Discovery of Novel Potential Reversible Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Inhibitor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. GST-PAD4 and HisTag-PPAD Kinetics
2.2. Analysis of GST-PAD4 and HisTag-PPAD Inhibition by Compounds 1–6
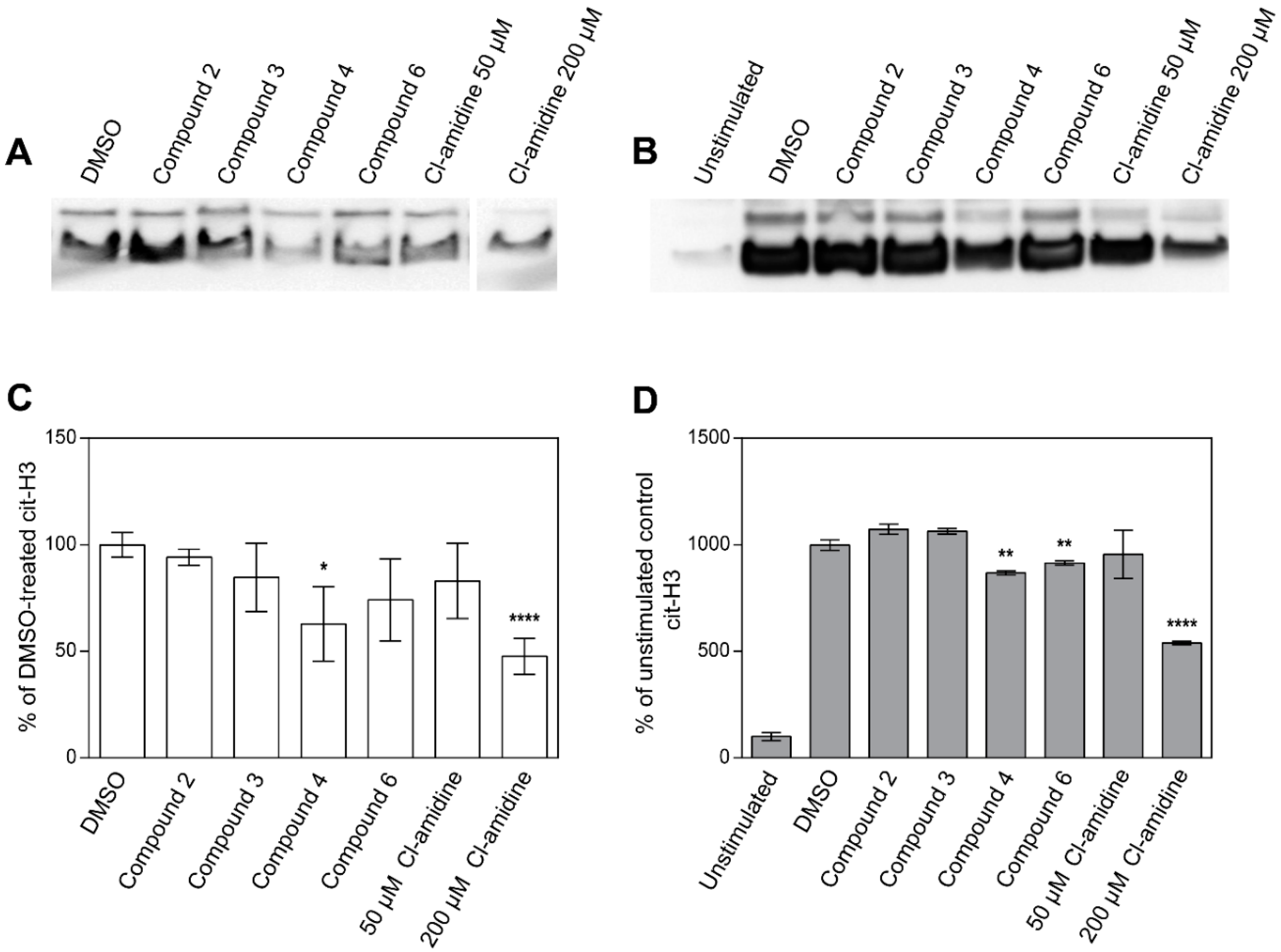
2.3. Inhibition of Histone H3 Citrullination and NET Formation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds
4.2. Patient Samples
4.3. Reagents
4.4. Measurement of Enzyme Kinetics
4.5. Measurement of Inhibitor Constants and IC50
4.6. Measurement of Inhibitory Activity in Serum and Synovial Fluid
4.7. Histone H3 Citrullination Assay
4.8. Histone H3 Citrullination in Neutrophils Stimulated with Calcium Ionophore
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. NET Assays
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bicker, K.L.; Thompson, P.R. The protein arginine deiminases: Structure, function, inhibition, and disease. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Zendman, A.J.W.; Van Venrooij, W.J.; Pruijn, G.J.M. PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: Genes, features and involvement in disease. BioEssays 2003, 25, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmann, N.S.; Hansen, N.U.B.; Jensen, A.C.B.; Karsdal, M.A.; Siebuhr, A.S. Biological relevance of citrullinations: Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic options. Autoimmunity 2015, 48, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzhalin, A.E.; Gordon-Weeks, A.N.; Tognoli, M.L.; Jones, K.; Markelc, B.; Konietzny, R.; Fischer, R.; Muth, A.; O’Neill, E.; Thompson, P.R.; et al. Colorectal cancer liver metastatic growth depends on PAD4-driven citrullination of the extracellular matrix. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, Z.; György, B.; Géher, P.; Buzás, E.I.; Falus, A.; Nagy, G. Citrullination under physiological and pathological conditions. Joint. Bone. Spine Rev. Du Rhum. 2012, 79, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Venrooij, W.J.; van Beers, J.J.B.C.; Pruijn, G.J.M. Anti-CCP Antibody, a Marker for the Early Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1143, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulquier, C.; Sebbag, M.; Clavel, C.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Al Badine, R.; Méchin, M.-C.; Vincent, C.; Nachat, R.; Yamada, M.; Takahara, H.; et al. Peptidyl arginine deiminase type 2 (PAD-2) and PAD-4 but not PAD-1, PAD-3, and PAD-6 are expressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovium in close association with tissue inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3541–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, A.; Yamada, R.; Chang, X.; Tokuhiro, S.; Sawada, T.; Suzuki, M.; Nagasaki, M.; Nakayama-Hamada, M.; Kawaida, R.; Ono, M.; et al. Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plenge, R.M.; Padyukov, L.; Remmers, E.F.; Purcell, S.; Lee, A.T.; Karlson, E.W.; Wolfe, F.; Kastner, D.L.; Alfredsson, L.; Altshuler, D.; et al. Replication of putative candidate-gene associations with rheumatoid arthritis in >4,000 samples from North America and Sweden: Association of susceptibility with PTPN22, CTLA4, and PADI4. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.P.; Lee, H.-S.; Ju, H.; Cho, H.; Kang, C.; Bae, S.-C. A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with increased rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Koreans. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, M.; Lindberg, M.R.; Kennett, M.J.; Xiong, N.; Wang, Y. PAD4 is essential for antibacterial innate immunity mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, H.D.; Liddle, J.; Coote, J.E.; Atkinson, S.J.; Barker, M.D.; Bax, B.D.; Bicker, K.L.; Bingham, R.P.; Campbell, M.