Glycidamide Promotes the Growth and Migratory Ability of Prostate Cancer Cells by Changing the Protein Expression of Cell Cycle Regulators and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)-Associated Proteins with Prognostic Relevance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of GA on the Doubling-Time, Cell Viability, and Cell Mobility of Prostate Cancer Cells
2.2. Alteration of Regulators of Cell Cycle and the Epithelial–to–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in GA-Treated Prostate Cancer Cells
2.3. GA-Mediated mRNA Expression of Regulators of the Cell Cycle and EMT in Prostate Cancer Tissues
2.4. Prognostic Relevance of GA-Mediated mRNA Expression of Regulators of the Cell Cycle and EMT in Prostate Cancer Tissues
2.5. CombinationThree-Gene Signature Predicted Survival in Prostate CancerPatients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Method
4.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Doubling-Time Determination.
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. In Vitro Migration Assay
4.7. Oncomine Database Analysis
4.8. SurvExpress Database Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | acrylamide |
| GA | glycidamide |
| EMT | epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| CYP2E1 | cytochrome P450 2E1 |
| EMT-TFs | EMT-related transcription factors |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
References
- Ehlers, A.; Lenze, D.; Broll, H.; Zagon, J.; Hummel, M.; Lampen, A. Dose dependent molecular effects of acrylamide and glycidamide in human cancer cell lines and human primary hepatocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 217, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourson, M.; Hertzberg, R.; Allen, B.; Haber, L.; Parker, A.; Kroner, O.; Maier, A.; Kohrman, M. Evidence-based dose-response assessment for thyroid tumorigenesis from acrylamide. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, 264–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kamendulis, L.M.; Friedman, M.A.; Klaunig, J.E. Acrylamide-induced cellular transformation. