Mechanisms of Iodide–Triiodide Exchange Reactions in Ionic Liquids: A Reactive Molecular-Dynamics Exploration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
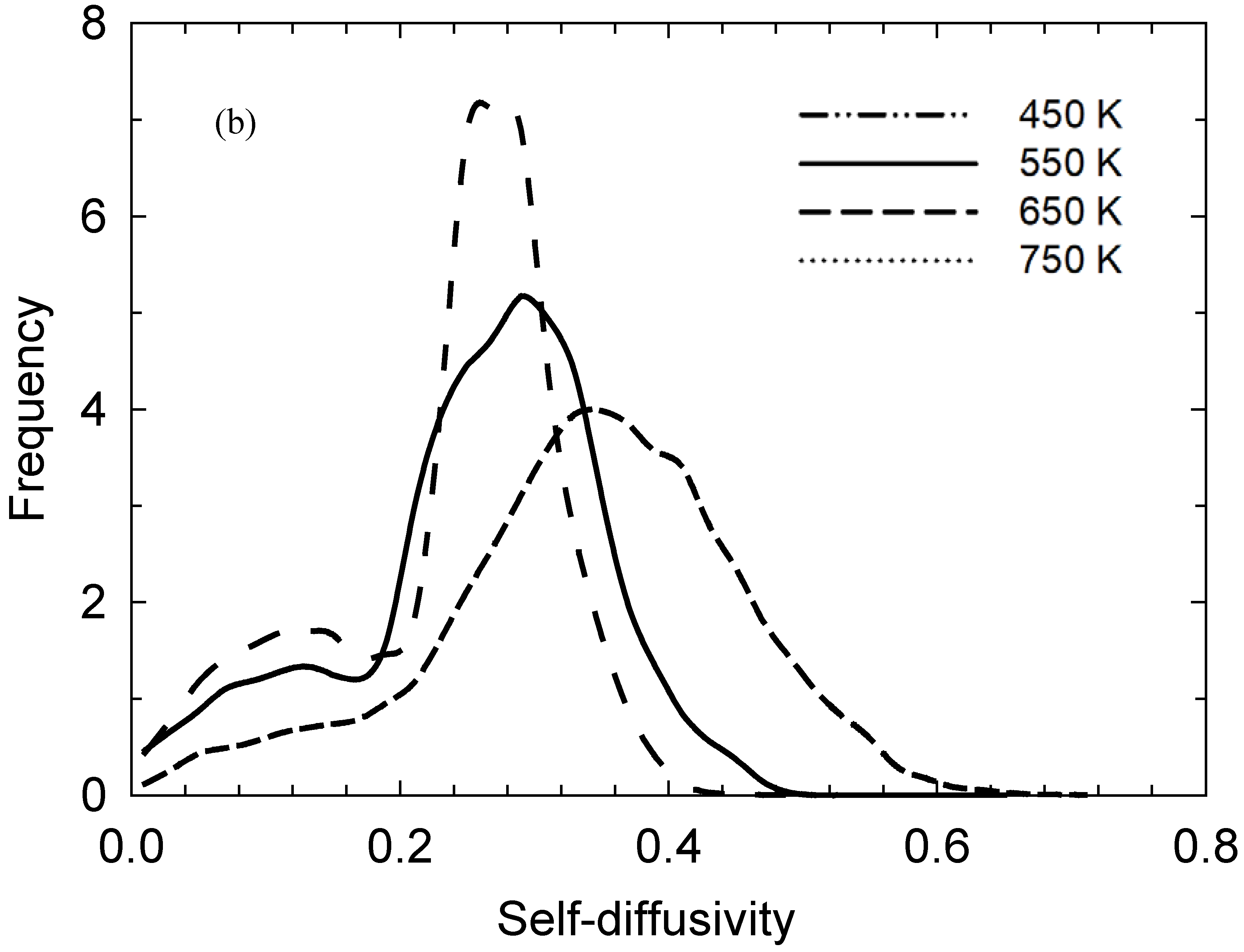
2. Results and Discussion
3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohno, H. Electrochemical Aspects of Ionic Liquids; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grätzel, M. Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature 2001, 414, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Angell, C.A. Solvent-Free Electrolytes with Aqueous Solution-Like Conductivities. Science 2003, 302, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyashiro, H.; Ohno, Y.; Usami, A.; Mita, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Terada, N. Highly reversible lithium metal secondary battery using a room temperature/mixture and a surface-coated cathode active material. Chem. Commun. 2006, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Keim, P. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kawano, R. High performance Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells using Ionic Liquids as their Electrolytes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2004, 164, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Kawano, R.; Kubo, W.; Masaki, N.; Kitamura, T.; Wada, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yanagida, S. Dye-Sensitized TiO2 Solar Cells Using Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Crystal Systems as Effective Electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4763–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Pringle, J.M.; Cheng, Y.-B. Improved Efficiency and Stability of Flexible Dye Sensitised Solar Cells on ITO/PEN Substrates Using an Ionic Liquid Electrolyte. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, J.M.; Armel, V. The influence of ionic liquid and plastic crystal electrolytes on the photovoltaic characteristics of dye-sensitized solar cells. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2011, 30, 371–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, W.; Kitamura, T.; Hanabusa, K.; Wada, Y.; Yanagida, S. Quasi-solid-state-sensitized solar cells using room temperature molten salts and a low molecular weight. Chem. Commun. 2002, 374–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, R.; Watanabe, M. Equilibrium potentials and charge transport of I−/I3− redox couple in an ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2003, 330–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, R.; Watanabe, M. Anomaly of charge transport of an iodide/tri-iodide redox couple in an ionic liquid and its importance in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2005, 2107–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Li, R.; Wang, P.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. High-performance dye-sensitized solar cells based on solvent-free electrolytes produced from eutectic melts. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, N.; Athanassov, Y.; Armand, M.; Bonhte, P.; Pettersson, H.; Azam, A.; Grätzel, M. The Performance and Stability of Ambient Temperature Molten Salts for Solar Cell Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zistler, M.; Wachter, P.; Wasserscheid, P.; Gerhard, D.; Hinsch, A.; Sastrawan, R.; Gores, H.J. Comparison of electrochemical methods for triiodide diffusion coefficient measurements and observation of non-Stokesian diffusion behaviour in binary mixtures of two ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsmølle, V.K.; Rothenberger, G.; Topgaard, D.; Brauer, J.C.; Kuang, D.-B.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Lindman, B.; Grätzel, M.; Moser, J.-E. Extraordinarily Efficient Conduction in a Redox-Active Ionic Liquid. ChemPhysChem 2011, 12, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grotthuss, C.J.T. Mémoire sur la décomposition de l’eau: Et des corps qu’elle tient en dissolution à l’aide de l’électricité galvanique. Ann. Chim. (Paris) 1806, 58, 54–73. [Google Scholar]