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. Inhibition of PAD4 activity is sufficient to disrupt mouse and human NET formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuthbert, G.L.; Daujat, S.; Snowden, A.W.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Hagiwara, T.; Yamada, M.; Schneider, R.; Gregory, P.D.; Tempst, P.; Bannister, A.J.; et al. Histone deimination antagonizes arginine methylation. Cell 2004, 118, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrah, E.; Rosen, A.; Giles, J.T.; Andrade, F. Peptidylarginine deiminase 2, 3 and 4 have distinct specificities against cellular substrates: Novel insights into autoantigen selection in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandpur, R.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Gizinski, A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Knight, J.S.; Friday, S.; Li, S.; Patel, R.M.; Subramanian, V.; et al. NETs are a source of citrullinated autoantigens and stimulate inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 178ra40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsiero, E.; Bombardieri, M.; Carlotti, E.; Pratesi, F.; Robinson, W.; Migliorini, P.; Pitzalis, C. Single cell cloning and recombinant monoclonal antibodies generation from RA synovial B cells reveal frequent targeting of citrullinated histones of NETs. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, K.M.J.; de Smit, M.J.; Withaar, C.; Brouwer, E.; van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Vissink, A.; Westra, J. Autoantibodies against citrullinated histone H3 in rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis patients. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratesi, F.; Dioni, I.; Tommasi, C.; Alcaro, M.C.; Paolini, I.; Barbetti, F.; Boscaro, F.; Panza, F.; Puxeddu, I.; Rovero, P.; et al. Antibodies from patients with rheumatoid arthritis target citrullinated histone 4 contained in neutrophils extracellular traps. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGraw, W.T.; Potempa, J.; Farley, D.; Travis, J. Purification, characterization, and sequence analysis of a potential virulence factor from Porphyromonas gingivalis, peptidylarginine deiminase. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3248–3256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabarrini, G.; Chlebowicz, M.A.; Vega Quiroz, M.E.; Veloo, A.C.M.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Laine, M.L.; van Dijl, J.M.; van Winkelhoff, A.J. Conserved Citrullinating Exoenzymes in Porphyromonas Species. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssen, K.M.J.; Vissink, A.; de Smit, M.J.; Westra, J.; Brouwer, E. Lessons to be learned from periodontitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2013, 25, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potempa, J.; Mydel, P.; Koziel, J. The case for periodontitis in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuckley, B.; Luo, Y.; Thompson, P.R. Profiling Protein Arginine Deiminase 4 (PAD4): A novel screen to identify PAD4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Knuckley, B.; Lee, Y.-H.; Stallcup, M.R.; Thompson, P.R. A fluoroacetamidine-based inactivator of protein arginine deiminase 4: Design, synthesis, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1092–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.E.; Slack, J.L.; Fang, P.; Zhang, X.; Subramanian, V.; Causey, C.P.; Coonrod, S.A.; Guo, M.; Thompson, P.R. Synthesis and screening of a haloacetamidine containing library to identify PAD4 selective inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, Y.; Hagiwara, T.; Yamada, M. Methylation of the guanidino group of arginine residues prevents citrullination by peptidylarginine deiminase IV. