Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CB1 Signaling
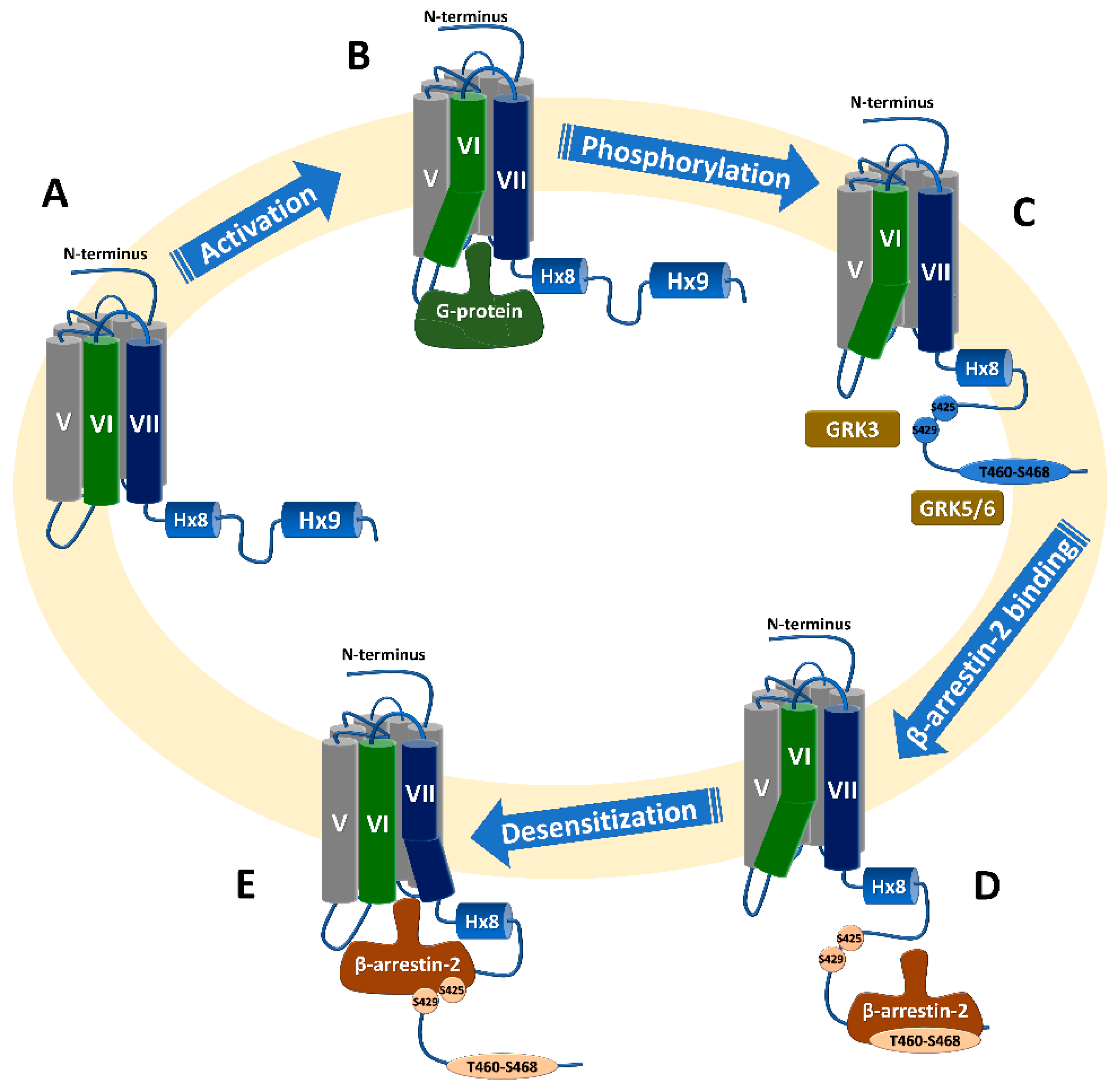
Phosphorylation and Subsequent β-Arrestin Recruitment
3. Structural Determinant of G-Protein Coupling versus β-Arrestin Coupling at CB1: Insights from Mutation Studies and Crystal Structures
3.1. Structural Determinant of Biased Signaling in the Cytoplasmic Transmembrane Domain of the Receptor
3.2. Structural Determinants at the C-Terminus and the IC Loops
3.2.1. G-Protein Interaction with the C-Terminus and IC loops
3.2.2. β-Arrestin2 Recruitment to Phosphorylated C-Terminus Proximal to the Transmembrane Domain Results in Receptor Desensitization
3.2.3. β-Arrestin2 Recruitment to Phosphorylated C-Terminus Distal to the Transmembrane Domain Results in Receptor Internalization
3.2.4. β-Arrestin1 Recruitment to the Receptor Results in G-Protein Independent Signal
