Mapping Semaphorins and Netrins in the Pathogenesis of Human Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
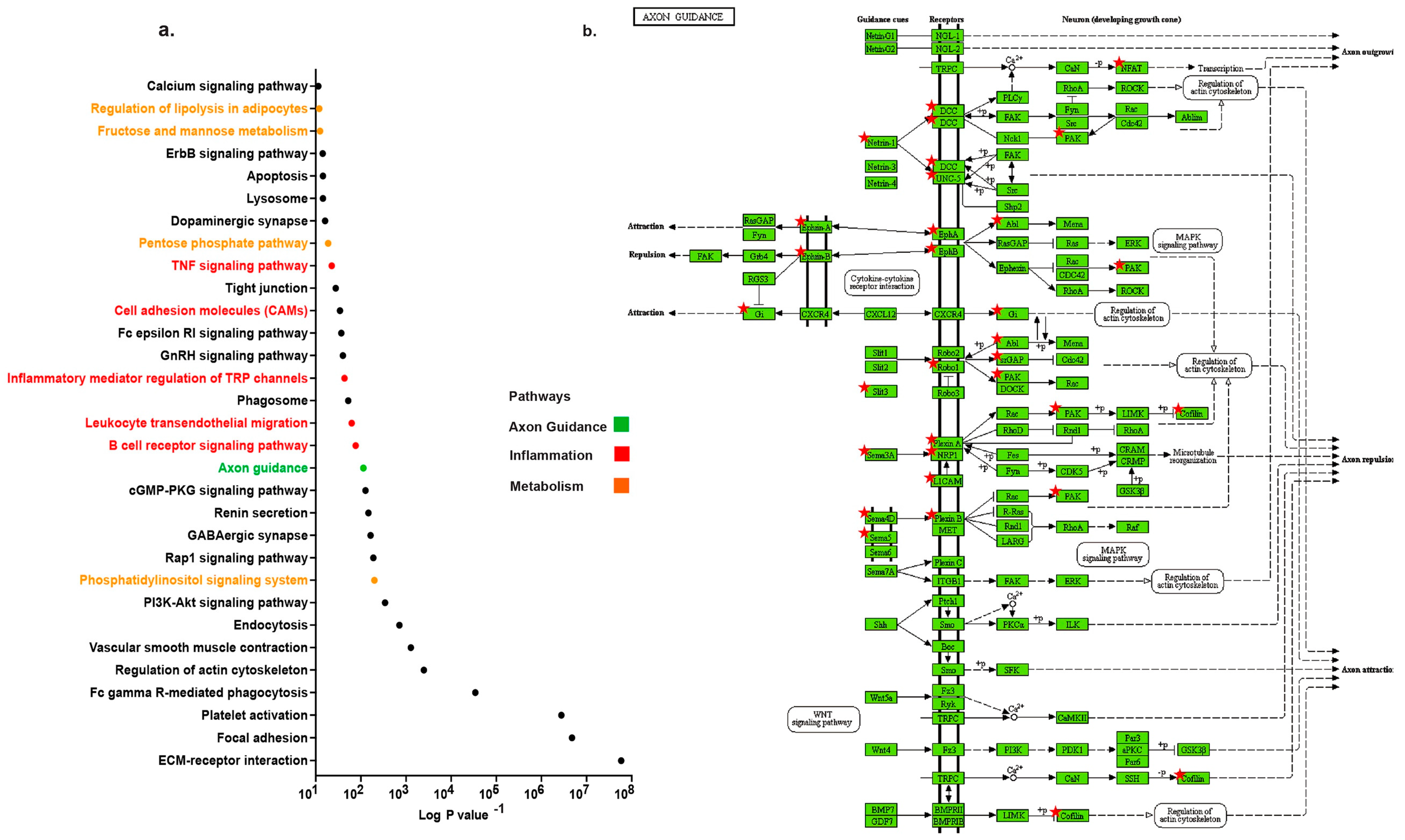
2.1. Distinct Up-Regulation of Axonal Guidance Pathway in TAA
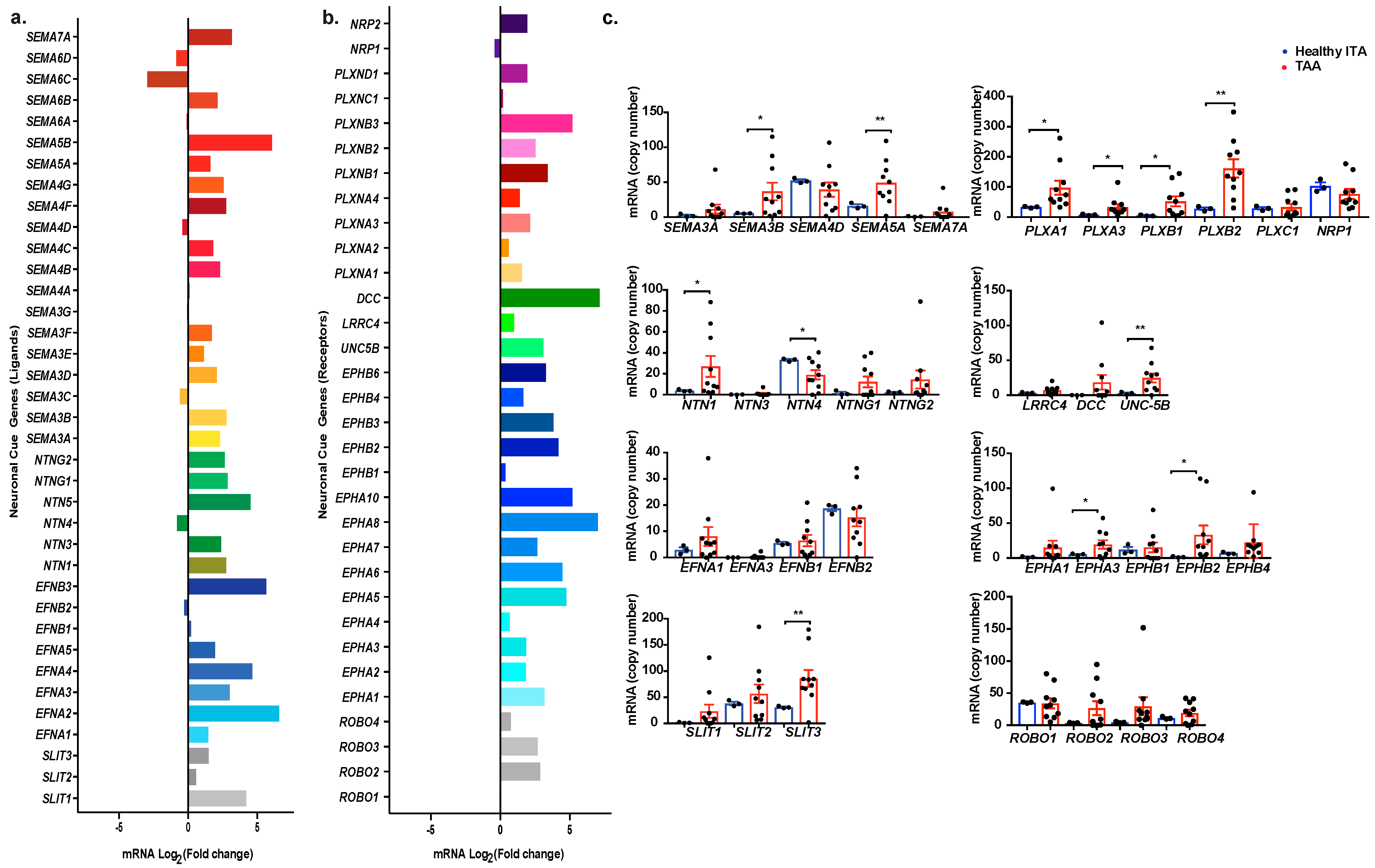
2.2. Profiling Neuronal Guidance Subfamily Cues in TAA
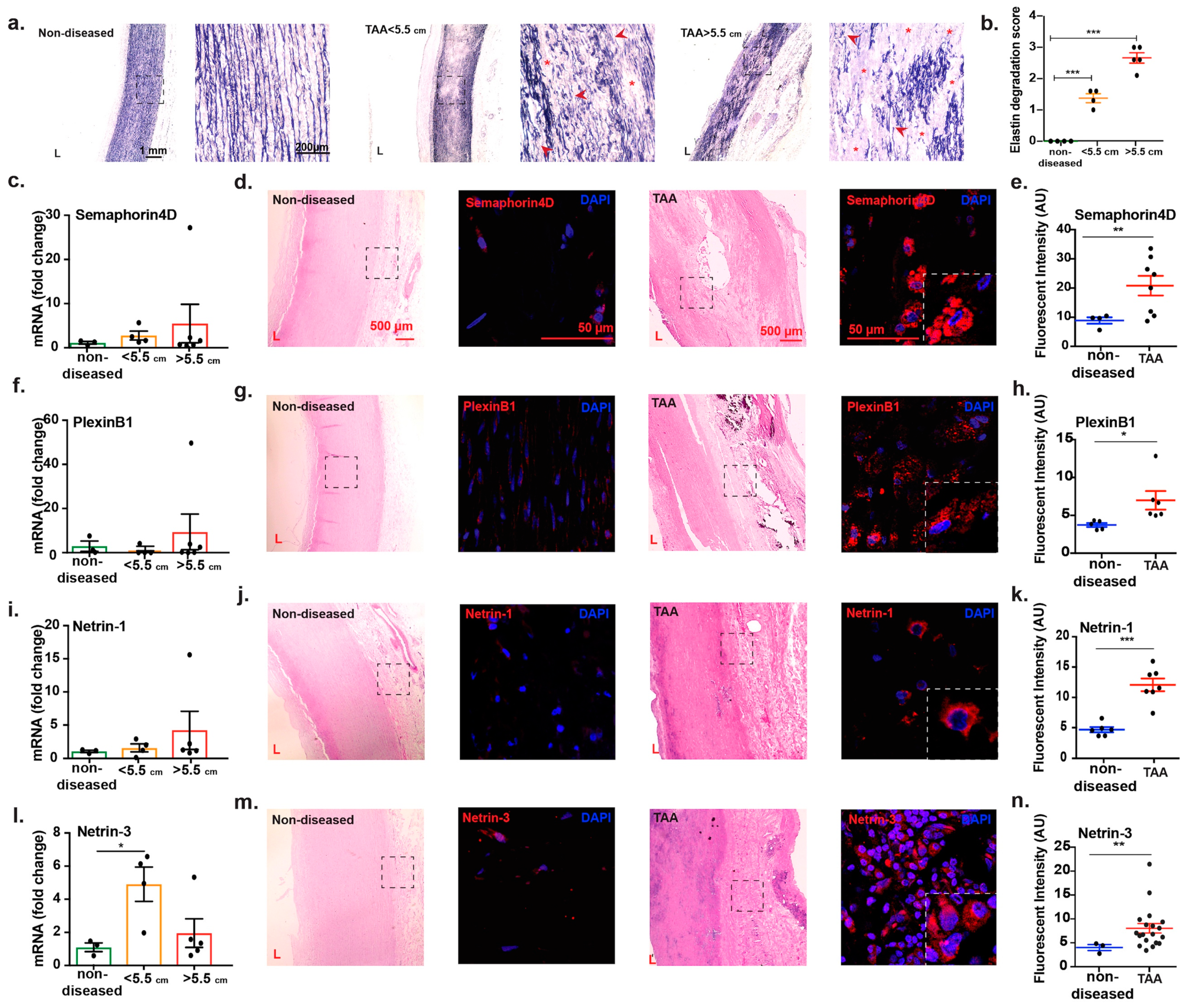
2.3. Transcript Analysis and Protein Localization of Netrins and Semaphorins in TAA Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Samples
4.2. RNA Isolation
4.3. RNA Sequencing
4.4. Real Time and Quantitative PCR
4.5. Histological Preparation and Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.H.; Na, C.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Du Kim, Y.; Kwon, J.B.; Chung, M.Y.; Hong, J.M.; Park, C.B. Integration of gene-expression profiles and pathway analysis in ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 24, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Qamar, A.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, A. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: A comprehensive review. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2011, 16, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Perko, M.J.; Norgaard, M.; Herzog, T.M.; Olsen, P.S.; Schroeder, T.V.; Pettersson, G. Unoperated aortic aneurysm: A survey of 170 patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1995, 59, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmik, G.A.; Sang, A.X.; Elefteriades, J.A. Natural history of thoracic aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 56, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Gehle, P.; Doelken, S.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; von Kodolitsch, Y.; Hetzer, R.; Robinson, P.N. Induction of macrophage chemotaxis by aortic extracts from patients with marfan syndrome is related to elastin binding protein. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Booms, P.; Halushka, M.; Dietz, H.C.; Ney, A.; Stricker, S.; Hecht, J.; Mundlos, S.; Robinson, P.N. Induction of macrophage chemotaxis by aortic extracts of the mgr marfan mouse model and a gxxpg-containing fibrillin-1 fragment. Circulation 2006, 114, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Lee, S.Y.; Gayraud, B.; Andrikopoulos, K.; Shapiro, S.D.; Bunton, T.; Biery, N.J.; Dietz, H.C.; Sakai, L.Y.; Ramirez, F. Pathogenetic sequence for aneurysm revealed in mice underexpressing fibrillin-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3819–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, T.; Boytard, L.; Silvestro, M.; Alebrahim, D.; Jacob, S.; Feinstein, J.; Barone, K.; Spiro, W.; Hutchison, S.; Simon, R.; et al. Macrophage-derived netrin-1 promotes abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by activating mmp3 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gils, J.M.; Derby, M.C.; Fernandes, L.R.