Clobetasol Modulates Adult Neural Stem Cell Growth via Canonical Hedgehog Pathway Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
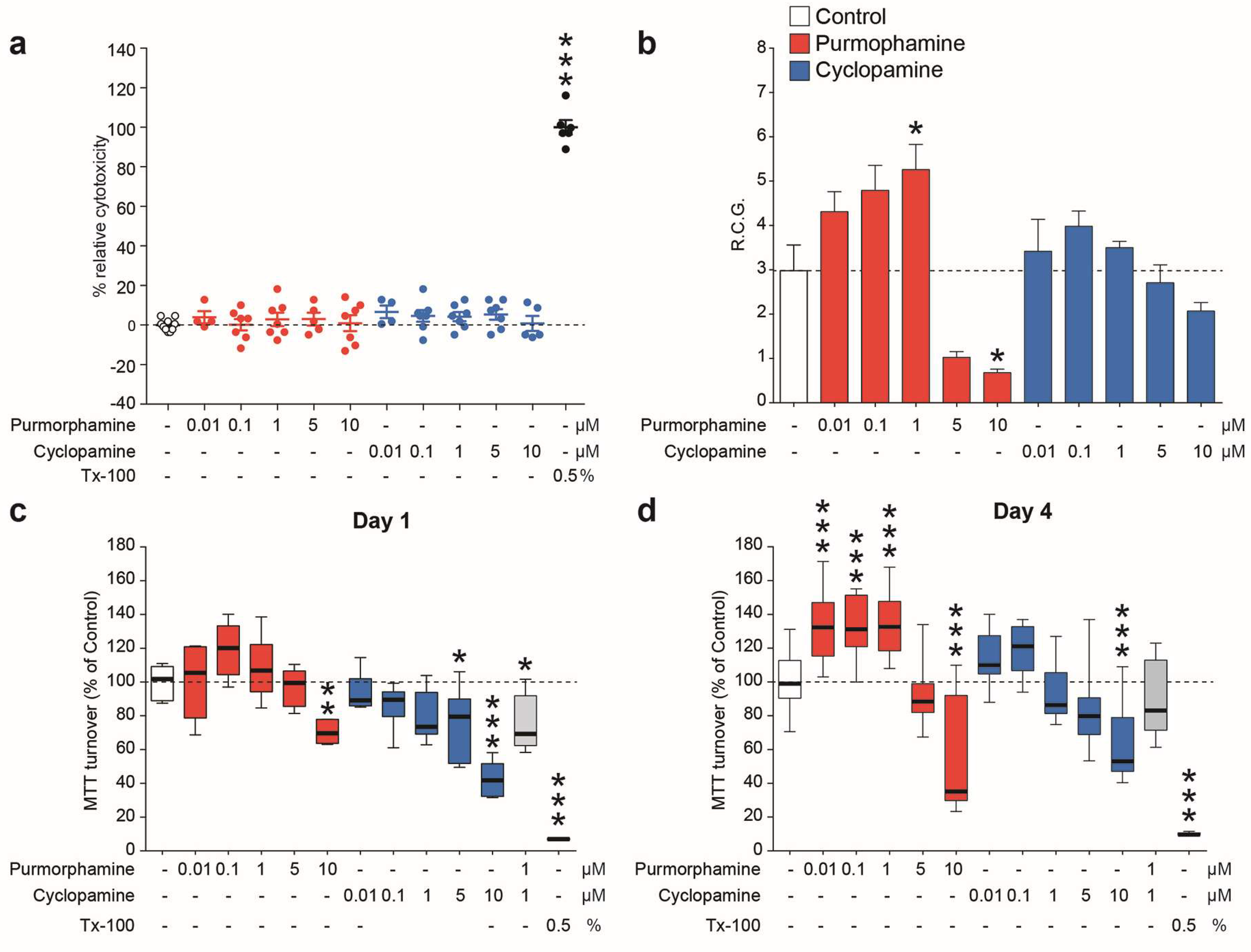
2.1. Purmorphamine Increases the Growth Rate and Metabolism of NSCs
2.2. Purmorphamine Activates “Canonical” Gli1-Dependent Shh Signaling in NSCs
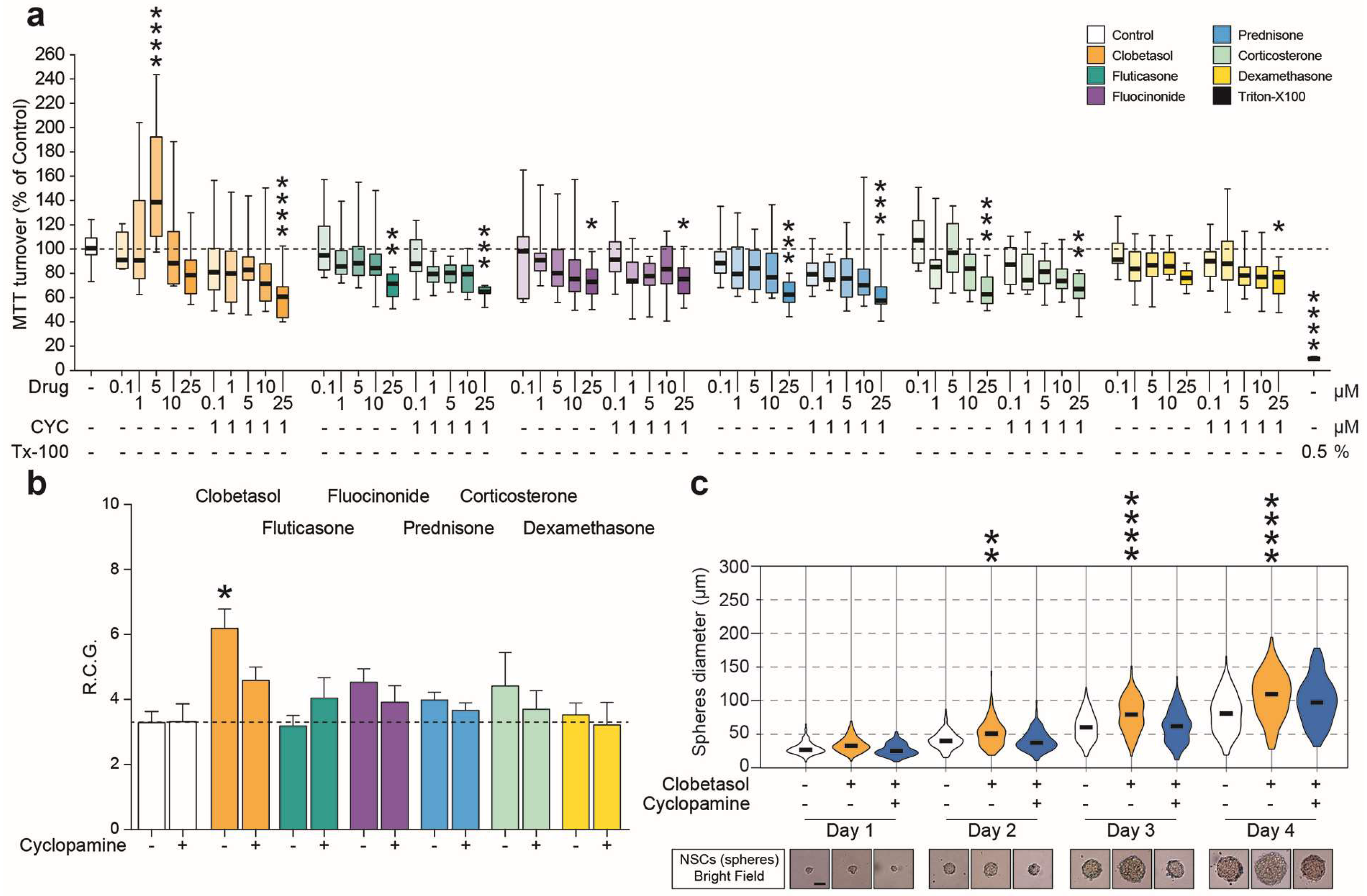
2.3. Clobetasol Increases Proliferation and Dimension of NSCs Neurospheres
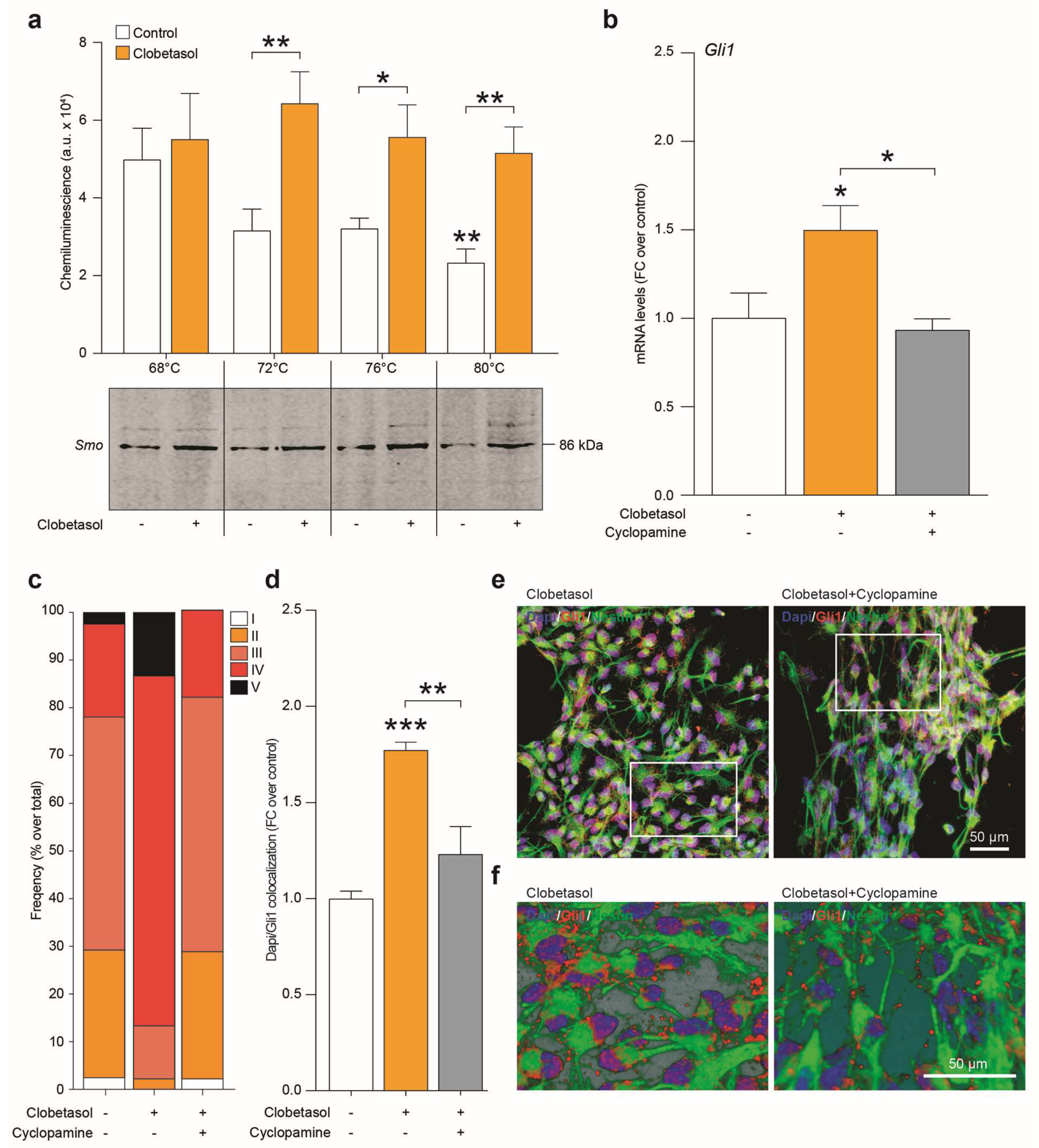
2.4. Clobetasol Activates Canonical Shh Signaling by Smo Agonism and Gli1 Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Neural Stem Cell Derivation and Culture
4.2. Shh Pathway Modulation in NSCs
4.3. LDH and MTT Cytotoxicity/Viability Assays
4.4. Target Engagement Assay by CETSA and Immunoblot
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. mRNA Quantification
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| Boc | Biregional Cdon binding protein |
| Cdon | Cell adhesion molecule-related/down-regulated by oncogenes |
| CETSA | Cellular thermal shift assay |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| EBSS | Earle’s balanced salt solution |
| EDTA | Ethilenediaminotetraacetic acid |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| Gli1 | GLI-Kruppel family members 1 |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-Yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NGS | Normal goat serum |
| NR3C1 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 3 Group C Member 1 |
| NSCs | Neural stem cells |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| Ptch1 | Patched |
| RCG | Rate of cell growth |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| Shh | Sonic hedgehog |
| Smo | Smoothened |
| SVZ | Subventricular zone |
References
- Ruiz i Altaba, A.; Palma, V.; Dahmane, N. Hedgehog-gli signalling and the growth of the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Ihrie, R.A. Sonic hedgehog signaling in the postnatal brain. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 33, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, Y.H.; Hamilton, A.M.; Shim, S.; Spencer, K.A.; Borodinsky, L.N. The many hats of sonic hedgehog signaling in nervous system development and disease. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuccillo, M.; Joyner, A.L.; Fishell, G. Morphogen to mitogen: The multiple roles of hedgehog signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placzek, M.; Briscoe, J. Sonic hedgehog in vertebrate neural tube development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 62, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferey, L.; Delaunay, N.; Rutledge, D.N.; Huertas, A.; Raoul, Y.; Gareil, P.; Vial, J. Use of response surface methodology to optimize the simultaneous separation of eight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by capillary zone electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1302, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villavicencio, E.H.; Walterhouse, D.O.; Iannaccone, P.M. The sonic hedgehog-patched-gli pathway in human development and disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orentas, D.M.; Hayes, J.E.; Dyer, K.L.; Miller, R.H. Sonic hedgehog signaling is required during the appearance of spinal cord oligodendrocyte precursors. Development 1999, 126, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ugbode, C.I.; Smith, I.; Whalley, B.J.; Hirst, W.D.; Rattray, M. Sonic hedgehog signalling mediates astrocyte crosstalk with neurons to confer neuroprotection. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Drannik, A.; Jiang, F.; Peterson, R.; Turnbull, J. Crosstalk between notch and sonic hedgehog signaling in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, R.; Turnbull, J. Sonic hedgehog is cytoprotective against oxidative challenge in a cellular model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 47, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drannik, A.; Martin, J.; Peterson, R.; Ma, X.; Jiang, F.; Turnbull, J. Cerebrospinal fluid from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis inhibits sonic hedgehog function. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chechneva, O.V.; Mayrhofer, F.; Daugherty, D.J.; Krishnamurty, R.G.; Bannerman, P.; Pleasure, D.E.; Deng, W. A smoothened receptor agonist is neuroprotective and promotes regeneration after ischemic brain injury. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, N.P.; Yu, W.P.; Guthrie, S.; Roelink, H.; Lumsden, A.; Peterson, A.C.; Richardson, W.D. Determination of neuroepithelial cell fate: Induction of the oligodendrocyte lineage by ventral midline cells and sonic hedgehog. Dev. Biol. 1996, 177, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podjaski, C.; Alvarez, J.I.; Bourbonniere, L.; Larouche, S.; Terouz, S.; Bin, J.M.; Lecuyer, M.A.; Saint-Laurent, O.; Larochelle, C.; Darlington, P.J.; et al. Netrin 1 regulates blood-brain barrier function and neuroinflammation. Brain 2015, 138, 1598–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abballe, L.; Mastronuzzi, A.; Miele, E.; Carai, A.; Besharat, Z.M.; Moretti, M.; De Smaele, E.; Giangaspero, F.; Locatelli, F.; Ferretti, E.; et al. Numb isoforms deregulation in medulloblastoma and role of p66 isoform in cancer and neural stem cells. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Qiao, L.; Guo, Z.; Lin, J. Sonic hedgehog regulation of the neural precursor cell fate during chicken optic tectum development. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitter, K.L.; Tamagno, I.; Feng, X.; Ghosal, K.; Amankulor, N.; Holland, E.C.; Hambardzumyan, D. The shh/gli pathway is reactivated in reactive glia and drives proliferation in response to neurodegeneration-induced lesions. GLIA 2014, 62, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Armstrong, R.C. Transplanted adult neural stem cells express sonic hedgehog in vivo and suppress white matter neuroinflammation after experimental traumatic brain injury. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9342534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Barak, L.S.; Mook, R.A., Jr.; Chen, W. Glucocorticoid hedgehog agonists in neurogenesis. Vitam. Horm. 2011, 87, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Hadden, M.K. Hedgehog pathway agonism: Therapeutic potential and small-molecule development. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruat, M.; Hoch, L.; Faure, H.; Rognan, D. Targeting of smoothened for therapeutic gain. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2014, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Bond, M.C.; Chen, M.; Ren, X.R.; Lyerly, H.K.; Barak, L.S.; Chen, W. Identification of select glucocorticoids as smoothened agonists: Potential utility for regenerative medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9323–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, R.J. Regenerative medicines for remyelination: From aspiration to reality. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 576–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, F.J.; Madhavan, M.; Zaremba, A.; Shick, E.; Karl, R.T.; Factor, D.C.; Miller, T.E.; Nevin, Z.S.; Kantor, C.; Sargent, A.; et al. Drug-based modulation of endogenous stem cells promotes functional remyelination in vivo. Nature 2015, 522, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcu, G.; Serone, E.; De Nardis, V.; Di Giandomenico, D.; Lucisano, G.; Scardapane, M.; Poma, A.; Ragnini-Wilson, A. Clobetasol and halcinonide act as smoothened agonists to promote myelin gene expression and rxrgamma receptor activation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Chen, J.K. Purmorphamine activates the hedgehog pathway by targeting smoothened. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, V.; Lim, D.A.; Dahmane, N.; Sanchez, P.; Brionne, T.C.; Herzberg, C.D.; Gitton, Y.; Carleton, A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Ruiz i Altaba, A. Sonic hedgehog controls stem cell behavior in the postnatal and adult brain. Development 2005, 132, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Kaspar, B.K.; Gage, F.H.; Schaffer, D.V. Sonic hedgehog regulates adult neural progenitor proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.G.; Spassky, N.; Romaguera-Ros, M.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Aguilar, A.; Schneider-Maunoury, S.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambakidis, N.C.; Wang, R.Z.; Franic, L.; Miller, R.H. Sonic hedgehog-induced neural precursor proliferation after adult rodent spinal cord injury. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Barnett, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Luo, Y. Poststroke sonic hedgehog agonist treatment improves functional recovery by enhancing neurogenesis and angiogenesis. Stroke 2017, 48, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambakidis, N.C.; Horn, E.M.; Nakaji, P.; Theodore, N.; Bless, E.; Dellovade, T.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Preul, M.C.; Coons, S.W.; et al. Endogenous stem cell proliferation induced by intravenous hedgehog agonist administration after contusion in the adult rat spinal cord. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2009, 10, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulino, R.; Perciavalle, V.; Gulisano, M. Expression of cell fate determinants and plastic changes after neurotoxic lesion of adult mice spinal cord by cholera toxin-b saporin. