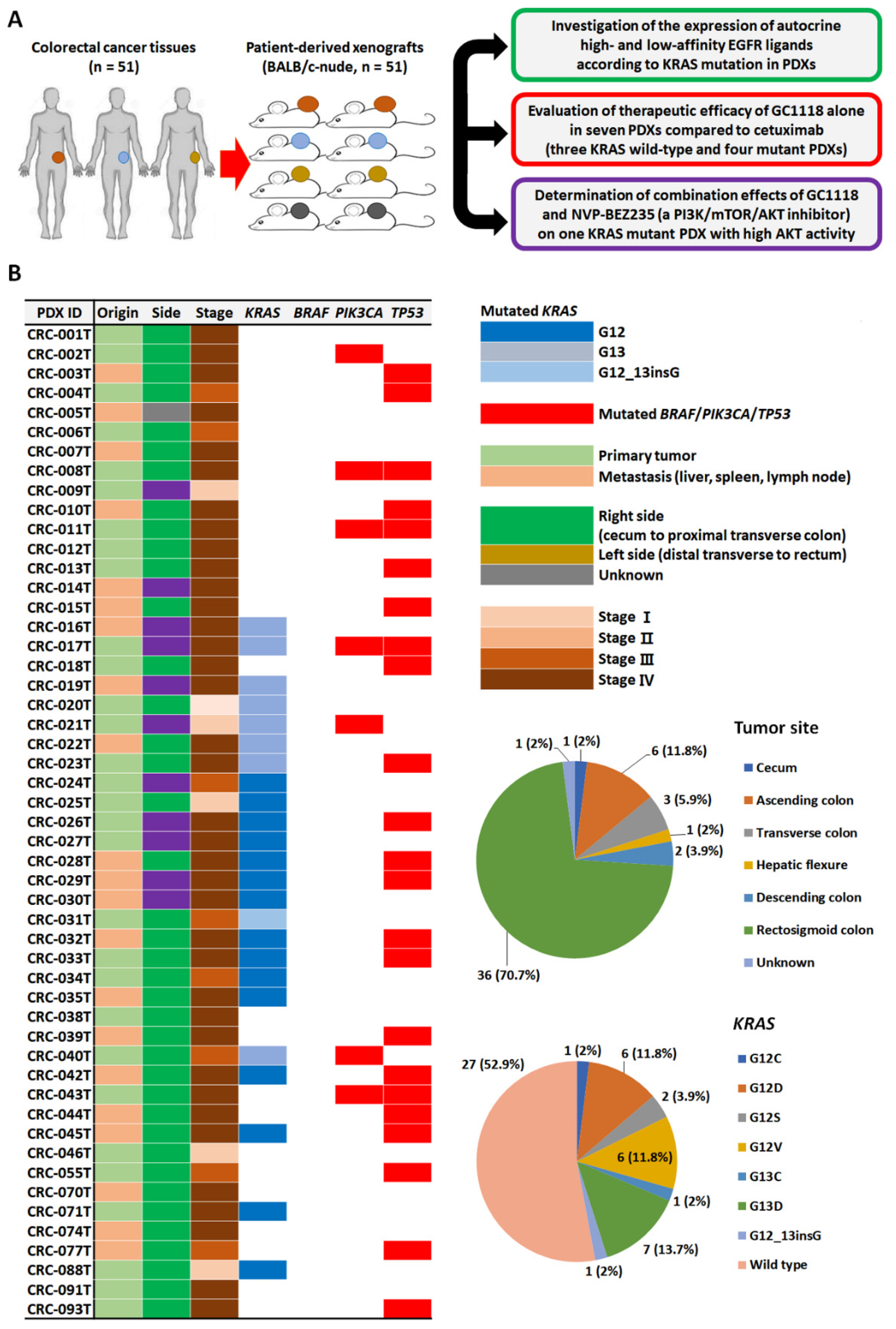
2.1. Genomic Characterization of CRC PDX Models and Expression Levels of High- and Low-Affinity EGFR Ligands According to KRAS Status
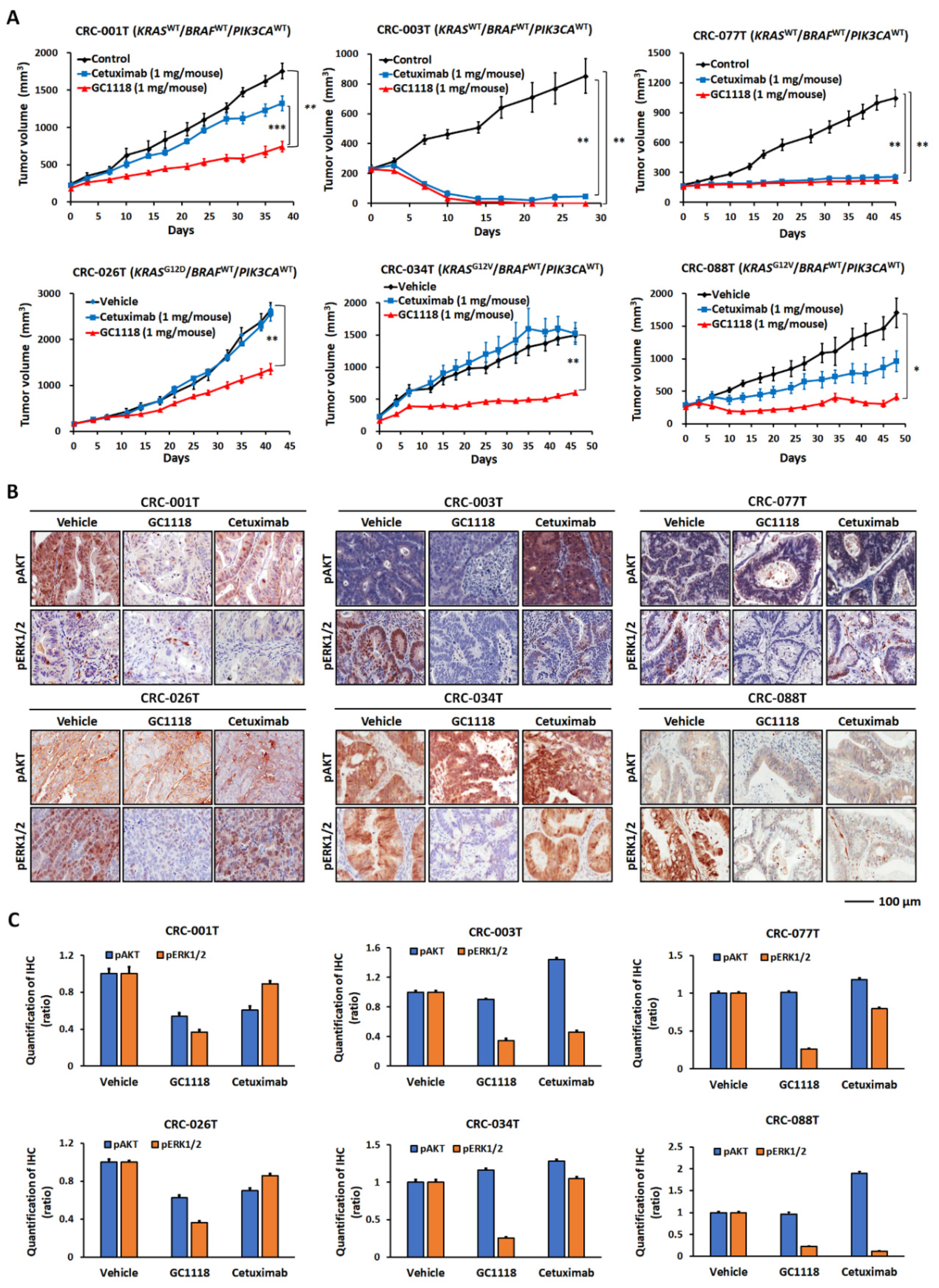
2.2. GC1118 is More Active Than Cetuximab against KRAS-Mutant CRC PDXs
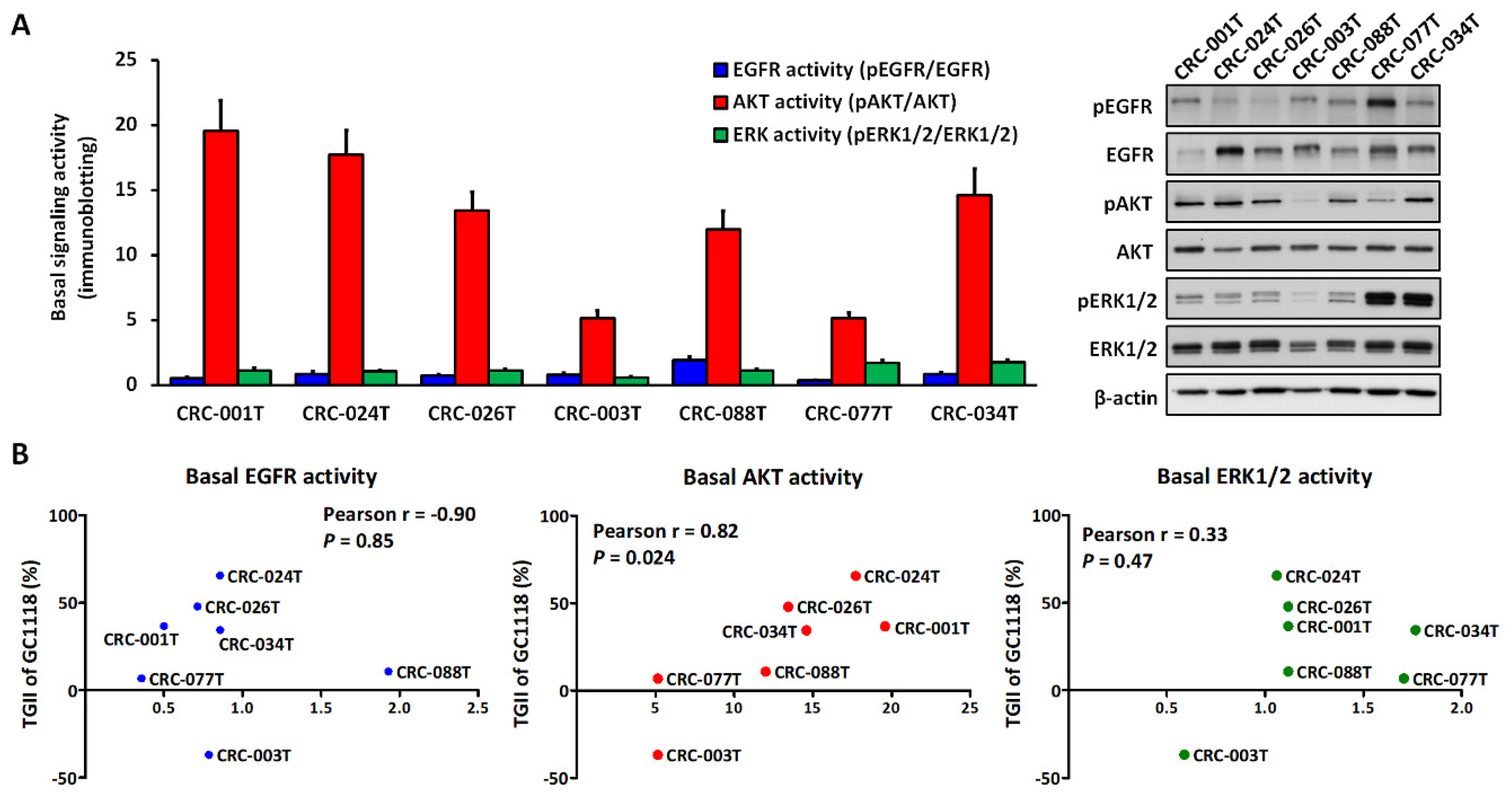
2.3. Activation of AKT Signaling Confers Resistance to GC1118 Monotherapy in KRAS-Mutant CRC PDX Models
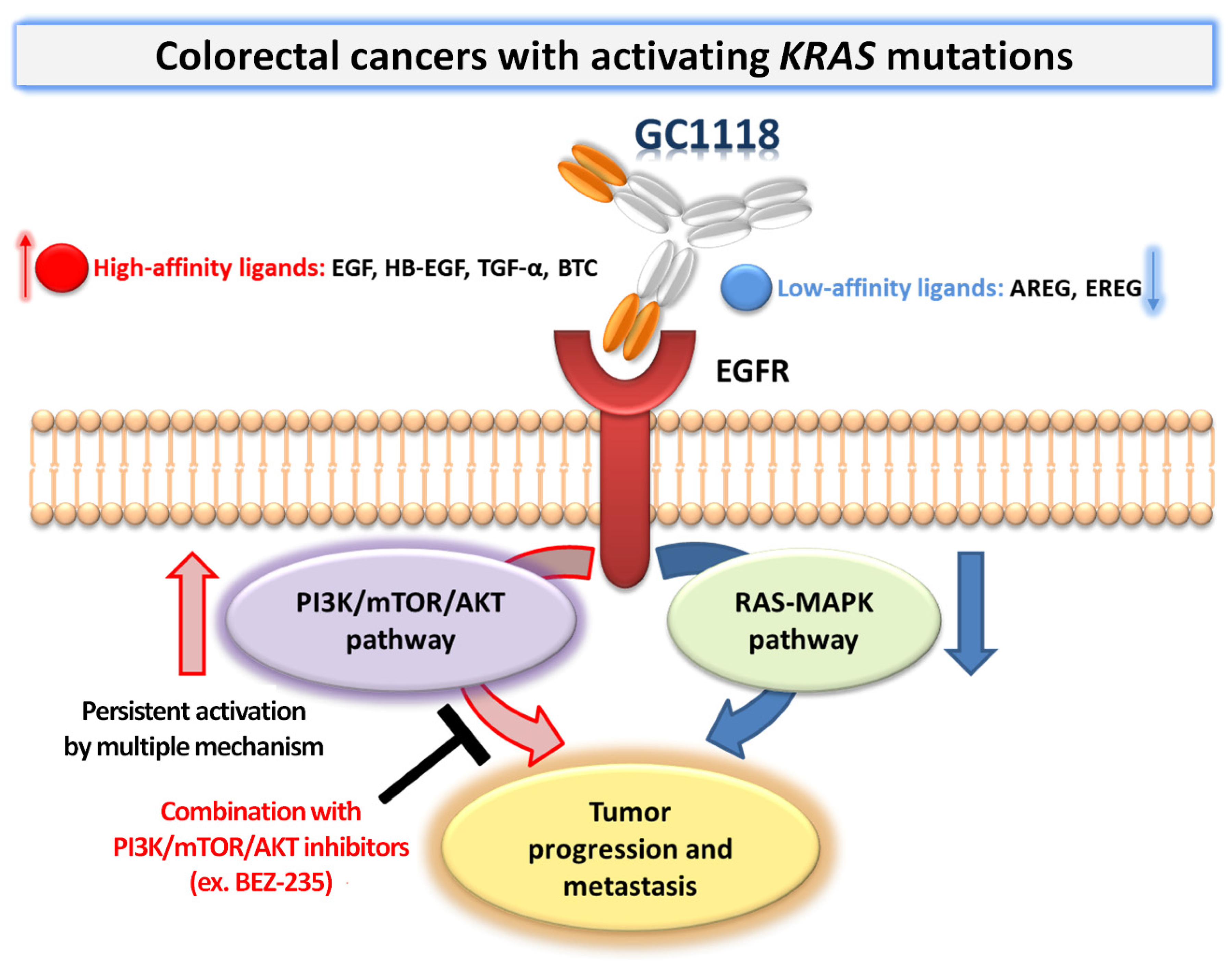
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. CRC Patient Clinical Information
4.2. Establishment of CRC PDXs and Analysis of EGFR Ligand Expression
4.3. In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy Evaluation Using a Panel of CRC PDX Models
4.4. IHC
4.5. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.6. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| mCRC | metastatic colorectal cancer |
| PDXs | patient-derived xenografts |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| IGF1R | insulin like growth factor 1 receptor |
| TGF-α | transforming growth factor α |
| HB-EGF | heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor |
| BTC | betacellulin |
| AREG | amphiregulin |
| EREG | Epiregulin |
| RAS | rat sarcoma |
| RAF | rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma |
| ADCC | antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| KRAS | KRAS proto-oncogene GTPase |
| PIK3CA | phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| TP53 | Tumor Protein P53 |
| MEK | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
| BALB | Bagg albino |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
References
- Riihimaki, M.; Hemminki, A.; Sundquist, J.; Hemminki, K. Patterns of metastasis in colon and rectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, S.; Zwenger, A.O.; Croce, M.V.; Abba, M.C.; Lacunza, E. From Molecular Biology to Clinical Trials: Toward Personalized Colorectal Cancer Therapy. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2016, 15, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Mattia, E.; Cecchin, E.; Toffoli, G. Pharmacogenomics of intrinsic and acquired pharmacoresistance in colorectal cancer: Toward targeted personalized therapy. Drug Resist. Updates 2015, 20, 39–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.A.; Yousef, Z.; Saleh, A.M.; Mohammad, S.; Al Knawy, B. Towards personalized medicine of colorectal cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 118, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.A.; Luwor, R.B.; Burgess, A.W. Epidermal growth factor receptor: Structure-function informing the design of anticancer therapeutics. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 371, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koustas, E.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Mihailidou, C.; Schizas, D.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Co-targeting of EGFR and autophagy signaling is an emerging treatment strategy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Yoo, J.; Kim, M.S.; Hur, M.; Lee, E.H.; Hur, H.S.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, S.N.; Park, T.W.; Lee, K.; et al. GC1118, an Anti-EGFR Antibody with a Distinct Binding Epitope and Superior Inhibitory Activity against High-Affinity EGFR Ligands. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Bronte, G.; Silvestris, N.; Castiglia, M.; Galvano, A.; Passiglia, F.; Sortino, G.; Cicero, G.; Rolfo, C.; Peeters, M.; Bazan, V.; et al. New findings on primary and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Do all roads lead to RAS? Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24780–24796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, L.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, M.; Sun, L.; Peng, P.; Yu, Q.; Yuan, X. Mechanisms of resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustoni, F.; Suda, K.; Yu, H.; Ren, S.; Rivard, C.J.; Ellison, K.; Caldwell, C., Jr.; Rozeboom, L.; Brovsky, K.; Hirsch, F.R. EGFR-directed monoclonal antibodies in combination with chemotherapy for treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: An updated review of clinical trials and new perspectives in biomarkers analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 72, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temraz, S.; Mukherji, D.; Shamseddine, A. Dual Inhibition of MEK and PI3K Pathway in KRAS and BRAF Mutated Colorectal Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22976–22988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roock, W.; De Vriendt, V.; Normanno, N.; Ciardiello, F.; Tejpar, S. KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, and PTEN mutations: Implications for targeted therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent-Puig, P.; Cayre, A.; Manceau, G.; Buc, E.; Bachet, J.B.; Lecomte, T.; Rougier, P.; Lievre, A.; Landi, B.; Boige, V.; et al. Analysis of PTEN, BRAF, and EGFR status in determining benefit from cetuximab therapy in wild-type KRAS metastatic colon cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5924–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misale, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer: From heterogeneity to convergent evolution. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirripa, M.; Procaccio, L.; Lonardi, S.; Loupakis, F. The role of pharmacogenetics in the new ESMO colorectal cancer guidelines. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, M.; Vakiani, E.; Zeng, Z.; Pratilas, C.A.; Taylor, B.S.; Chitale, D.; Halilovic, E.; Wilson, M.; Huberman, K.; Ricarte Filho, J.C.; et al. Genomic and biological characterization of exon 4 KRAS mutations in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5901–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.K.; Lucas, F.A.; Overman, M.J.; Eng, C.; Morelli, M.P.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Luthra, R.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Maru, D.; Scheet, P.; et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and gene expression analyses of non-KRAS 12/13, RAS-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupakis, F.; Ruzzo, A.; Cremolini, C.; Vincenzi, B.; Salvatore, L.; Santini, D.; Masi, G.; Stasi, I.; Canestrari, E.; Rulli, E.; et al. KRAS codon 61, 146 and BRAF mutations predict resistance to cetuximab plus irinotecan in KRAS codon 12 and 13 wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Jin, M.H.; Hur, M.; Nam, A.R.; Bang, J.H.; Won, J.; Oh, D.Y.; Bang, Y.J. GC1118, a novel anti-EGFR antibody, has potent KRAS mutation-independent antitumor activity compared with cetuximab in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligmann, J.F.; Elliott, F.; Richman, S.D.; Jacobs, B.; Hemmings, G.; Brown, S.; Barrett, J.H.; Tejpar, S.; Quirke, P.; Seymour, M.T. Combined Epiregulin and Amphiregulin Expression Levels as a Predictive Biomarker for Panitumumab Therapy Benefit or Lack of Benefit in Patients With RAS Wild-Type Advanced Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Han, S.W.; Kim, J.W.; Shin, J.W.; Jo, S.J.; Won, J.; Hahn, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, W.H.; et al. A First-in-Human Phase I Study of GC1118, a Novel Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Antibody, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1037-e636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swick, A.D.; Prabakaran, P.J.; Miller, M.C.; Javaid, A.M.; Fisher, M.M.; Sampene, E.; Ong, I.M.; Hu, R.; Iida, M.; Nickel, K.P.; et al. Cotargeting mTORC and EGFR Signaling as a Therapeutic Strategy in HNSCC. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, M.; Vrignaud, P.; Vacher, S.; Richon, S.; Lievre, A.; Cacheux, W.; Weiswald, L.B.; Massonnet, G.; Chateau-Joubert, S.; Nicolas, A.; et al. Evaluating patient-derived colorectal cancer xenografts as preclinical models by comparison with patient clinical data. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiampoura, A.; Raghav, K.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Menter, D.G.; Varkaris, A.; Morelli, M.P.; Manuel, S.; Wu, J.; Sorokin, A.V.; Rizi, B.S.; et al. Modeling of Patient-Derived Xenografts in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Yamaura, T.; Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Sakai, Y.; Taketo, M.M. A Chemosensitivity Study of Colorectal Cancer Using Xenografts of Patient-Derived Tumor-Initiating Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.S.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Pagano, N.C.; Poulikakos, P.I.; Scaltriti, M.; Moskatel, E.; Baselga, J.; Guichard, S.; Rosen, N. mTOR kinase inhibition causes feedback-dependent biphasic regulation of AKT signaling. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.N.; Fong, M.K.; Jagosky, M. Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers in the Era of Personalized Medicine. J. Pers Med. 2019, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambata-Ford, S.; Garrett, C.R.; Meropol, N.J.; Basik, M.; Harbison, C.T.; Wu, S.; Wong, T.W.; Huang, X.; Takimoto, C.H.; Godwin, A.K.; et al. Expression of epiregulin and amphiregulin and K-ras mutation status predict disease control in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3230–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, T.; Kitaura, K.; Miyata, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Kaneda, G.; Kanazawa, H.; Suzuki, S.; Hamada, Y.; Suzuki, R. Downregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor family receptors and ligands in a mutant K-ras group of patients with colorectal cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3514–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Lehmann, K.; Jefferies, H.B.; McMahon, M.; Downward, J. Analysis of the transcriptional program induced by Raf in epithelial cells. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauck, P.J.; Bagby, S.M.; Capasso, A.; Bradshaw-Pierce, E.L.; Selby, H.M.; Spreafico, A.; Tentler, J.J.; Tan, A.C.; Kim, J.; Arcaroli, J.J.; et al. Antitumor activity of the polo-like kinase inhibitor, TAK-960, against preclinical models of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmanno, K.; Chell, S.D.; Gillings, A.S.; Hayat, S.; Cook, S.J. Intrinsic resistance to the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) is associated with weak ERK1/2 signalling and/or strong PI3K signalling in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2332–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, S.; Jagani, Z.; Xiang, K.X.; Loo, A.; Dorsch, M.; Yao, Y.M.; Sellers, W.R.; Lengauer, C.; Stegmeier, F. PI3K pathway activation mediates resistance to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant cancers. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4286–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; D’Aiuto, E.; Morgillo, F.; Vitagliano, D.; Capasso, A.; Costantino, S.; Ciuffreda, L.P.; Merolla, F.; Vecchione, L.; et al. Antitumor activity of pimasertib, a selective MEK 1/2 inhibitor, in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitors or with multi-targeted kinase inhibitors in pimasertib-resistant human lung and colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, H.; Corcoran, R.B.; Singh, A.; Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Lifshits, E.; Ryan, D.P.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Benes, C.; Settleman, J.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinases exert dominant control over PI3K signaling in human KRAS mutant colorectal cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4311–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnekamp, J.F.; Wang, X.; Medema, J.P.; Vermeulen, L. Colorectal cancer heterogeneity and targeted therapy: A case for molecular disease subtypes. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehls, M.; Pfeifer, D.; Schorpp, M.; Hedrich, H.; Boehm, T. New member of the winged-helix protein family disrupted in mouse and rat nude mutations. Nature 1994, 372, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jifu, E.; Xing, J.; Gong, H.; He, J.; Zhang, W. Combine MEK inhibition with PI3K/mTOR inhibition exert inhibitory tumor growth effect on KRAS and PIK3CA mutation CRC xenografts due to reduced expression of VEGF and matrix metallopeptidase-9. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Temraz, S.; Mukherji, D.; Shamseddine, A. Sequencing of treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: Where to fit the target. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, R.; Cowell, E.; Chou, J.F.; Gewirtz, A.N.; Borsu, L.; Vakiani, E.; Solit, D.B.; Rosen, N.; Capanu, M.; Ladanyi, M.; et al. RAS mutations affect pattern of metastatic spread and increase propensity for brain metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer 2015, 121, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Xia, D.; Xu, E.; Lai, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Mutations of key driver genes in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaj, C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Lamprecht, S.; Hermeking, H.; Jung, A.; Kirchner, T.; Horst, D. Oncogenic Effects of High MAPK Activity in Colorectal Cancer Mark Progenitor Cells and Persist Irrespective of RAS Mutations. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Salazar, R.; Tabernero, J. Overcoming Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2015, 35, e149–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentheroudakis, G.; Kotoula, V.; De Roock, W.; Kouvatseas, G.; Papakostas, P.; Makatsoris, T.; Papamichael, D.; Xanthakis, I.; Sgouros, J.; Televantou, D.; et al. Biomarkers of benefit from cetuximab-based therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Interaction of EGFR ligand expression with RAS/RAF, PIK3CA genotypes. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Vilar, E.; Tabernero, J. Molecular predictors of response to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer J. 2011, 17, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelwatty, S.; Essapen, S.; Bagwan, I.; Green, M.; Seddon, A.; Modjtahedi, H. The impact of co-expression of wild-type EGFR and its ligands determined by immunohistochemistry for response to treatment with cetuximab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 7666–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobor, S.; Van Emburgh, B.O.; Crowley, E.; Misale, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Bardelli, A. TGFalpha and amphiregulin paracrine network promotes resistance to EGFR blockade in