Identification, Characterization, and Regulatory Mechanisms of a Novel EGR1 Splicing Isoform
Abstract
1. Introduction
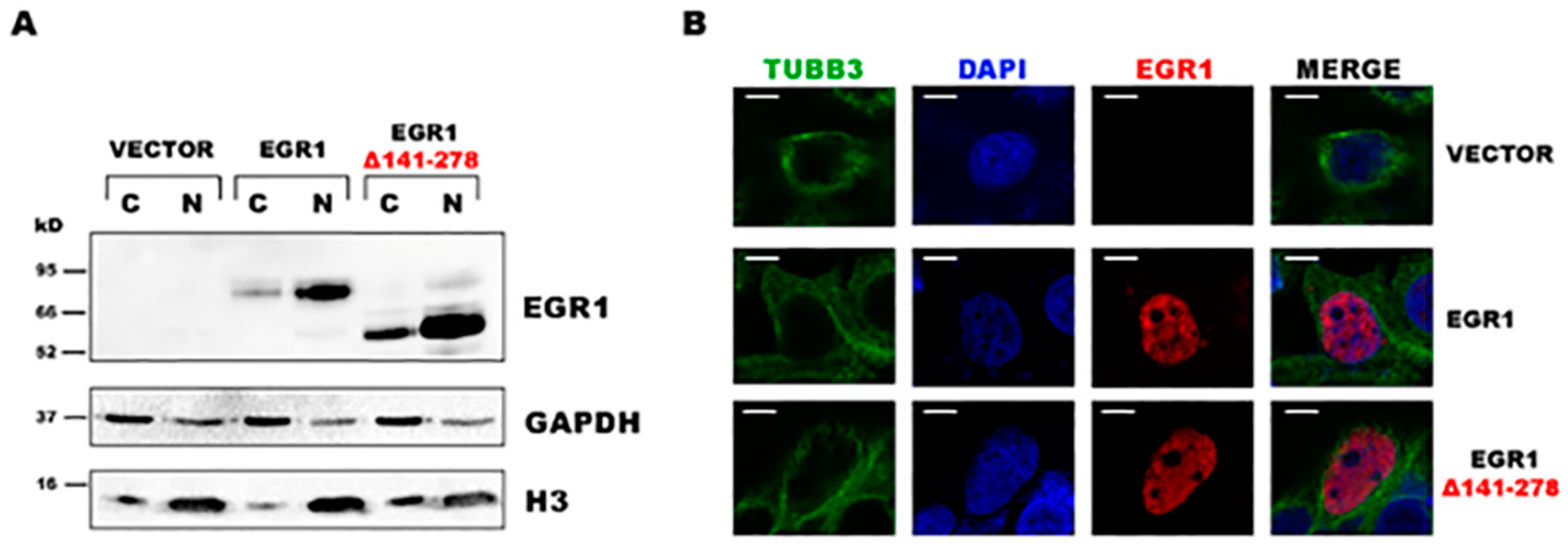
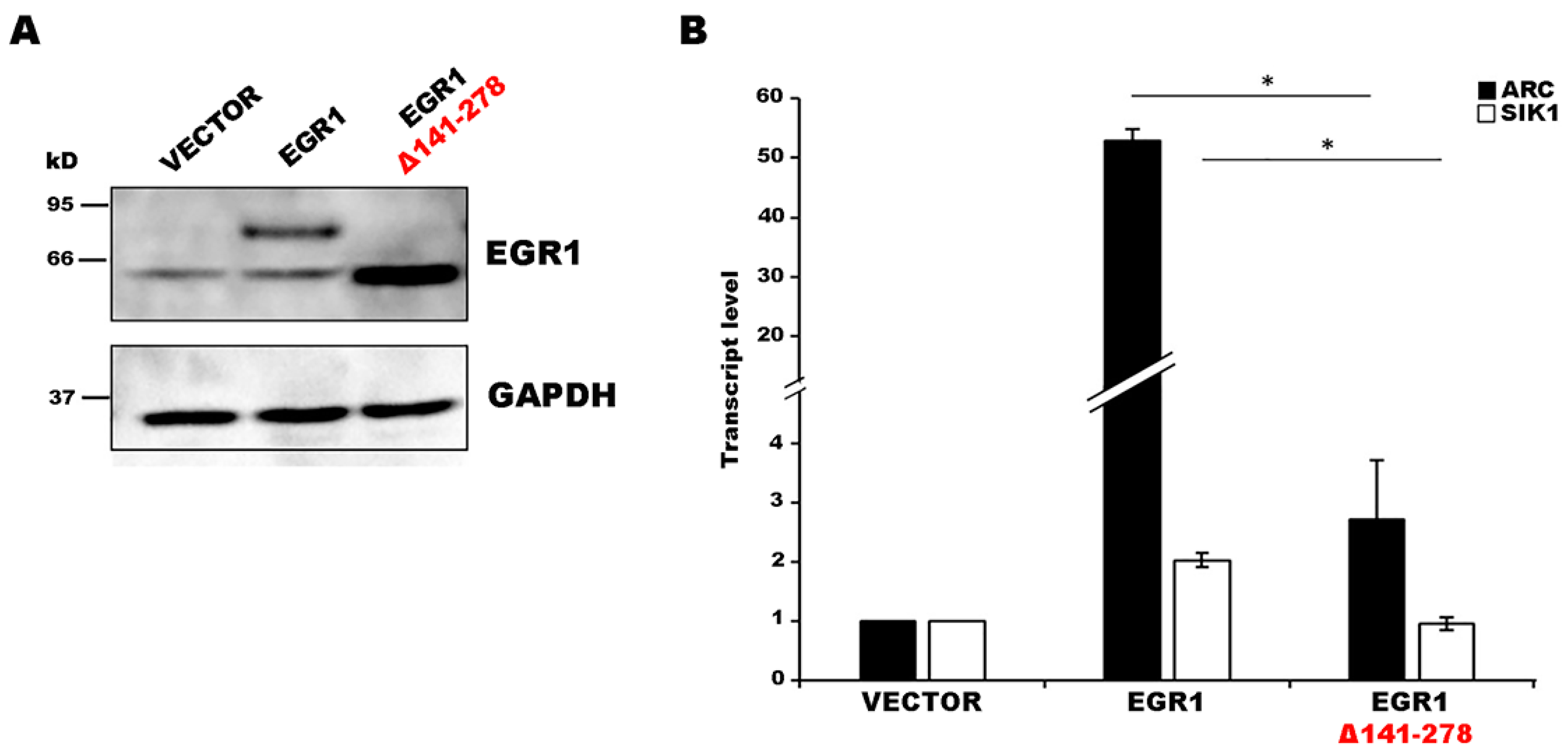
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. RNA Isolation, Retrotranscription, RT-PCR, and qPCR
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.4. Western Immunoblot Analysis
4.5. Cloning of EGR1 Alternative Isoform and Iper-Expression Experiments
4.6. Nuclear/Cytoplasmic Fractionation
4.7. Immunofluorescence Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gashler, A.L.; Swaminathan, S.; Sukhatme, V.P. A novel repression module, an extensive activation domain, and a bipartite nuclear localization signal defined in the immediate-early transcription factor Egr-1. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 4556–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.W.; Sevetson, B.R.; Milbrandt, J. Identification of NAB1, a repressor of NGFI-A- and Krox20-mediated transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6873–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svaren, J.; Sevetson, B.R.; Apel, E.D.; Zimonjic, D.B.; Popescu, N.C.; Milbrandt, J. NAB2, a corepressor of NGFI-A (Egr-1) and Krox20, is induced by proliferative and differentiative stimuli. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, G.; Kaufmann, K.; Magin, A.; Lietz, M.; Bach, K.; Cramer, M. The human transcriptional repressor protein NAB1: Expression and biological activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000, 1493, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, G.; Cibelli, G. Regulation of life and death by the zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1. J. Cell Physiol. 2002, 193, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagel, J.I.; Deindl, E. Early growth response 1--a transcription factor in the crossfire of signal transduction cascades. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 48, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Knapska, E.; Kaczmarek, L. A gene for neuronal plasticity in the mammalian brain: Zif268/Egr-1/NGFI-A/Krox-24/TIS8/ZENK? Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 74, 183–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penke, Z.; Morice, E.; Veyrac, A.; Gros, A.; Chagneau, C.; LeBlanc, P.; Samson, N.; Baumgärtel, K.; Mansuy, I.M.; Davis, S.; et al. Zif268/Egr1 gain of function facilitates hippocampal synaptic plasticity and long-term spatial recognition memory. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 369, 20130159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyrac, A.; Besnard, A.; Caboche, J.; Davis, S.; Laroche, S. The transcription factor Zif268/Egr1, brain plasticity, and memory. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 122, 89–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclot, F.; Kabbaj, M. The Role of Early Growth Response 1 (EGR1) in Brain Plasticity and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, V.; Adamson, E.D.; Calogero, A.; Ragona, G.; Mercola, D. The transcription factor Egr1 is a direct regulator of multiple tumor suppressors including TGFbeta1, PTEN, p53, and fibronectin. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, J.; de Belle, I.; Huang, R.P.; Adamson, E.; Mercola, D. The transcription factor EGR-1 suppresses transformation of human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells by coordinated induction of transforming growth factor-beta1, fibronectin, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 4400–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virolle, T.; Krones-Herzig, A.; Baron, V.; De Gregorio, G.; Adamson, E.D.; Mercola, D. Egr1 promotes growth and survival of prostate cancer cells. Identification of novel Egr1 target genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11802–11810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogero, A.; Lombari, V.; De Gregorio, G.; Porcellini, A.; Ucci, S.; Arcella, A.; Caruso, R.; Gagliardi, F.M.; Gulino, A.; Lanzetta, G.; et al. Inhibition of cell growth by EGR-1 in human primary cultures from malignant glioma. Cancer Cell Int. 2004, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadir, S.A. Mechanisms of prostate tumorigenesis: Roles for transcription factors Nkx3.1 and Egr1. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2005, 1059, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Guang, W.; Han, W.; Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; Gu, Y. EGR1 decreases the malignancy of human non-small cell lung carcinoma by regulating KRT18 expression. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.L.; Wu, X.J.; Gong, C.C.; Pei, D.S. Egr-1 suppresses breast cancer cells proliferation by arresting cell cycle progression via down-regulating CyclinDs. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 10212–10222. [Google Scholar]
- Fairman, J.; Chumakov, I.; Chinault, A.C.; Nowell, P.C.; Nagarajan, L. Physical mapping of the minimal region of loss in 5q- chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7406–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronski, K.; Sanders, M.; Burleson, J.A.; Moyo, V.; Benn, P.; Fang, M. Early growth response gene 1 (EGR1) is deleted in estrogen receptor-negative human breast carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 104, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joslin, J.M.; Fernald, A.A.; Tennant, T.R.; Davis, E.M.; Kogan, S.C.; Anastasi, J.; Crispino, J.D.; Le Beau, M.M. Haploinsufficiency of EGR1, a candidate gene in the del(5q), leads to the development of myeloid disorders. Blood 2007, 110, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.P.; Darland, T.; Okamura, D.; Mercola, D.; Adamson, E.D. Suppression of v-sis-dependent transformation by the transcription factor, Egr-1. Oncogene 1994, 9, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.P.; Liu, C.; Fan, Y.; Mercola, D.; Adamson, E.D. Egr-1 negatively regulates human tumor cell growth via the DNA-binding domain. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 5054–5062. [Google Scholar]
- de Belle, I.; Huang, R.P.; Fan, Y.; Liu, C.; Mercola, D.; Adamson, E.D. p53 and Egr-1 additively suppress transformed growth in HT1080 cells but Egr-1 counteracts p53-dependent apoptosis. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3633–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yao, J.; Mercola, D.; Adamson, E. The transcription factor EGR-1 directly transactivates the fibronectin gene and enhances attachment of human glioblastoma cell line U251. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20315–20323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, B.; Bepler, G.; Sharma, S.; Cantor, A.; Haura, E.B. EGR1 predicts PTEN and survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thigpen, A.E.; Cala, K.M.; Guileyardo, J.M.; Molberg, K.H.; McConnell, J.D.; Russell, D.W. Increased expression of early growth response-1 messenger ribonucleic acid in prostatic adenocarcinoma. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.A.; Kumar, M.V.; Iczkowski, K.A.; Bostwick, D.G.; Tindall, D.J. Expression of early growth response genes in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baron, V.; De Gregorio, G.; Krones-Herzig, A.; Virolle, T.; Calogero, A.; Urcis, R.; Mercola, D. Inhibition of Egr-1 expression reverses transformation of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2003, 22, 4194–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulkadir, S.A.; Carbone, J.M.; Naughton, C.K.; Humphrey, P.A.; Catalona, W.J.; Milbrandt, J. Frequent and early loss of the EGR1 corepressor NAB2 in human prostate carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, E.D.; and Mercola, D. Egr1 transcription factor: Multiple roles in prostate tumor cell growth and survival. Tumour Biol. 2002, 23, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbrandt, J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science 1987, 238, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhatme, V.P.; Cao, X.M.; Chang, L.C.; Tsai-Morris, C.H.; Stamenkovich, D.; Ferreira, P.C.; Cohen, D.R.; Edwards, S.A.; Shows, T.B.; Curran, T.; et al. A zinc finger-encoding gene coregulated with c-fos during growth and differentiation, and after cellular depolarization. Cell 1988, 53, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christy, B.A.; Lau, L.F.; Nathans, D. A gene activated in mouse 3T3 cells by serum growth factors encodes a protein with “zinc finger” sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7857–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, P.; Revelant, O.; Bravo, R.; Charnay, P. Two mouse genes encoding potential transcription factors with identical DNA-binding domains are activated by growth factors in cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4691–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; You, J.; Xiao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Brewer, G.; Ma, W.J. HuR posttranscriptionally regulates early growth response-1 (Egr-1) expression at the early stage of T cell activation. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 4319–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliperti, V.; Donizetti, A. Long Non-coding RNA in Neurons: New Players in Early Response to BDNF Stimulation. Front. Mol Neurosci. 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.P.; Fan, Y.; deBelle, I.; Ni, Z.; Matheny, W.; Adamson, E.D. Egr-1 inhibits apoptosis during the UV response: Correlation of cell survival with Egr-1 phosphorylation. Cell Death Differ. 1998, 5, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manente, A.G.; Pinton, G.; Tavian, D.; Lopez-Rodas, G.; Brunelli, E.; Moro, L. Coordinated sumoylation and ubiquitination modulate EGF induced EGR1 expression and stability. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; de Belle, I.; Liang, H.; Adamson, E.D. Coactivating factors p300 and CBP are transcriptionally crossregulated by Egr1 in prostate cells, leading to divergent responses. Mol. Cell. 2004, 15, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Mahendran, R.; Guy, G.R.; Tan, Y.H. Protein phosphatase inhibitors induce the sustained expression of the Egr-1 gene and the hyperphosphorylation of its gene product. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 12991–12997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Mahendran, R.; Philp, R.; Guy, G.R.; Tan, Y.H.; Cao, X. Casein kinase II associates with Egr-1 and acts as a negative modulator of its DNA binding and transcription activities in NIH 3T3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13530–13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.P.; and Adamson, E.D. The phosphorylated forms of the transcription factor, Egr-1, bind to DNA more efficiently than non-phosphorylated. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 200, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, G.R.; Olivier, K.R.; Mitchell, R.F., Jr.; Jenkins, R.B.; Tindall, D.J. Regulation of expression of the early growth response gene-1 (EGR-1) in malignant and benign cells of the prostate. Prostate 2005, 63, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, P.; Schott, K.; Williams, R.W.; Schaeffel, F. Posttranscriptional regulation of the immediate-early gene EGR1 by light in the mouse retina. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 3371–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelbronn, M.; Harter, P.; Warth, A.; Lupescu, A.; Schilbach, K.; Vollmann, H.; Capper, D.; Goeppert, B.; Frei, K.; Bertalanffy, H.; et al. EGR-1 is regulated by N-methyl-D-aspartate-receptor stimulation and associated with patient survival in human high grade astrocytomas. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera, D.; Orozco, M.; de la Cruz, X. Alternative splicing of transcription factors’ genes: Beyond the increase of proteome diversity. Comp. Funct. Genomics. 2009, 905894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, Y.; Höpfler, M.; Ayatollahi, Z.; Barta, A.; Kalyna, M. Unmasking alternative splicing inside protein-coding exons defines exitrons and their role in proteome plasticity. Genome. Res. 2015, 25, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, L.; Xing, Y. The Expanding Landscape of Alternative Splicing Variation in Human Populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagurovskaya, M.; Shareef, M.M.; Das, A.; Reeves, A.; Gupta, S.; Sudol, M.; Bedford, M.T.; Prichard, J.; Mohiuddin, M.; Ahmed, M.M. EGR-1 forms a complex with YAP-1 and upregulates Bax expression in irradiated prostate carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aliperti, V.; Sgueglia, G.; Aniello, F.; Vitale, E.; Fucci, L.; Donizetti, A. Identification, Characterization, and Regulatory Mechanisms of a Novel EGR1 Splicing Isoform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071548
Aliperti V, Sgueglia G, Aniello F, Vitale E, Fucci L, Donizetti A. Identification, Characterization, and Regulatory Mechanisms of a Novel EGR1 Splicing Isoform. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(7):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071548
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliperti, Vincenza, Giulia Sgueglia, Francesco Aniello, Emilia Vitale, Laura Fucci, and Aldo Donizetti. 2019. "Identification, Characterization, and Regulatory Mechanisms of a Novel EGR1 Splicing Isoform" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 7: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071548
APA StyleAliperti, V., Sgueglia, G., Aniello, F., Vitale, E., Fucci, L., & Donizetti, A. (2019). Identification, Characterization, and Regulatory Mechanisms of a Novel EGR1 Splicing Isoform. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(7), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071548