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 65, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tareke, E.; Rydberg, P.; Karlsson, P.; Eriksson, S.; Tornqvist, M. Analysis of acrylamide, a carcinogen formed in heated foodstuffs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4998–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingarilho, M.; Oliveira, N.G.; Martins, C.; Gomes, B.C.; Fernandes, A.S.; Martins, V.; Labilloy, A.; de Lima, J.P.; Rueff, J.; Gaspar, J.F. Induction of sister chromatid exchange by acrylamide and glycidamide in human lymphocytes: role of polymorphisms in detoxification and DNA-repair genes in the genotoxicity of glycidamide. Mutat. Res. 2013, 752, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, M.; Fauth, E.; Fritzen, S.; Herrmann, A.; Mertes, P.; Merz, K.; Rudolphi, M.; Zankl, H.; Eisenbrand, G. Acrylamide and glycidamide: genotoxic effects in V79-cells and human blood. Mutat. Res. 2005, 580, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, F.C.; Dip, R.; Naegeli, H. Expression profile of human cells in culture exposed to glycidamide, a reactive metabolite of the heat-induced food carcinogen acrylamide. Toxicology 2007, 240, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olstorn, H.B.; Paulsen, J.E.; Alexander, J. Effects of perinatal exposure to acrylamide and glycidamide on intestinal tumorigenesis in Min/+ mice and their wild-type litter mates. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3855–3864. [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst, J.G.; Schouten, L.J.; Konings, E.J.; Goldbohm, R.A.; van den Brandt, P.A. Dietary acrylamide intake and brain cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2009, 18, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hogervorst, J.G.; de Bruijn-Geraets, D.; Schouten, L.J.; van Engeland, M.; de Kok, T.M.; Goldbohm, R.A.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Weijenberg, M.P. Dietary acrylamide intake and the risk of colorectal cancer with specific mutations in KRAS and APC. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogervorst, J.G.; Schouten, L.J.; Konings, E.J.; Goldbohm, R.A.; van den Brandt, P.A. Lung cancer risk in relation to dietary acrylamide intake. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.M.; Mucci, L.A.; Cho, E.; Hunter, D.J.; Chen, W.Y.; Willett, W.C. Dietary acrylamide intake and risk of premenopausal breast cancer. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.M.; Mucci, L.A.; Rosner, B.A.; Willett, W.C. A prospective study on dietary acrylamide intake and the risk for breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.M.; Giovannucci, E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Mucci, L.A. Dietary acrylamide and risk of prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semla, M.; Goc, Z.; Martiniakova, M.; Omelka, R.; Formicki, G. Acrylamide: a common food toxin related to physiological functions and health. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist, M.; Paulsson, B.; Vikstrom, A.C.; Granath, F. Approach for cancer risk estimation of acrylamide in food on the basis of animal cancer tests and in vivo dosimetry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6004–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirfalt, E.; Paulsson, B.; Tornqvist, M.; Axmon, A.; Hagmar, L. Associations between estimated acrylamide intakes, and hemoglobin AA adducts in a sample from the Malmo Diet and Cancer cohort. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhivagui, M.; Ng, A.W.T.; Ardin, M.; Churchwell, M.I.; Pandey, M.; Renard, C.; Villar, S.; Cahais, V.; Robitaille, A.; Bouaoun, L.; et al. Experimental and pan-cancer genome analyses reveal widespread contribution of acrylamide exposure to carcinogenesis in humans. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, J.F.; Latendresse, J.R.; Delongchamp, R.R.; Muskhelishvili, L.; Warbritton, A.R.; Thomas, M.; Tareke, E.; McDaniel, L.P.; Doerge, D.R. The effects of subchronic acrylamide exposure on gene expression, neurochemistry, hormones, and histopathology in the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis of male Fischer 344 rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 230, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjanatha, M.G.; Guo, L.W.; Shelton, S.D.; Doerge, D.R. Acrylamide-induced carcinogenicity in mouse lung involves mutagenicity: cII gene mutations in the lung of big blue mice exposed to acrylamide and glycidamide for up to 4 weeks. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarra, S.; Fernandes, A.S.; Magro, I.; Guerreiro, P.S.; Pingarilho, M.; Churchwell, M.I.; Gil, O.M.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Goncalves, S.; Rueff, J.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the cytotoxicity and genotoxicity induced by glycidamide in human mammary cells. Mutagenesis 2013, 28, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Obon-Santacana, M.; Lujan-Barroso, L.; Travis, R.C.; Freisling, H.; Ferrari, P.; Severi, G.; Baglietto, L.