colorectal cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6429–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; Napolitano, S.; Vitagliano, D.; Ciuffreda, L.P.; Costantino, S.; Morgillo, F.; Capasso, A.; Sforza, V.; Nappi, A.; et al. Increased TGF-alpha as a mechanism of acquired resistance to the anti-EGFR inhibitor cetuximab through EGFR-MET interaction and activation of MET signaling in colon cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6751–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihle, N.T.; Lemos, R., Jr.; Wipf, P.; Yacoub, A.; Mitchell, C.; Siwak, D.; Mills, G.B.; Dent, P.; Kirkpatrick, D.L.; Powis, G. Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway predict for antitumor activity of the inhibitor PX-866 whereas oncogenic Ras is a dominant predictor for resistance. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sos, M.L.; Fischer, S.; Ullrich, R.; Peifer, M.; Heuckmann, J.M.; Koker, M.; Heynck, S.; Stuckrath, I.; Weiss, J.; Fischer, F.; et al. Identifying genotype-dependent efficacy of single and combined PI3K- and MAPK-pathway inhibition in cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18351–18356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halilovic, E.; She, Q.B.; Ye, Q.; Pagliarini, R.; Sellers, W.R.; Solit, D.B.; Rosen, N. PIK3CA mutation uncouples tumor growth and cyclin D1 regulation from MEK/ERK and mutant KRAS signaling. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6804–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janku, F.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Wang, X.; Luthra, R.; Hong, D.S.; Naing, A.; Falchook, G.S.; Moroney, J.W.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; et al. PIK3CA mutations in patients with advanced cancers treated with PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haagensen, E.J.; Kyle, S.; Beale, G.S.; Maxwell, R.J.; Newell, D.R. The synergistic interaction of MEK and PI3K inhibitors is modulated by mTOR inhibition. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.S.; Karapetis, C.S. Personalized treatment for advanced colorectal cancer: KRAS and beyond. Cancer Manag. Res. 2013, 5, 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Vitiello, P.P.; Cardone, C.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Belli, V.; Matrone, N.; Barra, G.; Napolitano, S.; Della Corte, C.; Turano, M.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinase-dependent PI3K activation is an escape mechanism to vertical suppression of the EGFR/RAS/MAPK pathway in KRAS-mutated human colorectal cancer cell lines. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, V.; Rosa, R.; D’Amato, C.; Formisano, L.; Marciano, R.; Nappi, L.; Raimondo, L.; Di Mauro, C.; Servetto, A.; Fusciello, C.; et al. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PKI-587 enhances sensitivity to cetuximab in EGFR-resistant human head and neck cancer models. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2887–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, S.; Wei, F.; Bellail, A.C.; Hao, C.; Liu, T. Simultaneous targeting of EGFR and mTOR inhibits the growth of colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Belmont, P.J.; Jiang, P.; McKee, T.D.; Xie, T.; Isaacson, J.; Baryla, N.E.; Roper, J.; Sinnamon, M.J.; Lee, N.V.; Kan, J.L.; et al. Resistance to dual blockade of the kinases PI3K and mTOR in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer models results in combined sensitivity to inhibition of the receptor tyrosine kinase EGFR. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutten, B.; Rouschop, K.M. EGFR signaling and autophagy dependence for growth, survival, and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharewicz, K.; Dudkowska, M.; Zawadzka, A.; Ogrodnik, M.; Szczepankiewicz, A.A.; Czarnocki, Z.; Sikora, E. Simultaneous induction and blockade of autophagy by a single agent. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Baehrecke, E.H. Autophagy, cell death, and cancer. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 2, e985913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, S.; Lochhead, P.; Giovannucci, E.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Fuchs, C.S.; Chan, A.T. Discovery of colorectal cancer PIK3CA mutation as potential predictive biomarker: Power and promise of molecular pathological epidemiology. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, M.; Morikawa, T.; Kuchiba, A.; Imamura, Y.; Qian, Z.R.; Nishihara, R.; Liao, X.; Waldron, L.; Hoshida, Y.; Huttenhower, C.; et al. Assessment of colorectal cancer molecular features along bowel subsites challenges the conception of distinct dichotomy of proximal versus distal colorectum. Gut 2012, 61, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, M.; Lochhead, P.; Morikawa, T.; Huttenhower, C.; Chan, A.T.; Giovannucci, E.; Fuchs, C.; Ogino, S. Colorectal cancer: A tale of two sides or a continuum? Gut 2012, 61, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Morikawa, T.; Lochhead, P.; Imamura, Y.; Kuchiba, A.; Yamauchi, M.; Nosho, K.; Qian, Z.R.; Nishihara, R.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; et al. Prognostic role of PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer: Cohort study and literature review. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barault, L.; Veyrie, N.; Jooste, V.; Lecorre, D.; Chapusot, C.; Ferraz, J.M.; Lievre, A.; Cortet, M.; Bouvier, A.M.; Rat, P.; et al. Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI(3)K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a population-based series of colon cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2255–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roock, W.; Claes, B.; Bernasconi, D.; De Schutter, J.; Biesmans, B.; Fountzilas, G.; Kalogeras, K.T.; Kotoula, V.; Papamichael, D.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: A retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tol, J.; Dijkstra, J.R.; Klomp, M.; Teerenstra, S.; Dommerholt, M.; Vink-Borger, M.E.; van Cleef, P.H.; van Krieken, J.H.; Punt, C.J.; Nagtegaal, I.D. Markers for EGFR pathway activation as predictor of outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with or without cetuximab. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, P.G.; Colangelo, L.H.; Fumagalli, D.; Tanaka, N.; Remillard, M.Y.; Yothers, G.; Kim, C.; Taniyama, Y.; Kim, S.I.; Choi, H.J.; et al. Mutation profiling and microsatellite instability in stage II and III colon cancer: An assessment of their prognostic and oxaliplatin predictive value. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6531–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Tang, Y. PIK3CA mutation is associated with poor survival among patients with metastatic colorectal cancer following anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody therapy: A meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubaker, J.; Bavi, P.; Al-Harbi, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Siraj, A.K.; Al-Sanea, N.; Abduljabbar, A.; Ashari, L.H.; Alhomoud, S.; Al-Dayel, F.; et al. Clinicopathological analysis of colorectal cancers with PIK3CA mutations in Middle Eastern population. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3539–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosho, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Ohnishi, M.; Suemoto, Y.; Kirkner, G.J.; Zepf, D.; Yan, L.; Longtine, J.A.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ogino, S. PIK3CA mutation in colorectal cancer: Relationship with genetic and epigenetic alterations. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velho, S.; Oliveira, C.; Ferreira, A.; Ferreira, A.C.; Suriano, G.; Schwartz, S., Jr.; Duval, A.; Carneiro, F.; Machado, J.C.; Hamelin, R.; et al. The prevalence of PIK3CA mutations in gastric and colon cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Liao, X.; Lochhead, P.; Kuchiba, A.; Yamauchi, M.; Qian, Z.R.; Nishihara, R.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Haigis, K.M.; et al. Specific mutations in KRAS codons 12 and 13, and patient prognosis in 1075 BRAF wild-type colorectal cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4753–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, F.L.; Jorissen, R.N.; Lipton, L.; Mouradov, D.; Sakthianandeswaren, A.; Christie, M.; Li, S.; Tsui, C.; Tie, J.; Desai, J.; et al. PIK3CA and PTEN gene and exon mutation-specific clinicopathologic and molecular associations in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simi, L.; Pratesi, N.; Vignoli, M.; Sestini, R.; Cianchi, F.; Valanzano, R.; Nobili, S.; Mini, E.; Pazzagli, M.; Orlando, C. High-resolution melting analysis for rapid detection of KRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA gene mutations in colorectal cancer. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 130, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehall, V.L.; Rickman, C.; Bond, C.E.; Ramsnes, I.; Greco, S.A.; Umapathy, A.; McKeone, D.; Faleiro, R.J.; Buttenshaw, R.L.; Worthley, D.L.; et al. Oncogenic PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancers and polyps. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosty, C.; Young, J.P.; Walsh, M.D.; Clendenning, M.; Sanderson, K.; Walters, R.J.; Parry, S.; Jenkins, M.A.; Win, A.K.; Southey, M.C.; et al. PIK3CA activating mutation in colorectal carcinoma: Associations with molecular features and survival. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Greshock, J.; Holbrook, J.D.; Gilmartin, A.; Zhang, X.; McNeil, E.; Conway, T.; Moy, C.; Laquerre, S.; Bachman, K.; et al. Comprehensive predictive biomarker analysis for MEK inhibitor GSK1120212. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Simon, I.; Moreno, V.; Roepman, P.; Tabernero, J.; Snel, M.; van’t Veer, L.; Salazar, R.; Bernards, R.; Capella, G. A combined oncogenic pathway signature of BRAF, KRAS and PI3KCA mutation improves colorectal cancer classification and cetuximab treatment prediction. Gut 2013, 62, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Martini, M.; Molinari, F.; Veronese, S.; Nichelatti, M.; Artale, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Saletti, P.; De Dosso, S.; Mazzucchelli, L.; et al. PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with clinical resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenen, H.; De Schutter, J.; Jacobs, B.; De Roock, W.; Biesmans, B.; Claes, B.; Lambrechts, D.; Van Cutsem, E.; Tejpar, S. PIK3CA mutations are not a major determinant of resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3184–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhawer, M.; Goel, S.; Wilson, A.J.; Montagna, C.; Ling, Y.H.; Byun, D.S.; Nasser, S.; Arango, D.; Shin, J.; Klampfer, L.; et al. PIK3CA mutation/PTEN expression status predicts response of colon cancer cells to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cetuximab. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, F.; Lampis, A.; Orsenigo, M.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Gevorgyan, A.; Losa, M.; Frattini, M.; Riva, C.; Andreola, S.; Bajetta, E.; et al. PI3KCA/PTEN deregulation contributes to impaired responses to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, S.; Nosho, K.; Kirkner, G.J.; Shima, K.; Irahara, N.; Kure, S.; Chan, A.T.; Engelman, J.A.; Kraft, P.; Cantley, L.C.; et al. PIK3CA mutation is associated with poor prognosis among patients with curatively resected colon cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgenske, D.M.; Monsma, D.J.; Dylewski, D.; Scott, S.B.; Sayfie, A.D.; Kim, D.G.; Luchtefeld, M.; Martin, K.R.; Stephenson, P.; Hostetter, G.; et al. Establishment of genetically diverse patient-derived xenografts of colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 824–837. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, B.Y.; Lee, W.Y.; Jung, S.; Hong, H.K.; Nam, D.H.; Park, Y.A.; Huh, J.W.; Yun, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Chun, H.K.; et al. Correlation between tumor engraftment in patient-derived xenograft models and clinical outcomes in colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16059–16068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, I.; Molla, A.; Grazia, G.; Cleris, L.; Nicolini, G.; Perrone, F.; Picciani, B.; Del Vecchio, M.; de Braud, F.; Mortarini, R.; et al. Primary cross-resistance to BRAFV600E-, MEK1/2- and PI3K/mTOR-specific inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanoma cells counteracted by dual pathway blockade. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3947–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletsch, A.; Pinkerneil, M.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Jaguva Vasudevan, A.A.; Wang, C.; Hansen, F.K.; Wiek, C.; Hanenberg, H.; Gertzen, C.; Gohlke, H.; et al. Effects of novel HDAC inhibitors on urothelial carcinoma cells. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Peng, K.; Qiu, C.; Skibba, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Liang, D.; Zou, C.; et al. Novel Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Kidney Fibrosis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 356, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.W.; Son, E.; Lee, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-C.; Lim, Y.; Hur, M.; Kim, D.; Nam, D.-H. Promising Therapeutic Efficacy of GC1118, an Anti-EGFR Antibody, against KRAS Mutation-Driven Colorectal Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235894
Lee HW, Son E, Lee K, Lee Y, Kim Y, Lee J-C, Lim Y, Hur M, Kim D, Nam D-H. Promising Therapeutic Efficacy of GC1118, an Anti-EGFR Antibody, against KRAS Mutation-Driven Colorectal Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):5894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235894
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hye Won, Eunju Son, Kyoungmin Lee, Yeri Lee, Yejin Kim, Jae-Chul Lee, Yangmi Lim, Minkyu Hur, Donggeon Kim, and Do-Hyun Nam. 2019. "Promising Therapeutic Efficacy of GC1118, an Anti-EGFR Antibody, against KRAS Mutation-Driven Colorectal Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 5894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235894
APA StyleLee, H. W., Son, E., Lee, K., Lee, Y., Kim, Y., Lee, J.-C., Lim, Y., Hur, M., Kim, D., & Nam, D.-H. (2019). Promising Therapeutic Efficacy of GC1118, an Anti-EGFR Antibody, against KRAS Mutation-Driven Colorectal Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 5894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235894