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4088–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritzker, L.B.; Moscarello, M.A. A novel microtubule independent effect of paclitaxel: The inhibition of peptidylarginine deiminase from bovine brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1388, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumanevich, A.A.; Causey, C.P.; Knuckley, B.A.; Jones, J.E.; Poudyal, D.; Chumanevich, A.P.; Davis, T.; Matesic, L.E.; Thompson, P.R.; Hofseth, L.J. Suppression of colitis in mice by Cl-amidine: A novel peptidylarginine deiminase inhibitor. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G929–G938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, V.C.; Gizinski, A.M.; Banda, N.K.; Causey, C.P.; Knuckley, B.; Cordova, K.N.; Luo, Y.; Levitt, B.; Glogowska, M.; Chandra, P.; et al. N-α-Benzoyl-N5-(2-Chloro-1-Iminoethyl)-l-Ornithine Amide, a Protein Arginine Deiminase Inhibitor, Reduces the Severity of Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawalkowska, J.; Quirke, A.M.; Ghari, F.; Davis, S.; Subramanian, V.; Thompson, P.R.; Williams, R.O.; Fischer, R.; La Thangue, N.B.; Venables, P.J. Abrogation of collagen-induced arthritis by a peptidyl arginine deiminase inhibitor is associated with modulation of T cell-mediated immune responses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, X.A.; Wu, J.; Fisher, M.; Oshaben, K.; Zhao, N.; Gu, Y.; et al. Anticancer peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitors regulate the autophagy flux and the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 25941–25953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuckley, B.; Causey, C.P.; Jones, J.E.; Bhatia, M.; Christina, J.; Osborne, T.; Takahara, H.; Thompson, P.R. Substrate specificity and kinetic studies of PADs 1, 3, and 4 identify potent and selective inhibitors of Protein Arginine Deiminase 3. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4852–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Peptidylarginine deiminases in citrullination, gene regulation, health and pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirai, H.; Blundell, T.L.; Mizuguchi, K. A novel superfamily of enzymes that catalyze the modification of guanidino groups. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, A.B.; Kopec, J.; Shrestha, L.; Thezenas, M.-L.; Burgess-Brown, N.A.; Fischer, R.; Yue, W.W.; Venables, P.J. Crystal structure of Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase: Implications for autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.N.; Farmer, E.A.; Spargo, L.; Logan, R.; Gully, N. Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase substrate specificity. Anaerobe 2013, 23, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Nijenhuis, S.; Helsen, M.M.A.; van der Heijden, A.; Senshu, T.; van den Berg, W.B.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Joosten, L.A.B. Citrullination of synovial proteins in murine models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, X.; Yamada, R.; Suzuki, A.; Sawada, T.; Yoshino, S.; Tokuhiro, S.; Yamamoto, K. Localization of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) and citrullinated protein in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005, 44, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willis, V.C.; Banda, N.K.; Cordova, K.N.; Chandra, P.E.; Robinson, W.H.; Cooper, D.C.; Lugo, D.; Mehta, G.; Taylor, S.; Tak, P.P.; et al. Protein arginine deiminase 4 inhibition is sufficient for the amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 188, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.E.; Causey, C.P.; Knuckley, B.; Slack-Noyes, J.L.; Thompson, P.R. Protein arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4): Current understanding and future therapeutic potential. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2009, 12, 616–627. [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi, N.; Tachiwana, H.; Saito, K.; Osakabe, A.; Sato, M.; Yamada, M.; Akashi, S.; Nishimura, Y.; Kagawa, W.; Kurumizaka, H. Structural and biochemical analyses of the human PAD4 variant encoded by a functional haplotype gene. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielecka, E.; Scavenius, C.; Kantyka, T.; Jusko, M.; Mizgalska, D.; Szmigielski, B.; Potempa, B.; Enghild, J.J.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Blom, A.M.; et al. Peptidyl arginine deiminase from porphyromonas gingivalis abolishes anaphylatoxin C5a activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32481–32487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shechter, D.; Dormann, H.L.; Allis, C.D.; Hake, S.B. Extraction, purification and analysis of histones. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. Enzymes-A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism and Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-471-35929-6. [Google Scholar]






| Compound | Ki (μM) a | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1b | - | - |
| 2 | 0.94 ± 0.31 | 1.40 ± 0.26 |
| 3 | 0.71 ± 0.17 | 1.65 ± 1.34 |
| 4 | 1.00 ± 0.16 | 1.88 ± 0.26 |
| 5b | - | - |
| 6 | 0.61 ± 0.12 | 1.28 ± 0.30 |
| Compound | 4SC Catalogue | Available Commercially | Chemical Structure | Manufacturer | Cat. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SC100288 | Yes | Yes | Vitas-M Ltd. | STK816131 |
| 2 | SC100449 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| 3 | SC101037 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| 4 | SC97362 | Yes | Yes | Labotest OHG | LT02193089 |
| 5 | SC99514 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| 6 | SC101038 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| Cl-amidine | - | Yes | Yes | Sigma-Aldrich | 506282-10MG |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aliko, A.; Kamińska, M.; Falkowski, K.; Bielecka, E.; Benedyk-Machaczka, M.; Malicki, S.; Kozieł, J.; Wong, A.; Bryzek, D.; Kantyka, T.; et al. Discovery of Novel Potential Reversible Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Inhibitor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092174
Aliko A, Kamińska M, Falkowski K, Bielecka E, Benedyk-Machaczka M, Malicki S, Kozieł J, Wong A, Bryzek D, Kantyka T, et al. Discovery of Novel Potential Reversible Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Inhibitor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092174
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliko, Ardita, Marta Kamińska, Katherine Falkowski, Ewa Bielecka, Malgorzata Benedyk-Machaczka, Stanisław Malicki, Joanna Kozieł, Alicia Wong, Danuta Bryzek, Tomasz Kantyka, and et al. 2019. "Discovery of Novel Potential Reversible Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Inhibitor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092174
APA StyleAliko, A., Kamińska, M., Falkowski, K., Bielecka, E., Benedyk-Machaczka, M., Malicki, S., Kozieł, J., Wong, A., Bryzek, D., Kantyka, T., & Mydel, P. (2019). Discovery of Novel Potential Reversible Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Inhibitor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2174. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092174





