CXCR4 Cardiac Specific Knockout Mice Develop a Progressive Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
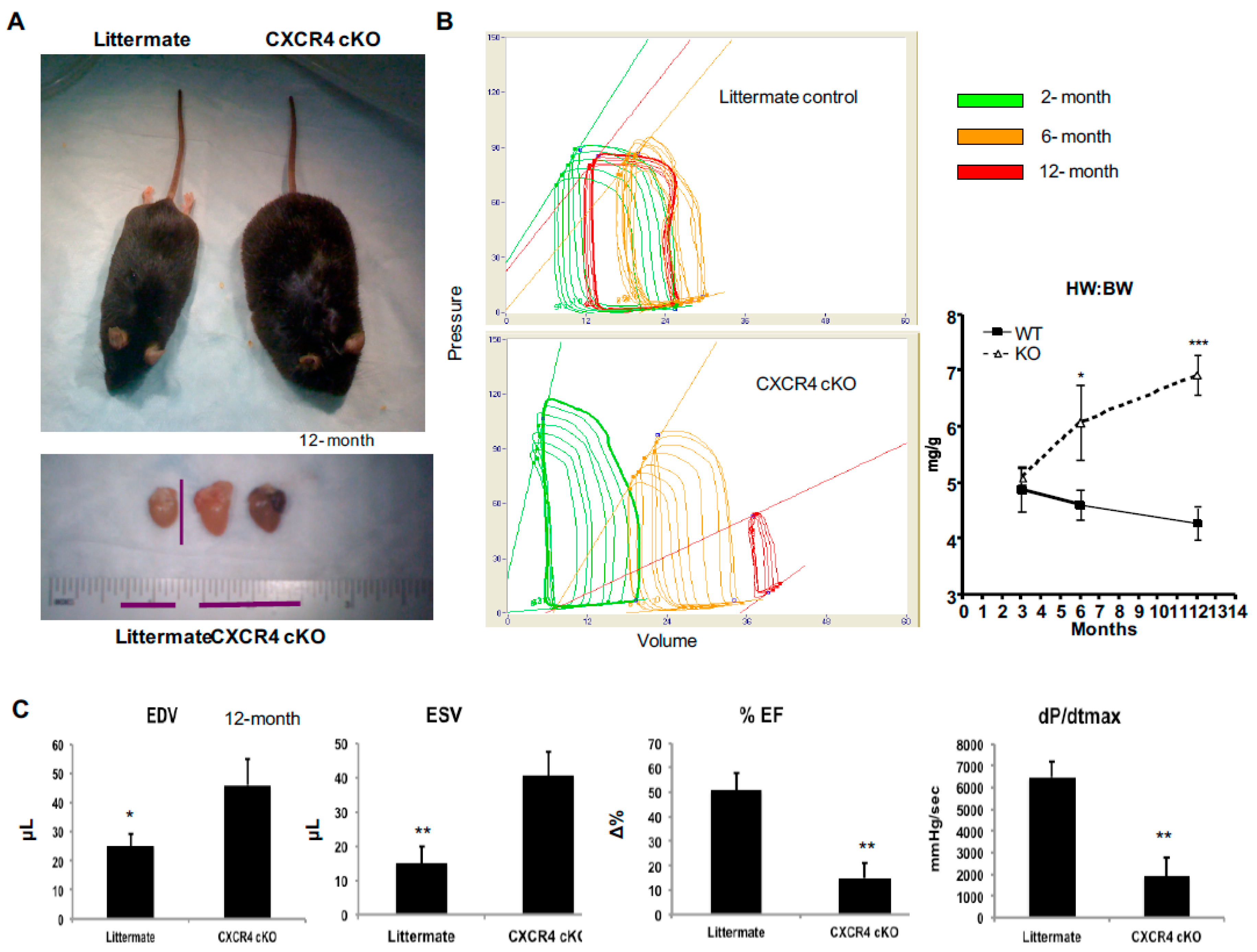
2.1. CXCR4 Cardiac-Specific Knockout (CXCR4-cKO) Mice Develop a Progressive Cardiomyopathy Leading to Clinical Heart Failure
2.2. Abnormal Histopathological Features Were Evident in CXCR4 cKO Heart
2.3. CXCR4 cKO Mice Have Significant Baseline Defects in Myocardial Function Beginning at 4-Months of Age as Assessed by MRI and In Vivo Hemodynamics
2.4. CXCR4 cKO Mice Are More Sensitive to an Acute Isoproterenol Challenge In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Material
4.1. Generation of CXCR4 Cardiac Specific Knockouts
4.2. Staining Procedures for Structural Abnormalities and Interstitial Fibrosis in Cxcr4 cKO Hearts
4.3. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription–PCR Assays
4.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.5. Non-Invasive Cardiac Imaging: Gated Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
4.6. In Vivo Hemodynamic
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaasenbrood, L.; Bhatt, D.L.; Dorresteijn, J.A.N.; Wilson, P.W.F.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; Massaro, J.M.; van der Graaf, Y.; Cramer, M.J.M.; Kappelle, L.J.; de Borst, G.J.; et al. Estimated Life Expectancy Without Recurrent Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Vascular Disease: The SMART-REACH Model. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslett, L.J.; Alagona, P., Jr.; Clark, B.A., 3rd; Drozda, J.P., Jr.; Saldivar, F.; Wilson, S.R.; Poe, C.; Hart, M. The worldwide environment of cardiovascular disease: prevalence, diagnosis, therapy, and policy issues: a report from the American College of Cardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, S1–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, B.M.; Maddox, T.M. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Epidemiology, biological mechanisms, treatment recommendations and future research. World J. Diab. 2015, 6, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukrust, P.; Damas, J.K.; Gullestad, L.; Froland, S.S. Chemokines in myocardial failure—pathogenic importance and potential therapeutic targets. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 124, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukrust, P.; Ueland, T.; Muller, F.; Andreassen, A.K.; Nordoy, I.; Aas, H.; Kjekshus, J.; Simonsen, S.; Frøland, S.S.; Gullestad, L. Elevated circulating levels of C–C chemokines in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 1998, 97, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christia, P.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Targeting inflammatory pathways in myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 43, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faxon, D.P.; Gibbons, R.J.; Chronos, N.A.; Gurbel, P.A.; Sheehan, F. The effect of blockade of the CD11/CD18 integrin receptor on infarct size in patients with acute myocardial infarction treated with direct angioplasty: the results of the HALT-MI study. J. Am. College Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Russo, I.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Inflammation as a therapeutic target in myocardial infarction: learning from past failures to meet future challenges. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRocca, T.J.; Schwarzkopf, M.; Altman, P.; Zhang, S.; Gupta, A.; Gomes, I.; Alvin, Z.; Champion, H.C.; Haddad, G.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. β2-Adrenergic receptor signaling in the cardiac myocyte is modulated by interactions with CXCR4. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 56, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, R.T.; Sui, J.; Dhume, A.; Palomeque, J.; Blaxall, B.C.; Diaz, G.; Tunstead, J.; Logothetis, D.E.; Hajjar, R.J.; Schecter, A.D. CXCR4 modulates contractility in adult cardiac myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 41, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segret, A.; Rucker-Martin, C.; Pavoine, C.; Flavigny, J.; Deroubaix, E.; Châtel, M.A.; Lombet, A.; Renaud, J.F. Structural localization and expression of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in rat heart and isolated cardiac myocytes. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Jones, D.; Borghesani, P.R.; Segal, R.A.; Nagasawa, T.; Kishimoto, T.; Bronson, R.T.; Springer, T.A. Impaired B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, and derailed cerebellar neuron migration in CXCR4- and SDF-1-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9448–9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, T.; Tachibana, K.; Kishimoto, T. A novel CXC chemokine PBSF/SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4: their functions in development, hematopoiesis and HIV infection. Seminars Immunol. 1998, 10, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, K.; Hirota, S.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshida, H.; Kawabata, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Matsushima, K.; Yoshida, N.; Nishikawa, S. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature 1998, 393, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doring, Y.; Pawig, L.; Weber, C.; Noels, H. The CXCL12/CXCR4 chemokine ligand/receptor axis in cardiovascular disease. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balabanian, K.; Lagane, B.; Infantino, S.; Chow, K.Y.; Harriague, J.; Moepps, B.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Thelen, M.; Bachelerie, F. The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35760–35766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierro, F.; Biben, C.; Martinez-Munoz, L.; Mellado, M.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Li, M.; Woehl, B.; Leung, H.; Groom, J.; Batten, M. Disrupted cardiac development but normal hematopoiesis in mice deficient in the second CXCL12/SDF-1 receptor, CXCR7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14759–14764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, U.; Cameroni, E.; Pruenster, M.; Mahabaleshwar, H.; Raz, E.; Zerwes, H.G.; Rot, A.; Thelen, M. CXCR7 functions as a scavenger for CXCL12 and CXCL11. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Kim, J.; Ahn, S.; Craig, S.; Lam, C.M.; Gerard, N.P.; Gerard, C.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Beta-arrestin- but not G protein-mediated signaling by the "decoy" receptor CXCR7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceholski, D.K.; Turnbull, I.C.; Pothula, V.; Lecce, L.; Jarrah, A.A.; Kho, C.; Lee, A.; Hadri, L.; Costa, K.D.