Normal FGF-21-Serum Levels in Patients with Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase II (CPT II) Deficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Controls
4.2. Measurement of FGF-21 Serum Concentration
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suomalainen, A. Biomarkers for mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholle, L.M.; Lehmann, D.; Deschauer, M.; Kraya, T.; Zierz, S. FGF-21 as a Potential Biomarker for Mitochondrial Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2070–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.L.; Liang, C.; Edema-Hildebrand, F.; Riley, C.; Needham, M.; Sue, C.M. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is a sensitive biomarker of mitochondrial disease. Neurology 2013, 81, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koene, S.; de Laat, P.; van Tienoven, D.H.; Vriens, D.; Brandt, A.M.; Sweep, F.C.; Rodenburg, R.J.; Donders, A.R.; Janssen, M.C.; Smeitink, J.A. Serum FGF21 levels in adult m.3243A>G carriers: Clinical implications. Neurology 2014, 83, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morovat, A.; Weerasinghe, G.; Nesbitt, V.; Hofer, M.; Agnew, T.; Quaghebeur, G.; Sergeant, K.; Fratter, C.; Guha, N.; Mirzazadeh, M. Use of FGF-21 as a Biomarker of Mitochondrial Disease in Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suomalainen, A.; Elo, J.M.; Pietilainen, K.H.; Hakonen, A.H.; Sevastianova, K.; Korpela, M.; Isohanni, P.; Marjavaara, S.K.; Tyni, T.; Kiuru-Enari, S.; et al. FGF-21 as a biomarker for muscle-manifesting mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies: A diagnostic study. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Zheng, J.; Lv, J.; Xu, J.; Ji, X.; Luo, Y.B.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, C. Skeletal muscle increases FGF21 expression in mitochondrial disorders to compensate for energy metabolic insufficiency by activating the mTOR-YY1-PGC1alpha pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 84, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mraz, M.; Bartlova, M.; Lacinova, Z.; Michalsky, D.; Kasalicky, M.; Haluzikova, D.; Matoulek, M.; Dostalova, I.; Humenanska, V.; Haluzik, M. Serum concentrations and tissue expression of a novel endocrine regulator fibroblast growth factor-21 in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, S.; Bartlett, K.; Pourfarzam, M. Mammalian mitochondrial beta-oxidation. Biochem. J. 1996, 320 Pt 2, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, J.; Hoppel, C. Fatty acid import into mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2000, 1486, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, J.D.; Brown, N.F. The mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase system. From concept to molecular analysis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 244, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badman, M.K.; Koester, A.; Flier, J.S.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Maratos-Flier, E. Fibroblast growth factor 21-deficient mice demonstrate impaired adaptation to ketosis. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4931–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandanmagsar, B.; Warfel, J.D.; Wicks, S.E.; Ghosh, S.; Salbaum, J.M.; Burk, D.; Dubuisson, O.S.; Mendoza, T.M.; Zhang, J.; Noland, R.C.; et al. Impaired Mitochondrial Fat Oxidation Induces FGF21 in Muscle. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Scafidi, S.; Wolfgang, M.J. Hepatic Fatty Acid Oxidation Restrains Systemic Catabolism during Starvation. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Selen Alpergin, E.S.; Zhao, L.; Hartung, T.; Scafidi, S.; Riddle, R.C.; Wolfgang, M.J. Loss of Hepatic Mitochondrial Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Confers Resistance to Diet-Induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ellis, J.M.; Wolfgang, M.J. Adipose fatty acid oxidation is required for thermogenesis and potentiates oxidative stress-induced inflammation. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hurtado, E.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Wolfgang, M.J. Fatty acid oxidation is required for active and quiescent brown adipose tissue maintenance and thermogenic programing. Mol. Metab. 2018, 7, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.R.; Deschauer, M.; Zierz, S. Phenotype of carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT II) deficiency: A questionnaire-based survey. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 59, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschauer, M.; Wieser, T.; Zierz, S. Muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency: Clinical and molecular genetic features and diagnostic aspects. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isackson, P.J.; Bennett, M.J.; Vladutiu, G.D. Identification of 16 new disease-causing mutations in the CPT2 gene resulting in carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2006, 89, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierz, S.; Engel, A.G. Regulatory properties of a mutant carnitine palmitoyltransferase in human skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Biochem. 1985, 149, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, D.; Zierz, S. Normal protein content but abnormally inhibited enzyme activity in muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 339, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.; Nielsen, J.; Hansen, C.N.; Nielsen, L.B.; Wibrand, F.; Stride, N.; Schroder, H.D.; Boushel, R.; Helge, J.W.; Dela, F.; et al. Biomarkers of mitochondrial content in skeletal muscle of healthy young human subjects. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 3349–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina, A.J.; Bharadwaj, M.S.; Van Horn, C.; Nicklas, B.J.; Lyles, M.F.; Eggebeen, J.; Haykowsky, M.J.; Brubaker, P.H.; Kitzman, D.W. Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Content, Oxidative Capacity, and Mfn2 Expression Are Reduced in Older Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction and Are Related to Exercise Intolerance. JACC Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, L.; Golbik, R.; Sippl, W.; Zierz, S. Malony-CoA inhibits the S113L variant of carnitine-palmitoyltransferase II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, L.; Golbik, R.; Sippl, W.; Zierz, S. Stabilization of the thermolabile variant S113L of carnitine palmitoyltransferase II. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