3.2.5. Recruitment of β-Arrestins to the C-Terminus Can be Altered in the Presence of Other Regulatory Proteins
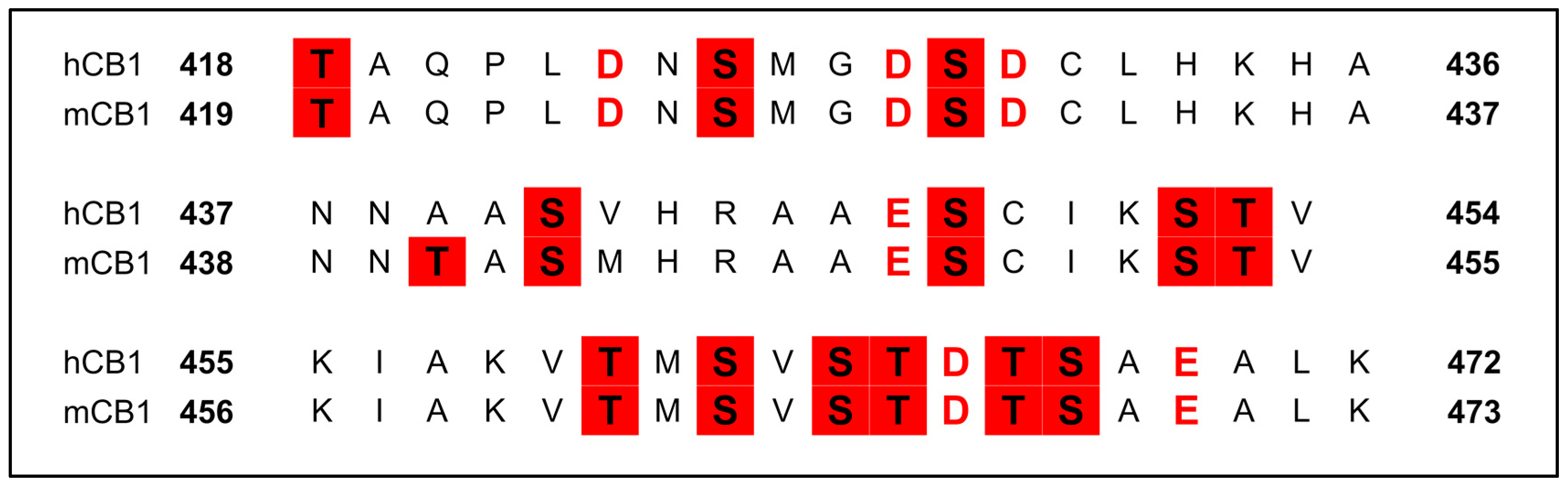
3.2.6. Phosphorylation of the C-Terminus
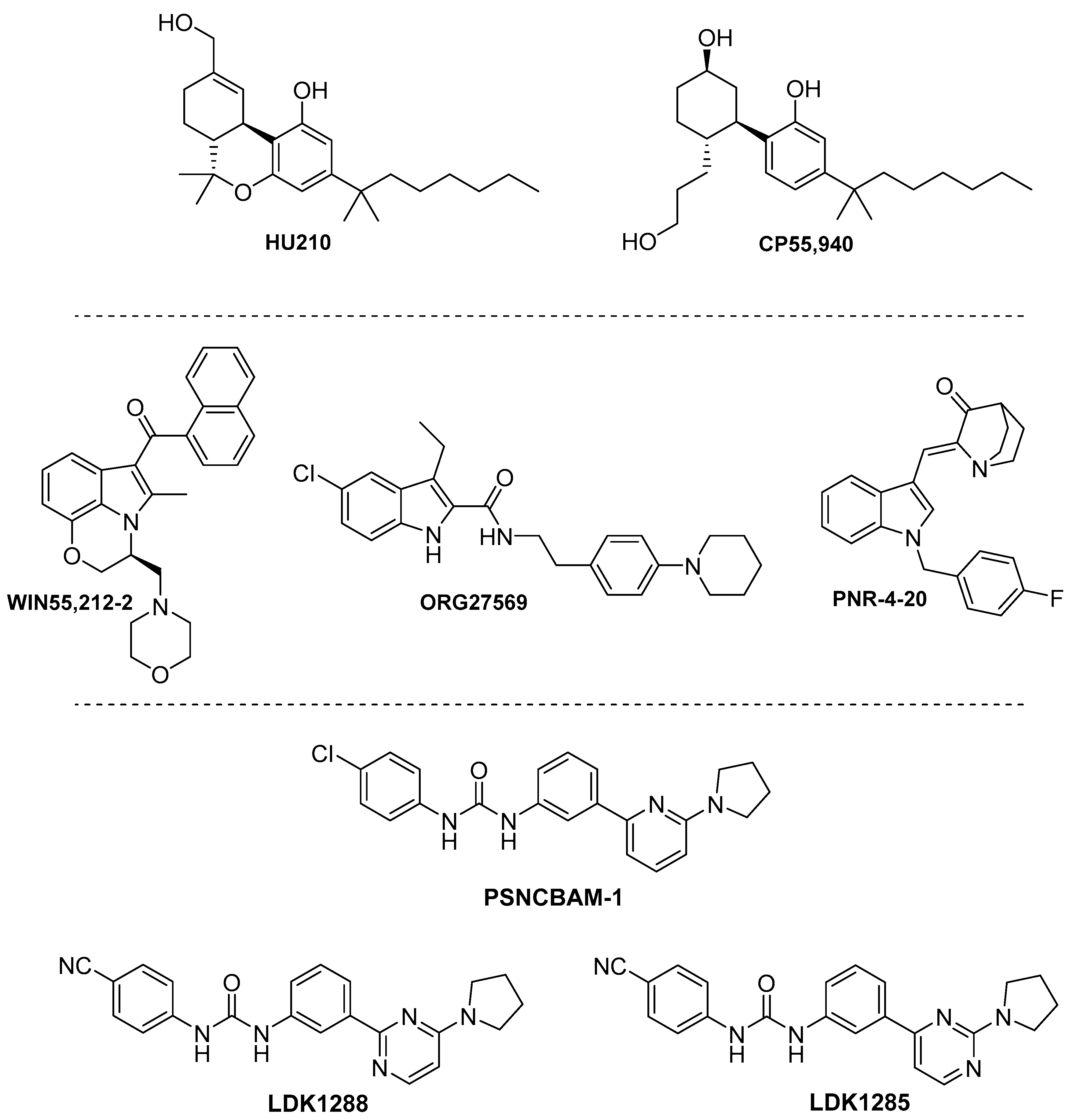
4. CB1 Biased Ligands
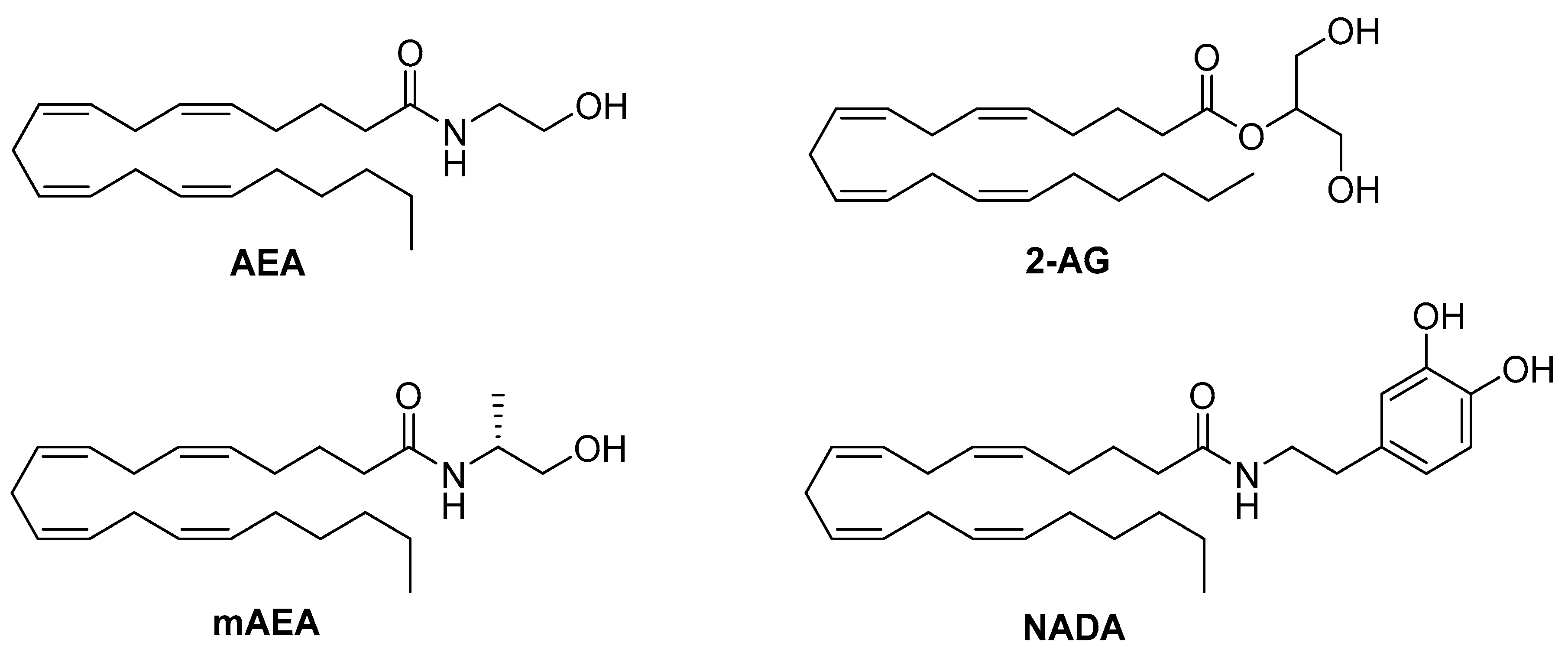
4.1. Endocannabinoids
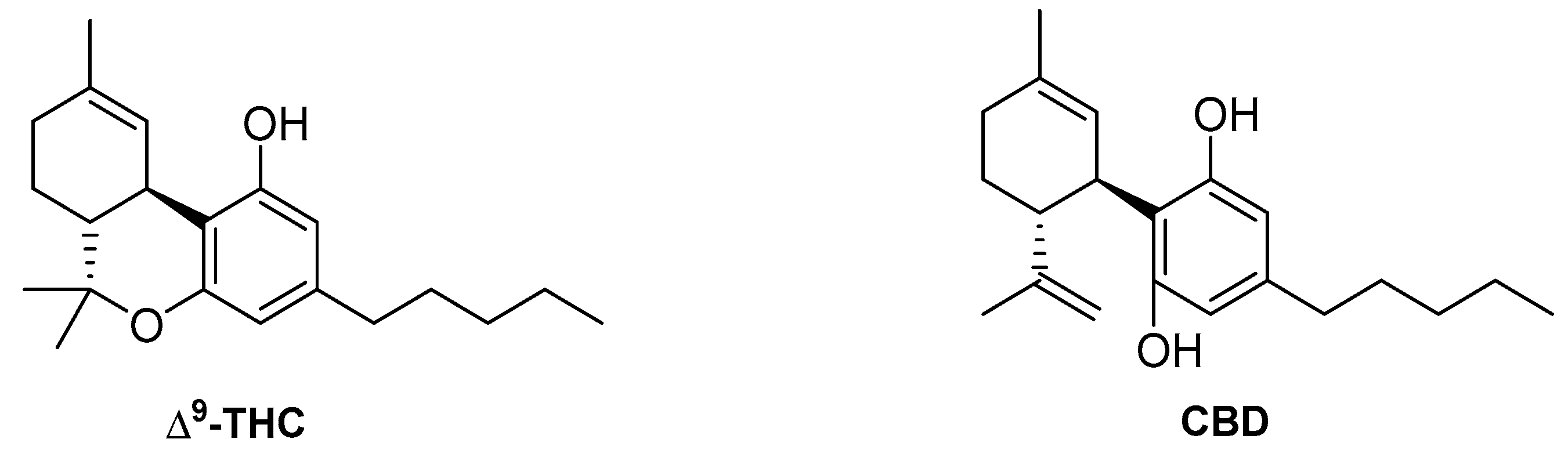
4.2. Phytocannabinoids
4.3. Synthetic Cannabinoids
4.3.1. Phytocannabinoid Synthetic Derivatives.
4.3.2. Indoles
4.3.3. Biphenylureas
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CB1 | Cannabinoid receptor type 1 |
| THC | Tetrahydrocannabinol |
| CBD | Cannabidiol |
| pERK1/2 | Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| AEA | Anandamide |
| 2-AG | 2-Arachidonoylglycerol |
| PWR | Plasmon Wave-guide Resonance |
| PTX | Pertussis Toxin |
| HD | Huntington’s Disease |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases |
| GIRK | G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels |
| GRK | G-protein-coupled Receptor Kinase |
| TMH | Transmembrane helix |
| pERK | Phosphorylated extracellular regulated kinases |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| FRET | Förster resonance energy transfer |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
References
- Devane, W.A.; Dysarz, F.A.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; Howlett, A.C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.M.; Mollereau, C.; Vassart, G.; Parmentier, M. Molecular cloning of a human cannabinoid receptor which is also expressed in testis. Biochem. J. 1991, 279, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Romero, J.; Ramos, J.A. Endocannabinoids and Neurodegenerative Disorders: Parkinson’s Disease, Huntington’s Chorea, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Others. In Endocannabinoids; Pertwee, R.G., Ed.; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 231, pp. 233–259. ISBN 354022565X. [Google Scholar]
- Pertwee, R.G. The pharmacology of cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: An overview. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30 (Suppl. 1), S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggio, P.H. Endocannabinoid Binding to the Cannabinoid Receptors: What Is Known and What Remains Unknown. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S. Cannabinoid Receptors in Brain: Pharmacogenetics, neuropharmacology, neurotoxicology, and potential therapeutic applications. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2009, 88, 335–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- More, S.V.; Choi, D.-K. Promising cannabinoid-based therapies for Parkinson’s disease: Motor symptoms to neuroprotection. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrida, A.; McMahon, L.R. In vivo pharmacology of endocannabinoids and their metabolic inhibitors: Therapeutic implications in Parkinson’s disease and abuse liability. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 91, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Otero, J.; Ahn, K.H.; Delgado-Peraza, F.; Mackie, K.; Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Ligand-specific endocytic dwell times control functional selectivity of the cannabinoid receptor 1. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Kelly, M.E.M.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Neuropharmacology Cannabinoids increase type 1 cannabinoid receptor expression in a cell culture model of striatal neurons: Implications for Huntington’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2013, 72, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Biased Type 1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling Influences Neuronal Viability in a Cell Culture Model of Huntington Disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Peraza, F.; Ahn, K.H.H.; Nogueras-Ortiz, C.; Mungrue, I.N.N.; Mackie, K.; Kendall, D.A.A.; Yudowski, G.A.A. Mechanisms of Biased β-Arrestin-Mediated Signaling Downstream from the Cannabinoid 1 Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gábor, T.; László, H.; Turu, G.; Hunyady, L. Signal transduction of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 44, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of Cannabinoid Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Dupré, D.J.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Type 1 cannabinoid receptor ligands display functional selectivity in a cell culture model of striatal medium spiny projection neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24845–24862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.; Felder, C.C. Concurrent stimulation of cannabinoid CB1 and dopamine D2 receptors augments cAMP accumulation in striatal neurons: Evidence for a Gs linkage to the CB1 receptor. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5327–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, D.B.; Cawston, E.E.; Grimsey, N.L.; Hunter, M.R.; Korde, A.; Vemuri, V.K.; Makriyannis, A.; Glass, M. Gα s signalling of the CB 1 receptor and the influence of receptor number. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2545–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Antona, A.M.; Ahn, K.H.; Wang, L.; Mierke, D.F.; Lucas-Lenard, J.; Kendall, D.A. A cannabinoid receptor 1 mutation proximal to the DRY motif results in constitutive activity and reveals intramolecular interactions involved in receptor activation. Brain Res. 2006, 1108, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadji, V.; Lucas-Lenard, J.M.; Chin, C.N.; Kendall, D.A. Involvement of the carboxyl terminus of the third intracellular loop of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in constitutive activation of G(s). J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 2032–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. The cannabinoid agonist WIN55,212-2 increases intracellular calcium via CB(1) receptor coupling to G(q/11) G proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19144–19149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, E.; Lefkowitz, R.J. GRKs and ??-arrestins: Roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobles, K.N.; Xiao, K.; Ahn, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Lam, C.M.; Rajagopal, S.; Strachan, R.T.; Huang, T.-Y.; Bressler, E.A.; Hara, M.R.; et al. Distinct Phosphorylation Sites on the β2-Adrenergic Receptor Establish a Barcode That Encodes Differential Functions of β-Arrestin. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisler, J.W.; DeWire, S.M.; Whalen, E.J.; Violin, J.D.; Drake, M.T.; Ahn, S.; Shenoy, S.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. A unique mechanism of beta-blocker action: Carvedilol stimulates beta-arrestin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16657–16662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Rajagopal, S. The β-arrestins: Multifunctional regulators of G protein-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8969–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Brown, S.; Roche, J.P.; Hsieh, C.; Celver, J.P.; Kovoor, A.; Chavkin, C.; Mackie, K. Distinct domains of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor mediate desensitization and internalization. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 3773–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breivogel, C.S.; Lambert, J.M.; Gerfin, S.; Huffman, J.W.; Razdan, R.K. Sensitivity to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol is selectively enhanced in beta-arrestin2-/- mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2008, 19, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, T.L.; Kearn, C.S.; Mackie, K. Rapid CB(1) cannabinoid receptor desensitization defines the time course of ERK1/2 MAP kinase signaling. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttrell, L.M.; Miller, W.E. Arrestins as regulators of kinases and phosphatases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 118, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Premont, R.T.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Physiological roles of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leterrier, C.; Laine, J.; Darmon, M.; Boudin, H.; Rossier, J.; Lenkei, Z. Constitutive activation drives compartment-selective endocytosis and axonal targeting of type 1 cannabinoid receptors. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Blume, L.C.; Dalton, G.D. CB(1) Cannabinoid Receptors and their Associated Proteins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.K.; Violin, J.D.; Whalen, E.J.; Gesty-Palmer, D.; Shenoy, S.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Distinct conformational changes in beta-arrestin report biased agonism at seven-transmembrane receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9988–9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajehali, E.; Malone, D.T.; Glass, M.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A.; Leach, K. Biased Agonism and Biased Allosteric Modulation at the CB 1 Cannabinoid Receptor s. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Homan, K.T.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Manglik, A.; Tesmer, J.J.G.; Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. G protein-coupled receptor kinases of the GRK4 protein subfamily phosphorylate inactive G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 10775–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Schmid, C.L.; Raehal, K.M.; Selley, D.E.; Bohn, L.M.; Sim-Selley, L.J. β-Arrestin2 Regulates Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Signaling and Adaptation in a Central Nervous System Region–Dependent Manner. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivogel, C.S.; Vaghela, M.S. The effects of beta-arrestin1 deletion on acute cannabinoid activity, brain cannabinoid receptors and tolerance to cannabinoids in mice. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2015, 35, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivogel, C.S.; Puri, V.; Lambert, J.M.; Hill, D.K.; Huffman, J.W.; Razdan, R.K. The influence of beta-arrestin2 on cannabinoid CB1 receptor coupling to G-proteins and subcellular localization and relative levels of beta-arrestin1 and 2 in mouse brain. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2013, 33, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, T.; Viganò, D.; Premoli, F.; Castiglioni, C.; Bianchessi, S.; Zippel, R.; Parolaro, D. Changes in the expression of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and β-arrestins in mouse brain during cannabinoid tolerance: A role for Ras-ERK cascade. Mol. Neurobiol. 