- Stegemann, H.; Reiche, A.; Schnittke, A.; Füllbier, H. Room-temperature molten polyiodides. Electrochim. Acta 1992, 37, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, P.-H.; Kloo, L. Synthesis, Structure and Bonding in Polyiodide and Metal Iodide-Iodine Systems. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1649–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachter, P.; Zistler, M.; Schreiner, C.; Fleischmann, M.; Gerhard, D.; Wasserscheid, P.; Barthel, J.; Gores, H.J. Temperature Dependence of the Non-Stokesian Charge Transport in Binary Blends of Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, C.L.; Bond, A.M.; Hollenkamp, A.F.; Mahon, P.J.; Zhang, J. Electrode Reaction and Mass-Transport Mechanisms Associated with the Iodide/Triiodide Couple in the Ionic Liquid 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 22439–22449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Park, N. First-Principles Identification of Iodine Exchange Mechanism in Iodide Ionic Liquid Ranjit. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 3065–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, J.; Kohanoff, J.K.; English, N.J.; Bringa, E.M.; Del Popolo, M.G. On the Mechanism of the Iodide-Triiodide Exchange Reaction in a Solid-State Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6436–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.K.; Shan, T.-R.; Liang, T.; Noordhoek, M.J. Variable charge many-body interatomic potentials. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakakoshi, M.; Shiro, M.; Fujimoto, T.; Machinami, T.; Seki, H.; Tashiro, M.; Nishikawa, K. Crystal Structure of 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Iodide. Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 1400–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, J.G.; Yethiraj, A. Grotthuss Transport of Iodide in EMIM/I3 Ionic Crystal. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, N.J. Molecular dynamics simulations of microwave effects on water using different long-range electrostatics methodologies. Mol. Phys. 2006, 104, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, P.K.; English, N.J. Role of hydration layer in dynamical crossover in proteins: Insights from translational self-diffusivity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 12031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänggi, P.; Talkner, P.; Borkovec, M. Reaction-rate theory: Fifty years after Kramers. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1990, 62, 251–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Deschamps, J.; Pádua, A.A.H. Modeling Ionic Liquids Using a Systematic All-Atom Force-Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.P.; Tildesley, D.J. Computer Simulation of Liquids, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Shin, B.K.; Lee, H. Physical and electrochemical properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium iodide, and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2004, 21, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenoweth, K.; van Duin, A.C.T.; Goddard, W.A., III. ReaxFF Reactive Force Field for Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Hydrocarbon Oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattsson, T.R.; Lane, J.M.D.; Cochrane, K.R.; Desjarlais, M.P.; Thompson, A.P.; Pierce, F.; Grest, G.S. Reactive MD-force field: General-purpose hydrocarbon parameterization. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappe, A.K.; Goddard, W.A., III. Charge Equilibration for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 3358–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, A. Parallel Multilevel Preconditioned Conjugate-Gradient Approach to Variable-Charge Molecular Dynamics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1997, 104, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hundertmark, D.; Martínez, T.J. A unified theoretical framework for fluctuating-charge models in atom-space and in bond-space. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 214113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilmer, C.E.; Kim, K.C.; Snurr, R.Q. An Extended Charge Equilibration Method. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, D. Split charge equilibration method with correct dissociation limits. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 224103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müser, M.H. The chemical hardness of molecules and the band gap of solids within charge equilibration formalisms: Toward force field-based simulations of redox reactions. Eur. Phys. J. B 2012, 85, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Kolesov, G.; Verstraelen, T.; Kaxiras, E.; van Duin, A.C.T. eReaxFF: A Pseudoclassical Treatment of Explicit Electrons within Reactive Force Field Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 3463–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aktulga, H.M.; Fogarty, J.C.; Pandit, S.A.; Grama, A.Y. Parallel Reactive Molecular Dynamics: Numerical Methods and Algorithmic Techniques. J. Parallel Comput. 2012, 38, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, O.; Pfadenhauer, S.; Leitsmann, R.; Plänitz, P.; Schreiner, E.; Schreiber, M. ReaxFF+: A New Reactive Force Field Method for the Accurate Description of Ionic Systems and Its Application to the Hydrolyzation of Aluminosilicates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 10849–10856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommert, F.; Wendler, K.; Berger, R.; Delle Site, L.; Holm, C. Force Fields for Studying the Structure and Dynamics of Ionic Liquids: A Critical Review of Recent Developments. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2012, 13, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senftle, T.P.; Islam, M.M.; Kylasa, S.B.; Zheng, Y.; Shin, Y.K.; Junkermeier, C.; Engel-Herbert, R.; Janik, M.J.; Aktulga, H.M.; et al. The ReaxFF reactive force-field: Development, applications and future directions. Npj Comput. Mater. 2016, 2, 15011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlt, E.; Ray, P.; Hansen, A.; Malberg, F.; Grimme, S.; Kirchner, B. Finding the best density functional approximation to describe interaction energies and structures of ionic liquids in molecular dynamics studies. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 193835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Voth, G.A. Kinetics of Proton Migration in Liquid Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Byrne, A.; Bringa, E.M.; Del Pópolo, M.G.; Kohanoff, J.J.; Galassi, V.; English, N.J. Mechanisms of Iodide–Triiodide Exchange Reactions in Ionic Liquids: A Reactive Molecular-Dynamics Exploration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051123
Byrne A, Bringa EM, Del Pópolo MG, Kohanoff JJ, Galassi V, English NJ. Mechanisms of Iodide–Triiodide Exchange Reactions in Ionic Liquids: A Reactive Molecular-Dynamics Exploration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051123
Chicago/Turabian StyleByrne, Aaron, Eduardo M. Bringa, Mario G. Del Pópolo, Jorge J. Kohanoff, Vanesa Galassi, and Niall J. English. 2019. "Mechanisms of Iodide–Triiodide Exchange Reactions in Ionic Liquids: A Reactive Molecular-Dynamics Exploration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051123
APA StyleByrne, A., Bringa, E. M., Del Pópolo, M. G., Kohanoff, J. J., Galassi, V., & English, N. J. (2019). Mechanisms of Iodide–Triiodide Exchange Reactions in Ionic Liquids: A Reactive Molecular-Dynamics Exploration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051123