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Fortner, R.T.; Ose, J.; et al. Acrylamide and Glycidamide Hemoglobin Adducts and Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study in Nonsmoking Postmenopausal Women from the EPIC Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stott-Miller, M.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Stanford, J.L. Consumption of deep-fried foods and risk of prostate cancer. Prostate 2013, 73, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, B.J.; Tran, N. Exposure to acrylamide: placing exposure in context. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2005, 561, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Settels, E.; Bernauer, U.; Palavinskas, R.; Klaffke, H.S.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Appel, K.E. Human CYP2E1 mediates the formation of glycidamide from acrylamide. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.M. The carcinogenicity of acrylamide. Mutat. Res. 2005, 580, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Hitomi, M.; Stacey, D.W. Variations in cyclin D1 levels through the cell cycle determine the proliferative fate of a cell. Cell Div. 2006, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaei, M.; Karami-Tehrani, F.; Panjehpour, M.; Salami, S.; Fallahian, F. Adenosine induces cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in androgen-dependent and -independent prostate cancer cell lines, LNcap-FGC-10, DU-145, and PC3. Prostate 2012, 72, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnave, P.; Aboukhatwa, E.; Kosaka, N.; Thompson, J.; Hill, M.A.; Aboobaker, A.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factors control pluripotent adult stem cell migration in vivo in planarians. Development 2017, 144, 3440–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.N.; Bhowmick, N.A. Role of EMT in Metastasis and Therapy Resistance. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Hwang, K.A.; Choi, K.C. Diverse pathways of epithelial mesenchymal transition related with cancer progression and metastasis and potential effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on epithelial mesenchymal transition process. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 457, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, M.D.; Davies, G.; Jiang, W.G. Cell adhesion molecules and adhesion abnormalities in prostate cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 41, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus, H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Gamboa, R.; Gomez-Rueda, H.