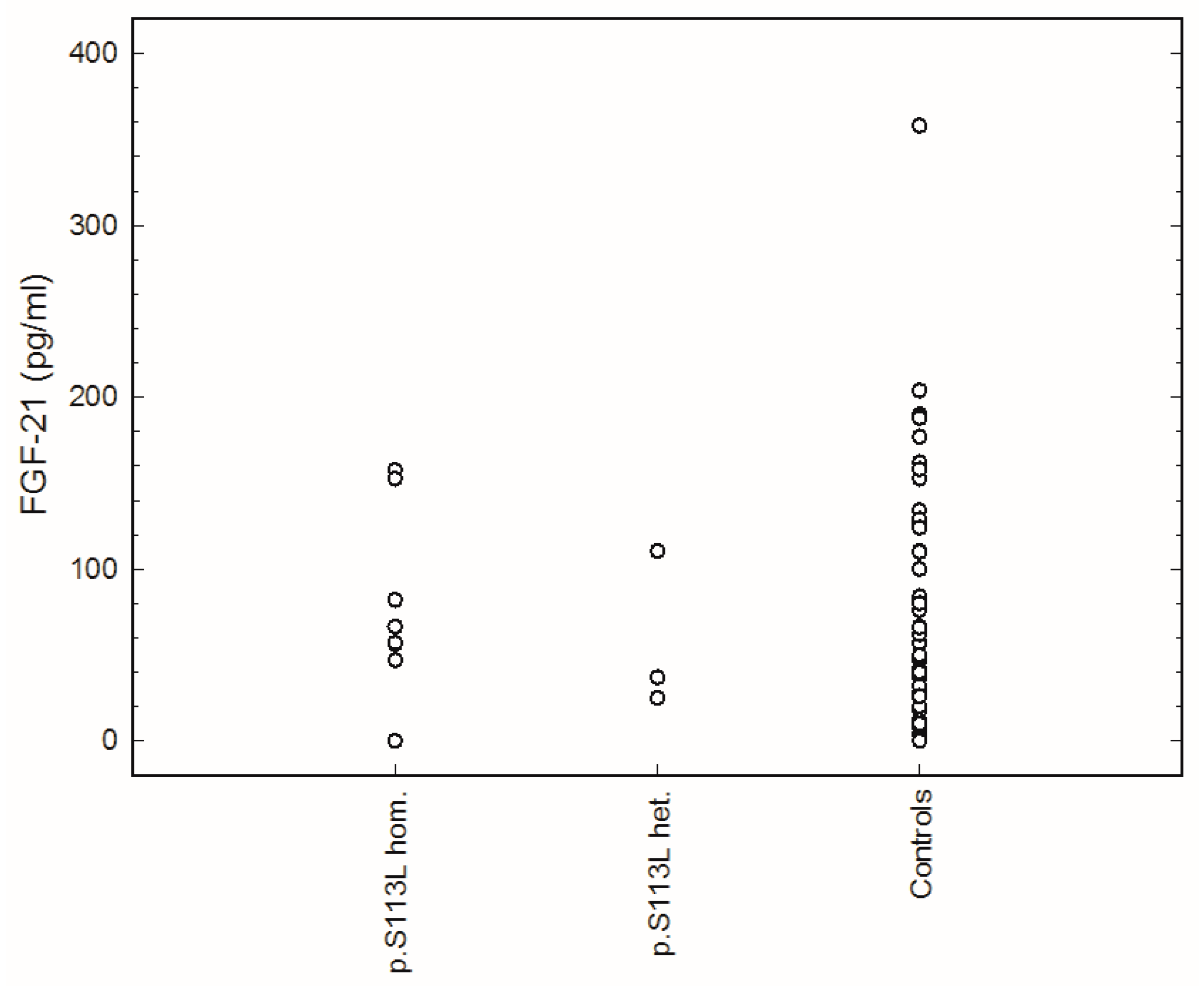
| Patients | Gender | Age at Diagnosis (yrs.) | Age of First Attack (yrs.) | Attacks Per Year (n) | Intensity of Pain* | BMI | Genotype | FGF-21 (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 19 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 23.9 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Ser113Leu | 47.0 |
| 2 | F | 34 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 25.9 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Ser113Leu | 66.5 |
| 3 | M | 33 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 26.6 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Ser113Leu | 152.5 |
| 4 | M | 53 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 27.1 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Ser113Leu | 82.0 |
| 5 | M | 21 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 24.2 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Ser113Leu | 57.0 |
| 6 | M | 54 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 24.2 | p.Ser113Leu/c.1238delAG | 37.0 |
| 7 | M | 25 | 4 | 85 | 4 | 30.7 | p.Ser113Leu/c.340 + 1G > A | 110.5 |
| 8 | M | 24 | 9 | 10 | 7 | 26.6 | p.Ser113Leu/c.340 + 5G > A | 25.5 |
| 9 | M | 45 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 30.0 | p.Ser113Leu/c.182_203del22 | 56.5 |
| 10 | M | 22 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 26.4 | p.Arg231Trp/p.Glu487Lys | 12.0 |
| 11 | M | 57 | 17 | 11 | 5 | 24.9 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Ser113Leu | 0 |
| 12 | F | 53 | 18 | 50 | 4 | 27.9 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Arg151Gln | 57.5 |
| 13 | F | 39 | 15 | 6 | 5 | 20.4 | p.Ser113Leu/p.Pro50His | 57.0 |
| Mean | 8.8 | 26.3 | 66.2 | |||||
| Range (CI) | 6.1–11.5 | 25.0–27.7 | 36.8–95.6 | |||||
| Controls (FGF-21) | Range (CI) | Mean | ||||||
| All (n = 50) | 46.4–90.6 | 68.5 | ||||||
| M (n = 23) | 52.8–108.9 | 80.9 | ||||||
| F (n = 27) | 23.4–92.4 | 57.9 | ||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motlagh Scholle, L.; Lehmann, D.; Joshi, P.R.; Zierz, S. Normal FGF-21-Serum Levels in Patients with Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase II (CPT II) Deficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061400
Motlagh Scholle L, Lehmann D, Joshi PR, Zierz S. Normal FGF-21-Serum Levels in Patients with Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase II (CPT II) Deficiency. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061400
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotlagh Scholle, Leila, Diana Lehmann, Pushpa Raj Joshi, and Stephan Zierz. 2019. "Normal FGF-21-Serum Levels in Patients with Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase II (CPT II) Deficiency" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061400
APA StyleMotlagh Scholle, L., Lehmann, D., Joshi, P. R., & Zierz, S. (2019). Normal FGF-21-Serum Levels in Patients with Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase II (CPT II) Deficiency. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061400





