Modified Carboxyl-Terminated PAMAM Dendrimers as Great Cytocompatible Nano-Based Drug Delivery System
Abstract
1. Introduction
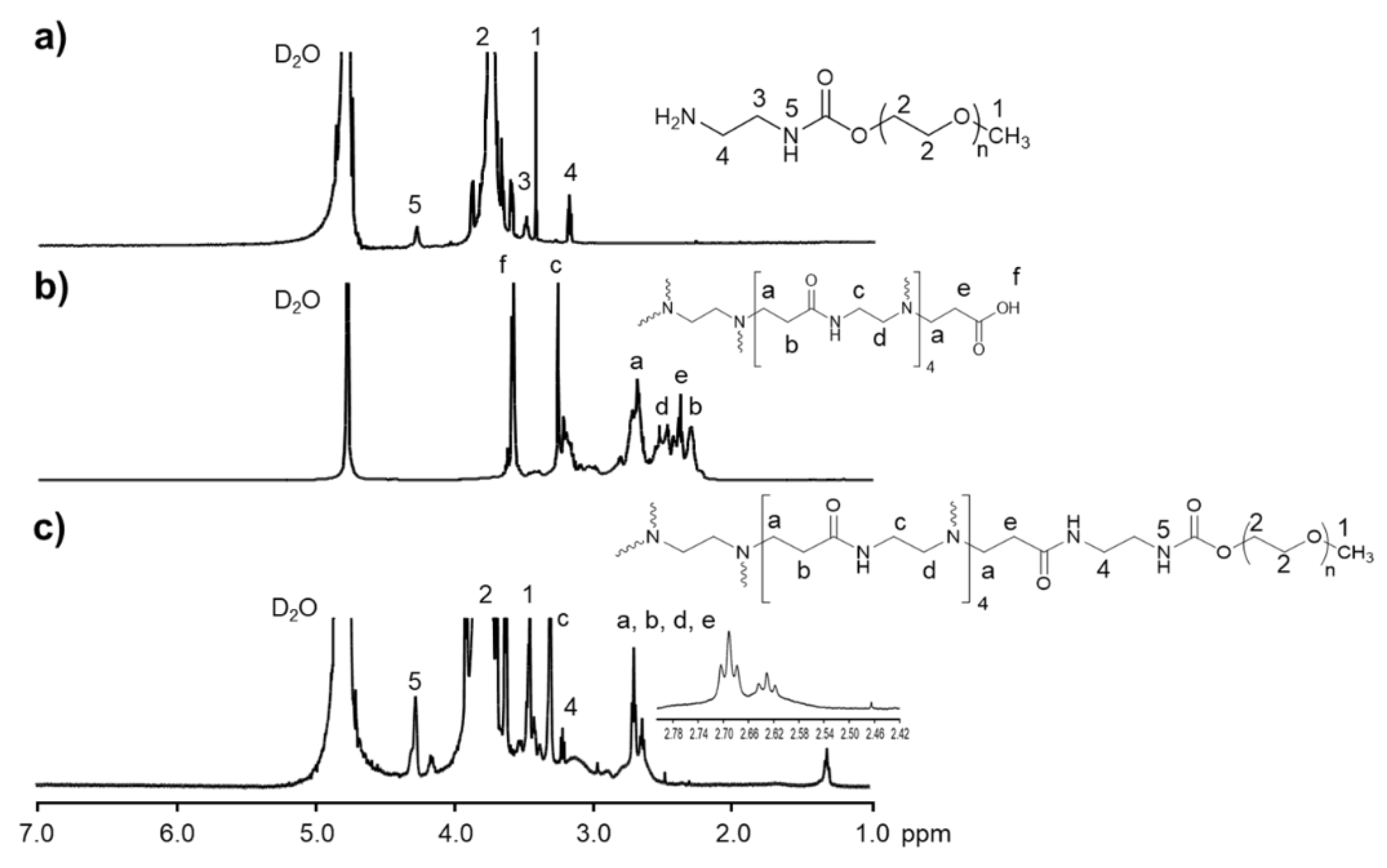
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Carboxyl-Terminated PAMAM G3.5 Dendrimer
3.3. Amination of mPEG
3.4. Conjugation of mPEG to PAMAM G3.5 (mPEG-G3.5)
3.5. Characterizations
3.6. Preparation of CPT/mPEG-G3.5 and Drug Loading Capacity
3.7. In Vitro Release Study
3.8. Cell Viability Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Shen, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zou, D.; Gao, Z.; Yue, C. Prodrug-based nano-drug delivery system for co-encapsulate paclitaxel and carboplatin for lung cancer treatment. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2575–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, G.F.; Wlodarczyk, S.R.; Monteiro, G. Carboplatin: Molecular mechanisms of action associated with chemoresistance. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 50, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, C.T.; Zwahlen, C.H.; Kirschner, S.; Nakamura, R.K. Evaluation of carboplatin sustained-release delivery system in dogs with cancer. Collect. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 2, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.; Kerby, I.J.; Rocker, I.; Evans, A.; Johansen, K.; Franks, C.R. A comparison of the toxicity and efficacy of cisplatin and carboplatin in advanced ovarian cancer. Acta Oncol. 1989, 28, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.P. Platinum and palladium polyamine complexes as anticancer agents: The structural factor. Int. Sch. Res. Not. Spectrosc. 2013, 2013, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogliotti, L.; Carteni, G.; Siena, S.; Bertetto, O.; Martoni, A.; Bono, A.; Amadori, D.; Onat, H.; Marini, L. Gemcitabine plus cisplatin versus gemcitabine plus carboplatin as first-line chemotherapy in advanced transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelium: Results of a randomized phase 2 trial. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalba, S.; Garrido, M.J. Liposomes, a promising strategy for clinical application of platinum derivatives. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vijgh, W.J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of carboplatin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1991, 21, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, S.M.; Banks, T.A. Small Animal Oncology: An Introduction; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahinimaf, M.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, A.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Shahemabadi, H.E.; Hasanzadegan, M.; Moradi-Sardareh, H.; Madadizadeh, H.; Rezaee-diyan, J. Preparation, characterization and cytotoxic effects of pegylated nanoliposomal containing carboplatin on ovarian cancer cell lines. Idian J. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 32, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Alex, A.T.; Joseph, A.; Shavi, G.; Rao, J.V.; Udupa, N. Development and evaluation of carboplatin-loaded pcl nanoparticles for intranasal delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, M.; Haase, D.; Hampel, S.; Oswald, S.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Klingeler, R.; Schulze, R.; Ritschel, M.; Leonhardt, A.; Fuessel, S.; et al. Delivery of carboplatin by carbon-based nanocontainers mediates increased cancer cell death. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 335101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, D.; Kesharwani, P.; Deshmukh, R.; Amin, M.C.I.M.; Gupta, U.; Greish, K.; Iyer, A.K. Pegylated pamam dendrimers: Enhancing efficacy and mitigating toxicity for effective anticancer drug and gene delivery. Acta Biomater. 2016, 43, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.C.; Nguyen, C.K.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, N.Q. Highly lipophilic pluronics-conjugated polyamidoamine dendrimer nanocarriers as potential delivery system for hydrophobic drugs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.Q.; Nguyen, C.K.; Nguyen, T.P. Dendrimer-based nanocarriers demonstrating a high efficiency for loading and releasing anticancer drugs against cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-Y.; Tang, G.-T.; Zhang, L.-H.; Kong, S.-Y.; Zhu, S.-J.; Pei, Y.-Y. Pegylated pamam dendrimers as a potential drug delivery carrier: In vitro and in vivo comparative evaluation of covalently conjugated drug and noncovalent drug inclusion complex. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Lohiya, G.K.; Limburkar, P.P.; Dharbale, N.B.; Mourya, V.K. Dendrimer a versatile polymer in drug delivery. Asian J. Parm. 2009, 3, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, N.S.; Hejl, M.; Klose, M.H.M.; Schreiber-Brynzak, E.; Bileck, A.; Meier, S.M.; Gerner, C.; Jakupec, M.A.; Galanski, M.; Keppler, B.K. Low-generation polyamidoamine dendrimers as drug carriers for platinum(IV) complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2017, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Das, M.K. Dendrimers and their applications as novel drug delivery carriers. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tomas, H.; She, M.; Shi, X. Antitumor efficacy of doxorubicin encapsulated within pegylated poly(amidoamine) dendrimers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.K.; Tran, N.Q.; Nguyen, T.P.; Nguyen, D.H. Biocompatible nanomaterials based on dendrimers, hydrogels and hydrogel nanocomposites for use in biomedicine. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Kurokawa, Y.; Win-Shwe, T.-T.; Zeng, Q.; Hirano, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sone, H. Effects of pamam dendrimers with various surface functional groups and multiple generations on cytotoxicy and neuronal differentiation using human neural progenitor cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Cheng, L. Redox and ph dual responsive poly (amidoamine) dendrimer-poly (ethylene glycol) conjugates for intracellular delivery of doxorubicin. Acta Biomater. 2016, 36, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, N.H.; Tran, N.Q.; Nguyen, C.K. Improved method for preparing cisplatin-dendrimer nanocomplex and its behavior against nci-h460 lung cancer cell. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 4106–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Durairaj, C.; Kompella, U.B.; O’Brien, J.M.; Grossniklaus, H.E. Subconjunctival nanoparticle carboplatin in the treatment of murine retinoblastoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2009, 127, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhari, H.; Pooja, D.; Singh, M.K.; Chauhan, A.S. Optimization of carboxylate-terminated poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-mediated cisplatin formulation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Evagorou, E.G.; Duncan, R. Dendrimer-platinate: A novel approach to cancer chemotherapy. Anticancer Drugs 1999, 10, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, G.J.; Plumb, J.A.; Sutcliffe, O.B.; Flint, D.J.; Wheate, N.J. Evaluation of anionic half generation 3.5–6.5 poly(amidoamine) dendrimers as delivery vehicles for the active component of the anticancer drug cisplatin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Hong, M.; Zhang, L.; Tang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Pei, Y. Pegylated pamam dendrimer-doxorubicin conjugates: In vitro evaluation and in vivo tumor accumulation. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, V.M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, T.V.; Ngoc, U.P.; Ho, M.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Chau, Y.N.T.; Le, V.T.; Tran, N.Q.; Nguyen, C.K.; et al. Low systemic toxicity nanocarriers fabricated from heparin-mpeg and pamam dendrimers for controlled drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 82, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.Q.; Le, N.H.; Nguyen, D.H.T.; Tran, T.V.; Pham, L.P.T.; Bach, L.G.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, D.H. Evolution and present scenario of multifunctionalized mesoporous nanosilica platform: A mini review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 912–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, T.U.; Tran, N.Q.; Hoang, T.K.D.; Phan, K.N.; Truong, H.N.; Nguyen, C.K. Pegylated dendrimer and its effect in fluorouracil loading and release for enhancing antitumor activity. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, R.; Koushik, O.S.; Kumar, V.P. Surface modification of cationic dendrimers eases drug delivery of anticancer drugs. Nano Sci. Nano Technol. Indian J. 2016, 10, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, A.; Periasamy, J.; Gunasekaran, A.; Kumaresan, G.; Naicker, S.; Gunasekaran, P.; Murugesan, R. Polyethylene glycol-modified gelatin/polylactic acid nanoparticles for enhanced photodynamic efficacy of a hypocrellin derivative in vitro. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Klutz, A.M.; Jacobson, K.A. Systematic investigation of polyamidoamine dendrimers surface-modified with poly(ethylene glycol) for drug delivery applications: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of cytotoxicity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, K.; Yang, H. Encapsulation and extended release of anti-cancer anastrozole by stealth nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.D.; Kumar, P.V.; Selvam, T.P.; Rao, K.R.S.S. Prolonged drug delivery system of pegylated pamam dendrimers with a anti-HIV drug. Res. Pharm. 2013, 3, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; He, H.; Lu, W.; Jia, X. A poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-based drug carrier for delivering dox to gliomas cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15475–15481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lopina, S.T.; DiPersio, L.P.; Schmidt, S.P. Stealth dendrimers for drug delivery: Correlation between pegylation, cytocompatibility, and drug payload. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Mochida, A.