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Ray, T.D.; Rayner, K.J.; Parathath, S.; Distel, E.; Feig, J.L.; Alvarez-Leite, J.I.; et al. The neuroimmune guidance cue netrin-1 promotes atherosclerosis by inhibiting the emigration of macrophages from plaques. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkhelawon, B.; Hennessy, E.J.; Menager, M.; Ray, T.D.; Sheedy, F.J.; Hutchison, S.; Wanschel, A.; Oldebeken, S.; Geoffrion, M.; Spiro, W.; et al. Netrin-1 promotes adipose tissue macrophage retention and insulin resistance in obesity. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagri, A.; Cheng, H.J.; Yaron, A.; Pleasure, S.J.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. Stereotyped pruning of long hippocampal axon branches triggered by retraction inducers of the Semaphorin family. Cell 2003, 113, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.E.; Serafini, T.; de la Torre, J.R.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. Netrins are diffusible chemotropic factors for commissural axons in the embryonic spinal cord. Cell 1994, 78, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanschel, A.; Seibert, T.; Hewing, B.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Ray, T.D.; van Gils, J.M.; Rayner, K.J.; Feig, J.E.; O’Brien, E.R.; Fisher, E.A.; et al. Neuroimmune guidance cue Semaphorin 3e is expressed in atherosclerotic plaques and regulates macrophage retention. Arter. Thromb Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.A.; Ruddy, J.M.; Bouges, S.; Zavadzkas, J.A.; Brinsa, T.A.; Stroud, R.E.; Mukherjee, R.; Spinale, F.G.; Ikonomidis, J.S. Alterations in membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase abundance after the induction of thoracic aortic aneurysm in a murine model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H114–H124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rabkin, S.W. The role matrix metalloproteinases in the production of aortic aneurysm. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 147, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghigo, A.; Laffargue, M.; Li, M.; Hirsch, E. Pi3k and calcium signaling in cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, S.; Mandal, M.; Das, S.; Mandal, A.; Chakraborti, T. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: An overview. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2003, 253, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketani, T.; Imai, Y.; Morota, T.; Maemura, K.; Morita, H.; Hayashi, D.; Yamazaki, T.; Nagai, R.; Takamoto, S. Altered patterns of gene expression specific to thoracic aortic aneurysms: Microarray analysis of surgically resected specimens. Int. Heart J. 2005, 46, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulkava, M.; Raitoharju, E.; Mennander, A.; Levula, M.; Seppala, I.; Lyytikainen, L.P.; Jarvinen, O.; Illig, T.; Klopp, N.; Mononen, N.; et al. Differentially expressed genes and canonical pathways in the ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm—The tampere vascular study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, J.; Ramkhelawon, B. Netrins & Semaphorins: Novel regulators of the immune response. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 3183–3189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabkin, S.W. Differential expression of mmp-2, mmp-9 and timp proteins in thoracic aortic aneurysm—comparison with and without bicuspid aortic valve: A meta-analysis. Vasa 2014, 43, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theruvath, T.P.; Jones, J.A.; Ikonomidis, J.S. Matrix metalloproteinases and descending aortic aneurysms: Parity, disparity, and switch. J. Card Surg. 2012, 27, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.H.; LeMaire, S.A. Thoracic aortic dissection: Are matrix metalloproteinases involved? Vascular 2009, 17, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.J.; Heo, R.; Chang, H.J.; Shin, S.; Shim, C.Y.; Hong, G.R.; Min, J.K.; Chung, N. Correlation between coronary artery calcium score and aortic diameter in a high-risk population of elderly male hypertensive patients. Coron. Artery Dis. 2014, 25, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, C.; Quayle, J.; Burdyga, T.; Wray, S. Atherosclerosis differentially affects calcium signalling in endothelial cells from aortic arch and thoracic aorta in apolipoprotein e knockout mice. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, K.; Strickland, P.; Valdes, A.; Shin, G.C.; Hinck, L. Netrin-1/neogenin interaction stabilizes multipotent progenitor cap cells during mammary gland morphogenesis. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Kalil, K. Netrin-1 induces axon branching in developing cortical neurons by frequency-dependent calcium signaling pathways. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6702–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elefteriades, J.A.; Farkas, E.A. Thoracic aortic aneurysm clinically pertinent controversies and uncertainties. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 841–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.S.; Kolodkin, A.L.; Luo, Y.; Püschel, A.W.; Raper, J.A. Unified nomenclature for the Semaphorins/collapsins. Cell 1999, 97, 551–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.S.; Kolodkin, A.L.; Bharadwaj, R. Semaphorin regulation of cellular morphology. Annu Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 263–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, U.; Terman, J.R. The Semaphorins. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikutani, H.; Kumanogoh, A. Semaphorins in interactions between t cells and antigen-presenting cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alto, L.T.; Terman, J.R. Semaphorins and their signaling mechanisms. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1493, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M. To move or not to move? Semaphorin signalling in cell migration. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, K.; Borges, L.F.; Ho-Tin-Noe, B.; Jondeau, G.; Michel, J.B.; Vranckx, R. Angiogenesis and remodelling in human thoracic aortic aneurysms. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 104, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serini, G.; Valdembri, D.; Zanivan, S.; Morterra, G.; Burkhardt, C.; Caccavari, F.; Zammataro, L.; Primo, L.; Tamagnone, L.; Logan, M.; et al. Class 3 Semaphorins control vascular morphogenesis by inhibiting integrin function. Nature 2003, 424, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, W.; Isogai, S.; Sato-Maeda, M.; Obinata, M.; Kuwada, J.Y. Semaphorin3a1 regulates angioblast migration and vascular development in zebrafish embryos. Development 2003, 130, 3227–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussolino, F.; Valdembri, D.; Caccavari, F.; Serini, G. Semaphoring vascular morphogenesis. Endothelium 2006, 13, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadanandam, A.; Rosenbaugh, E.G.; Singh, S.; Varney, M.; Singh, R.K. Semaphorin 5a promotes angiogenesis by increasing endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and decreasing apoptosis. Microvasc. Res. 2010, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, H.; Okuno, T.; Kumanogoh, A. Regulation of immune cell responses by Semaphorins and their receptors. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanogoh, A.; Watanabe, C.; Lee, I.