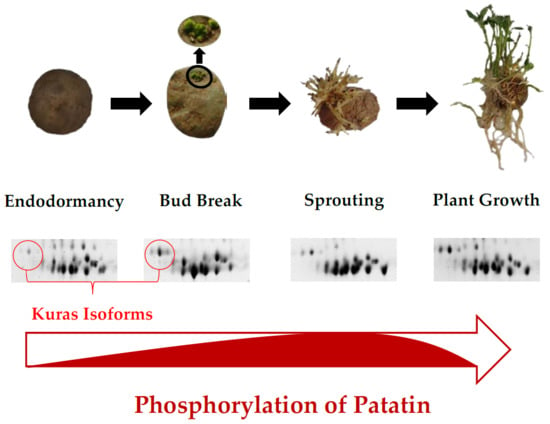
The Major Storage Protein in Potato Tuber Is Mobilized by a Mechanism Dependent on Its Phosphorylation Status
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Reference Patatin Profiles throughout the Tuber Life Cycle
2.2. Changes in Patatin Abundance in the Tuber Life Cycle
2.3. Identification of Phosphorylated Patatin Isoforms along the Tuber Life Cycle
2.4. Changes in Patatin Phosphorylation Status during Tuber Life Cycle
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Tuber Protein Extraction
3.3. Protein Chemical Dephosphorylation
3.4. Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis (2-DE)
3.5. Gel Staining for Total Protein and Phosphoproteins
3.6. Image Analysis
3.7. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-DE | Two-dimensional electrophoresis |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| HF-P | Hydrogen fluoride-pyridine |
| LAH | Lipid acyl hydrolase |
| Mr | Relative molecular mass |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| pI | Isoelectric point |
| PR | Phosphorylation rate |
| SSP | Seed storage protein |
| VSP | Vegetative storage protein |
References
- De Souza Cândido, E.; Pinto, M.F.; Pelegrini, P.B.; Lima, T.B.; Silva, O.N.; Pogue, R.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F.; Franco, O.L. Plant storage proteins with antimicrobial activity: Novel insights into plant defense mechanisms. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3290–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan-Wilson, A.L.; Wilson, K.A. Mobilization of seed protein reserves. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müntz, K. Deposition of storage proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 38, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, H.; Borisjuk, L.; Wobus, U. Molecular physiology of legume seed development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnewald, S.; Sonnewald, U. Regulation of potato tuber sprouting. Planta 2014, 239, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, G.K.; Thelen, J.J. Large-scale identification and quantitative profiling of phosphoproteins expressed during seed filling in oilseed rape. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2006, 5, 2044–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.J.; Gao, J.; Xu, D.; Thelen, J.J. Phosphoproteomic analysis of seed maturation in Arabidopsis, rapeseed, and soybean. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzo, D.; Bernal, J.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Franco, D.; Zapata, C. Advances in the biology of seed and vegetative storage proteins based on two-dimensional electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry. Molecules 2018, 23, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irar, S.; Oliveira, E.; Pagès, M.; Goday, A. Towards the identification of late-embryogenic-abundant phosphoproteome in Arabidopsis by 2-DE and MS. Proteomics 2006, 6, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Ross, A.R.S.; Yang, J.; Hegedus, D.D.; Kermode, A.R. Phosphorylation of the 12 S globulin cruciferin in wild-type and abi1-1 mutant Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) seeds. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelis, T.; Bolbach, G.; Clodic, G.; Habricot, Y.; Miginiac, E.; Sotta, B.; Jeannette, E. Protein tyrosine kinases and protein tyrosine phosphatases are involved in abscisic acid-dependent processes in Arabidopsis seeds and suspension cells. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1668–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezawa, T.; Sugiyama, N.; Takahashi, F.; Anderson, J.C.; Ishihama, Y.; Peck, S.C.; Shinozaki, K. Genetics and phosphoproteomics reveal a protein phosphorylation network in the abscisic acid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol. 2013, 6, rs8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capraro, J.; Scarafoni, A.; Magni, C.; Consonni, A.; Duranti, M.M. Proteomic studies on the lupin seed storage proteins phosphorylation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Food-omics, Cesena, Italy, 22–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, I.; Regente, M.; Pagnussat, L.; Maldonado, A.; Jorrín, J.; de la Canal, L. Phosphorylated 11S globulins in sunflower seeds. Seed Sci. Res. 2013, 23, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, K.; Yang, P. Gel-based comparative phosphoproteomic analysis on rice during germination. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1376–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Zhen, S.; Cheng, Z.; Cao, H.; Ge, P.; Yah, Y. Proteomic analysis reveals key proteins and phosphoproteins upon seed germination of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pedrouso, M.; Alonso, J.; Zapata, C. Evidence for phosphorylation of the major seed storage protein of the common bean and its phosphorylation-dependent degradation during germination. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2014, 84, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardmore, T.; Wetzel, S.; Burgess, D.; Charest, P.J. Characterization of seed storage proteins in Populus and their homology with Populus vegetative storage proteins. Tree Physiol. 1996, 16, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racusen, D.; Foote, M.A. A major soluble glycoprotein from potato tubers. J. Food Biochem. 1980, 4, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racusen, D. Lipid acyl hydrolase of patatin. Can. J. Bot. 1984, 62, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-W.; Han, C.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Hsu, F.-L.; Hou, W.-C. Patatin, the tuber protein of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) exhibits antioxidant activity in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R. Tuber storage proteins. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Franco, D.; Bravo, S.; García, L.; Zapata, C. Identification and mapping of phosphorylated isoforms of the major storage protein of potato based on two-dimensional electrophoresis. In Advances in Seed Biology; Jimenez-Lopez, J.C., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 65–82. ISBN 978-953-51-3621-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mouzo, D.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Bernal, J.; García, L.; Franco, D.; Zapata, C. Association of patatin-based proteomic distances with potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) quality traits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11864–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, R.; Pelloux, J.; van der Ploeg, A.; Gillespie, T.; Marquis, N.; Roberts, A.G.; Hancock, R.D. Symplastic connection is required for bud outgrowth following dormancy in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, M.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Alonso, J.; Santalla, M.; de Ron, A.M.; Alvarez, G.; Zapata, C. In-depth characterization of the phaseolin protein diversity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) based on two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 50, 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- López-Pedrouso, M.; Bernal, J.; Franco, D.; Zapata, C. Evaluating two-dimensional electrophoresis profiles of the protein phaseolin as markers of genetic differentiation and seed protein quality in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7200–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauw, G.; Nielsen, H.V.; Emmersen, J.; Nielsen, K.L.; Jørgensen, M.; Welinder, K.G. Patatin, Kunitz protease inhibitors and other major proteins in tuber of potato cv. Kuras. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 3569–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehesranta, S.J.; Davies, H.V.; Shepherd, L.V.T.; Koistinen, K.M.; Massat, N.; Nunan, N.; McNicol, J.W.; Kärenlampi, S.O. Proteomic analysis of the potato tuber life cycle. Proteomics 2006, 6, 6042–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weeda, S.M.; Kumar, G.N.M.; Knowles, N.R. Correlative changes in proteases and protease inhibitors during mobilization of protein from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) seed tubers. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachem, C.; Van der Hoeven, R.; Lucker, J.; Oomen, R.; Casarini, E.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R. Functional genomic analysis of potato tuber life-cycle. Potato Res. 2000, 43, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronning, C.M.; Stegalkina, S.S.; Ascenzi, R.A.; Bougri, O.; Hart, A.L.; Utterbach, T.R.; Vanaken, S.E.; Riedmuller, S.B.; White, J.A.; Cho, J.; et al. Comparative analyses of potato expressed sequence tag libraries. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Segear, E.; Beers, L.; Knauber, D.; Suttle, J. Dormancy in potato tuber meristems: Chemically induced cessation in dormancy matches the natural process based on transcript profiles. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2008, 8, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pots, A.M.; Gruppen, H.; van Diepenbeek, R.; van der Lee, J.J.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Wijngaards, G.; Voragen, A.G.J. The effect of whole potatoes of three cultivars on the patatin and protease inhibitor content; a study using capillary electrophoresis and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeda, S.M.; Kumar, G.N.M.; Knowles, N.R. Developmentlly linked changes in proteases and protease inhibitors suggest a role for potato multicystatin in regulating protein content of potato tubers. Planta 2009, 230, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosti, F.; Beaudoin, N.; Serizet, C.; Webb, A.A.; Vartanian, N.; Giraudat, J. ABI1 protein phosphatase 2C is a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwików, A. Targeting proteins for proteasomal degradation—A new function of Arabidopsis ABI1 protein phosphatase 2C. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pots, A.M.; de Jongh, H.H.J.; Gruppen, H.; Hamer, R.J.; Voragen, A.G.J. Heat-induced conformational changes of patatin, the major potato tuber protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 252, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralet, M.-C.; Guéguen, J. Fractionation of potato proteins: Solubility, thermal, coagulation and emulsifying properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.D.; Blackwood, C.; Mignery, G.A.; Hermodson, M.A.; Lister, R.M. Analysis of the heterogeneity of the 40,000 molecular weight tuber glycoprotein of potatoes by immunological methods and by NH2- terminal sequence analysis. Plant Physiol. 1983, 71, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignery, G.A.; Pikaard, C.S.; Hannapel, D.J.; Park, W.D. Isolation and sequence analysis of cDNAs for the major tuber protein, patatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 7987–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pots, A.M.; Gruppen, H.; Hessing, M.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Voragen, A.G.J. Isolation and characterization of patatin isoforms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4587–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.-Q.; Hardin, S.C.; Dewey, R.; Huber, S.C. A novel C-terminal proteolytic processing of cytosolic pyruvate kinase, its phosphorylation and degradation by the proteasome in developing soybean seeds. Plant J. 2003, 34, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Kermode, A.R. Programmed cell death of the megagametophyte during post-germinative growth of white spruce (Picea glauca) seeds is regulated by reactive oxygen species and the ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic system. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, H.J.H.B.; Simons, J.-W.F.A.; Dekker, N.; Egmond, M.R. Cloning, expression, purification and characterization of patatin, a novel phospholipase A. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5037–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rydel, T.J.; Williams, J.M.; Krieger, E.; Moshiri, F.; Stallings, W.C.; Brown, S.M.; Pershing, J.C.; Purcell, J.P.; Alibhai, M.F. The crystal structure, mutagenesis, and activity studies reveal that patatin is a lipid acyl hydrolase with a Ser-Asp catalytic dyad. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 6696–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.A.; Orr, G.L.; Walsh, T.A. Inhibition of diabrotica larval growth by patatin, the lipid acyl hydrolase from potato tubers. Plant Physiol. 1995, 109, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, K.; Senda, K.; Doke, N. Factors, affecting in vitro activation of potato phospholipase A2. Plant Sci. 1993, 92, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, K.; Yoshioka, H.; Doke, N.; Kawakita, K. A cytosolic phospholipase A2 from potato tissues appears to be patatin. Plant Cell Physiol. 