Platinum(II) O,S Complexes Inhibit the Aggregation of Amyloid Model Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
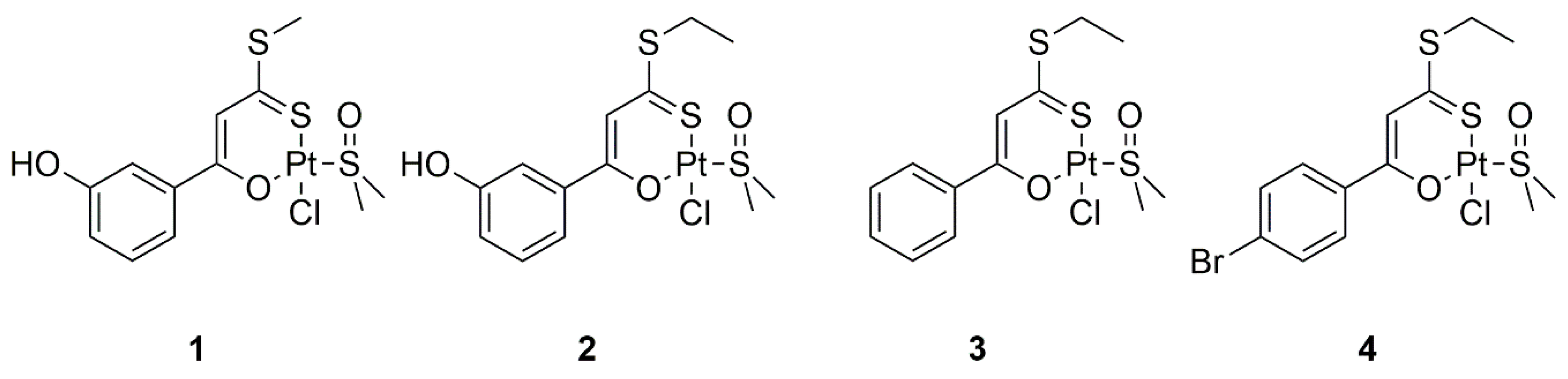
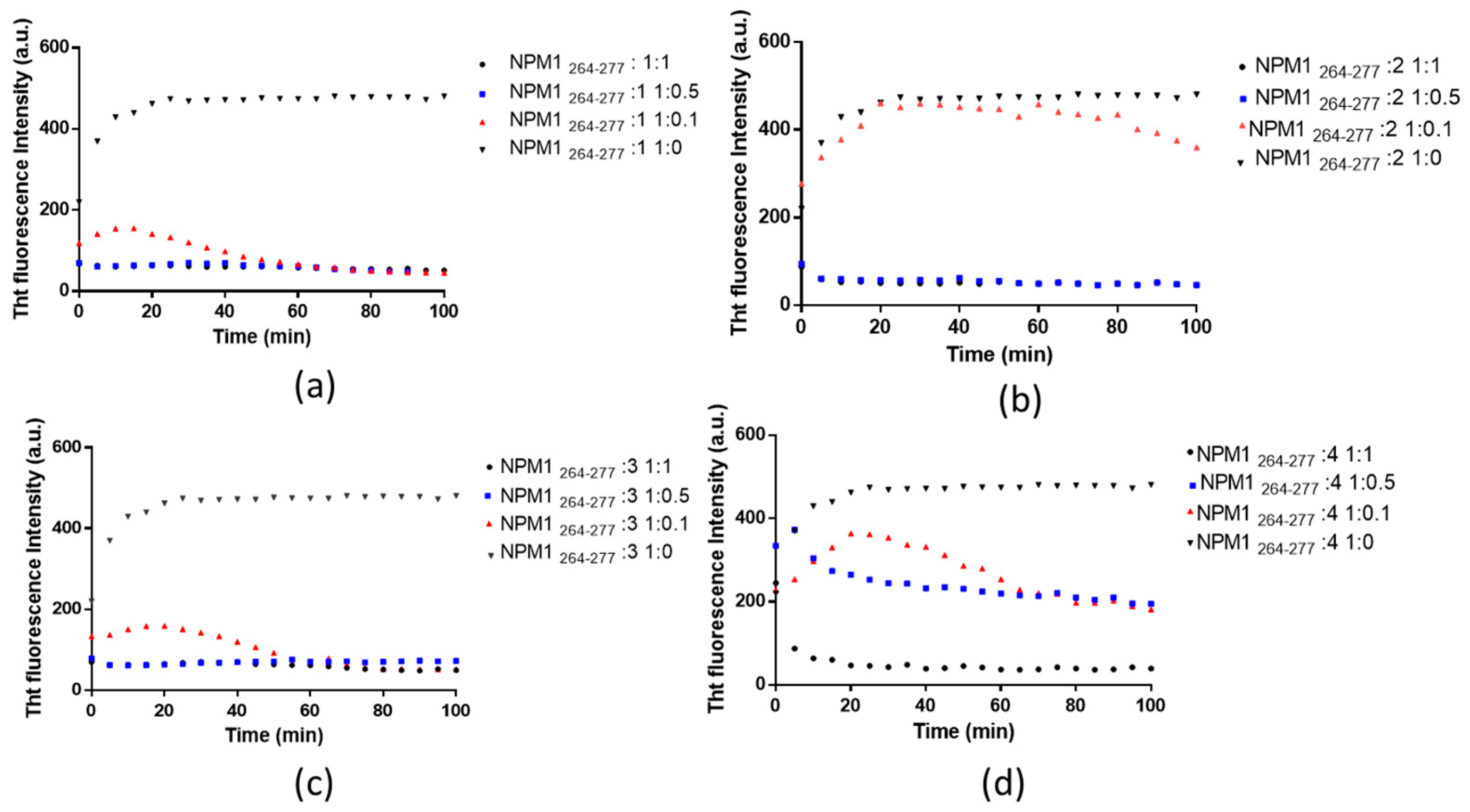
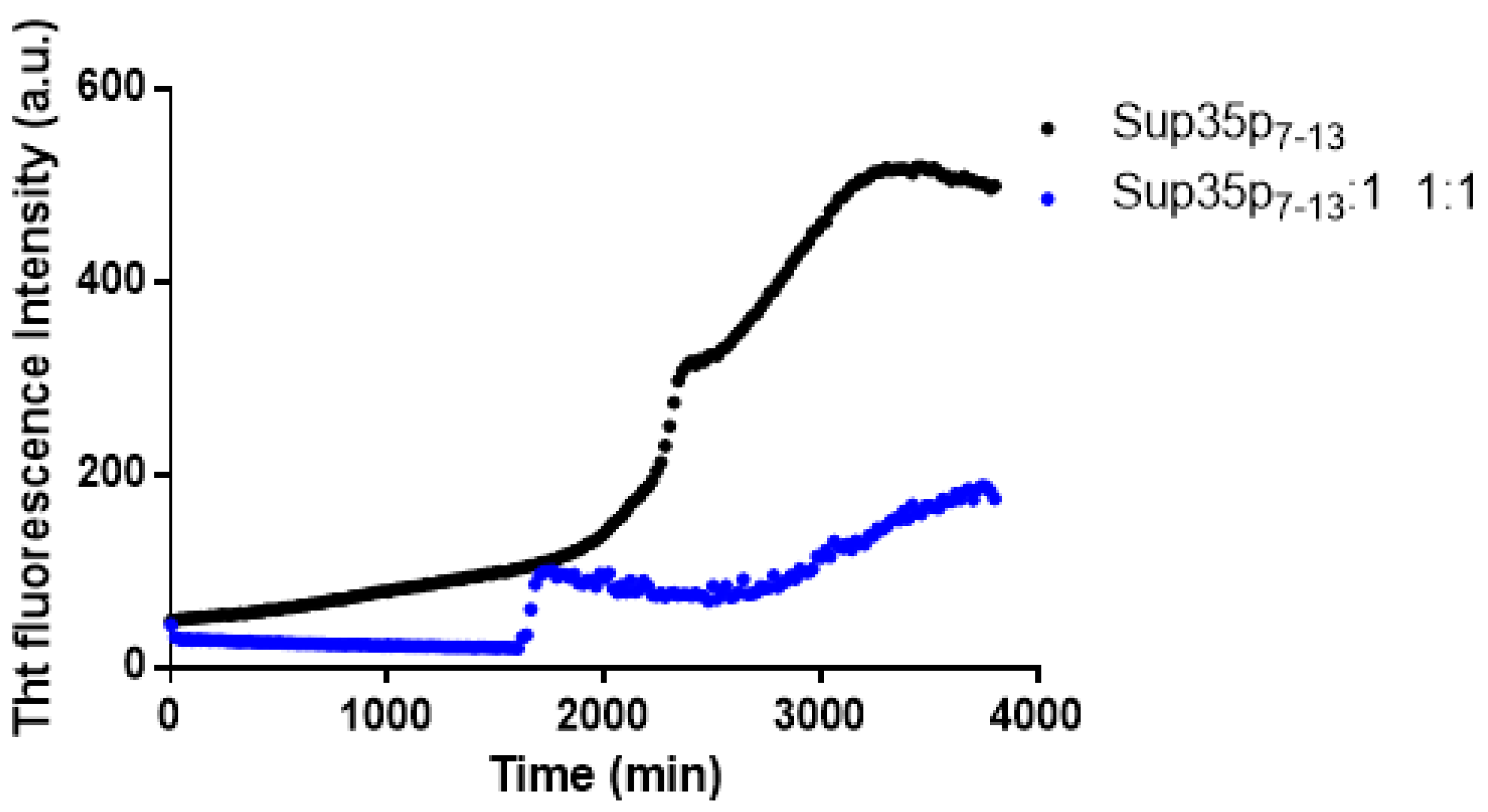
2.1. Pt(II) Complexes with Bidentate Ligands Inhibit the Aggregation of Amyloidogenic Peptides
2.2. Pt Complexes Inhibit Conformational β-Transition
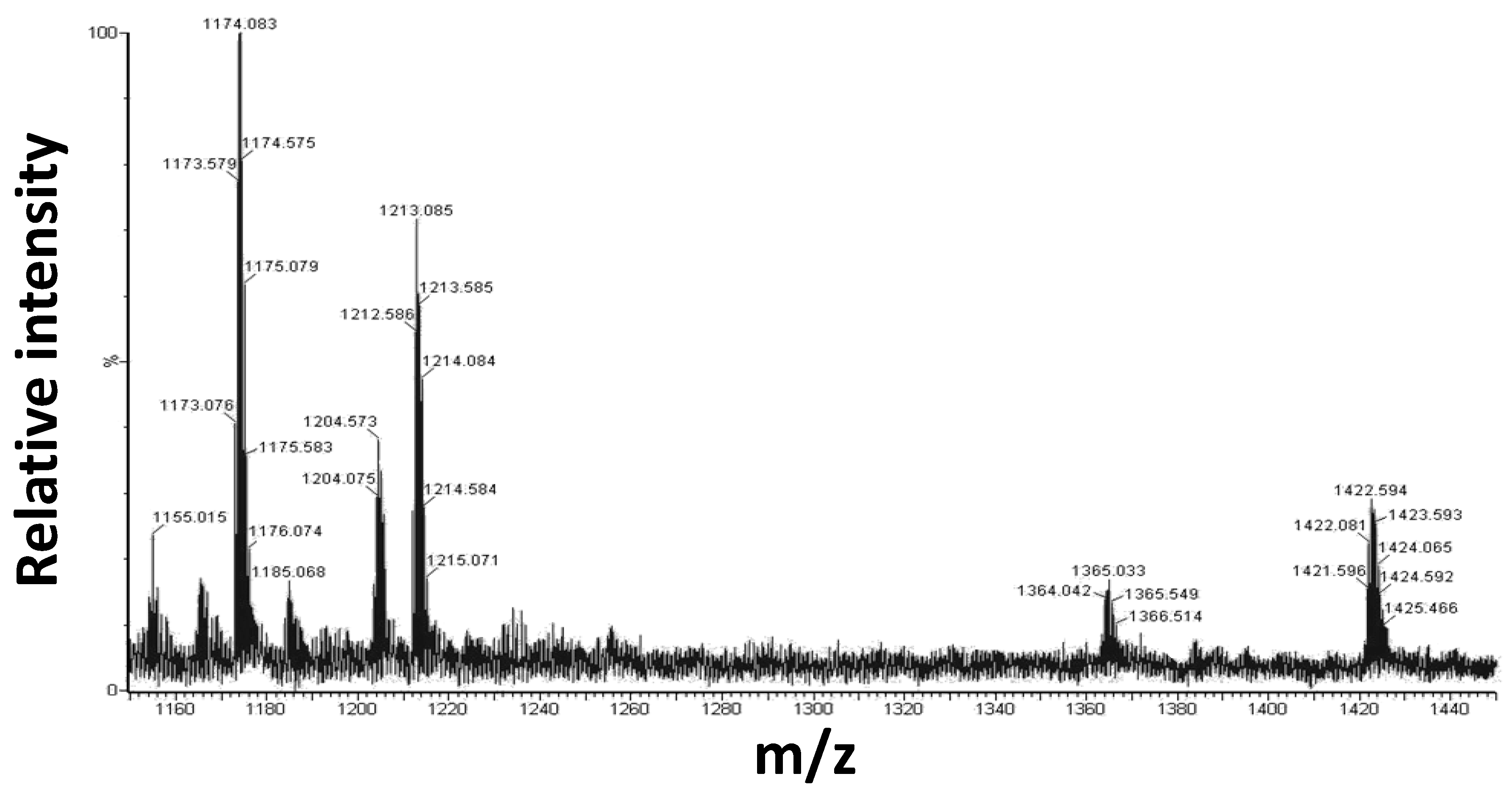
2.3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.4. Inhibition of Cytotoxic Effects of NPM1264–277 Peptide in SH-SY5Y Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Peptide Synthesis
3.2. Synthesis of the Complexes
3.3. Fluorescence Assays
3.4. Far-UV CD Spectroscopy
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. MTT Reduction Assay
3.7. ESI MS Analysis of the Complexes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ1–16 | The peptide encompassing residues 1–16 of the Aβ peptide |
| Aβ21–40 | The peptide encompassing residues 21–40 of the Aβ peptide |
| cisplatin | cis-Pt(NH3)2Cl2 |
| CD | circular dichroism |
| hIAPP | human islet amyloid polypeptide |
| H2 | Helix 2 (residues 264–277) C-terminal domain of nucleophosmin 1 |
| HFIP | hexafluoroisopropanol |
| MOA | Mechanism of action |
| NPM1 | Nucleophosmin 1 |
| NPM1264–277 | Residues of helix 2 of Nucleophosmin 1 |
| Pt-phen | Phenanthroline-based Pt compounds |
| phen | 1,10-phenanthroline |
| PrP | Prion protein |
| Sup35p | Yeast Prion Protein |
| Sup35p7–13 | Residues 7–13 (sequence:GNNQQNY) of Sup35p |
| ThT | thioflavin T |
References
- Takahara, P.M.; Rosenzweig, A.C.; Frederick, C.A.; Lippard, S.J. Crystal structure of double-stranded DNA containing the major adduct of the anticancer drug cisplatin. Nature 1995, 377, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A.; Mastrobuoni, G.; Temperini, C.; Gabbiani, C.; Francese, S.; Moneti, G.; Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A.; Messori, L. ESI mass spectrometry and X-ray diffraction studies of adducts between anticancer platinum drugs and hen egg white lysozyme. Chem. Commun. 2007, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanley, S.W.; Diederichs, K.; Kroon-Batenburg, L.M.; Levy, C.; Schreurs, A.M.; Helliwell, J.R. Carboplatin binding to histidine. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2014, 70, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanley, S.W.; Diederichs, K.; Kroon-Batenburg, L.M.; Levy, C.; Schreurs, A.M.; Helliwell, J.R. Response from Tanley et al. to Crystallography and chemistry should always go together: A cautionary tale of protein complexes with cisplatin and carboplatin. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 1982–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanley, S.W.; Helliwell, J.R. Structural dynamics of cisplatin binding to histidine in a protein. Struct. Dynam. 2014, 1, 034701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messori, L.; Marzo, T.; Michelucci, E.; Russo Krauss, I.; Navarro-Ranninger, C.; Quiroga, A.G.; Merlino, A. Interactions between anticancer trans-platinum compounds and proteins: Crystal structures and ESI-MS spectra of two protein adducts of trans-(dimethylamino)(methylamino)dichloridoplatinum(II). Inorgan. Chem. 2014, 53, 7806–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, L.; Merlino, A. Cisplatin binding to proteins: Molecular structure of the ribonuclease a adduct. Inorgan. Chem. 2014, 53, 3929–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Du, Y.; Cui, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Comprehensive identification of the binding sites of cisplatin in hen egg white lysozyme. Analyt. Bioanalyt. Chem. 2014, 406, 3537–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, G.; Pica, A.; Russo Krauss, I.; Pane, F.; Amoresano, A.; Merlino, A. Effect of temperature on the interaction of cisplatin with the model protein hen egg white lysozyme. J. Biol. Inorgan. Chem. 2016, 21, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, L.; Merlino, A. Cisplatin binding to proteins: A structural perspective. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2016, 315, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugge, C.; Marzo, T.; Massai, L.; Hildebrandt, J.; Ferraro, G.; Rivera-Fuentes, P.; Metzler-Nolte, N.; Merlino, A.; Messori, L.; Weigand, W. Platinum(II) Complexes with O,S Bidentate Ligands: Biophysical Characterization, Antiproliferative Activity, and Crystallographic Evidence of Protein Binding. Inorgan. Chem. 2015, 54, 8560–8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugge, C.; Liu, R.; Gorls, H.; Gabbiani, C.; Michelucci, E.; Rudiger, N.; Clement, J.H.; Messori, L.; Weigand, W. Novel platinum(II) compounds with O,S bidentate ligands: Synthesis, characterization, antiproliferative properties and biomolecular interactions. Dalton Transact. 