IL-36 Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammatory Responses and Their Emerging Role in Immunology of Reproduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Immune System and Pregnancy
1.2. Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Responses during Pregnancy
2. The IL-1 Superfamily Members and Their Function in Reproduction
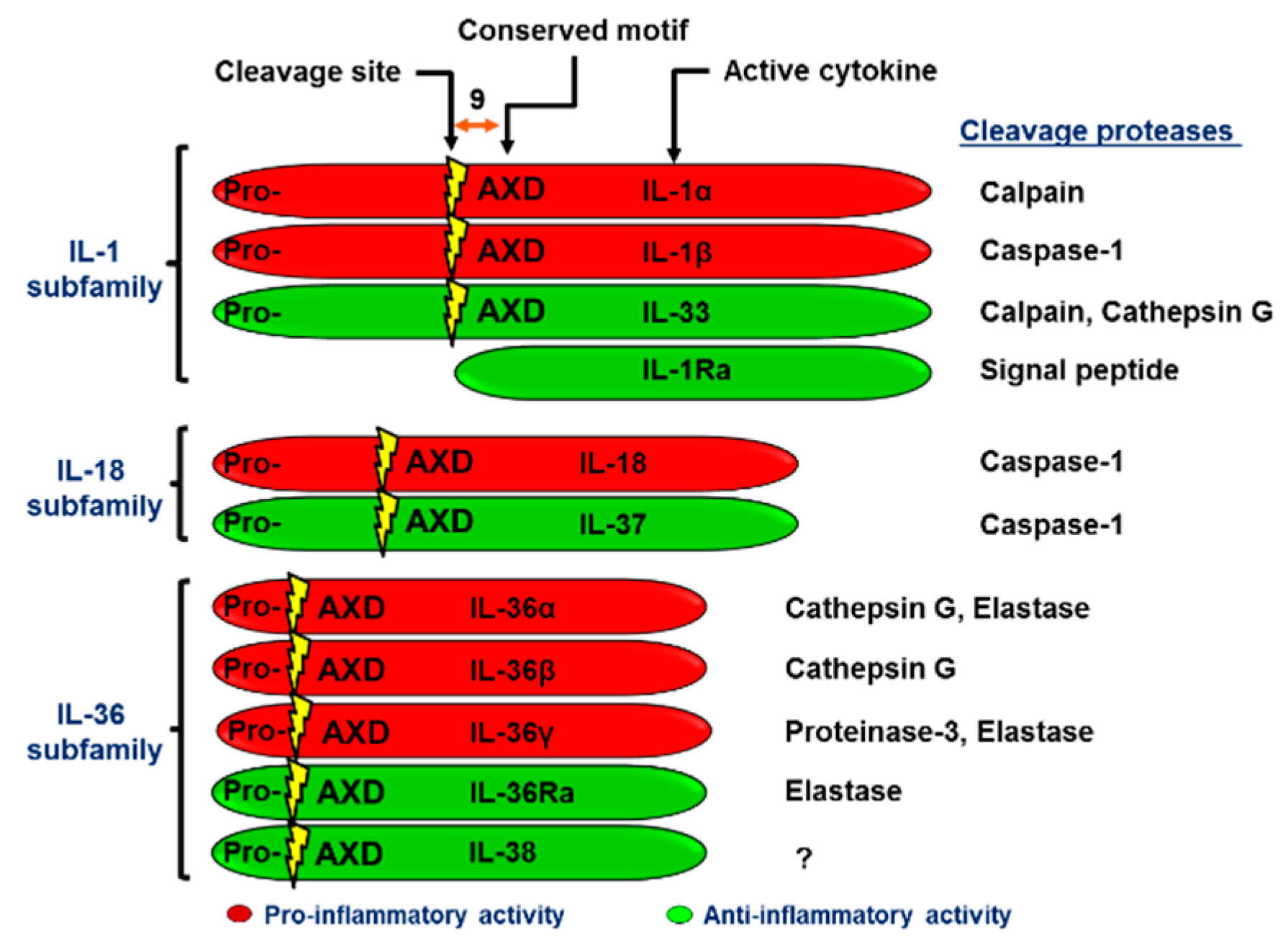
2.1. The IL-1 Subfamily
2.2. The IL-18 Subfamily
2.3. The IL-36 Subfamily
3. Biology of the IL-36 Subfamily
3.1. Processing and Secretion of IL-36 (α, β, γ) and IL-36Ra.
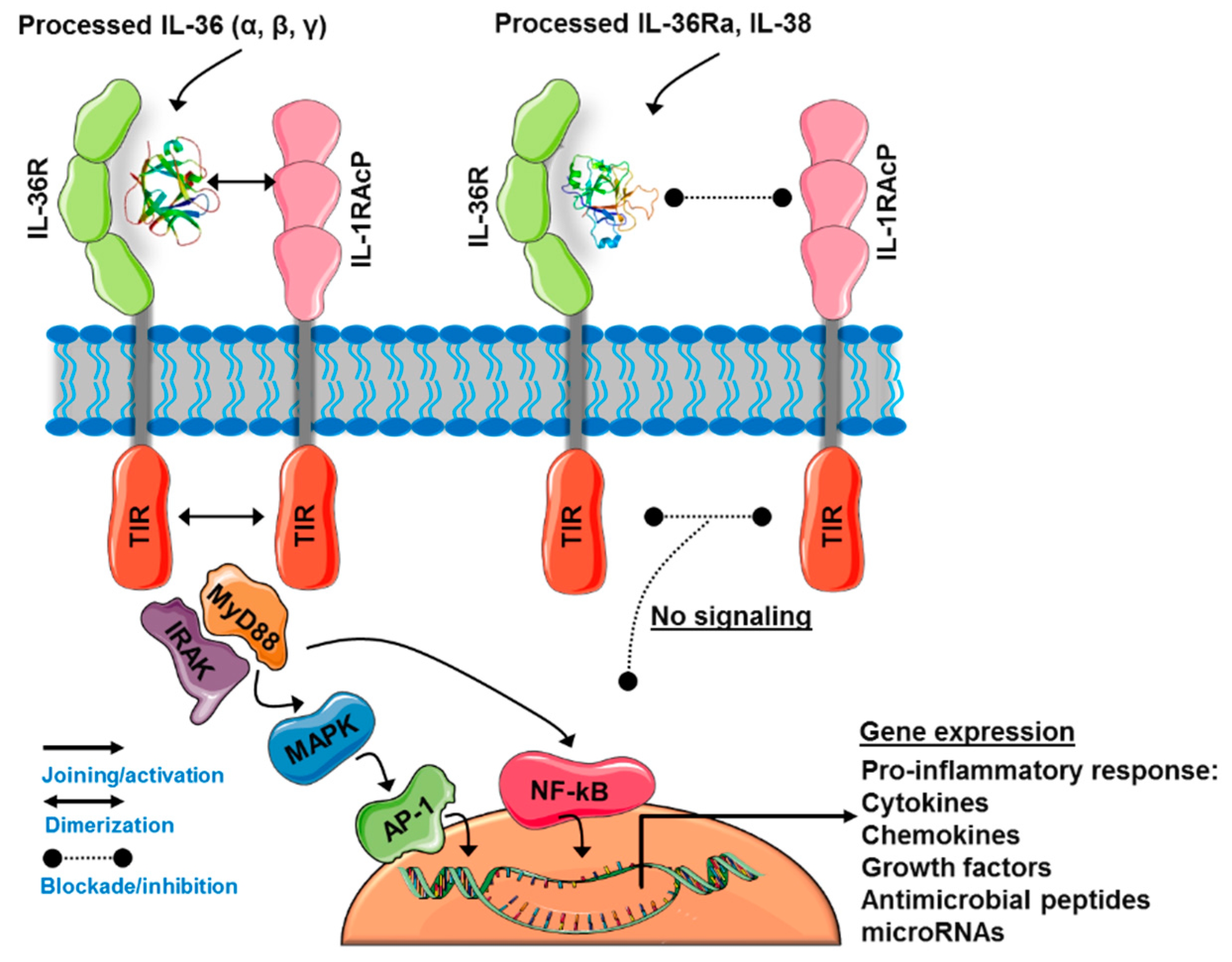
3.2. The IL-36 Receptor Complex
3.3. IL-36-Induced Signaling Pathways
3.4. IL-36Ra and IL-38: The Negative Regulators of IL-36R Activity
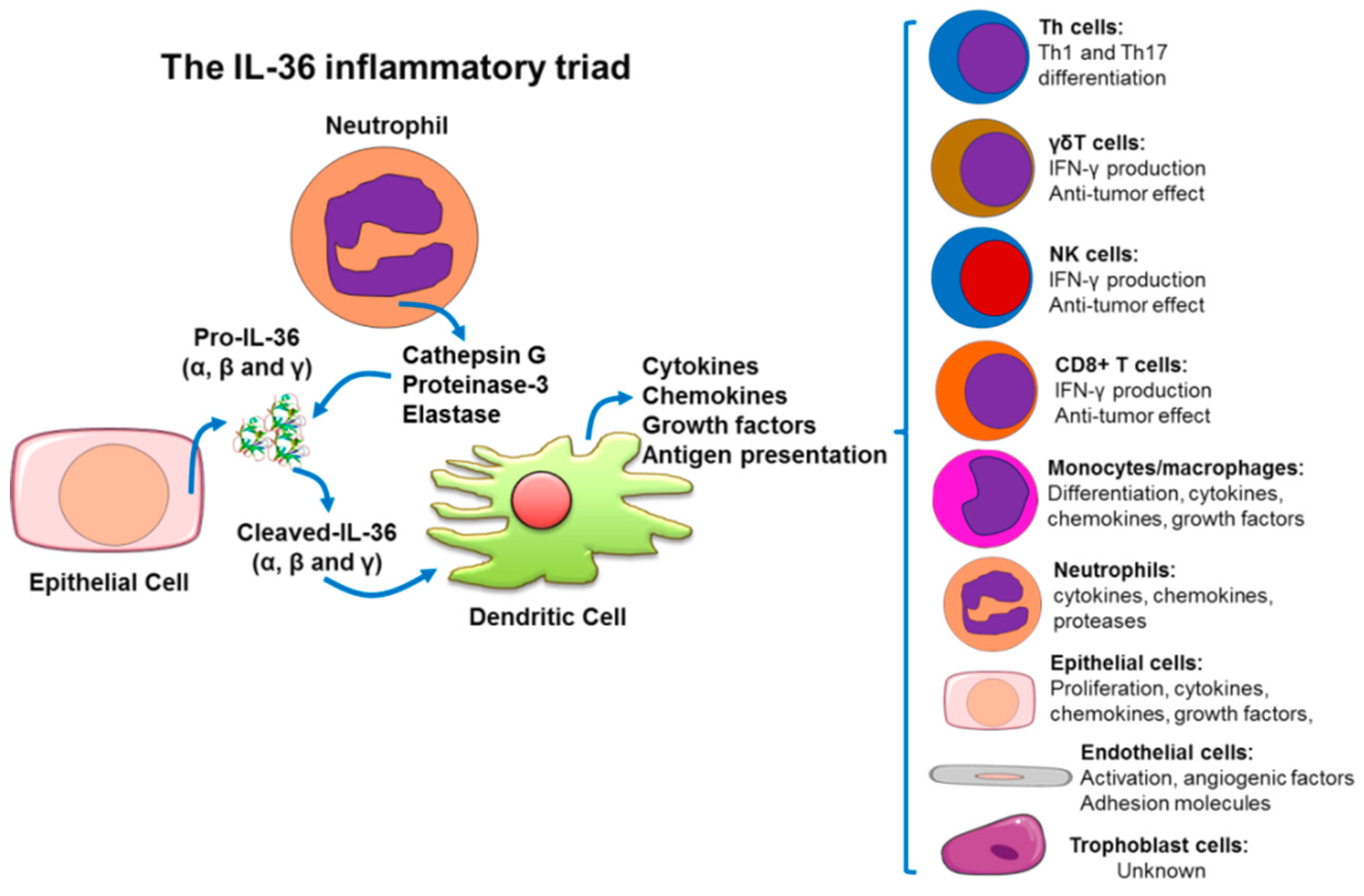
4. IL-36(α, β, γ) Cytokines as Amplifiers of the Inflammatory Response
4.1. Skin Immunopathophysiology as a Model to Understand The IL-36-Trigered Inflammatory Response
4.2. Inflammatory Pathologies Related with the IL-36 Dysregulation
5. IL-36 Cytokines in Female Reproductive Tissues and Pregnancy
6. Future Issues for IL-36 Cytokines in Pregnancy
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APCs | Antigen presenting cells |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BCG | Bacillus chalmette–guerin |
| BMDCs | Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells |
| BMDMs | Bone marrow derived macrophages |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| DSS | Dextran sodium sulfate |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| HBD | Human beta-defensin |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| HLA | Human leucocyte antigen |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IL-1RacP | Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein |
| IMQ | Imiquimod |
| IRAK | Interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase |
| ISRE | Interferon-stimulated response element |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPKs | mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MDDCs | Monocyte-derived dendritic cells |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 |
| NALP3 | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 |
| NF-kB | nuclear factor ‘kappa-light-chain-enhancer’ of activated B-cells |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular pattern |
| TCR | T Cell Receptor |
| Th | T helper |
| TILs | Tubulointerstitial lesions |
| TIR | Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TRAF-6 | TNF receptor-associated factor 6 |
| Tregs | T regulatory cells |
| uNKs | Uterine natural killer cells |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Medawar, P.B. Immunity to homologous grafted skin; the fate of skin homografts transplanted to the brain, to subcutaneous tissue, and to the anterior chamber of the eye. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1948, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.K.; Lichtman, A.H.; Pillai, S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 7th ed.; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; p. x. 545p. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, A.R.; Griffith, O.W.; Wagner, G.P. The inflammation paradox in the evolution of mammalian pregnancy: Turning a foe into a friend. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2017, 47, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, O.W.; Chavan, A.R.; Protopapas, S.; Maziarz, J.; Romero, R.; Wagner, G.P. Embryo implantation evolved from an ancestral inflammatory attachment reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6566–E6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Romero, R.; Aldo, P.B.; Abrahams, V.M. Is the trophoblast an immune regulator? The role of Toll-like receptors during pregnancy. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 25, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiehm, E.R.; Ochs, H.D.; Winkelstein, J.A. Immunologic Disorders in Infants & Children, 5th ed.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004; p. xxi. 1512p. [Google Scholar]
- Leber, A.; Teles, A.; Zenclussen, A.C. Regulatory T cells and their role in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Baranov, V. The role of placental exosomes in reproduction. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Prieto, D.M.; Ospina-Prieto, S.; Chaiwangyen, W.; Schoenleben, M.; Markert, U.R. Pregnancy-associated miRNA-clusters. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2013, 97, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohner, C.; Plosch, T.; Faas, M.M. Immune-modulatory effects of syncytiotrophoblast extracellular vesicles in pregnancy and preeclampsia. Placenta 2017, 60 (Suppl. 1), S41–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatila, T.A.; Williams, C.B. Regulatory T cells: Exosomes deliver tolerance. Immunity 2014, 41, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, I.; Means, R.E.; Aldo, P.; Koga, K.; Lang, S.M.; Booth, C.J.; Manzur, A.; Oyarzun, E.; Romero, R.; Mor, G. Viral infection of the placenta leads to fetal inflammation and sensitization to bacterial products predisposing to preterm labor. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Cardenas, I. The immune system in pregnancy: A unique complexity. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Cardenas, I.; Abrahams, V.; Guller, S. Inflammation and pregnancy: The role of the immune system at the implantation site. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1221, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, V.M.; Kim, Y.M.; Straszewski, S.L.; Romero, R.; Mor, G. Macrophages and apoptotic cell clearance during pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2004, 51, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fest, S.; Aldo, P.B.; Abrahams, V.M.; Visintin, I.; Alvero, A.; Chen, R.; Chavez, S.L.; Romero, R.; Mor, G. Trophoblast-macrophage interactions: A regulatory network for the protection of pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2007, 57, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, V.M.; Visintin, I.; Aldo, P.B.; Guller, S.; Romero, R.; Mor, G. A role for TLRs in the regulation of immune cell migration by first trimester trophoblast cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 8096–8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, P.M.; Sargent, I.L.; Redman, C.W. Cell populations in human early pregnancy decidua: Characterization and isolation of large granular lymphocytes by flow cytometry. Immunology 1988, 65, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.; Makino, T.; Sugi, T.; Matsubayashi, H.; Ozawa, N.; Nozawa, S. Flow-cytometric analysis of immune cell populations in human decidua from various types of first-trimester pregnancy. Hum. Immunol. 1992, 34, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Goldman-Wohl, D.; Hamani, Y.; Avraham, I.; Greenfield, C.; Natanson-Yaron, S.; Prus, D.; Cohen-Daniel, L.; Arnon, T.I.; Manaster, I.; et al. Decidual NK cells regulate key developmental processes at the human fetal-maternal interface. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, T.; Schust, D.J. The contribution of macrophages to normal and pathological pregnancies. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, A. Immune surveillance of the maternal/fetal interface: Controversies and implications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilburgs, T.; Schonkeren, D.; Eikmans, M.; Nagtzaam, N.M.; Datema, G.; Swings, G.M.; Prins, F.; van Lith, J.M.; van der Mast, B.J.; Roelen, D.L.; et al. Human decidual tissue contains differentiated CD8+ effector-memory T cells with unique properties. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4470–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.X.; Duan, J.; Li, M.Q.; Xu, B.; Li, D.J.; Jin, L.P. The decidual gamma-delta T cells up-regulate the biological functions of trophoblasts via IL-10 secretion in early human pregnancy. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 141, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyborne, K.D.; Cranfill, R.L.; Carding, S.R.; Born, W.K.; O’Brien, R.L. Characterization of gamma delta T lymphocytes at the maternal-fetal interface. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor, L.M.; Colucci, F. Uterine Natural Killer Cells: Functional Distinctions and Influence on Pregnancy in Humans and Mice. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, A.; Loke, C. Immunology of placentation in eutherian mammals. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagana, A.S.; Giordano, D.; Loddo, S.; Zoccali, G.; Vitale, S.G.; Santamaria, A.; Buemi, M.; D’Anna, R. Decreased Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) and increased Natural Killer (NK) cells in peripheral blood as possible early markers of preeclampsia: A case-control analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 295, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskarin, G.; Kammerer, U.; Rukavina, D.; Thomson, A.W.; Fernandez, N.; Blois, S.M. Antigen-presenting cells and materno-fetal tolerance: An emerging role for dendritic cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2007, 58, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.; Toth, B.; Brunnhuber, R.; Rampf, E.; Weissenbacher, T.; Santoso, L.; Friese, K.; Jeschke, U. Glycodelin A induces a tolerogenic phenotype in monocyte-derived dendritic cells in vitro. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2008, 60, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G. Inflammation and pregnancy: The role of toll-like receptors in trophoblast-immune interaction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1127, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.K.; Tay, C.S.; Erlebacher, A. Dendritic cell entrapment within the pregnant uterus inhibits immune surveillance of the maternal/fetal interface in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, A.A.; McSorley, S.J.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Ehst, B.D.; Ingulli, E.; Rudensky, A.Y.; Jenkins, M.K. Distinct dendritic cell populations sequentially present antigen to CD4 T cells and stimulate different aspects of cell-mediated immunity. Immunity 2003, 19, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenspach, E.J.; Lemos, M.P.; Porrett, P.M.; Turka, L.A.; Laufer, T.M. Migratory and lymphoid-resident dendritic cells cooperate to efficiently prime naive CD4 T cells. Immunity 2008, 29, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsalem, H.; Kwan, M.; Hazan, A.; Zhang, J.; Jones, R.L.; Whittle, W.; Kingdom, J.C.; Croy, B.A.; Lye, S.J.; Dunk, C.E. Identification of a novel neutrophil population: Proangiogenic granulocytes in second-trimester human decidua. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3070–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaks, V.; Birnberg, T.; Berkutzki, T.; Sela, S.; BenYashar, A.; Kalchenko, V.; Mor, G.; Keshet, E.; Dekel, N.; Neeman, M.; et al. Uterine DCs are crucial for decidua formation during embryo implantation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3954–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, A. Mechanisms of T cell tolerance towards the allogeneic fetus. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, G.; Koga, K. Macrophages and pregnancy. Reprod. Sci. 2008, 15, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, G. Pregnancy reconceived. Nat. Hist. 2007, 116, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Dekel, N.; Gnainsky, Y.; Granot, I.; Mor, G. Inflammation and implantation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Mor, G. Toll-like receptors at the maternal-fetal interface in normal pregnancy and pregnancy disorders. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Abrahams, V.M. Immunology of implantation. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2002, 22, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Espinoza, J.; Goncalves, L.F.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Friel, L.A.; Nien, J.K. Inflammation in preterm and term labour and delivery. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006, 11, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, R.; Espinoza, J.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Gotsch, F.; Hassan, S.; Erez, O.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Mazor, M. The preterm parturition syndrome. BJOG 2006, 113 (Suppl. 3), 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiofalo, B.; Lagana, A.S.; Vaiarelli, A.; La Rosa, V.L.; Rossetti, D.; Palmara, V.; Valenti, G.; Rapisarda, A.M.C.; Granese, R.; Sapia, F.; et al. Do miRNAs Play a Role in Fetal Growth Restriction? A Fresh Look to a Busy Corner. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6073167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospina-Prieto, S.; Chaiwangyen, W.; Herrmann, J.; Groten, T.; Schleussner, E.; Markert, U.R.; Morales-Prieto, D.M. MicroRNA-141 is upregulated in preeclamptic placentae and regulates trophoblast invasion and intercellular communication. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2016, 172, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagana, A.S.; Vitale, S.G.; Sapia, F.; Valenti, G.; Corrado, F.; Padula, F.; Rapisarda, A.M.C.; D’Anna, R. miRNA expression for early diagnosis of preeclampsia onset: Hope or hype? J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Nakashima, A.; Shima, T.; Ito, M. Th1/Th2/Th17 and regulatory T-cell paradigm in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassoy, E.Y.; Towne, J.E.; Gabay, C. Regulation and function of interleukin-36 cytokines. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gery, I.; Gershon, R.K.; Waksman, B.H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J. Exp. Med. 1972, 136, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. The history of fever, leukocytic pyrogen and interleukin-1. Temperature 2015, 2, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.L.; Renshaw, B.R.; Garka, K.E.; Smith, D.E.; Sims, J.E. Genomic organization of the interleukin-1 locus. Genomics 2002, 79, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklin, M.J.; Barton, J.L.; Nguyen, M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Duff, G.W.; Kornman, K. A sequence-based map of the nine genes of the human interleukin-1 cluster. Genomics 2002, 79, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.E.; Nicklin, M.J.; Bazan, J.F.; Barton, J.L.; Busfield, S.J.; Ford, J.E.; Kastelein, R.A.; Kumar, S.; Lin, H.; Mulero, J.J.; et al. A new nomenclature for IL-1-family genes. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 536–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.; Arend, W.; Sims, J.; Smith, D.; Blumberg, H.; O’Neill, L.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Pizarro, T.; Hoffman, H.; Bufler, P.; et al. IL-1 family nomenclature. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.E.; Smith, D.E. The IL-1 family: Regulators of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarlasci, V.; Cosmi, L.; Maggi, L.; Liotta, F.; Annunziato, F. IL-1 and T Helper Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Kobayashi, Y. Selective release of a processed form of interleukin 1 alpha. Cytokine 1994, 6, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, P.; Kaplanov, I.; Romzova, M.; Bernardis, L.; Braiman, A.; Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N. The transcription of the alarmin cytokine interleukin-1 alpha is controlled by hypoxia inducible factors 1 and 2 alpha in hypoxic cells. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, P.; Carmi, Y.; Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N. Interleukin-1alpha. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Kono, H.; Golenbock, D.; Reed, G.; Akira, S.; Rock, K.L. Identification of a key pathway required for the sterile inflammatory response triggered by dying cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Bull, H.G.; Calaycay, J.R.; Chapman, K.T.; Howard, A.D.; Kostura, M.J.; Miller, D.K.; Molineaux, S.M.; Weidner, J.R.; Aunins, J.; et al. A novel heterodimeric cysteine protease is required for interleukin-1 beta processing in monocytes. Nature 1992, 356, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancais, E.; Roga, S.; Gautier, V.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.; Monsarrat, B.; Girard, J.P.; Cayrol, C. IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. An IL-1 family member requires caspase-1 processing and signals through the ST2 receptor. Immunity 2005, 23, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Overview of the interleukin-1 family of ligands and receptors. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horai, R.; Saijo, S.; Tanioka, H.; Nakae, S.; Sudo, K.; Okahara, A.; Ikuse, T.; Asano, M.; Iwakura, Y. Development of chronic inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in interleukin 1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, M.; Sanford, T.R.; Wood, G.W. Expression of interleukin 1, interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha in mouse uterus during the peri-implantation period of pregnancy. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1993, 97, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, Y.J.; Liong, S.; Permezel, M.; Rice, G.E.; Di Quinzio, M.K.; Georgiou, H.M. The interplay of the interleukin 1 system in pregnancy and labor. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebisch, G.; Neumaier-Wagner, P.M.; Huch, R.; von Mandach, U. Maternal serum interleukin-1 beta, -6 and -8 levels and potential determinants in pregnancy and peripartum. J. Perinat. Med. 2004, 32, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlock, C.I.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Tatum, K.; Adams, H.P.; Tan, F.; Lou, Y. Unique temporal and spatial expression patterns of IL-33 in ovaries during ovulation and estrous cycle are associated with ovarian tissue homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, V.; Mairhofer, M.; Otti, G.R.; Hiden, U.; Spittler, A.; Zeisler, H.; Fiala, C.; Knofler, M.; Pollheimer, J. Macrophage-derived IL-33 is a critical factor for placental growth. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3734–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granne, I.; Southcombe, J.H.; Snider, J.V.; Tannetta, D.S.; Child, T.; Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L. ST2 and IL-33 in pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Okamura, H. Interleukin-18 is a unique cytokine that stimulates both Th1 and Th2 responses depending on its cytokine milieu. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Tsutsi, H.; Komatsu, T.; Yutsudo, M.; Hakura, A.; Tanimoto, T.; Torigoe, K.; Okura, T.; Nukada, Y.; Hattori, K.; et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-gamma production by T cells. Nature 1995, 378, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledee-Bataille, N.; Dubanchet, S.; Coulomb-L’hermine, A.; Durand-Gasselin, I.; Frydman, R.; Chaouat, G. A new role for natural killer cells, interleukin (IL)-12, and IL-18 in repeated implantation failure after in vitro fertilization. Fertil. Steril. 2004, 81, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledee-Bataille, N.; Olivennes, F.; Kadoch, J.; Dubanchet, S.; Frydman, N.; Chaouat, G.; Frydman, R. Detectable levels of interleukin-18 in uterine luminal secretions at oocyte retrieval predict failure of the embryo transfer. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 1968–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokmadzic, V.S.; Tsuji, Y.; Bogovic, T.; Laskarin, G.; Cupurdija, K.; Strbo, N.; Koyama, K.; Okamura, H.; Podack, E.R.; Rukavina, D. IL-18 is present at the maternal-fetal interface and enhances cytotoxic activity of decidual lymphocytes. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2002, 48, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuki, M.; Kusumoto, K.; Murakami, Y.; Kanayama, M.; Takeuchi, S.; Takahashi, S. Expression of interleukin-18 receptor mRNA in the mouse endometrium. J. Reprod. Dev. 2007, 53, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, A.; Tsuji, Y.; Muranaka, J.; Kanazawa, R.; Nakata, Y.; Adachi, S.; Okamura, H.; Koyama, K. IL-18 in pregnancy; the elevation of IL-18 in maternal peripheral blood during labour and complicated pregnancies. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2000, 47, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Hanning, C.R.; Brigham-Burke, M.R.; Rieman, D.J.; Lehr, R.; Khandekar, S.; Kirkpatrick, R.B.; Scott, G.F.; Lee, J.C.; Lynch, F.J.; et al. Interleukin-1F7B (IL-1H4/IL-1F7) is processed by caspase-1 and mature IL-1F7B binds to the IL-18 receptor but does not induce IFN-gamma production. Cytokine 2002, 18, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torales-Cardena, A.; Martinez-Torres, I.; Rodriguez-Martinez, S.; Gomez-Chavez, F.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C.; Vazquez-Sanchez, E.A.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E. Cross Talk between Proliferative, Angiogenic, and Cellular Mechanisms Orchestred by HIF-1alpha in Psoriasis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 607363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensen, J.T.; Dawson, P.A.