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. CXCR4 and CXCR7 play distinct roles in cardiac lineage specification and pharmacologic beta-adrenergic response. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 23, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larocca, T.J.; Jeong, D.; Kohlbrenner, E.; Lee, A.; Chen, J.; Hajjar, R.J.; Tarzami, S.T. CXCR4 gene transfer prevents pressure overload induced heart failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.R.; Jarrah, A.A.; Benard, L.; Chen, J.; Schwarzkopf, M.; Hadri, L.; Tarzami, S.T. Deletion of CXCR4 in cardiomyocytes exacerbates cardiac dysfunction following isoproterenol administration. Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, U.; Ghalayini, W.; Dong, F.; Weber, K.; Zou, Y.R.; Rabbany, S.Y.; Rafii, S.; Penn, M.S. Role of cardiac myocyte CXCR4 expression in development and left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, D.; Esler, M. Sympathetic neuronal regulation of the heart in aging and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 66, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bristow, M.R. Why does the myocardium fail? Insights from basic science. Lancet 1998, 352, SI8–SI14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santulli, G.; Iaccarino, G. Adrenergic signaling in heart failure and cardiovascular aging. Maturitas 2016, 93, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, M.R. Mechanistic and clinical rationales for using beta-blockers in heart failure. J. Cardiac Failure 2000, 6, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bristow, M.R.; Ginsburg, R.; Minobe, W.; Cubicciotti, R.S.; Sageman, W.S.; Lurie, K.; Billingham, M.E.; Harrison, D.C.; Stinson, E.B. Decreased catecholamine sensitivity and β-adrenergic-receptor density in failing human hearts. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brum, P.C.; Rolim, N.P.; Bacurau, A.V.; Medeiros, A. Neurohumoral activation in heart failure: The role of adrenergic receptors. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2006, 78, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, P.A.; Ceholski, D.K.; Hajjar, R.J. Altered myocardial calcium cycling and energetics in heart failure--a rational approach for disease treatment. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, A.; Jones, W.K.; Gulick, J.; Wert, S.; Neumann, J.; Robbins, J. Tissue-specific regulation of the alpha-myosin heavy chain gene promoter in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 24613–24620. [Google Scholar]
- Petrich, B.G.; Molkentin, J.D.; Wang, Y. Temporal activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in adult transgenic heart via cre-loxP-mediated DNA recombination. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Waite, J.; Brewer, F.; Sunshine, M.J.; Littman, D.R.; Zou, Y.R. The role of CXCR4 in maintaining peripheral B cell compartments and humoral immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, R.; Frenkel, P.A.; French, B.A.; Michael, L.H.; Overbeek, P.A.; Schneider, M.D. Gene recombination in postmitotic cells. Targeted expression of Cre recombinase provokes cardiac-restricted, site-specific rearrangement in adult ventricular muscle in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 1997, 100, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chemaly, E.; Liang, L.; Kho, C.; Lee, A.; Park, J.; Altman, P.; Schecter, A.D.; Hajjar, R.J.; Tarzami, S.T. Effects of CXCR4 gene transfer on cardiac function after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, R.J.; Ishikawa, K.; Kovacic, J.C.; Fuster, V. Cardiovascular Research Center at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Translational Mission. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Litermate WT | stdev | CXCR4 cKO | stdev |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ejection Fraction (%) * | 79.41875 | 9.492518012 | 68.04285714 | 5.701349882 |
| ED volume (µL) * | 22.6825 | 6.270105376 | 28.19714286 | 4.227228068 |
| ES Volume (µL) * | 4.8 | 3.195000559 | 9.088571429 | 2.392247399 |
| ED Volume Index (µL/g) | 0.9225 | 0.273663419 | 1.127142857 | 0.168593622 |
| ES Volume Index (µL/g) | 0.2525 | 0.155857841 | 0.364285714 | 0.096411815 |
| Stroke Volume (µL) | 17.88 | 4.868516935 | 19.10714286 | 2.815402365 |
| Stroke Volume Index (µL/g) | 0.675 | 0.155026879 | 0.764285714 | 0.112673147 |
| Cardiac Output (ml/min) | 6.2225 | 1.05787129 | 6.835714286 | 2.328482032 |
| ED Myocard Mass (mg) | 46.14625 | 10.08292607 | 44.24142857 | 5.795801436 |
| ES Myocard Mass (mg) | 48.625 | 6.825544458 | 50.58 | 6.131728957 |
| Heart Rate (bpm) | 375 | 50 | 360 | 111.9523708 |
| Item | Littermate WT (4-Month) | CXCR4 cKO (4-Month) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | ISO, 1 min | Baseline | ISO, 1 min | |
| Heart Rate, bpm | 548 ± 17 | 618 ± 15 * | 510 ± 8.5 | 604.3 ± 22.4 * |
| LVPmax, mmHg | 97.5 ± 3.3 | 95.3 ± 5.1 | 64.3 ± 4.6 | 95.3 ± 9.3 * |
| Pes, mmHg | 88.8 ± 3.8 | 87.1 ± 2.3 | 55.7 ± 5.5 | 72.0 ± 13.6 |
| Ped, mmHg | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.2 |
| dP/dTmax, mmHg/sec | 8192 ± 701 | 12060 ± 868 ** | 3322 ± 253.2 | 10780 ± 121.9 *** |
| dP/dTmax/LVPmax, s−1 | 90.1 ± 5.8 | 127.1 ± 5.3 ** | 51.7 ± 2.6 | 115.3 ± 11.2 ** |
| CO, uL/min | 16000 ± 1290 | 22630 ± 1982 * | 12270 ± 1840 | 20850 ± 1539 * |
| SV, uL | 29 ± 1.8 | 38.2 ± 2.7 * | 24.0 ± 3.5 | 34.7 ± 3.3 |
| EF, % | 59.8 ± 3.5 | 80.2 ± 3.2 ** | 42.0 ± 6.1 | 90.3 ± 2.9 ** |
| Ved, uL | 47.3 ± 2.1 | 44.2 ± 2.7 | 55.7 ± 0.3 | 38.3 ± 2.9 ** |
| Age, weeks | 11.5 | 12.1 | ||
| Weight, g | 26.2 | 26.1 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
LaRocca, T.J.; Altman, P.; Jarrah, A.A.; Gordon, R.; Wang, E.; Hadri, L.; Burke, M.W.; Haddad, G.E.; Hajjar, R.J.; Tarzami, S.T. CXCR4 Cardiac Specific Knockout Mice Develop a Progressive Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092267
LaRocca TJ, Altman P, Jarrah AA, Gordon R, Wang E, Hadri L, Burke MW, Haddad GE, Hajjar RJ, Tarzami ST. CXCR4 Cardiac Specific Knockout Mice Develop a Progressive Cardiomyopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092267
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaRocca, Thomas J., Perry Altman, Andrew A. Jarrah, Ron Gordon, Edward Wang, Lahouaria Hadri, Mark W. Burke, Georges E. Haddad, Roger J. Hajjar, and Sima T. Tarzami. 2019. "CXCR4 Cardiac Specific Knockout Mice Develop a Progressive Cardiomyopathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092267
APA StyleLaRocca, T. J., Altman, P., Jarrah, A. A., Gordon, R., Wang, E., Hadri, L., Burke, M. W., Haddad, G. E., Hajjar, R. J., & Tarzami, S. T. (2019). CXCR4 Cardiac Specific Knockout Mice Develop a Progressive Cardiomyopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092267