2014, 43, 3072–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, G.; Marzo, T.; Infrasca, T.; Cilibrizzi, A.; Vilar, R.; Messori, L.; Merlino, A. A case of extensive protein platination: The reaction of lysozyme with a Pt(ii)-terpyridine complex. Dalton Transact. 2018, 47, 8716–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, G.; De Benedictis, I.; Malfitano, A.; Morelli, G.; Novellino, E.; Marasco, D. Interactions of cisplatin analogues with lysozyme: A comparative analysis. Biometals 2017, 30, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasco, D.; Messori, L.; Marzo, T.; Merlino, A. Oxaliplatin vs. cisplatin: Competition experiments on their binding to lysozyme. Dalton Transact. 2015, 44, 10392–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo Krauss, I.; Messori, L.; Cinellu, M.A.; Marasco, D.; Sirignano, R.; Merlino, A. Interactions of gold-based drugs with proteins: The structure and stability of the adduct formed in the reaction between lysozyme and the cytotoxic gold(III) compound Auoxo3. Dalton Transact. 2014, 43, 17483–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.; Pearson, C.S.; Green, C.M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Belfort, G.; Shekhtman, A.; Li, H.M.; Belfort, M. Exploring Intein Inhibition by Platinum Compounds as an Antimicrobial Strategy. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22661–22670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayne, D.J.; Lim, S.; Donnelly, P.S. Metal complexes designed to bind to amyloid-beta for the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6701–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.M.; Kim, G.; Kang, J.; Lim, M.H. Strategies Employing Transition Metal Complexes To Modulate Amyloid-beta Aggregation. Inorgan. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnham, K.J.; Kenche, V.B.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Smith, D.P.; Tew, D.J.; Liu, X.; Perez, K.; Cranston, G.A.; Johanssen, T.J.; Volitakis, I.; et al. Platinum-based inhibitors of amyloid-beta as therapeutic agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6813–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telpoukhovskaia, M.A.; Orvig, C. Werner coordination chemistry and neurodegeneration. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Wang, E.; Wei, H.; Wei, K.; Zhu, P.; Liu, Y. PtCl2(phen) disrupts the metal ions binding to amyloid-beta peptide. Metallomics 2013, 5, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pithadia, A.S.; Lim, M.H. Metal-associated amyloid-beta species in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 16, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hureau, C.; Faller, P. Platinoid complexes to target monomeric disordered peptides: A forthcoming solution against amyloid diseases? Dalton Transact. 2014, 43, 4233–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, B.Y.W.; Chan, H.M.; Leung, C.H.; Chan, D.S.H.; Bai, L.P.; Jiang, Z.H.; Li, H.W.; Ma, D.L. Group 9 metal-based inhibitors of beta-amyloid (1-40) fibrillation as potential therapeutic agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qu, Y.W.; Wang, X.H. Amyloid beta-targeted metal complexes for potential applications in Alzheimer’s disease. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 679–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messori, L.; Camarri, M.; Ferraro, T.; Gabbiani, C.; Franceschini, D. Promising in Vitro anti-Alzheimer Properties for a Ruthenium(III) Complex. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Mu, C.; Wang, M.C.; Webb, M.I.; Walsby, C.J.; Storr, T. Modulation of the Abeta peptide aggregation pathway by KP1019 limits Abeta-associated neurotoxicity. Metallomics 2015, 7, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellol, G.S.; Yellol, J.G.; Kenche, V.B.; Liu, X.M.; Barnham, K.J.; Donaire, A.; Janiak, C.; Ruiz, J. Synthesis of 2-pyridyl-benzimidazole iridium(III), ruthenium(II), and platinum(II) complexes. study of the activity as inhibitors of amyloid-beta aggregation and neurotoxicity evaluation. Inorgan. Chem. 2015, 54, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Lee, S.J.; Nam, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, M.G.; Korshavn, K.J.; Kim, H.T.; Cho, J.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Rhee, H.W.; et al. An Iridium(III) Complex as a Photoactivatable Tool for Oxidation of Amyloidogenic Peptides with Subsequent Modulation of Peptide Aggregation. Chemistry 2017, 23, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffern, M.C.; Velasco, P.T.; Matosziuk, L.M.; Coomes, J.L.; Karras, C.; Ratner, M.A.; Klein, W.L.; Eckermann, A.L.; Meade, T.J. Modulation of amyloid-beta aggregation by histidine-coordinating Cobalt(III) Schiff base complexes. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrick, J.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Nam, E.; Tak, H.; Kang, J.