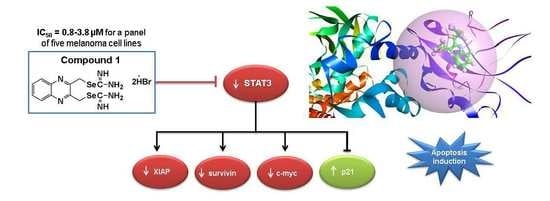
Identification of a Novel Quinoxaline-Isoselenourea Targeting the STAT3 Pathway as a Potential Melanoma Therapeutic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of Compounds 1, 2, and 3
2.2. Compounds 1 and 3 Reduced the Viability of Different Melanoma Cancer Cells
2.3. Compound 1 Suppressed the Proliferative Ability of Melanoma Cells (1205Lu and UACC903)
2.4. Compound 1 Increased Melanoma Cell Death in Vitro
2.5. Compound 1 Induced Apoptosis in Melanoma Cells
2.6. Compound 1 did not Inhibit the Phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2
2.7. Compound 1 Inhibited STAT3 and Related Proteins Expression
2.8. Compound 1 Induced the Cell Cycle Inhibitor p21
2.9. Compound 1 Inhibited the Phosphorylation of STAT3, Increased the Expression of p21, and Induced Apoptotic Cell Death in Different Melanoma Cell Lines
2.10. Docking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Viability
4.5. Colony Formation Assay
4.6. Live-and-Dead Assay
4.7. Annexin V Assay
4.8. Caspase-3/7 Assay
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Docking Methodology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| c-myc | Avian myelocytomatosis virus oncogene cellular homolog |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PARP | Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase |
| PBISe | Se,Se’-1,4-phenylenebis(1,2-ethanediyl)bisisoselenourea |
| PBIT | S,S’-1,4-phenylenebis(1,2-ethanediyl)bisisothiourea |
| PMSF | Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| XIAP | X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein |
References
- Leiter, U.; Eigentler, T.; Garbe, C. Epidemiology of skin cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 810, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Trolio, R.; Simeone, E.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Buonerba, C.; Ascierto, P.A. The use of interferon in melanoma patients: A systematic review. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzuka, A.; Huang, L.; Theodosakis, N.; Bosenberg, M. Melanoma treatments: Advances and mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 2626–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, G.; Bowman, T.; Huang, M.; Shivers, S.; Reintgen, D.; Daud, A.; Chang, A.; Kraker, A.; Jove, R.; Yu, H. Roles of activated Src and Stat3 signaling in melanoma tumor cell growth. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7001–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, T.X.; Wei, D.; Liu, M.; Gao, A.C.; Ali-Osman, F.; Sawaya, R.; Huang, S. Stat3 activation regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3550–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siveen, K.S.; Sikka, S.; Surana, R.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusaba, T.; Nakayama, T.; Yamazumi, K.; Yakata, Y.; Yoshizaki, A.; Inoue, K.; Nagayasu, T.; Sekine, I. Activation of STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strickland, L.R.; Pal, H.C.; Elmets, C.A.; Afaq, F. Targeting drivers of melanoma with synthetic small molecules and phytochemicals. Cancer Lett. 2015, 359, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, N.; Schwan, J.V.; Fujita, M.; Norris, D.A.; Shellman, Y.G. Alternative treatments for melanoma: Targeting Bcl-2 family members to de-bulk and kill cancer stem cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Cao, J.; Wu, J.; Sullivan, K.; Shen, J.; Ryu, B.; Xu, Z.; Wei, W.; Cui, R. Stat3-targeted therapies overcome the acquired resistance to vemurafenib in melanomas. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, T.M.; Boyd, S.C.; Mijatov, B.; Gowrishankar, K.; Snoyman, S.; Pupo, G.M.; Scolyer, R.A.; Mann, G.J.; Kefford, R.F.; Zhang, X.D.; et al. Mutant B-RAF-Mcl-1 survival signaling depends on the STAT3 transcription factor. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.P.; Gandin, V. Selenium compounds as therapeutic agents in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 1642–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Desai, D.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Huh, S.J.; Robertson, G.P.; Amin, S. Synthesis and anticancer activity comparison of phenylalkyl isoselenocyanates with corresponding naturally occurring and synthetic isothiocyanates. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7820–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Prabhu, K.S.; Mastro, A.M. Is selenium a potential treatment for cancer metastasis? Nutrients 2013, 5, 1149–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Desai, D.; Huh, S.J.; Mosca, P.; Amin, S.; Robertson, G.P. Targeting Akt3 signaling in malignant melanoma using isoselenocyanates. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Sharma, A.; Nguyen, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Desai, D.; Huh, S.J.; Amin, S.; Meyers, C.; Robertson, G.P. Melanoma chemoprevention in skin reconstructs and mouse xenografts using isoselenocyanate-4. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, P.B.; Fain, H.D.; Cassidy, J.P., Jr.; Tran, S.M.; Moos, P.J.; Boucher, K.M.; Gerads, R.; Florell, S.R.; Grossman, D.; Leachman, S.A. Selenium for the prevention of cutaneous melanoma. Nutrients 2013, 5, 725–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhunapantula, S.V.; Desai, D.; Sharma, A.; Huh, S.J.; Amin, S.; Robertson, G.P. PBISe, a novel selenium-containing drug for the treatment of malignant melanoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karelia, D.N.; Sk, U.H.; Singh, P.; Gowda, A.S.P.; Pandey, M.K.; Ramisetti, S.R.; Amin, S.; Sharma, A.K. Design, synthesis, and identification of a novel napthalamide-isoselenocyanate compound NISC-6 as a dual Topoisomerase-IIalpha and Akt pathway inhibitor, and evaluation of its anti-melanoma activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 135, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Desai, D.; Amin, S.; Robertson, G.P. Melanoma prevention using topical PBISe. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcolea, V.; Plano, D.; Karelia, D.N.; Palop, J.A.; Amin, S.; Sanmartin, C.; Sharma, A.K. Novel seleno- and thio-urea derivatives with potent in vitro activities against several cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 113, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez, E.; Plano, D.; Font, M.; Calvo, A.; Prior, C.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartin, C. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of novel symmetrical alkylthio- and alkylseleno-imidocarbamates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcolea, V.; Plano, D.; Encio, I.; Palop, J.A.; Sharma, A.K.; Sanmartin, C. Chalcogen containing heterocyclic scaffolds: New hybrids with antitumoral activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Engeland, M.; Nieland, L.J.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Schutte, B.; Reutelingsperger, C.P. Annexin V-affinity assay: A review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine exposure. Cytometry 1998, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, J.M.; Sharma, A.; Cheung, M.; Zimmerman, M.; Cheng, J.Q.; Bosenberg, M.W.; Kester, M.; Sandirasegarane, L.; Robertson, G.P. Deregulated Akt3 activity promotes development of malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7002–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Borrow, J.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Nguyen, T.; Hersey, P. Activation of ERK1/2 protects melanoma cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibiting Smac/DIABLO release from mitochondria. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2869–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fofaria, N.M.; Srivastava, S.K. Critical role of STAT3 in melanoma metastasis through anoikis resistance. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7051–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiuchi, N.; Nakajima, K.; Ichiba, M.; Fukada, T.; Narimatsu, M.; Mizuno, K.; Hibi, M.; Hirano, T. STAT3 is required for the gp130-mediated full activation of the c-myc gene. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishdorj, G.; Johnston, J.B.; Gibson, S.B. Inhibition of constitutive activation of STAT3 by curcurbitacin-I (JSI-124) sensitized human B-leukemia cells to apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 3302–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldani, C.; Scovassi, A.I. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: An update. Apoptosis 2002, 7, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coqueret, O.; Gascan, H. Functional interaction of STAT3 transcription factor with the cell cycle inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18794–18800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Groner, B.; Muller, C.W. Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3beta homodimer bound to DNA. Nature 1998, 394, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Robertson, D.H.; Brooks, C.L., 3rd; Vieth, M. Detailed analysis of grid-based molecular docking: A case study of CDOCKER-A CHARMm-based MD docking algorithm. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Deng, C.; Yang, L.; Yan, E.; Guo, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.X. Mechanism of the inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway by EGCG. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2691–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Kee, W.H.; Seow, K.T.; Fung, W.; Cao, X. The coiled-coil domain of Stat3 is essential for its SH2 domain-mediated receptor binding and subsequent activation induced by epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 7132–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Xiao, H.; Lin, J.; Li, C. Discovery of novel STAT3 small molecule inhibitors via in silico site-directed fragment-based drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4402–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, D.; Cisek, K.; Pandharkar, T.; Regan, N.; Li, C.; Pandit, B.; Lin, J.; Li, P.K. Design, synthesis, and studies of small molecule STAT3 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Lee, J.T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cho, H.; Mamo, S.; Bremer, R.; Gillette, S.; Kong, J.; Haass, N.K.; et al. Discovery of a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent antimelanoma activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanmartin, C.; Plano, D.; Palop, J.A. Selenium compounds and apoptotic modulation: A new perspective in cancer therapy. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagaram, H.R.; Desai, D.; Li, G.; Liu, D.; Rountree, C.B.; Gowda, K.; Berg, A.; Amin, S.; Staveley-O’Carroll, K.F.; Kimchi, E.T. A Selenium Containing Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.J.; Snowden, J.A.; Zeidler, M.P.; Danson, S.J. The role of JAK/STAT signalling in the pathogenesis, prognosis and treatment of solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotti, M.R.; Pedersen, M.; Sanchez-Laorden, B.; Viros, A.; Turajlic, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Zambon, A.; Sinclair, J.; Hayes, A.; Gore, M.; et al. Inhibiting EGF receptor or SRC family kinase signaling overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuazo, A.; Plano, D.; Anso, E.; Lizarraga, E.; Font, M.; Martinez Irujo, J.J. Cytotoxic and proapototic activities of imidoselenocarbamate derivatives are dependent on the release of methylselenol. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2479–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Comp. | Time (h) | Cell Lines | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM2664 | 1205Lu | A375M | UACC903 | CHL-1 | ||
| 1 | 24 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 2.6 ± 1.0 | 3.8 ± 1.6 | 2.9 ± 0.4 |
| 48 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.4 | |
| 72 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | |
| 3 | 24 | 32.7 ± 3.6 | 33.7 ± 10.1 | 38.7 ± 1.0 | 32.6 ± 1.9 | 29.3 ± 10.6 |
| 48 | 21.0 ± 2.9 | 11.3 ± 3.0 | 21.3 ± 0.8 | 24.7 ± 2.3 | 12.3 ± 2.2 | |
| 72 | 22.8 ± 7.0 | 8.3 ± 0.9 | 8.1 ± 4.2 | 22.3 ± 5.6 | 13.6 ± 1.7 | |
| PLX-4032 | 24 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | 38.5 ± 7.2 | >50.0 |
| 48 | 32.1 ± 14.2 | 31.4 ± 8.0 | 3.5 ± 1.1 | 10.3 ± 2.6 | 21.2 ± 3.4 | |
| 72 | 3.6 ± 1.5 | 9.3 ± 3.4 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 17.9 ± 1.3 | 12.2 ± 1.5 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcolea, V.; Karelia, D.N.; Pandey, M.K.; Plano, D.; Singh, P.; Palop, J.A.; Amin, S.; Sanmartín, C.; Sharma, A.K. Identification of a Novel Quinoxaline-Isoselenourea Targeting the STAT3 Pathway as a Potential Melanoma Therapeutic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030521
Alcolea V, Karelia DN, Pandey MK, Plano D, Singh P, Palop JA, Amin S, Sanmartín C, Sharma AK. Identification of a Novel Quinoxaline-Isoselenourea Targeting the STAT3 Pathway as a Potential Melanoma Therapeutic. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(3):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030521
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcolea, Verónica, Deepkamal N. Karelia, Manoj K. Pandey, Daniel Plano, Parvesh Singh, Juan Antonio Palop, Shantu Amin, Carmen Sanmartín, and Arun K. Sharma. 2019. "Identification of a Novel Quinoxaline-Isoselenourea Targeting the STAT3 Pathway as a Potential Melanoma Therapeutic" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 3: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030521
APA StyleAlcolea, V., Karelia, D. N., Pandey, M. K., Plano, D., Singh, P., Palop, J. A., Amin, S., Sanmartín, C., & Sharma, A. K. (2019). Identification of a Novel Quinoxaline-Isoselenourea Targeting the STAT3 Pathway as a Potential Melanoma Therapeutic. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(3), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030521