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Martinez-Torteya, A.; Chacolla-Huaringa, R.; Rodriguez-Barrientos, A.; Tamez-Pena, J.G.; Trevino, V. SurvExpress: an online biomarker validation tool and database for cancer gene expression data using survival analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, Z.; Tian, H. Twenty-gene-based prognostic model predicts lung adenocarcinoma survival. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 3415–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Yu, Q.; Liu, C.; Feng, J.; Deng, J.; Evers, B.M.; Zhou, B.P.; Wu, Y. Stabilization of the transcription factors slug and twist by the deubiquitinase dub3 is a key requirement for tumor metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75127–75140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.L.; Yang, H.J.; Liu, T.; Lin, Y.Z. Expression and significance of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, transforming growth factor-beta1 and Twist in prostate cancer. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Russo, M.V.; Airoldi, I.; Tupone, M.G.; Sorrentino, C.; Barbarito, G.; Di Meo, S.; Di Carlo, E. SNAI2/Slug gene is silenced in prostate cancer and regulates neuroendocrine differentiation, metastasis-suppressor and pluripotency gene expression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17121–17134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Patel, S.; Mirza, S.; Rawal, R.M. A multi-gene expression profile panel for predicting liver metastasis: An algorithmic approach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Sugimoto, Y.; Liu, S.; Chang, H.L.; Park, K.Y.; Kulp, S.K.; Lin, Y.C. The inhibitory effects of gossypol on human prostate cancer cells-PC3 are associated with transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFbeta1) signal transduction pathway. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.H.; Tang, W.C.; Cheng, Y.W.; Sia, P.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Jiang, H.Y.; Wu, M.H.; Lai, I.L.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Targeting of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways by Hsp90 inhibitor alone or in combination with berberine for treatment of colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.C.; Lee, P.T.; Wu, M.H.; Huang, C.C.; Ko, C.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Lin, D.Y.; Cheng, Y.W.; Lee, K.H. Distinct roles and differential expression levels of Wnt5a mRNA isoforms in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambler, G.; Seaman, S.; Omar, R.Z. An evaluation of penalised survival methods for developing prognostic models with rare events. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