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.H.; Park, K.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into Tunable Metal-Mediated Hydrolysis of Amyloid-beta Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2234–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, I.; Bijani, C.; Ladeira, S.; Bourdon, V.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C. Interference of a new cyclometallated Pt compound with Cu binding to amyloid-beta peptide. Dalton Transact. 2012, 41, 6404–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, F.; Sasaki, I.; Eury, H.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C. Pt(II) compounds interplay with Cu(II) and Zn(II) coordination to the amyloid-beta peptide has metal specific consequences on deleterious processes associated to Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2130–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Huang, F.; Pu, X.; Jia, L.; Jiang, T.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Identification of [PtCl2(phen)] binding modes in amyloid-beta peptide and the mechanism of aggregation inhibition. Chemistry 2011, 17, 11657–11666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Moody, L.; Olaivar, J.F.; Lewis, N.A.; Khade, R.L.; Holder, A.A.; Zhang, Y.; Rangachari, V. Inhibition of Abeta42 peptide aggregation by a binuclear ruthenium(II)-platinum(II) complex: Potential for multi-metal organometallics as anti-amyloid agents. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2010, 2010, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinato, O.; Musetti, C.; Sissi, C. Pt-based drugs: The spotlight will be on proteins. Metallomics 2014, 6, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, C.; He, L.; Du, W. Inhibitory effects of NAMI-A-like ruthenium complexes on prion neuropeptide fibril formation. Metallomics 2015, 7, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.H.; Wang, W.J.; Du, W.H. Binuclear ruthenium complexes inhibit the fibril formation of human islet amyloid polypeptide. Rsc. Adv. 2017, 7, 18512–18522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Gong, G.; Wang, W.; Du, W. Disaggregation of human islet amyloid polypeptide fibril formation by ruthenium polypyridyl complexes. J. Inorgan. Biochem. 2017, 170, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Du, W.; Xu, J.; Huang, X.; Yin, G. Regulation of heteronuclear Pt-Ru complexes on the fibril formation and cytotoxicity of human islet amyloid polypeptide. J. Inorgan. Biochem. 