2006, 33, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.A.; Roth, C.B.; Jo, E.; Griffith, M.T.; Scott, F.L.; Reinhart, G.; Desale, H.; Clemons, B.; Cahalan, S.M.; Schuerer, S.C.; et al. Crystal Structure of a Lipid G Protein–Coupled Receptor. Science (80-). 2012, 335, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, N.; Pardo, L.; Fabritiis, G. De The pathway of ligand entry from the membrane bilayer to a lipid G protein-coupled receptor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Byrne, N.; Wang, J.; Bricogne, G.; Brown, F.K.; Chobanian, H.R.; Colletti, S.L.; Di Salvo, J.; Thomas-Fowlkes, B.; Guo, Y.; et al. Structural basis for the cooperative allosteric activation of the free fatty acid receptor GPR40. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Pu, M.; Qu, L.; Han, G.W.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shui, W.; Li, S.; Korde, A.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Human Cannabinoid Receptor CB1. Cell 2016, 167, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Grzemska, M.; Clark, L.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.R.; Pertwee, R.G.; Stevenson, L.A.; Janero, D.R.; Hurst, D.P.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Laprairie, R.B.; Kulkarni, P.M.; Thakur, G.A.; Lynch, D.L.; et al. Mapping Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Allosteric Site(S): Critical Molecular Determinant and Signaling Profile of Gat100—A Novel, Potent and Irreversibly Binding Probe. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 776–798. [Google Scholar]
- Shore, D.M.; Baillie, G.L.; Hurst, D.H.; Navas, F.; Seltzman, H.H.; Marcu, J.P.; Abood, M.E.; Ross, R.A.; Reggio, P.H. Allosteric modulation of a cannabinoid G protein-coupled receptor: Binding site elucidation and relationship to G protein signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5828–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, M.; Vitiello, S.; Bellocchio, L.; Hébert-Chatelain, E.; Monlezun, S.; Martin-Garcia, E.; Kasanetz, F.; Baillie, G.L.; Panin, F.; Cathala, A.; et al. Pregnenolone Can Protect the Brain from Cannabis Intoxication. Science 2014, 343, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, B.; Tate, C.G. Active state structures of G protein-coupled receptors highlight the similarities and differences in the G protein and arrestin coupling interfaces. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 45, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. The Molecular Basis of G Protein–Coupled Receptor Activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glukhova, A.; Draper-Joyce, C.J.; Sunahara, R.K.; Christopoulos, A.; Wootten, D.; Sexton, P.M. Rules of engagement: GPCRs and G proteins. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 1, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Liapakis, G.; Xu, R.; Guarnieri, F.; Ballesteros, J.A.; Javitch, J.A. β2 Adrenergic Receptor Activation: Modulation of the proline kink in transmembrane 6 by a rotamer toggle switch. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40989–40996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenbach, C.; Kusnetzow, A.K.; Ernst, O.P.; Hofmann, K.P.; Hubbell, W.L. High-resolution distance mapping in rhodopsin reveals the pattern of helix movement due to activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7439–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Devree, B.T.; Zou, Y.; Kruse, A.C.; Chung, K.Y.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Chae, P.S.; Pardon, E.; Calinski, D.; et al. Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor—Gs protein complex. Nature 2011, 477, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna Kumar, K.; Shalev-Benami, M.; Robertson, M.J.; Hu, H.; Banister, S.D.; Hollingsworth, S.A.; Latorraca, N.R.; Kato, H.E.; Hilger, D.; Maeda, S.; et al. Structure of a Signaling Cannabinoid Receptor 1-G Protein Complex. Cell 2019, 176, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Wang, S.; McCorvy, J.D.; Betz, R.M.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Levit, A.; Lansu, K.; Schools, Z.L.; Che, T.; Nichols, D.E.; et al. Crystal Structure of an LSD-Bound Human Serotonin Receptor. Cell 2017, 168, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmeh, R.; Damian, M.; Cottet, M.; Orcel, H.; Mendre, C.; Durroux, T.; Sharma, K.S.; Durand, G.; Pucci, B.; Trinquet, E.; et al. Structural insights into biased G protein-coupled receptor signaling revealed by fluorescence spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6733–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Horst, R.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C.; Wüthrich, K. Biased signaling pathways in β(2)-adrenergic receptor characterized by (19)F-NMR. Science 2012, 335, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, T.J.; Thomsen, A.R.B.; Tarrasch, J.T.; Plouffe, B.; Nguyen, A.H.; Yang, F.; Huang, L.-Y.; Kahsai, A.W.; Bassoni, D.L.; Gavino, B.J.; et al. Distinct conformations of GPCR–β-arrestin complexes mediate desensitization, signaling, and endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, A.R.B.; Plouffe, B.; Cahill, T.J.; Shukla, A.K.; Tarrasch, J.T.; Dosey, A.M.; Kahsai, A.W.; Strachan, R.T.; Pani, B.; Mahoney, J.P.; et al. GPCR-G Protein-β-Arrestin Super-Complex Mediates Sustained G Protein Signaling. Cell 2016, 166, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calebiro, D.