Dose-Dependent Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Burn-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HBOT Dose-Dependent Effect on Mechanical Allodynia
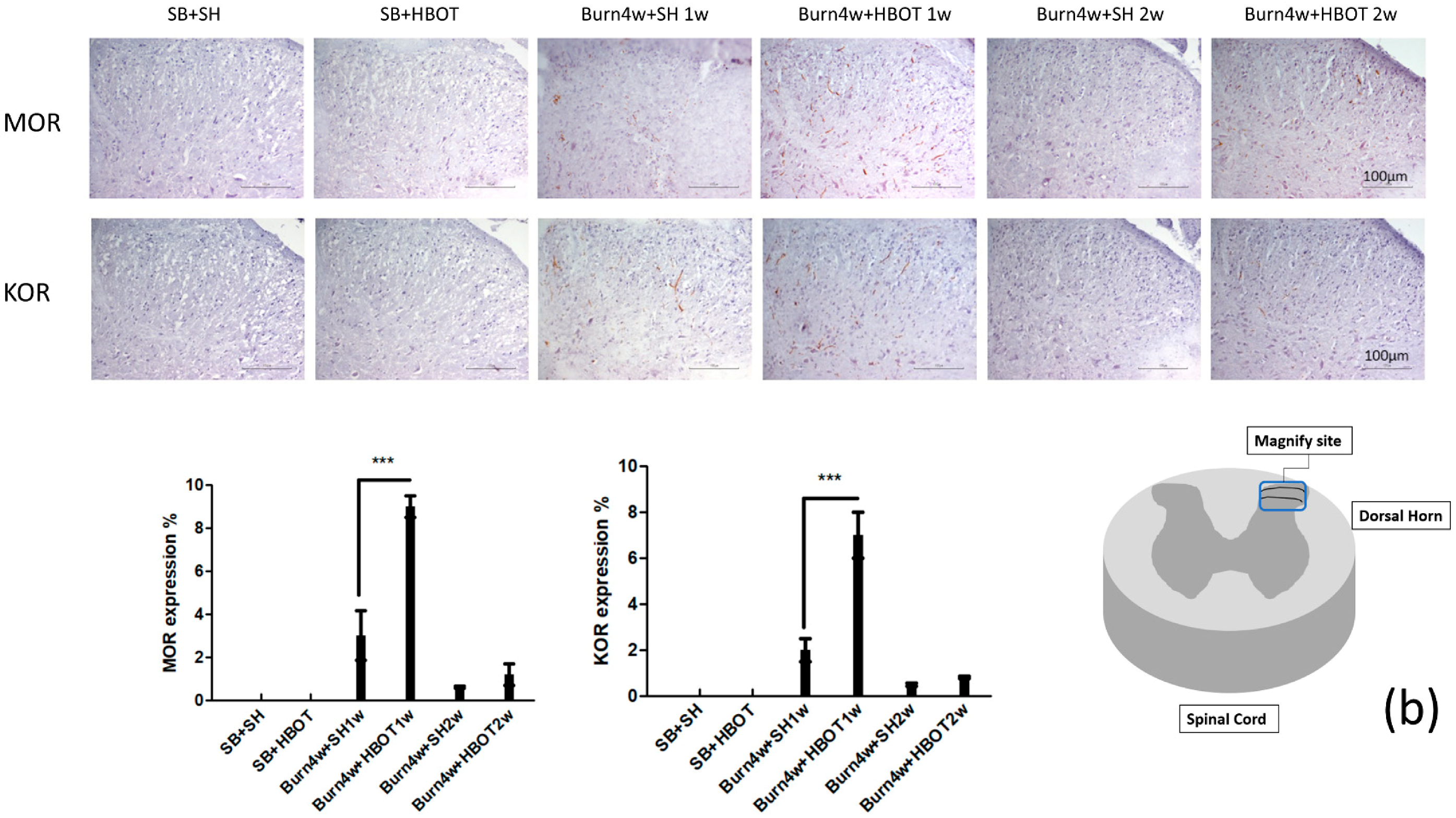
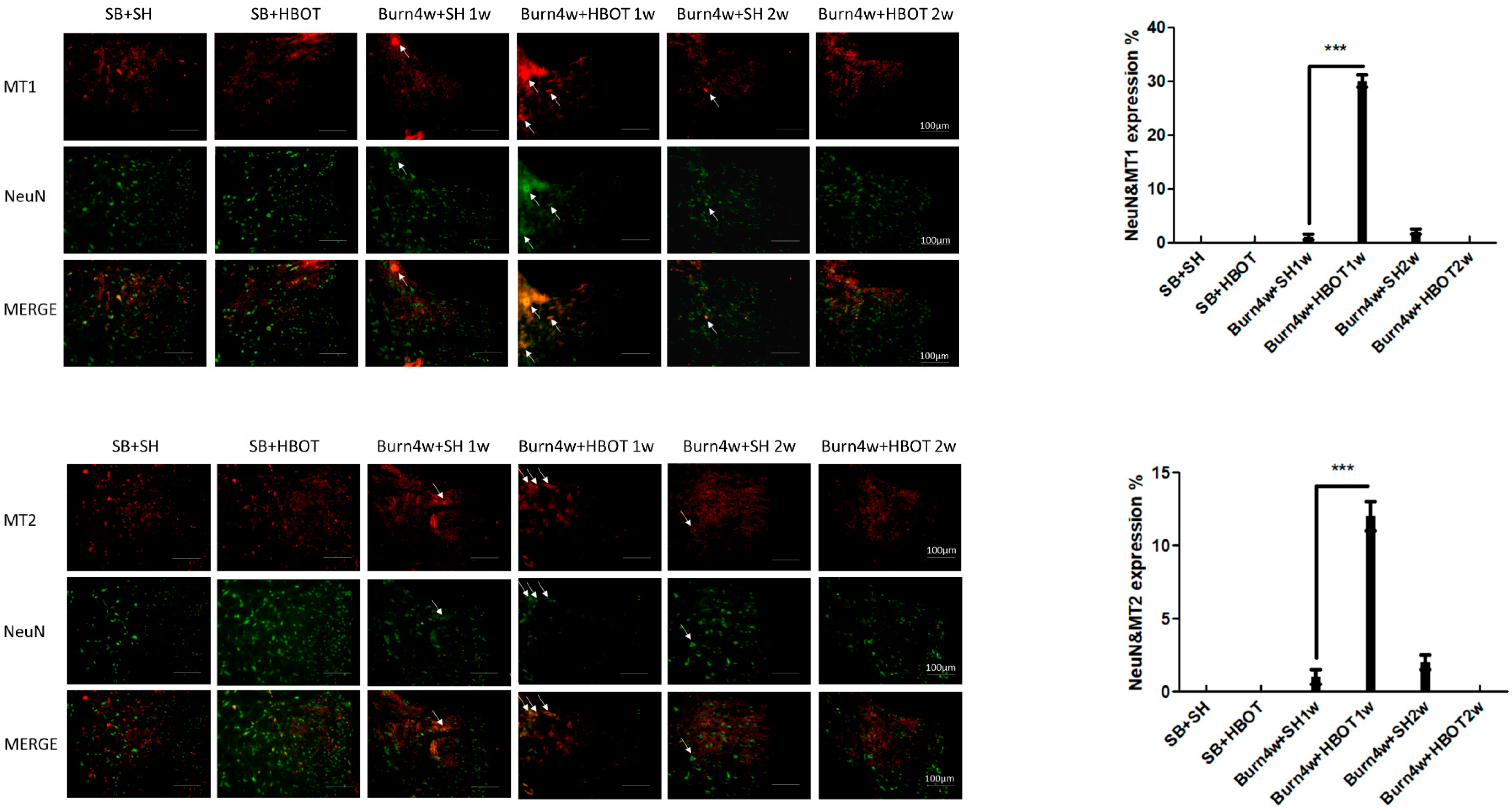
2.2. The Effect of HBOT on Expressions of MT1, MT2, MOR and KOR in the Dorsal Horn and Cuneate Nucleus
2.3. HBOT Suppression of Astrocyte Activation in the Dorsal Horn
2.4. HBOT Alleviation of Nociceptive Reaction in the Dorsal Horns and Right Hind Paw Skin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Full-Thickness Burn Injury Procedure
4.3. Dose-Dependent Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment
4.4. Assessment of Mechanical Withdrawal Threshold (MWT)
4.5. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Assay
4.6. Immunofluorescence (IF) Assay
4.7. Two-Step Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
- Rat MTNR1A-F: CACTGGCCTTCATCCTCATCTT
- Rat MTNR1A-R: CCTGCGTTCCTGAGCTTCTT
- Rat MTNR1B-F: TTCCTAACCATGTTCGCAGTGT
- Rat MTNR1B-R: GAGCCATTGCCTCTGGATTG
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouhassira, D.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Attal, N.; Laurent, B.; Touboul, C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 2008, 136, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanpaa, M.; Attal, N.; Backonja, M.; Baron, R.; Bennett, M.; Bouhassira, D.; Cruccu, G.; Hansson, P.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Iannetti, G.D.; et al. Neupsig guidelines on neuropathic pain assessment. Pain 2011, 152, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas, M.; Ojeda, B.; Salazar, A.; Mico, J.A.; Failde, I. A review of chronic pain impact on patients, their social environment and the health care system. J. Pain Res. 2016, 9, 457. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S.C.; Hsu, C.K.; Tsai, C.T.; Chieh, M.J. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Hu Li Za Zhi 2018, 65, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.K.; Cao, H.H.; Ying, X.; Zhang, H.T.; Yu, H.L. The effects of hyperbaric oxygen on macrophage polarization after rat spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2015, 1606, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.; Howell, R.S.; Boinpally, H.; Jimenez, E.; Chalas, E.; Musa, F.; Gorenstein, S. Using advanced wound care and hyperbaric oxygen to manage wound complications following treatment of vulvovaginal carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 24, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.D.; Uhelski, M.L.; Wilson, J.R.; Fuchs, P.N. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment decreases pain in two nerve injury models. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 66, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Fang, L.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z.; Nandi, J.; Thomas, S.; Chen, C.; Camporesi, E. Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy alleviates chronic constrictive injury-induced neuropathic pain and reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sabato, F.; Rocco, M.; Martelletti, P.; Giacovazzo, M. Hyperbaric oxygen in chronic cluster headaches: Influence on serotonergic pathways. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 1997, 24, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, S.; Uzun, G.; Kiralp, M.Z. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in chronic pain management. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2006, 10, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, A.M.; Clarke, H.A.; Katz, J.; Katznelson, R. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: A new treatment for chronic pain? Pain Pract. 2016, 16, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-S.; Lo, J.-J.; Wu, S.-H.; Wang, C.-Z.; Chen, R.-F.; Lee, S.-S.; Chai, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-H. Early Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment Attenuates Burn-Induced Neuroinflammation by Inhibiting the Galectin-3-Dependent Toll-Like Receptor-4 Pathway in a Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: The chemical expression of darkness. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1991, 79, C153–C158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Yin, T.C.; Sung, P.H.; Chiang, J.Y.; Sun, C.K.; Yip, H.K. Melatonin enhances survival and preserves functional integrity of stem cells: A review. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, G.E. Circadian rhythm of nociception in the golden hamster. Brain Res. 1987, 425, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mease, P. Fibromyalgia syndrome: Review of clinical presentation, pathogenesis, outcome measures, and treatment. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2005, 75, 6–21. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.H.; Leng, P.H.; Gwee, K.A.; Moochhala, S.M.; Ho, K.Y. Melatonin improves abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome patients who have sleep disturbances: A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study. Gut 2005, 54, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posa, L.; de Gregorio, D.; Gobbi, G.; Comai, S. Targeting melatonin MT2 receptors: A novel pharmacological avenue for inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3866–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambriz-Tututi, M.; Rocha-González, H.I.; Cruz, S.L.; Granados-Soto, V. Melatonin: A hormone that modulates pain. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, D.; Davidson, K.; Hough, K.A.; Teh, M.T. Melatonin, melatonin receptors and melanophores: A moving story. Pigment Cell Res. 2004, 17, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reppert, S.M.; Godson, C.; Mahle, C.D.; Weaver, D.R.; Slaugenhaupt, S.A.; Gusella, J.F. Molecular characterization of a second melatonin receptor expressed in human retina and brain: The mel1b melatonin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8734–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.Y.; Leong, M.K.; Liang, H.; Paxinos, G. Melatonin receptors: Distribution in mammalian brain and their respective putative functions. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2921–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoste, B.; Angeloni, D.; Dominguez-Lopez, S.; Calderoni, S.; Mauro, A.; Fraschini, F.; Descarries, L.; Gobbi, G. Anatomical and cellular localization of melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors in the adult rat brain. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.B.; Hsieh, M.C.; Lai, C.Y.; Cheng, J.K.; Wang, H.H.; Chau, Y.P.; Chen, G.D.; Peng, H.Y. Melatonin relieves neuropathic allodynia through spinal MT2-enhanced PP2Ac and downstream HDAC4 shuttling-dependent epigenetic modification of hmgb1 transcription. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambriz-Tututi, M.; Granados-Soto, V. Oral and spinal melatonin reduces tactile allodynia in rats via activation of MT2 and opioid receptors. Pain 2007, 132, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.; Zakaria, R.; Jeet Singh, H.