2018, 189, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, J.; Hafner, N.; Gorls, H.; Kritsch, D.; Ferraro, G.; Durst, M.; Runnebaum, I.B.; Merlino, A.; Weigand, W. Platinum(ii) O,S complexes as potential metallodrugs against Cisplatin resistance. Dalton Transact. 2016, 45, 18876–18891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Natale, C.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Cascella, R.; Cecchi, C.; Russo, A.; Leone, M.; Penco, A.; Relini, A.; Federici, L.; Di Matteo, A.; et al. Nucleophosmin contains amyloidogenic regions that are able to form toxic aggregates under physiological conditions. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3689–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Diaferia, C.; La Manna, S.; Giannini, C.; Sibillano, T.; Accardo, A.; Morelli, G.; Novellino, E.; Marasco, D. Insights into amyloid-like aggregation of H2 region of the C-terminal domain of nucleophosmin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1865, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, P.L.; Di Natale, C.; Leone, M.; Cascella, R.; Cecchi, C.; Lirussi, L.; Antoniali, G.; Riccardi, D.; Morelli, G.; Tell, G.; et al. Destabilisation, aggregation, toxicity and cytosolic mislocalisation of nucleophosmin regions associated with acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59129–59143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, A.; La Manna, S.; Krauss, I.R.; Malfitano, A.M.; Novellino, E.; Federici, L.; De Cola, A.; Di Matteo, A.; D’Errico, G.; Marasco, D. Nucleophosmin-1 regions associated with acute myeloid leukemia interact differently with lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1862, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Manna, S.; Roviello, V.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Diaferia, C.; Giannini, C.; Sibillano, T.; Morelli, G.; Novellino, E.; Marasco, D. Amyloid fibers deriving from the aromatic core of C-terminal domain of nucleophosmin 1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 122, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; La Manna, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Di Somma, S.; Florio, D.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Novellino, E.; Netti, P.A.; Marasco, D. Structural insights into amyloid structures of the C-terminal region of nucleophosmin 1 in type A mutation of acute myeloid leukemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbirnie, M.; Grothe, R.; Eisenberg, D.S. An amyloid-forming peptide from the yeast prion Sup35 reveals a dehydrated beta-sheet structure for amyloid. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2375–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, L.L.; Mortishire-Smith, R.J.; Pollack, S.J.; Shearman, M.S. The toxicity in vitro of beta-amyloid protein. Biochem. J. 1995, 311, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pica, A.; Leone, S.; Di Girolamo, R.; Donnarumma, F.; Emendato, A.; Rega, M.F.; Merlino, A.; Picone, D. pH driven fibrillar aggregation of the super-sweet protein Y65R-MNEI: A step-by-step structural analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gener. Subj. 2018, 1862, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, A.; Hashemi, M.; Zhang, Y.; Breydo, L.; Uversky, V.N.; Lyubchenko, Y.L. Role of monomer arrangement in the amyloid self-assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1854, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.J.; Soto-Ortega, D.D.; Kotarek, J.A.; Gonzalez-Velasquez, F.J.; Sivakumar, K.; Wu, L.; Wang, Q.; Moss, M.A. Comparative study of inhibition at multiple stages of amyloid-beta self-assembly provides mechanistic insight. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 76, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, J.; Bernas, T.; Trzybinski, D.; Wozniak, K.; Ferraro, G.; Marasco, D.; Merlino, A.; Shafikov, M.Z.; Czerwieniec, R.; Kowalski, K. Mitochondria Targeting with Luminescent Rhenium(I) Complexes. Molecules 2017, 22, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, J.R.; Raymond, G.J.; Hughson, A.G.; Race, R.E.; Sim, V.L.; Hayes, S.F.; Caughey, B. The most infectious prion protein particles. Nature 2005, 437, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Jiao, Y.; Guo, Z.J. Inhibitory action of macrocyclic platiniferous chelators on metal-induced A beta aggregation. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doti, N.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Madonna, S.; Scarponi, C.; Ruvo, M.; Perretta, G.; Albanesi, C.; Marasco, D. New mimetic peptides of the kinase-inhibitory region (KIR) of SOCS1 through focused peptide libraries. Biochem. J. 2012, 443, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Peptide | Sequence | pI |
|---|---|---|
| NPM1264–277 | VEAKFINYVKNCFR | 9.2 |
| Sup35p7–13 | GNNQQNY | 5.5 |