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Gagliani, M.C.; De Filippis, T.; Dees, C.; Tacchetti, C.; Persani, L.; Lohse, M.J. Persistent cAMP-signals triggered by internalized G-protein-coupled receptors. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brailoiu, G.C.; Oprea, T.I.; Zhao, P.; Abood, M.E.; Brailoiu, E. Intracellular cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptors are activated by anandamide. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 29166–29174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, M.; Northup, J.K. Agonist selective regulation of G proteins by cannabinoid CB(1) and CB(2) receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, T.; Devanathan, S.; Stropova, D.; Park, C.K.; Salamon, Z.; Tollin, G.; Hruby, V.J.; Roeske, W.R.; Yamamura, H.I.; Varga, E. Unique agonist-bound cannabinoid CB1 receptor conformations indicate agonist specificity in signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 581, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.H.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Shim, J.Y.; Kendall, D.A. Distinct roles of b-arrestin 1 and b-arrestin 2 in ORG27569-induced biased signaling and internalization of the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9790–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, J.F.; Farrens, D.L. Structural dynamics and energetics underlying allosteric inactivation of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8469–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Zeng, H.; Ward, R.; Wu, N.; Ma, L.; Mu, X.; Li, Q.L.; Yang, Y.; An, S.; et al. Assessing the real-time activation of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor and the associated structural changes using a FRET biosensor. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 99, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katritch, V.; Fenalti, G.; Abola, E.E.; Roth, B.L.; Cherezov, V.; Stevens, R.C. Allosteric sodium: A key co-factor in class A GPCR signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Nikas, S.P.; Laprairie, R.B.; Wu, Y.; Qu, L.; Pu, M.; Korde, A.; Jiang, S.; Ho, J.H.; et al. Crystal structures of agonist-bound human cannabinoid receptor CB1. Nature 2017, 547, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, S.D.; Hurst, D.P.; Barnett-Norris, J.; Lynch, D.; Reggio, P.H.; Abood, M.E. Structural mimicry in class A G protein-coupled receptor rotamer toggle switches: The importance of the F3.36(201)/W6.48(357) interaction in cannabinoid CB1receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48024–48037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, S.D.; Rizvi, G.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Hurst, D.P.; Barnett-Norris, J.; Lynch, D.L.; Reggio, P.H.; Abood, M.E. An Aromatic Microdomain at the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Constitutes an Agonist/Inverse Agonist Binding Region. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 5139–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Hurst, D.P.; Barnett-Norris, J.; Lynch, D.L.; Reggio, P.H.; Guarnieri, F. Activation of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor may involve a W6.48/F3.36 rotamer toggle switch. J. Pept. Res. 2002, 60, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.H.; Scott, C.E.; Abrol, R.; Goddard, W.A., 3rd; Kendall, D.A. Computationally-predicted CB1 cannabinoid receptor mutants show distinct patterns of salt-bridges that correlate with their level of constitutive activity reflected in G protein coupling levels, thermal stability, and ligand binding. Proteins 2013, 81, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Antona, A.M.; Ahn, K.H.; Kendall, D.A. Mutations of CB1 T210 produce active and inactive receptor forms: Correlations with ligand affinity, receptor stability, and cellular localization. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 5606–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.H.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Kendall, D.A. Allosteric modulator ORG27569 induces CB1 cannabinoid receptor high affinity agonist binding state, receptor internalization, and Gi protein-independent ERK1/2 kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12070–12082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovati, G.E.; Capra, V.; Shaw, V.S.; Malik, R.U.; Sivaramakrishnan, S.; Neubig, R.R. The DRY motif and the four corners of the cubic ternary complex model. Cell. Signal. 2017, 35, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovati, G.E.; Capra, V.; Neubig, R.R. The highly conserved DRY motif of class AG protein-coupled receptors: Beyond the ground state. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyombolai, P.; Tóth, A.D.; Tímár, D.; Turu, G.; Hunyady, L. Mutations in the ‘DRY’ motif of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor result in biased receptor variants. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 54, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Ahn, S.; Shenoy, S.K.; Karnik, S.S.; Hunyady, L.; Luttrell, L.M.