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin and its agonists in pain modulation and its clinical application. Arch. Ital. Biol. 2012, 150, 274–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zöllner, C.; Stein, C. Opioids. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2007, 177, 31–63. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, C.; Machelska, H. Modulation of peripheral sensory neurons by the immune system: Implications for pain therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 860–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Schäfer, M.; Machelska, H. Attacking pain at its source: New perspectives on opioids. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, W.; Cheng, C.; Xu, Q.G.; Li, X.Q.; Zochodne, D.W. Mu opioid receptors and analgesia at the site of a peripheral nerve injury. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, J.S.; Pichette, V.; Leblond, F.; Desbiens, K.; Beaulieu, P. Behavioral, pharmacological and molecular characterization of the saphenous nerve partial ligation: A new model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, J.S.; Pichette, V.; Leblond, F.; Desbiens, K.; Beaulieu, P. Characterization of chronic constriction of the saphenous nerve, a model of neuropathic pain in mice showing rapid molecular and electrophysiological changes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 83, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, A.S.; Lue, J.H.; Sun, W.Z.; Shieh, J.Y.; Wen, C.Y. A β-fiber intensity stimulation of chronically constricted median nerve induces c-fos expression in thalamic projection neurons of the cuneate nucleus in rats with behavioral signs of neuropathic pain. Brain Res. 2001, 895, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, W.D.; Al-Chaer, E.D.; Quast, M.J.; Westlund, K.N. A visceral pain pathway in the dorsal column of the spinal cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7675–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katznelson, R.; Segal, S.C.; Clarke, H. Successful treatment of lower limb complex regional pain syndrome following three weeks of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Pain Res. Manag. 2016, 2016, 3458371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, M.J.; Chen, T.Y.; Cheng, Y.M.; Hsu, Y.C. The effect of postoperative hyperbaric oxygen treatment on intra-abdominal adhesions in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12224–12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinski, L.M.; Ohgami, Y.; Chung, E.; Shirachi, D.Y.; Quock, R.M. A prolonged nitric oxide-dependent, opioid-mediated antinociceptive effect of hyperbaric oxygen in mice. J. Pain 2009, 10, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Tang, G.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, C.; et al. Propionibacterium acnes induces discogenic low back pain via stimulating nucleus pulposus cells to secrete pro-algesic factor of IL-8/CINC-1 through TLR2–NF-κB p65 pathway. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttfarcken, P.S.; Han, P.; Joshi, S.K.; Neelands, T.R.; Gauvin, D.M.; Baker, S.J.; Lewis, L.G.; Bianchi, B.R.; Mikusa, J.P.; Koenig, J.R.; et al. A-995662 [(R)-8-(4-methyl-5-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)oxazol-2-ylamino)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydr onaphthalen-2-ol], a novel, selective TRPV1 receptor antagonist, reduces spinal release of glutamate and CGRP in a rat knee joint pain model. Pain 2010, 150, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Cui, W.; Li, L.B.; Zhang, Z.C.; Tian, B.P.; Zhang, G.S. Melatonin attenuates pain hypersensitivity and decreases astrocyte-mediated spinal neuroinflammation in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced pain. Inflammation 2017, 40, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Yang, C.H.; Wallace, C.G.; Lin, C.R.; Liu, C.K.; Yin, T.C.; Huang, T.