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 31, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulino, R.; Gulisano, M. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and sonic hedgehog in the spinal cord plasticity after neurotoxic partial removal of lumbar motoneurons. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 73, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, R.; Gulisano, M. Noggin and sonic hedgehog are involved in compensatory changes within the motoneuron-depleted mouse spinal cord. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 332, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, R.; Forte, S.; Parenti, R.; Gulisano, M. Tdp-43 as a modulator of synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of spinal motoneuron degeneration. CNS Neurol. Disord Drug Targets 2015, 14, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, R.; Parenti, R.; Gulisano, M. Novel mechanisms of spinal cord plasticity in a mouse model of motoneuron disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 654637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geevasinga, N.; Menon, P.; Ozdinler, P.H.; Kiernan, M.C.; Vucic, S. Pathophysiological and diagnostic implications of cortical dysfunction in als. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihei, K.; McKee, A.C.; Kowall, N.W. Patterns of neuronal degeneration in the motor cortex of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. ACTA Neuropathol. 1993, 86, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Liang, B.; Schroeder, D.; Zhang, Z.W.; Cox, G.A.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.T. Hyperactive somatostatin interneurons contribute to excitotoxicity in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, A.L.; Snyder, E.Y. Establishment and properties of neural stem cell clones: Plasticity in vitro and in vivo. Brain Pathol. 1999, 9, 569–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzotti-Jametti, L.; Bernstock, J.D.; Vicario, N.; Costa, A.S.H.; Kwok, C.K.; Leonardi, T.; Booty, L.M.; Bicci, I.; Balzarotti, B.; Volpe, G.; et al. Macrophage-derived extracellular succinate licenses neural stem cells to suppress chronic neuroinflammation. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicario, N.; Calabrese, G.; Zappala, A.; Parenti, C.; Forte, S.