| Aβ21–40 | AEDVGSNKGAIIGLMVGGVV | 4.5 |
| Peptide to Pt Compound Ratio | t1/2 (min) | Fluorescence Intensity (Arbitrary Unit) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPM1264–277 | 5 | 568 | |
| NPM1264–277:1 | 1:0.1 | 6.5 | 155 |
| NPM1264–277:1 | 1:0.5 | n.d. | 45 |
| NPM1264–277:1 | 1:1 | n. d. | 45 |
| NPM1264–277:2 | 1:0.1 | 7 | 410 |
| NPM1264–277:2 | 1:0.5 | n.d. | 49 |
| NPM1264–277:2 | 1:1 | n.d. | 48 |
| NPM1264–277:3 | 1:0.1 | 6 | 155 |
| NPM1264–277:3 | 1:0.5 | n.d. | 70 |
| NPM1264–277:3 | 1:1 | n.d. | 64 |
| NPM1264–277:4 | 1:0.1 | 10 | 363 |
| NPM1264–277:4 | 1:0.5 | n.d. | 220 |
| NPM1264–277:4 | 1:1 | n.d. | 43 |
| Experimental m/z, Charge | Experimental Monoisotopic Mass (Da) | Theoretical Monoisotopic Mass (Da) | Pt(II)-Peptide Complexes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1173.056, +2 | 2344.15 | 2346.39 | Aβ 21–40 + 1 × (1) − 1Cl − 1DMSO |
| 1212.586, +2 | 2422.16 | 2424.52 | Aβ 21–40 + 1 × (1) − 1Cl |
| 1421.596, +2 | 2841.16 | 2844.90 | Aβ 21–40 + 2 × (1) − 2Cl − 1DMSO |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Florio, D.; Malfitano, A.M.; Di Somma, S.; Mügge, C.; Weigand, W.; Ferraro, G.; Iacobucci, I.; Monti, M.; Morelli, G.; Merlino, A.; et al. Platinum(II) O,S Complexes Inhibit the Aggregation of Amyloid Model Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040829
Florio D, Malfitano AM, Di Somma S, Mügge C, Weigand W, Ferraro G, Iacobucci I, Monti M, Morelli G, Merlino A, et al. Platinum(II) O,S Complexes Inhibit the Aggregation of Amyloid Model Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(4):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040829
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlorio, Daniele, Anna Maria Malfitano, Sarah Di Somma, Carolin Mügge, Wolfgang Weigand, Giarita Ferraro, Ilaria Iacobucci, Maria Monti, Giancarlo Morelli, Antonello Merlino, and et al. 2019. "Platinum(II) O,S Complexes Inhibit the Aggregation of Amyloid Model Systems" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 4: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040829
APA StyleFlorio, D., Malfitano, A. M., Di Somma, S., Mügge, C., Weigand, W., Ferraro, G., Iacobucci, I., Monti, M., Morelli, G., Merlino, A., & Marasco, D. (2019). Platinum(II) O,S Complexes Inhibit the Aggregation of Amyloid Model Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(4), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040829