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Independent beta-arrestin 2 and G protein-mediated pathways for angiotensin II activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10782–10787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, J.P.; Bounds, S.; Brown, S.; Mackie, K. A mutation in the second transmembrane region of the CB1 receptor selectively disrupts G protein signaling and prevents receptor internalization. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcallister, S.D.; Griffin, G.; Satin, L.S.; Abood, M.E. Cannabinoid receptors can activate and inhibit G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels in a xenopus oocyte expression system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 291, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Lewis, D.L. Structural domains of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor that contribute to constitutive activity and G-protein sequestration. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 8758–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Abood, M.E. Mutation of a highly conserved aspartate residue in the second transmembrane domain of the cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2, disrupts G-protein coupling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.E.; He, Y.; de Waal, P.W.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Van Eps, N.; Yin, Y.; Pal, K.; Goswami, D.; White, T.A.; et al. Identification of Phosphorylation Codes for Arrestin Recruitment by G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Cell 2017, 170, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Xiao, K.; Reis, R.I.; Tseng, W.-C.; Staus, D.P.; Hilger, D.; Uysal, S.; Huang, L.-Y.; et al. Structure of active β-arrestin-1 bound to a G-protein-coupled receptor phosphopeptide. Nature 2013, 497, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.H.; Pellegrini, M.; Tsomaia, N.; Yatawara, A.K.; Kendall, D.A.; Mierke, D.F. Structural Analysis of the Human Cannabinoid Receptor One Carboxyl-Terminus Identifies Two Amphipathic Helices. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, K.; Mercier, R.W.; Pavlopoulos, S. Interaction of a fragment of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor C-terminus with arrestin-2. FEBS Lett. 2007, 85, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.N.; Bakshi, K.; Mercier, R.W.; Makriyannis, A.; Pavlopoulos, S. Binding between a Distal C-terminus fragment of cannabinoid receptor 1 and arrestin-2. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Howlett, A.C. CB1 receptor-G protein association: Subtype selectivity is determined by distinct intracellular domains. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Cowsik, S.M.; Lynn, A.M.; Welsh, W.J.; Howlett, A.C. Regulation of G(i) by the CB1 cannabinoid receptor C-terminal juxtamembrane region: Structural requirements determined by peptide analysis. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 3447–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Song, C.; Berglund, B.A.; Wilken, G.H.; Pigg, J.J. Characterization of CB1 cannabinoid receptors using receptor peptide fragments and site-directed antibodies. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.Y.; Ahn, K.H.; Kendall, D.A. Molecular basis of cannabinoid CB1 receptor coupling to the G protein heterotrimer Gαiβγ; Identification of key CB1 contacts with the C-terminal helix α5 of Gαi. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 32449–32465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; McIntosh, H.H.; Houston, D.B.; Howlett, A.C. The CB(1) cannabinoid receptor juxtamembrane C-terminal peptide confers activation to specific G proteins in brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulfers, A.L.; McMurry, J.L.; Miller, A.; Wang, L.; Kendall, D.A.; Mierke, D.F. Cannabinoid receptor-G protein interactions: G(alphai1)-bound structures of IC3 and a mutant with altered G protein specificity. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 2526–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldeeb, K.; Leone-Kabler, S.; Howlett, A.C. CB1cannabinoid receptor-mediated increases in cyclic AMP accumulation are correlated with reduced Gi/o function. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, B.K.; Lopez, J.; Wager-Miller, J.; Mackie, K.; Straiker, A. Expression of G protein-coupled receptors and related proteins in HEK293, AtT20, BV2, and N18 cell lines as revealed by microarray analysis. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, D.J.; Davis, B.J.; Kearn, C.S.; Marcus, D.; Cook, A.J.; Wager-Miller, J.; Straiker, A.; Myoga, M.H.; Karduck, J.; Leishman, E.; et al. Mutation of Putative GRK Phosphorylation Sites in the Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1R) Confers Resistance to Cannabinoid Tolerance and Hypersensitivity to Cannabinoids in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5152–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straiker, A.; Wager-Miller, J.; Mackie, K. The CB 1 cannabinoid receptor C-terminus regulates receptor desensitization in autaptic hippocampal neurones. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2652–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blume, L.C.; Patten, T.; Eldeeb, K.; Leone-Kabler, S.; Ilyasov, A.A.; Keegan, B.M.; O’Neal, J.E.; Bass, C.E.; Hantgan, R.R.; Lowther, W.T.