1996, 37, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, R.S.; Rose, J.K.C. A critical evaluation of sample extraction techniques for enhanced proteomic analysis of recalcitrant plant tissues. Proteomics 2004, 4, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyama, H.; Toda, C.; Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, K.; Nishimura, O. An efficient chemical method for dephosphorylation of phosphopeptides. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.K.; Thelen, J.J. Development of a simplified, economical polyacrylamide gel staining protocol for phosphoproteins. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4684–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.N.; Wilm, M.; Shevchenko, A.; Mann, M. Sample preparation methods for mass spectrometric peptide mapping directly from 2-DE gels. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorm, O.; Roepstorff, P.; Mann, M. Improved resolution and very high sensitivity in MALDI TOF of matrix surfaces made by fast evaporation. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 3281–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Mato, A.; Salgado, F.J.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Carrera, M.; Bravo, S.; Parrado, M.; Gallardo, J.M.; Zapata, C. Tackling proteome changes in the longissimus thoracis bovine muscle in response to pre-slaughter stress. J. Proteom. 2015, 122, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| PR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot Number a | pI | Endodormancy | Bud Break | Sprouting | Plant Growth | Mean (± SE) |
| 1 | 4.84 | N/A | 39.8 ± 2.5 | 51.9 ± 5.2 | 33.1 ± 5.6 | 41.6 ± 5.5 |
| 2 | 4.88 | 38.1 ± 5.3 | 41.2 ± 6.1 | 52.4 ± 5.9 | 39.6 ± 5.7 | 42.8 ± 3.3 |
| 3 | 4.90 | N/A | 43.1 ± 2.9 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 4 | 4.93 | N/A | N/A | 39.7 ± 5.4 | 23.0 ± 4.6 | 31.4 ± 8.4 |
| 5 | 4.96 | 27.1 ± 1.9 | 42.8 ± 2.0 | 43.2 ± 6.4 | 30.5 ± 4.4 | 35.9 ± 4.2 |
| 6 | 4.96 | N/A | 52.3 ± 4.1 | 38.4 ± 4.4 | 27.5 ± 5.2 | 39.4 ± 7.2 |
| 7 | 5.02 | 32.3 ± 4.5 | 39.0 ± 4.1 | 42.5 ± 5.9 | 26.9 ± 5.8 | 35.2 ± 3.5 |
| 8 | 5.02 | 15.3 ± 3.8 | 27.2 ± 5.6 | 27.0 ± 4.6 | 29.1 ± 5.1 | 24.6 ± 3.2 |
| 9 | 5.05 | 27.3 ± 2.4 | 32.5 ± 3.3 | 40.5 ± 5.1 | 31.4 ± 5.7 | 32.9 ± 2.8 |
| 10 | 5.12 | 32.0 ± 4.0 | 30.5 ± 4.7 | 23.5 ± 6.1 | 40.0 ± 6.4 | 31.5 ± 3.4 |
| 11 | 5.12 | 10.9 ± 6.9 | 25.1 ± 4.3 | 26.4 ± 4.4 | 25.2 ± 6.3 | 21.9 ± 3.7 |
| 12 | 5.13 | 28.3 ± 2.4 | 51.4 ± 5.5 | 52.7 ± 4.2 | 31.9 ± 7.0 | 41.1 ± 6.4 |
| 13 | 5.14 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 26.0 ± 7.2 | N/A |
| 14 | 5.16 | 50.1 ± 4.9 | 44.3 ± 9.4 | 53.2 ± 7.5 | 33.3 ± 5.9 | 45.2 ± 4.4 |
| 15 | 5.20 | 41.4 ± 2.4 | 41.9 ± 3.8 | 44.1 ± 5.5 | 28.0 ± 5.3 | 38.8 ± 3.7 |
| 16 | 5.20 | 12.8 ± 3.1 | 27.0 ± 8.4 | 17.2 ± 4.3 | 25.1 ± 5.1 | 20.6 ± 3.3 |
| 17 | 5.23 | 23.8 ± 3.6 | 36.0 ± 2.4 | 39.8 ± 6.3 | 29.3 ± 4.6 | 32.2 ± 3.5 |
| 18 | 5.25 | 29.6 ± 5.3 | 34.2 ± 4.1 | 51.6 ± 4.5 | 22.9 ± 4.6 | 34.5 ± 6.1 |
| 19 | 5.29 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 20 | 5.27 | 11.6 ± 2.0 | 11.9 ± 4.6 | 25.6 ± 6.3 | 29.2 ± 4.9 | 19.6 ± 4.6 |
| Mean (± SE) | 27.2 ± 3.1 | 36.5 ± 2.5 | 39.4 ± 2.8 | 29.6 ± 1.1 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernal, J.; Mouzo, D.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Franco, D.; García, L.; Zapata, C. The Major Storage Protein in Potato Tuber Is Mobilized by a Mechanism Dependent on Its Phosphorylation Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081889
Bernal J, Mouzo D, López-Pedrouso M, Franco D, García L, Zapata C. The Major Storage Protein in Potato Tuber Is Mobilized by a Mechanism Dependent on Its Phosphorylation Status. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081889
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernal, Javier, Daniel Mouzo, María López-Pedrouso, Daniel Franco, Lucio García, and Carlos Zapata. 2019. "The Major Storage Protein in Potato Tuber Is Mobilized by a Mechanism Dependent on Its Phosphorylation Status" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081889
APA StyleBernal, J., Mouzo, D., López-Pedrouso, M., Franco, D., García, L., & Zapata, C. (2019). The Major Storage Protein in Potato Tuber Is Mobilized by a Mechanism Dependent on Its Phosphorylation Status. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081889