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Bowden, D.W. Identification of a novel human cytokine gene in the interleukin gene cluster on chromosome 2q12-14. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2001, 21, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Stoeckman, A.K.; Wu, G.; Boeckermann, A.N.; Azam, T.; Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.; van der Meer, J.W.; Hao, R.; Kalabokis, V.; et al. IL-38 binds to the IL-36 receptor and has biological effects on immune cells similar to IL-36 receptor antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3001–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towne, J.E.; Renshaw, B.R.; Douangpanya, J.; Lipsky, B.P.; Shen, M.; Gabel, C.A.; Sims, J.E. Interleukin-36 (IL-36) ligands require processing for full agonist (IL-36alpha, IL-36beta, and IL-36gamma) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42594–42602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, J.L.; Herbst, R.; Bosisio, D.; Higgins, L.; Nicklin, M.J. A tissue specific IL-1 receptor antagonist homolog from the IL-1 cluster lacks IL-1, IL-1ra, IL-18 and IL-18 antagonist activities. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debets, R.; Timans, J.C.; Homey, B.; Zurawski, S.; Sana, T.R.; Lo, S.; Wagner, J.; Edwards, G.; Clifford, T.; Menon, S.; et al. Two novel IL-1 family members, IL-1 delta and IL-1 epsilon, function as an antagonist and agonist of NF-kappa B activation through the orphan IL-1 receptor-related protein 2. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero, J.J.; Pace, A.M.; Nelken, S.T.; Loeb, D.B.; Correa, T.R.; Drmanac, R.; Ford, J.E. IL1HY1: A novel interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 263, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.E.; Renshaw, B.R.; Ketchem, R.R.; Kubin, M.; Garka, K.E.; Sims, J.E. Four new members expand the interleukin-1 superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busfield, S.J.; Comrack, C.A.; Yu, G.; Chickering, T.W.; Smutko, J.S.; Zhou, H.; Leiby, K.R.; Holmgren, L.M.; Gearing, D.P.; Pan, Y. Identification and gene organization of three novel members of the IL-1 family on human chromosome 2. Genomics 2000, 66, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; McDonnell, P.C.; Lehr, R.; Tierney, L.; Tzimas, M.N.; Griswold, D.E.; Capper, E.A.; Tal-Singer, R.; Wells, G.I.; Doyle, M.L.; et al. Identification and initial characterization of four novel members of the interleukin-1 family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10308–10314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, U.; Scholler, J.; Gurgel, J.; Renshaw, B.; Sims, J.E.; Gabel, C.A. Externalization of the leaderless cytokine IL-1F6 occurs in response to lipopolysaccharide/ATP activation of transduced bone marrow macrophages. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4021–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, L.H.; Milora, K.A.; Manupipatpong, K.K.; Jensen, L.E. The double-stranded RNA analogue polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid induces keratinocyte pyroptosis and release of IL-36gamma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towne, J.E.; Garka, K.E.; Renshaw, B.R.; Virca, G.D.; Sims, J.E. Interleukin (IL)-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP to activate the pathway leading to NF-kappaB and MAPKs. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13677–13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.M.; Sullivan, G.P.; Clancy, D.M.; Afonina, I.S.; Kulms, D.; Martin, S.J. Neutrophil-Derived Proteases Escalate Inflammation through Activation of IL-36 Family Cytokines. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, T.; Doble, R.; McGonagle, D.; Wasson, C.W.; Alase, A.; Stacey, M.; Wittmann, M. Neutrophil Elastase-mediated proteolysis activates the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-36 Receptor antagonist. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ho, A.S.; Haley-Vicente, D.; Zhang, J.; Bernal-Fussell, J.; Pace, A.M.; Hansen, D.; Schweighofer, K.; Mize, N.K.; Ford, J.E. Cloning and characterization of IL-1HY2, a novel interleukin-1 family member. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20597–20602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.; Schlemmer, A.; Wittig, I.; Richter, F.; Putyrski, M.; Frank, A.C.; Han, Y.; Jung, M.; Ernst, A.; Weigert, A.; et al. Interleukin-38 is released from apoptotic cells to limit inflammatory macrophage responses. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, J.E.; March, C.J.; Cosman, D.; Widmer, M.B.; MacDonald, H.R.; McMahan, C.J.; Grubin, C.E.; Wignall, J.M.; Jackson, J.L.; Call, S.M.; et al. cDNA expression cloning of the IL-1 receptor, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Science 1988, 241, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraschi, D.; Tagliabue, A. The interleukin-1 receptor family. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfeder, S.A.; Nunes, P.; Kwee, L.; Labow, M.; Chizzonite, R.A.; Ju, G. Molecular cloning and characterization of a second subunit of the interleukin 1 receptor complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 13757–13765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korherr, C.; Hofmeister, R.; Wesche, H.; Falk, W. A critical role for interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein in interleukin-1 signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Crowe, P.D.; Liu, C.; Chalmers, D.T.; Liu, X.J.; Liaw, C.; Clevenger, W.; Oltersdorf, T.; De Souza, E.B.; Maki, R.A. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a novel interleukin-1 receptor related protein (IL 1R-rp2). J. Neuroimmunol. 1996, 70, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.; Ybe, J.A.; Saha, S.S.; Caviness, G.; Raymond, E.; Ganesan, R.; Mbow, M.L.; Kao, C.C. Structural and Functional Attributes of the Interleukin-36 Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16597–16609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, S.; Sundberg, E.J. Molecular determinants of agonist and antagonist signaling through the IL-36 receptor. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Niyonsaba, F.; Ushio, H.; Akiyama, T.; Kiatsurayanon, C.; Smithrithee, R.; Ikeda, S.; Okumura, K.; Ogawa, H. Interleukin-36 cytokines enhance the production of host defense peptides psoriasin and LL-37 by human keratinocytes through activation of MAPKs and NF-kappaB. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 68, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigne, S.; Palmer, G.; Lamacchia, C.; Martin, P.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Rodriguez, E.; Ronchi, F.; Sallusto, F.; Dinh, H.; Sims, J.E.; et al. IL-36R ligands are potent regulators of dendritic and T cells. Blood 2011, 118, 5813–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chustz, R.T.; Nagarkar, D.R.; Poposki, J.A.; Favoreto, S., Jr.; Avila, P.C.; Schleimer, R.P.; Kato, A. Regulation and function of the IL-1 family cytokine IL-1F9 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Chen, H.X.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.J.; Yue, Q.; Xiao, M.; Li, J.W. IL-36 cytokine expression and its relationship with p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways in psoriasis vulgaris skin lesions. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2013, 33, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Hidaka, K.; Kanda, T.; Imaeda, H.; Shioya, M.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Kitoh, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Andoh, A. Increased Expression of Interleukin-36, a Member of the Interleukin-1 Cytokine Family, in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumberg, H.; Dinh, H.; Trueblood, E.S.; Pretorius, J.; Kugler, D.; Weng, N.; Kanaly, S.T.; Towne, J.E.; Willis, C.R.; Kuechle, M.K.; et al. Opposing activities of two novel members of the IL-1 ligand family regulate skin inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, L.; Morelli, M.; Scarponi, C.; Eisenmesser, E.Z.; Doti, N.; Pagnanelli, G.; Gubinelli, E.; Mazzanti, C.; Cavani, A.; Ruvo, M.; et al. IL-38 has an anti-inflammatory action in psoriasis and its expression correlates with disease severity and therapeutic response to anti-IL-17A treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.D.; Huang, A.F. Role of Interleukin-38 in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towne, J.E.; Sims, J.E. IL-36 in psoriasis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewood, C.; Fearnley, G.W.; Berekmeri, A.; Laws, P.; Macleod, T.; Ponnambalam, S.; Stacey, M.; Graham, A.; Wittmann, M. IL-36gamma Is a Strong Inducer of IL-23 in Psoriatic Cells and Activates Angiogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, H.; Dinh, H.; Dean, C., Jr.; Trueblood, E.S.; Bailey, K.; Shows, D.; Bhagavathula, N.; Aslam, M.N.; Varani, J.; Towne, J.E.; et al. IL-1RL2 and its ligands contribute to the cytokine network in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4354–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortola, L.; Rosenwald, E.; Abel, B.; Blumberg, H.; Schafer, M.; Coyle, A.J.; Renauld, J.C.; Werner, S.; Kisielow, J.; Kopf, M. Psoriasiform dermatitis is driven by IL-36-mediated DC-keratinocyte crosstalk. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3965–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Erme, A.M.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Wagenpfeil, J.; Holzel, M.; Ferring-Schmitt, S.; Sternberg, S.; Wittmann, M.; Peters, B.; Bosio, A.; Bieber, T.; et al. IL-36gamma (IL-1F9) is a biomarker for psoriasis skin lesions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yamasaki, K.; Saito, R.; Fukushi-Takahashi, S.; Shimada-Omori, R.; Asano, M.; Aiba, S. Alarmin function of cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL37 through IL-36gamma induction in human epidermal keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5140–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, A.M.; Baliwag, J.; Chen, C.S.; Guzman, A.M.; Stoll, S.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Ward, N.L.; Johnston, A. IL-36 promotes myeloid cell infiltration, activation, and inflammatory activity in skin. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 6053–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.; Xing, X.; Guzman, A.M.; Riblett, M.; Loyd, C.M.; Ward, N.L.; Wohn, C.; Prens, E.P.; Wang, F.; Maier, L.E.; et al. IL-1F5, -F6, -F8, and -F9: A novel IL-1 family signaling system that is active in psoriasis and promotes keratinocyte antimicrobial peptide expression. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Scheiermann, P.; Hardle, L.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Muhl, H. IL-36gamma/IL-1F9, an innate T-bet target in myeloid cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 41684–41696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigne, S.; Palmer, G.; Martin, P.; Lamacchia, C.; Strebel, D.; Rodriguez, E.; Olleros, M.L.; Vesin, D.; Garcia, I.; Ronchi, F.; et al. IL-36 signaling amplifies Th1 responses by enhancing proliferation and Th1 polarization of naive CD4+ T cells. Blood 2012, 120, 3478–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichii, O.; Otsuka, S.; Sasaki, N.; Yabuki, A.; Ohta, H.; Takiguchi, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Endoh, D.; Kon, Y. Local overexpression of interleukin-1 family, member 6 relates to the development of tubulointerstitial lesions. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.H.; Hua, K.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Chu, C.L.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.J.; Ka, S.M.; Tsai, Y.L.; Liu, F.C.; Chen, A. IL-36 Signaling Facilitates Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2022–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadas, R.A.; Ewart, S.L.; Iwakura, Y.; Medoff, B.D.; LeVine, A.M. IL-36alpha exerts pro-inflammatory effects in the lungs of mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mozaffarian, A.; Arnett, H.A.; Dinh, H.; Trueblood, E.S.; Towne, J.E. IL-36 induces inflammation and collagen deposition in the lung. Cytokine 2013, 63, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.Z.; Pan, K.; Zhao, J.J.; Chen, J.G.; Li, J.J.; Lv, L.; Wang, D.D.; Zheng, H.X.; Jiang, S.S.; Zhang, X.F.; et al. Decreased expression of interleukin-36alpha correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Feng, C.; Weinstein, A.; Xia, R.; Wen, W.; Lv, Q.; Zuo, S.; Tang, P.; Yang, X.; et al. IL-36gamma Transforms the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes Type 1 Lymphocyte-Mediated Antitumor Immune Responses. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Contreras, O.; Harusato, A.; Nishio, H.; Flannigan, K.L.; Ngo, V.; Leoni, G.; Neumann, P.A.; Geem, D.; Lili, L.N.; Ramadas, R.A.; et al. Cutting Edge: IL-36 Receptor Promotes Resolution of Intestinal Damage. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.L.; Abo, H.; Maxim, E.; Harusato, A.; Geem, D.; Medina-Contreras, O.; Merlin, D.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Nusrat, A.; Denning, T.L. A cytokine network involving IL-36gamma, IL-23, and IL-22 promotes antimicrobial defense and recovery from intestinal barrier damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5076–E5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, M.A.; Bart, G.; Penhoat, M.; Amiaud, J.; Brulin, B.; Charrier, C.; Morel, F.; Lecron, J.C.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M.; Bourreille, A.; et al. Distinct expression of interleukin (IL)-36alpha, beta and gamma, their antagonist IL-36Ra and IL-38 in psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segueni, N.; Vigne, S.; Palmer, G.; Bourigault, M.L.; Olleros, M.L.; Vesin, D.; Garcia, I.; Ryffel, B.; Quesniaux, V.F.; Gabay, C. Limited Contribution of IL-36 versus IL-1 and TNF Pathways in Host Response to Mycobacterial Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costelloe, C.; Watson, M.; Murphy, A.; McQuillan, K.; Loscher, C.; Armstrong, M.E.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; O’Neill, L.A.; Mills, K.H.; et al. IL-1F5 mediates anti-inflammatory activity in the brain through induction of IL-4 following interaction with SIGIRR/TIR8. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1960–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, D.; Palmer, G.; Barton, J.L.; Mezin, F.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Bas, S.; Duffy, T.; Noger, M.; Guerne, P.A.; Nicklin, M.J.; et al. The new IL-1 family member IL-1F8 stimulates production of inflammatory mediators by synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamacchia, C.; Palmer, G.; Rodriguez, E.; Martin, P.; Vigne, S.; Seemayer, C.A.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Towne, J.E.; Gabay, C. The severity of experimental arthritis is independent of IL-36 receptor signaling. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derer, A.; Groetsch, B.; Harre, U.; Bohm, C.; Towne, J.; Schett, G.; Frey, S.; Hueber, A.J. Blockade of IL-36 receptor signaling does not prevent from TNF-induced arthritis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Towne, J.E. Regulation and function of interleukin-36 cytokines in homeostasis and pathological conditions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.A.; Lucs, A.V.; DeVoti, J.; Blanc, L.; Papoin, J.; Wu, R.; Papayannakos, C.J.; Abramson, A.; Bonagura, V.R.; Steinberg, B.M. Poly(I:C) induces controlled release of IL-36gamma from keratinocytes in the absence of cell death. Immunol. Res. 2015, 63, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, S.M.; Throop, A.L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. IL-36gamma Augments Host Defense and Immune Responses in Human Female Reproductive Tract Epithelial Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, J.K.