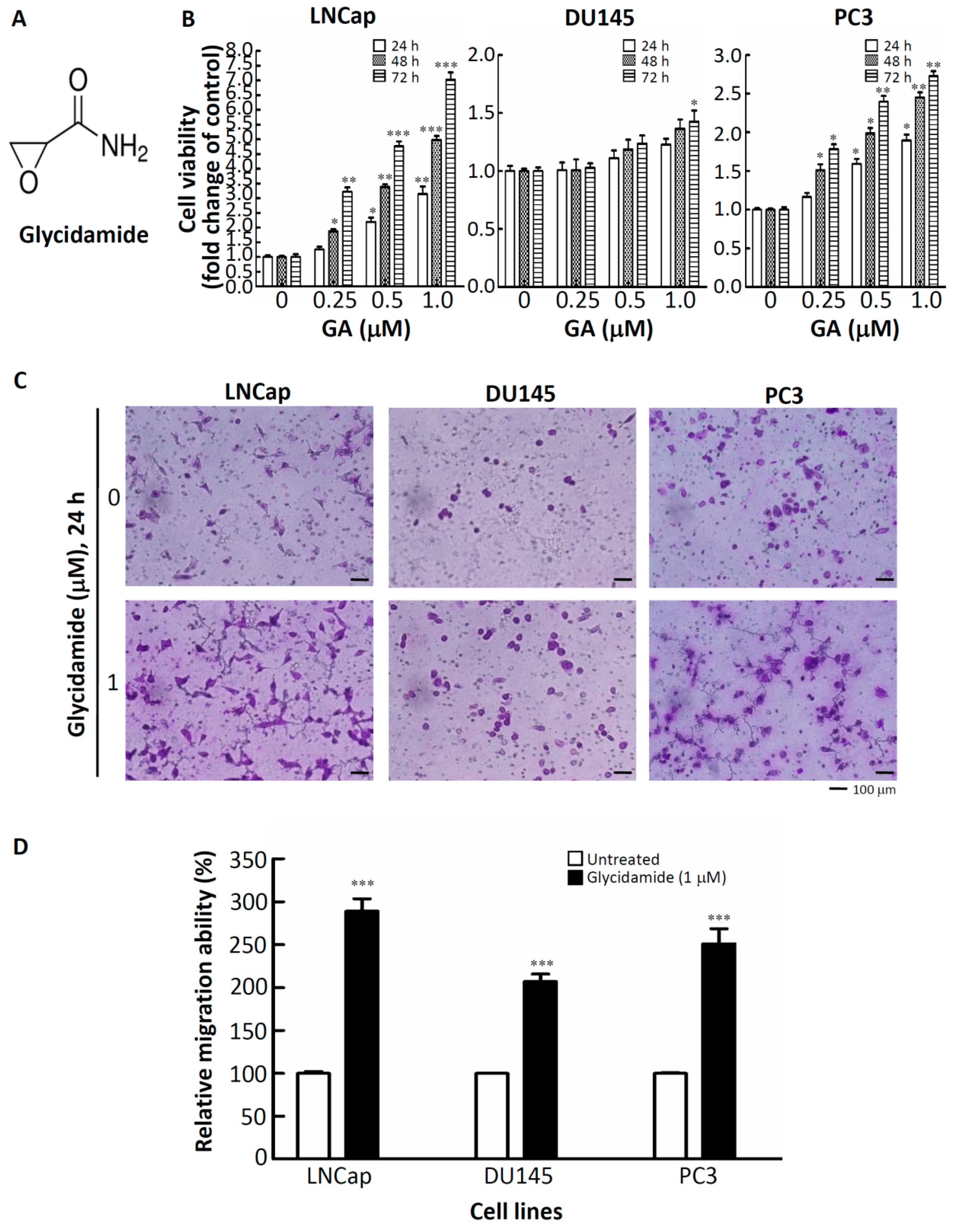

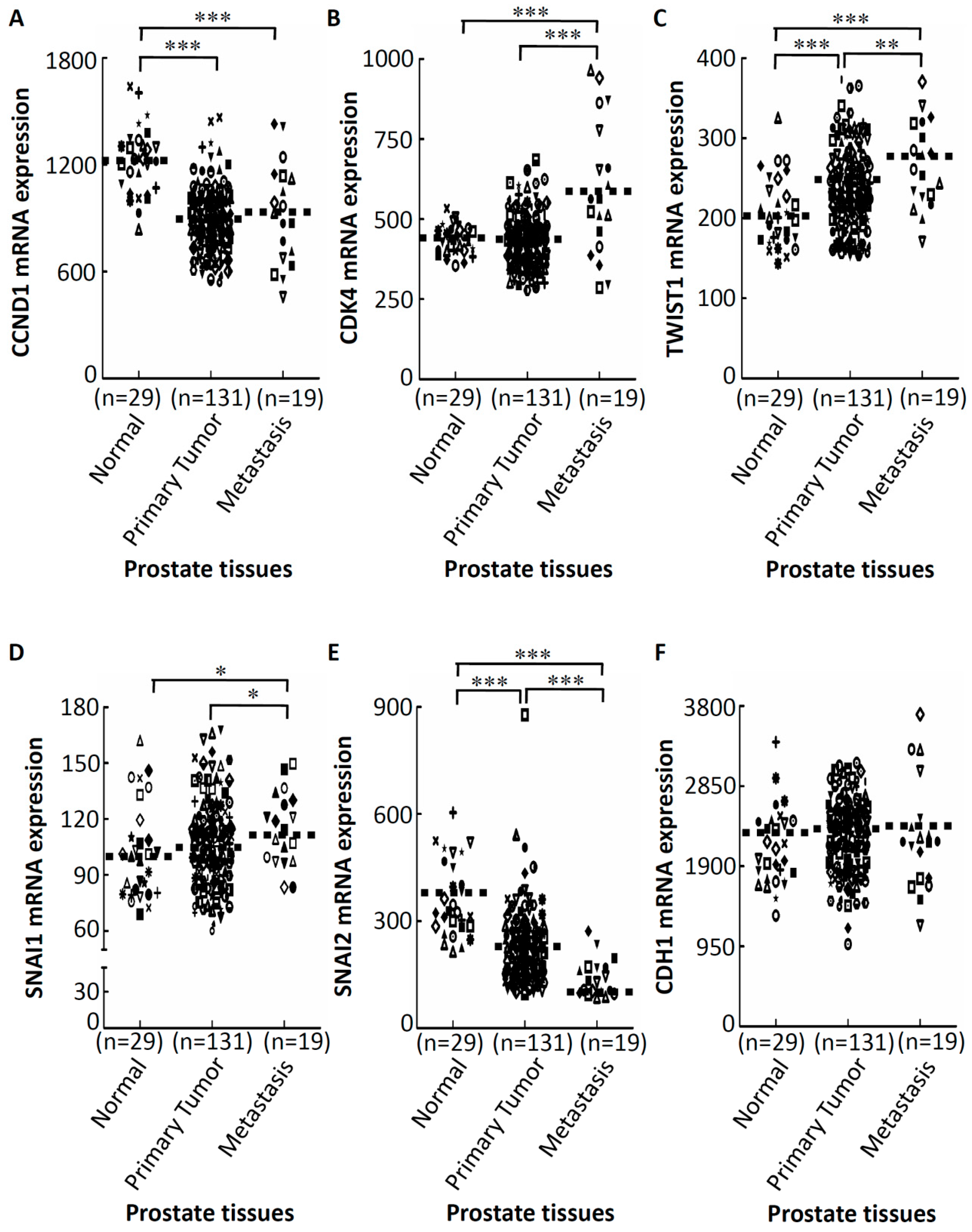

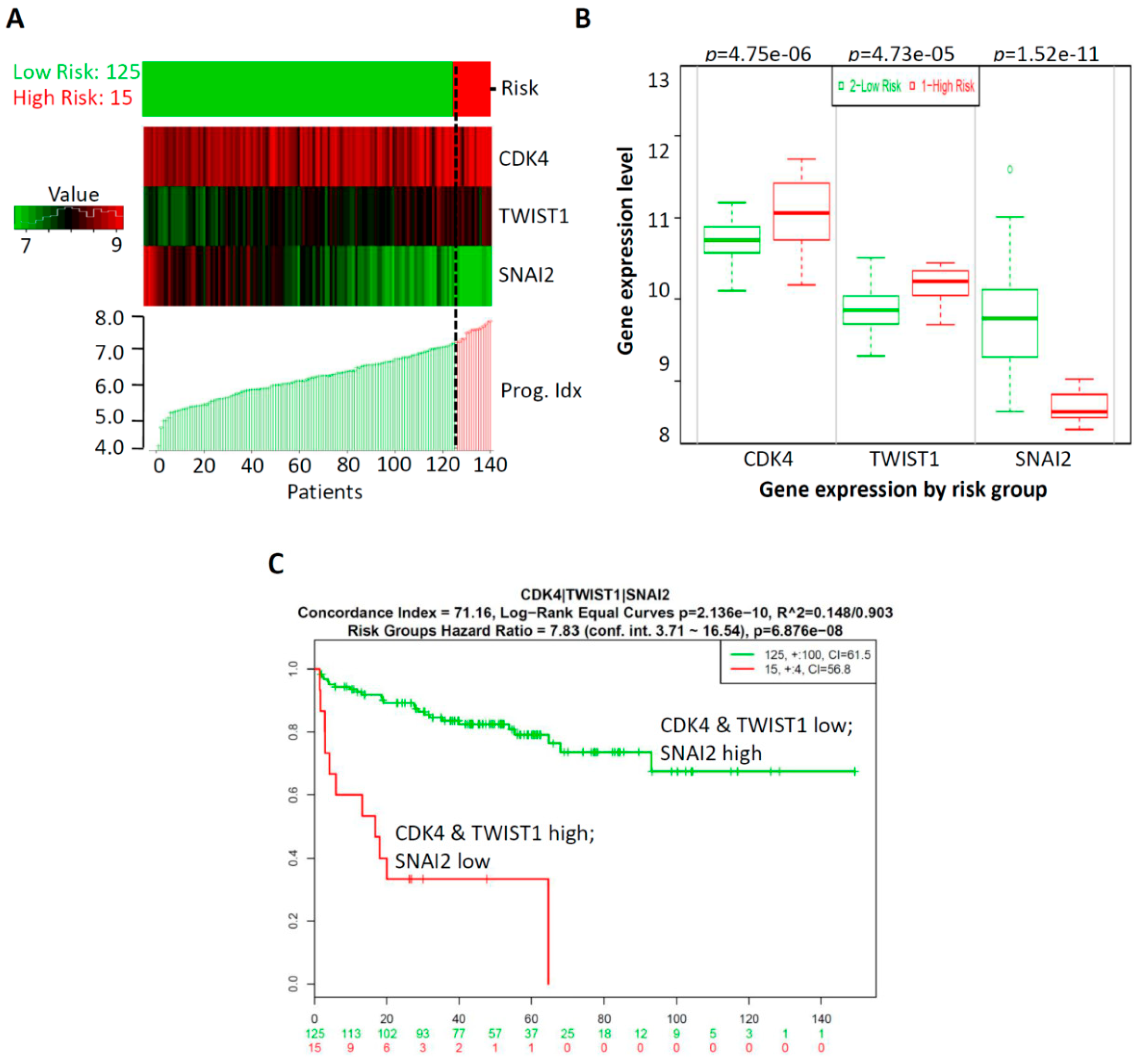
| Cell Type | Inoculated Density | Harvested Density | Doubling Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LNCap-N | 1.8 × 105 | 6.8 × 105 | 37.6 |
| LNCap-G | 1.8 × 105 | 4.8 × 106 | 15.2 |
| DU145-N | 1.8 × 105 | 7.5 × 105 | 35.0 |
| DU145-G | 1.8 × 105 | 6.1 × 106 | 14.2 |
| PC3-N | 1.8 × 105 | 7.5 × 105 | 35.0 |
| PC3-G | 1.8 × 105 | 7.8 × 106 | 13.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ekanem, T.I.; Huang, C.-C.; Wu, M.-H.; Lin, D.-Y.; Lai, W.-F.T.; Lee, K.-H. Glycidamide Promotes the Growth and Migratory Ability of Prostate Cancer Cells by Changing the Protein Expression of Cell Cycle Regulators and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)-Associated Proteins with Prognostic Relevance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092199
Ekanem TI, Huang C-C, Wu M-H, Lin D-Y, Lai W-FT, Lee K-H. Glycidamide Promotes the Growth and Migratory Ability of Prostate Cancer Cells by Changing the Protein Expression of Cell Cycle Regulators and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)-Associated Proteins with Prognostic Relevance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092199
Chicago/Turabian StyleEkanem, Titus Ime, Chi-Chen Huang, Ming-Heng Wu, Ding-Yen Lin, Wen-Fu T. Lai, and Kuen-Haur Lee. 2019. "Glycidamide Promotes the Growth and Migratory Ability of Prostate Cancer Cells by Changing the Protein Expression of Cell Cycle Regulators and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)-Associated Proteins with Prognostic Relevance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092199
APA StyleEkanem, T. I., Huang, C.-C., Wu, M.-H., Lin, D.-Y., Lai, W.-F. T., & Lee, K.-H. (2019). Glycidamide Promotes the Growth and Migratory Ability of Prostate Cancer Cells by Changing the Protein Expression of Cell Cycle Regulators and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)-Associated Proteins with Prognostic Relevance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092199