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Araki, H.; Hirata, H.; Iwahori, K.; Uchida, J.; Yasui, T.; et al. Identification of cd72 as a lymphocyte receptor for the class iv Semaphorin cd100: A novel mechanism for regulating b cell signaling. Immunity 2000, 13, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrotto, P.; Valdembri, D.; Corso, S.; Serini, G.; Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M.; Bussolino, F.; Giordano, S. Sema4d induces angiogenesis through met recruitment by plexin b1. Blood 2005, 105, 4321–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Collins, J.R.; Alvord, W.G.; Roayaei, J.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. The david gene functional classification tool: A novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. Kegg: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. Kegg: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. Kegg as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias Bechtel, J.F.; Noack, F.; Sayk, F.; Erasmi, A.W.; Bartels, C.; Sievers, H.H. Histopathological grading of ascending aortic aneurysm: Comparison of patients with bicuspid versus tricuspid aortic valve. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2003, 12, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sulkava, M.; Raitoharju, E.; Levula, M.; Seppala, I.; Lyytikainen, L.P.; Mennander, A.; Jarvinen, O.; Zeitlin, R.; Salenius, J.P.; Illig, T.; et al. Differentially expressed genes and canonical pathway expression in human atherosclerotic plaques—Tampere vascular study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alebrahim, D.; Nayak, M.; Ward, A.; Ursomanno, P.; Shams, R.; Corsica, A.; Sleiman, R.; Hyppolite Fils, K.; Silvestro, M.; Boytard, L.; et al. Mapping Semaphorins and Netrins in the Pathogenesis of Human Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092100
Alebrahim D, Nayak M, Ward A, Ursomanno P, Shams R, Corsica A, Sleiman R, Hyppolite Fils K, Silvestro M, Boytard L, et al. Mapping Semaphorins and Netrins in the Pathogenesis of Human Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092100
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlebrahim, Dornazsadat, Mangala Nayak, Alison Ward, Patricia Ursomanno, Rebecca Shams, Annanina Corsica, Rayan Sleiman, Kissinger Hyppolite Fils, Michele Silvestro, Ludovic Boytard, and et al. 2019. "Mapping Semaphorins and Netrins in the Pathogenesis of Human Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092100
APA StyleAlebrahim, D., Nayak, M., Ward, A., Ursomanno, P., Shams, R., Corsica, A., Sleiman, R., Hyppolite Fils, K., Silvestro, M., Boytard, L., Hadi, T., Gelb, B., & Ramkhelawon, B. (2019). Mapping Semaphorins and Netrins in the Pathogenesis of Human Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092100