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein 1a Competition with beta-Arrestin for CB1 Receptor Binding Sites. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, T.L.; Kwok, M.L.; Mackie, K. Regulation of CB1 cannabinoid receptor internalization by a promiscuous phosphorylation-dependent mechanism. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyombolai, P.; Boros, E.; Hunyady, L.; Turu, G. Differential β-arrestin2 requirements for constitutive and agonist-induced internalization of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 372, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, L.C.; Leone-Kabler, S.; Luessen, D.J.; Marrs, G.S.; Lyons, E.; Bass, C.E.; Chen, R.; Selley, D.E.; Howlett, A.C. Cannabinoid receptor interacting protein suppresses agonist-driven CB1receptor internalization and regulates receptor replenishment in an agonist-biased manner. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehaus, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Wallis, K.T.; Egertova, M.; Bhartur, S.G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Shi, S.; He, H.; Selley, D.E.; Howlett, A.C.; et al. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Activity Is Modulated by the Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein CRIP 1a. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.H.; Blume, L.C.; Straiker, A.; Cox, J.O.; David, B.G.; McVoy, J.R.S.; Sayers, K.W.; Poklis, J.L.; Abdullah, R.A.; Egertova, M.; et al. Cannabinoid Receptor-Interacting Protein 1a Modulates CB1 Receptor Signaling and Regulation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 87, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.; Brown, S.; Derleth, C.; Mackie, K. Internalization and recycling of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajkova, A.; Techlovska, S.; Dvorakova, M.; Chambers, J.N.; Kumpost, J.; Hubalkova, P.; Prezeau, L.; Blahos, J.; Dvo, M.; Alena, H.; et al. SGIP1 alters internalization and modulates signaling of activated cannabinoid receptor 1 in a biased manner. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahavadi, S.; Sriwai, W.; Huang, J.; Grider, J.R.; Murthy, K.S. Inhibitory signaling by CB1 receptors in smooth muscle mediated by GRK5/β-arrestin activation of ERK1/2 and Src kinase. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G535–G545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.E.; Brown, S.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. Protein Kinase C Disrupts Cannabinoid Actions by Phosphorylation of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Goya, P.; Jagerovic, N.; Hernandez-Folgado, L. Allosteric Modulators of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor: A Structural Update Review. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, G.A.; Nikas, S.P.; Makriyannis, A. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2005, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, R.; Mackie, K.; Straiker, A. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor-Dependent Long-Term Depression in Autaptic Excitatory Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 102, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Howlett, A.C. Chemically Distinct Ligands Promote Differential CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor-Gi Protein Interactions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, W.J.; Cawston, E.E.; Grimsey, N.L.; Stuart, J.; Edington, A.R.; Glass, M.; Connor, M. Identification of N-arachidonoyl dopamine as a highly biased ligand at cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Hurst, D.P.; Reggio, P.H. Molecular Targets of the Phytocannabinoids: A Complex Picture. In Phytocannabinoids: Unraveling the Complex Chemistry and Pharmacology of Cannabis Sativa; Kinghorn, A.D., Gibbons, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 103, pp. 103–131. ISBN 978-3-319-45539-6. [Google Scholar]
- McPartland, J.M.; Glass, M.; Pertwee, R.G. Meta-analysis of cannabinoid ligand binding affinity and receptor distribution: Interspecies differences. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Ross, R.A.; Craib, S.J.; Thomas, A. (-)-Cannabidiol antagonizes cannabinoid receptor agonists and noradrenaline in the mouse vas deferens. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 456, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Baillie, G.L.; Phillips, A.M.; Razdan, R.K.; Ross, R.A.; Pertwee, R.G. Cannabidiol displays unexpectedly high potency as an antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Bagher, A.M.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Cannabidiol is a negative allosteric modulator of the type 1 cannabinoid receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 20, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Sánchez de Medina, V.; Morales, P.; Casano, S.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Lillo, A.; Aguinaga, D.; Jagerovic, N.; et al. Cannabidiol skews biased agonism at cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors with smaller effect in CB1-CB2 heteroreceptor complexes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 157, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonhaus, D.W.; Chang, L.K.; Kwan, J.; Martin, G.R. Dual activation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by cannabinoid receptor agonists: Evidence for agonist-specific trafficking of intracellular responses. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 287, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bosier, B.; Muccioli, G.G.; Mertens, B.; Sarre, S.; Michotte, Y.; Lambert, D.M.; Hermans, E. Differential modulations of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine metabolism by cannabinoid agonists as evidence for functional selectivity in vivo. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Pharmacology of cannabinoid receptor ligands. Curr. Med. Chem. 1999, 6, 635–664. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, B.M.; Franks, L.N.; Tai, S.; Fantegrossi, W.E.; Stahl, E.L.; Berquist, M.D.; Cabanlong, C.V.; Wilson, C.D.; Penthala, N.R.; Crooks, P.A.; et al. Characterization of structurally novel G protein biased CB1 agonists: Implications for drug development. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 125, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneuf, Y.P.; Brotchie, J.M. Paradoxical action of the cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 in stimulated and basal cyclic AMP accumulation in rat globus pallidus slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 120, 1397–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.R.; Baillie, G.L.; Thomas, A.; Stevenson, L.A.; Easson, M.; Goodwin, R.; Mclean, A.; Mcintosh, L.; Goodwin, G.; Walker, G.; et al. Allosteric Modulation of the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, L.; Mackie, K.; Piomelli, D.; Kendall, D.A. Modulation of CB1 cannabinoid receptor by allosteric ligands: Pharmacology and therapeutic opportunities. Neuropharmacology 2017, 124, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.H.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Samala, S.; Lu, D.; Kendall, D.A. Profiling Two Indole-2-Carboxamides for Allosteric Modulation of the CB1 Receptor. J. Neurochem 2013, 29, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamage, T.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Abood, M.E. CB1 Allosteric Modulator Org27569 Is an Antagonist/Inverse Agonist of ERK1/2 Signaling. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, G.L.; Horswill, J.G.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Reggio, P.H.; Bolognini, D.; Abood, M.E.; McAllister, S.; Strange, P.G.; Stephens, G.J.; Pertwee, R.G.; et al. CB(1) receptor allosteric modulators display both agonist and signaling pathway specificity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, L.N.; Ford, B.M.; Madadi, N.R.; Penthala, N.R.; Crooks, P.A.; Prather, P.L. Characterization of the intrinsic activity for a novel class of cannabinoid receptor ligands: Indole quinuclidine analogs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 737, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madadi, N.R.; Penthala, N.R.; Brents, L.K.; Ford, B.M.; Prather, P.L.; Crooks, P.A. Evaluation of (Z)-2-((1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene)-quinuclidin-3-one analogues as novel, high affinity ligands for CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2019–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horswill, J.G.; Bali, U.; Shaaban, S.; Keily, J.F.; Jeevaratnam, P.; Babbs, A.J.; Reynet, C.; Wong Kai In, P. PSNCBAM-1, a novel allosteric antagonist at cannabinoid CB1 receptors with hypophagic effects in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 152, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, N.; Decker, A.M.; Gilmour, B.P.; Gay, E.A.; Wiley, J.L.; Thomas, B.F.; Zhang, Y. Diarylureas as Allosteric Modulators of the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor: Structure–Activity Relationship Studies on 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-{3-[6-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]phenyl}urea (PSNCBAM-1). J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7758–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, L.; Fu, B.-Q.Q.B.; Duddupudi, A.L.; Liao, Y.-H.H.; Immadi, S.S.; Kendall, D.A.; Lu, D. Pyrimidinyl Biphenylureas: Identification of New Lead Compounds as Allosteric Modulators of the Cannabinoid Receptor CB 1. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagla, C.A.D.D.; Scott, C.E.; Tang, Y.; Qiao, C.; Mateo-Semidey, G.E.; Yudowski, G.A.; Lu, D.; Kendall, D.A. Pyrimidinyl Biphenylureas Act as Allosteric Modulators to activate Cannabinoid Receptor 1 and initiate β-Arrestin-dependent Responses. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagher, A.M.; Laprairie, R.B.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. Antagonism of Dopamine Receptor 2 Long Affects Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Signaling in a Cell Culture Model of Striatal Medium Spiny Projection Neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Zoubi, R.; Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H. Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081837
Al-Zoubi R, Morales P, Reggio PH. Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081837
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Zoubi, Rufaida, Paula Morales, and Patricia H. Reggio. 2019. "Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081837
APA StyleAl-Zoubi, R., Morales, P., & Reggio, P. H. (2019). Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081837