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Sun, C.K.; Yip, H.K. Combination therapy with extracorporeal shock wave and melatonin markedly attenuated neuropathic pain in rat. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 4593–4606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulugol, A.; Dokmeci, D.; Guray, G.; Sapolyo, N.; Ozyigit, F.; Tamer, M. Antihyperalgesic, but not antiallodynic, effect of melatonin in nerve-injured neuropathic mice: Possible involvements of the l-arginine-NO pathway and opioid system. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.; Kurganova, J. Melatonin in chronic pain syndromes. Pain Ther. 2016, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz, T.; Arslan, A.D.; Kurtuncu, M.; Imbesi, M.; Akhisaroglu, M.; Dwivedi, Y.; Pandey, G.N.; Manev, H. The regional and cellular expression profile of the melatonin receptor MT1 in the central dopaminergic system. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 136, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, S.R.; Dai, X.; Peng, Y.L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, R. Effects of melatonin on orphanin FQ/nociceptin-induced hyperalgesia in mice. Brain Res. 2006, 1085, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Canul, M.; Palazzo, E.; Dominguez-Lopez, S.; Luongo, L.; Lacoste, B.; Comai, S.; Angeloni, D.; Fraschini, F.; Boccella, S.; Spadoni, G. Selective melatonin MT2 receptor ligands relieve neuropathic pain through modulation of brainstem descending antinociceptive pathways. Pain 2015, 156, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuvone, P.M.; Gan, J. Melatonin receptor-mediated inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation in chick retinal cell cultures. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanecek, J. Cellular mechanisms of melatonin action. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 687–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Yin, D.; Chen, L.; Qu, W.M.; Chen, C.R.; Laudon, M.; Cheng, N.N.; Urade, Y.; Huang, Z.L. Piromelatine exerts antinociceptive effect via melatonin, opioid, and 5HT1A receptors and hypnotic effect via melatonin receptors in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, C.R.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sayre, C.L.; Levitch, B.R.; Moehlmann, S.B.; Shirachi, D.Y.; Quock, R.M. Involvement of brain opioid receptors in the anti-allodynic effect of hyperbaric oxygen in rats with sciatic nerve crush-induced neuropathic pain. Brain Res. 2013, 1537, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Stolz, P.A.; Shirachi, D.Y.; Quock, R.M. Reduced antinociceptive responsiveness to hyperbaric oxygen in opioid-tolerant mice. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeman, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Shirachi, D.Y.; Quock, R.M. Involvement of spinal cord opioid mechanisms in the acute antinociceptive effect of hyperbaric oxygen in mice. Brain Res. 2013, 1540, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancall, E. Cerebellum. In Gray’s Clinical Neuroanatomy: The Anatomic Basis for Clinical Neuroscience; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.C.; Yeh, J.H.; Chen, C.L.; Chou, S.H.; Tsai, Y.J. Effects of local lidocaine treatment before and after median nerve injury on mechanical hypersensitivity and microglia activation in rat cuneate nucleus. Eur. J. Pain 2011, 15, 359–367. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, S.J.; Pitcher, M.H.; Stone, L.S.; Tarum, F.; Niu, G.; Chen, X.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Schweinhardt, P.; Bushnell, M.C. Chronic neuropathic pain reduces opioid receptor availability with associated anhedonia in rat. Pain 2018, 159, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.E.; Clauw, D.J.; Scott, D.J.; McLean, S.A.; Gracely, R.H.; Zubieta, J.K. Decreased central μ-opioid receptor availability in fibromyalgia. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10000–10006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porreca, F.; Tang, Q.B.; Bian, D.; Riedl, M.; Elde, R.; Lai, J. Spinal opioid μ receptor expression in lumbar spinal cord of rats following nerve injury. Brain Res. 1998, 795, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bao, L.; Shi, T.J.; Ju, G.; Elde, R.; Hokfelt, T. Down-regulation of mu-opioid receptors in rat and monkey dorsal root ganglion neurons and spinal cord after peripheral axotomy. Neuroscience 1998, 82, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yao, P.; Hong, T.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhou, G. The analgesic effect of early hyperbaric oxygen treatment in chronic constriction injury rats and its influence on nnos and inos expression and inflammatory factor production. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918765837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.D.; Wang, Z.B.; Han, G.; Zhao, P. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment attenuates neuropathic pain by elevating autophagy flux via inhibiting mtor pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2629–2638. [Google Scholar]
- Pezet, S.; McMahon, S.B. Neurotrophins: Mediators and modulators of pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, A.; Salio, C.; Ghirri, A.; Lossi, L.; Ferrini, F.; Betelli, C.; Bardoni, R. BDNF as a pain modulator. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.B.; Zuo, X.L.; Zhao, Q.J.; Chen, F.X.; Yang, J.; Dong, Y.Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.Q. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2012, 61, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmann, L.; Hatcher, J.P.; Hughes, J.P.; Chaumont, S.; Green, P.J.; Conquet, F.; Buell, G.N.; Reeve, A.J.; Chessell, I.P.; Rassendren, F. Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11263–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zanette, S.A.; Vercelino, R.; Laste, G.; Rozisky, J.R.; Schwertner, A.; Machado, C.B.; Xavier, F.; de Souza, I.C.; Deitos, A.; Torres, I.L.; et al. Melatonin analgesia is associated with improvement of the descending endogenous pain-modulating system in fibromyalgia: A phase II, randomized, double-dummy, controlled trial. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, J.; Zychowska, M.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Rojewska, E.; Przewlocka, B. Importance of glial activation in neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 716, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Ji, R.R. Targeting astrocyte signaling for chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Jiang, B.C.; Gao, Y.J. Chemokines in neuron-glial cell interaction and pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3275–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, C.I.; Brodin, E. Spinal astrocytes in pain processing: Non-neuronal cells as therapeutic targets. Mol. Interv. 