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Vanella, L.; Pellitteri, R.; Cardile, V.; Parenti, R. Inhibition of cx43 mediates protective effects on hypoxic/reoxygenated human neuroblastoma cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstock, J.D.; Ye, D.; Smith, J.A.; Lee, Y.J.; Gessler, F.A.; Yasgar, A.; Kouznetsova, J.; Jadhav, A.; Wang, Z.; Pluchino, S.; et al. Quantitative high-throughput screening identifies cytoprotective molecules that enhance sumo conjugation via the inhibition of sumo-specific protease (senp)2. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almqvist, H.; Axelsson, H.; Jafari, R.; Dan, C.; Mateus, A.; Haraldsson, M.; Larsson, A.; Martinez Molina, D.; Artursson, P.; Lundback, T.; et al. Cetsa screening identifies known and novel thymidylate synthase inhibitors and slow intracellular activation of 5-fluorouracil. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, R.; Puzzo, L.; Vecchio, G.M.; Gravina, L.; Salvatorelli, L.; Musumeci, G.; Vasquez, E.; Magro, G. Immunolocalization of Wilms’ Tumor protein (WT1) in developing human peripheral sympathetic and gastroenteric nervous system. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vicario, N.; Bernstock, J.D.; Spitale, F.M.; Giallongo, C.; Giunta, M.A.S.; Li Volti, G.; Gulisano, M.; Leanza, G.; Tibullo, D.; Parenti, R.; et al. Clobetasol Modulates Adult Neural Stem Cell Growth via Canonical Hedgehog Pathway Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081991
Vicario N, Bernstock JD, Spitale FM, Giallongo C, Giunta MAS, Li Volti G, Gulisano M, Leanza G, Tibullo D, Parenti R, et al. Clobetasol Modulates Adult Neural Stem Cell Growth via Canonical Hedgehog Pathway Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081991
Chicago/Turabian StyleVicario, Nunzio, Joshua D. Bernstock, Federica M. Spitale, Cesarina Giallongo, Maria A.S. Giunta, Giovanni Li Volti, Massimo Gulisano, Giampiero Leanza, Daniele Tibullo, Rosalba Parenti, and et al. 2019. "Clobetasol Modulates Adult Neural Stem Cell Growth via Canonical Hedgehog Pathway Activation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081991
APA StyleVicario, N., Bernstock, J. D., Spitale, F. M., Giallongo, C., Giunta, M. A. S., Li Volti, G., Gulisano, M., Leanza, G., Tibullo, D., Parenti, R., & Gulino, R. (2019). Clobetasol Modulates Adult Neural Stem Cell Growth via Canonical Hedgehog Pathway Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081991