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. IL-36gamma induces a transient HSV-2 resistant environment that protects against genital disease and pathogenesis. Cytokine 2018, 111, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrieta-Coxca, J.M.; Gomez-Chavez, F.; Baeza-Martinez, D.A.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C.; Perez-Tapia, S.M.; Reyes-Maldonado, E.; Rodriguez-Martinez, S. Estrous Cycle and Gestational Age-Dependent Expression of Members of the Interleukin-36 Subfamily in a Semi-Allogeneic Model of Infected and Non-Infected Murine Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrieta-Coxca, J.M.; Gómez-Chávez, F.; Cancino-Díaz, M.E.; Cancino-Díaz, J.C.; Rodríguez-Martínez, S. L. monocytogenes induces overexpression of proinflammatory IL-36 cytokines in a murine model of early pregnancy. J Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 115, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southcombe, J.H.; Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L.; Granne, I. Interleukin-1 family cytokines and their regulatory proteins in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, G.; Flores-Espinosa, P.; Preciado-Martinez, E.; Bermejo-Martinez, L.; Espejel-Nunez, A.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Maida-Claros, R.; Flores-Pliego, A.; Zaga-Clavellina, V. In vitro progesterone modulation on bacterial endotoxin-induced production of IL-1beta, TNFalpha, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, MIP-1alpha, and MMP-9 in pre-labor human term placenta. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2015, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, R.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Alpay Savasan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hussein, Y.; Dong, Z.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Kim, C.J.; Hassan, S.S. Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in preterm labor with intact membranes and preterm PROM: A study of the alarmin HMGB1. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 24, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrakchi, S.; Guigue, P.; Renshaw, B.R.; Puel, A.; Pei, X.Y.; Fraitag, S.; Zribi, J.; Bal, E.; Cluzeau, C.; Chrabieh, M.; et al. Interleukin-36-receptor antagonist deficiency and generalized pustular psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoufriadis, A.; Simpson, M.A.; Pink, A.E.; Di Meglio, P.; Smith, C.H.; Pullabhatla, V.; Knight, J.; Spain, S.L.; Nestle, F.O.; Burden, A.D.; et al. Mutations in IL36RN/IL1F5 are associated with the severe episodic inflammatory skin disease known as generalized pustular psoriasis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, W.I.; Lee, Y.H. The associations between interleukin-1 polymorphisms and susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis: A meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2012, 79, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.J.; Peddle, L.; Rahman, P.; Hu, P.; Greenwood, C.M.; Inman, R.D. Interleukin 1 polymorphisms in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in Korea. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Adair, C.D.; Weeks, J.W.; Lewis, D.F.; Alexander, J.S. Increased neutrophil-endothelial adhesion induced by placental factors is mediated by platelet-activating factor in preeclampsia. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 1999, 6, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Philibert, L.; Lucas, M.J. Neutrophil activation induced by placental factors in normal and pre-eclamptic pregnancies in vitro. Placenta 2001, 22, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murrieta-Coxca, J.M.; Rodríguez-Martínez, S.; Cancino-Diaz, M.E.; Markert, U.R.; Favaro, R.R.; Morales-Prieto, D.M. IL-36 Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammatory Responses and Their Emerging Role in Immunology of Reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071649
Murrieta-Coxca JM, Rodríguez-Martínez S, Cancino-Diaz ME, Markert UR, Favaro RR, Morales-Prieto DM. IL-36 Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammatory Responses and Their Emerging Role in Immunology of Reproduction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(7):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071649
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurrieta-Coxca, José Martin, Sandra Rodríguez-Martínez, Mario Eugenio Cancino-Diaz, Udo R. Markert, Rodolfo R. Favaro, and Diana M. Morales-Prieto. 2019. "IL-36 Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammatory Responses and Their Emerging Role in Immunology of Reproduction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 7: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071649
APA StyleMurrieta-Coxca, J. M., Rodríguez-Martínez, S., Cancino-Diaz, M. E., Markert, U. R., Favaro, R. R., & Morales-Prieto, D. M. (2019). IL-36 Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammatory Responses and Their Emerging Role in Immunology of Reproduction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(7), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071649