2010, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, U.K.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia: Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowrońska, K.; Obara-Michlewska, M.; Zielińska, M.; Albrecht, J. NMDA Receptors in Astrocytes: In Search for Roles in Neurotransmission and Astrocytic Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffo-Romero, A.; Arab, T.; Al-Amri, I.S.; Le Marrec-Croq, F.; Van Camp, C.; Lemaire, Q.; Salzet, M.; Vizioli, J.; Sautiere, P.-E.; Lefebvre, C. Medicinal Leech CNS as a Model for Exosome Studies in the Crosstalk between Microglia and Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. The Neuropathic Pain Triad: Neurons, Immune Cells and Glia. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, M.; Peng, C.; Zhao, G.; Gu, R. GFAP expression in injured astrocytes in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Qi, Y.; Jia, N.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment sensitizes gastric cancer cells to melatonin-induced apoptosis through multiple pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6723–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, K.; Topal, T.; Ay, H.; Oter, S.; Korkmaz, A. Protective effects of exogenously administered or endogenously produced melatonin on hyperbaric oxygen-induced oxidative stress in the rat brain. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, T.Z.; Zhang, C.K.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.L.; Ding, J.Q.; Chang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, C.; et al. Melatonin suppresses neuropathic pain via MT2-dependent and -independent pathways in dorsal root ganglia neurons of mice. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2015–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, L. RNAi-mediated knockdown of MTNR1B without disrupting the effects of melatonin on apoptosis and cell cycle in bovine granulose cells. PeerJ 2018, 6, e6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Gunzer, M.; Metze, D.; Luger, T.; Steinhoff, M. Localization of μ-opioid receptor 1A on sensory nerve fibers in human skin. Regul. Pept. 2002, 1, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porthé, G.; Frances, B.; Verrier, B.; Cros, J.; Meunier, J.C. The kappa-opioid receptor from human placenta: Hydrodynamic characteristics and evidence for its association with AG protein. Life Sci. 1988, 43, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.-S.; Wu, S.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Lo, J.-J.; Chai, C.-Y.; Wu, C.-S.; Huang, S.-H. Dose-Dependent Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Burn-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081951
Wu Z-S, Wu S-H, Lee S-S, Lin C-H, Chang C-H, Lo J-J, Chai C-Y, Wu C-S, Huang S-H. Dose-Dependent Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Burn-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081951
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zong-Sheng, Sheng-Hua Wu, Su-Shin Lee, Cen-Hung Lin, Chih-Hau Chang, Jing-Jou Lo, Chee-Yin Chai, Ching-Shuang Wu, and Shu-Hung Huang. 2019. "Dose-Dependent Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Burn-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081951
APA StyleWu, Z.-S., Wu, S.-H., Lee, S.-S., Lin, C.-H., Chang, C.-H., Lo, J.-J., Chai, C.-Y., Wu, C.-S., & Huang, S.-H. (2019). Dose-Dependent Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Burn-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081951