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Nanodrug delivery: Is the enhanced permeability and retention effect sufficient for curing cancer? Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 2225–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Choi, J.H.; Joung, Y.K.; Park, K.D. Disulfide-crosslinked heparin-pluronic nanogels as a redox-sensitive nanocarrier for intracellular protein delivery. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2011, 26, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Bae, J.W.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, K.D. Bioreducible cross-linked pluronic micelles: Ph-triggered release of doxorubicin and folate-mediated cellular uptake. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2013, 28, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Austin, L.A.; Mackey, M.A.; El-Sayed, M.A. Size matters: Gold nanoparticles in targeted cancer drug delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hua, Y.; Yin, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levchenko, T.S.; Rammohan, R.; Lukyanov, A.N.; Whiteman, K.R.; Torchilin, V.P. Liposome clearance in mice: The effect of a separate and combined presence of surface charge and polymer coating. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 240, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.; Molnar, L.K.; Farokhzad, O.C. Factors affecting the clearance and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, S.M.A.; Jahan, S.T.; Haddadi, A. Effects of size and surface charge of polymeric nanoparticles on in vitro and in vivo applications. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 7, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertesa, M.A.; Castillab, J.; Alonsoa, C.; Pérezc, J.M. Cisplatin biochemical mechanism of action: From cytotoxicity to induction of cell death through interconnections between apoptotic and necrotic pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hah, S.S.; Stivers, K.M.; de Vere White, R.W.; Henderson, P.T. Kinetics of carboplatin-DNA binding in genomic DNA and bladder cancer cells as determined by accelerator mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vu, M.T.; Bach, L.G.; Nguyen, D.C.; Ho, M.N.; Nguyen, N.H.; Tran, N.Q.; Nguyen, D.H.; Nguyen, C.K.; Hoang Thi, T.T. Modified Carboxyl-Terminated PAMAM Dendrimers as Great Cytocompatible Nano-Based Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082016
Vu MT, Bach LG, Nguyen DC, Ho MN, Nguyen NH, Tran NQ, Nguyen DH, Nguyen CK, Hoang Thi TT. Modified Carboxyl-Terminated PAMAM Dendrimers as Great Cytocompatible Nano-Based Drug Delivery System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082016
Chicago/Turabian StyleVu, Minh Thanh, Long Giang Bach, Duy Chinh Nguyen, Minh Nhat Ho, Ngoc Hoi Nguyen, Ngoc Quyen Tran, Dai Hai Nguyen, Cuu Khoa Nguyen, and Thai Thanh Hoang Thi. 2019. "Modified Carboxyl-Terminated PAMAM Dendrimers as Great Cytocompatible Nano-Based Drug Delivery System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082016
APA StyleVu, M. T., Bach, L. G., Nguyen, D. C., Ho, M. N., Nguyen, N. H., Tran, N. Q., Nguyen, D. H., Nguyen, C. K., & Hoang Thi, T. T. (2019). Modified Carboxyl-Terminated PAMAM Dendrimers as Great Cytocompatible Nano-Based Drug Delivery System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082016




