Molecular Characterization, Bioinformatic Analysis, and Expression Profile of Lin-28 Gene and Its Protein from Arabian Camel (Camelus dromedarius)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
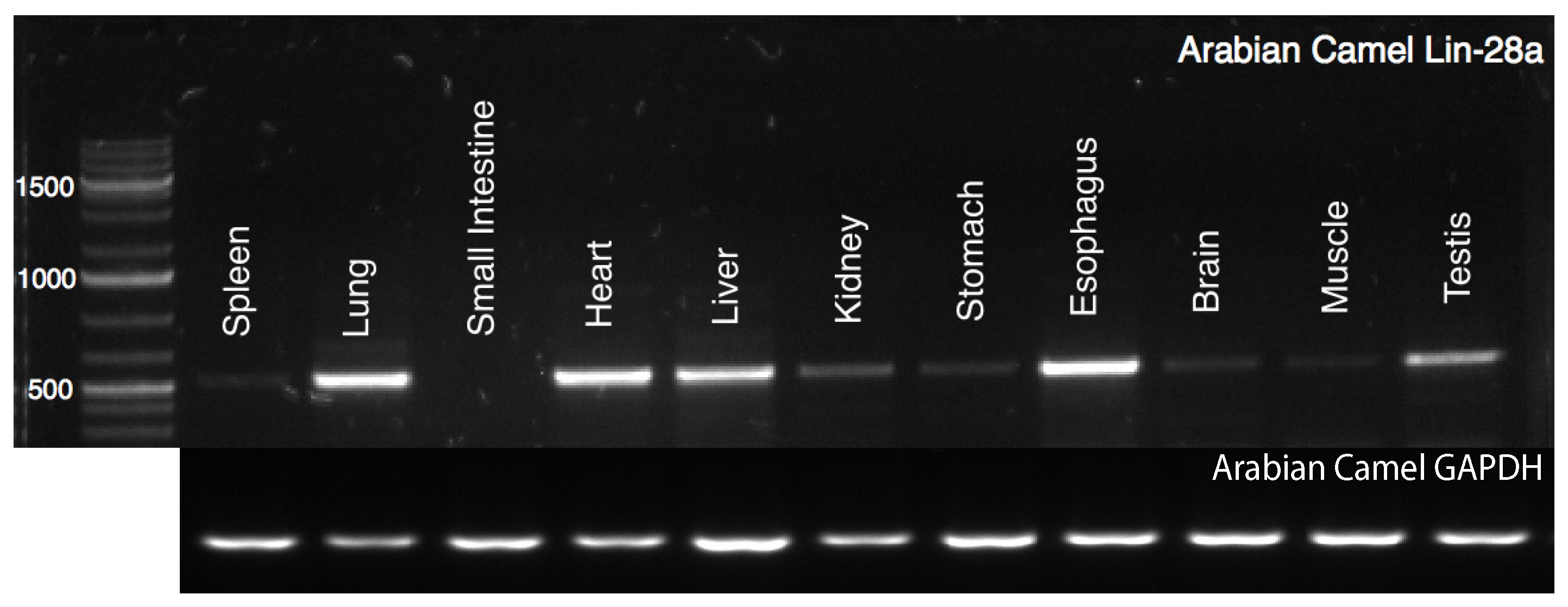
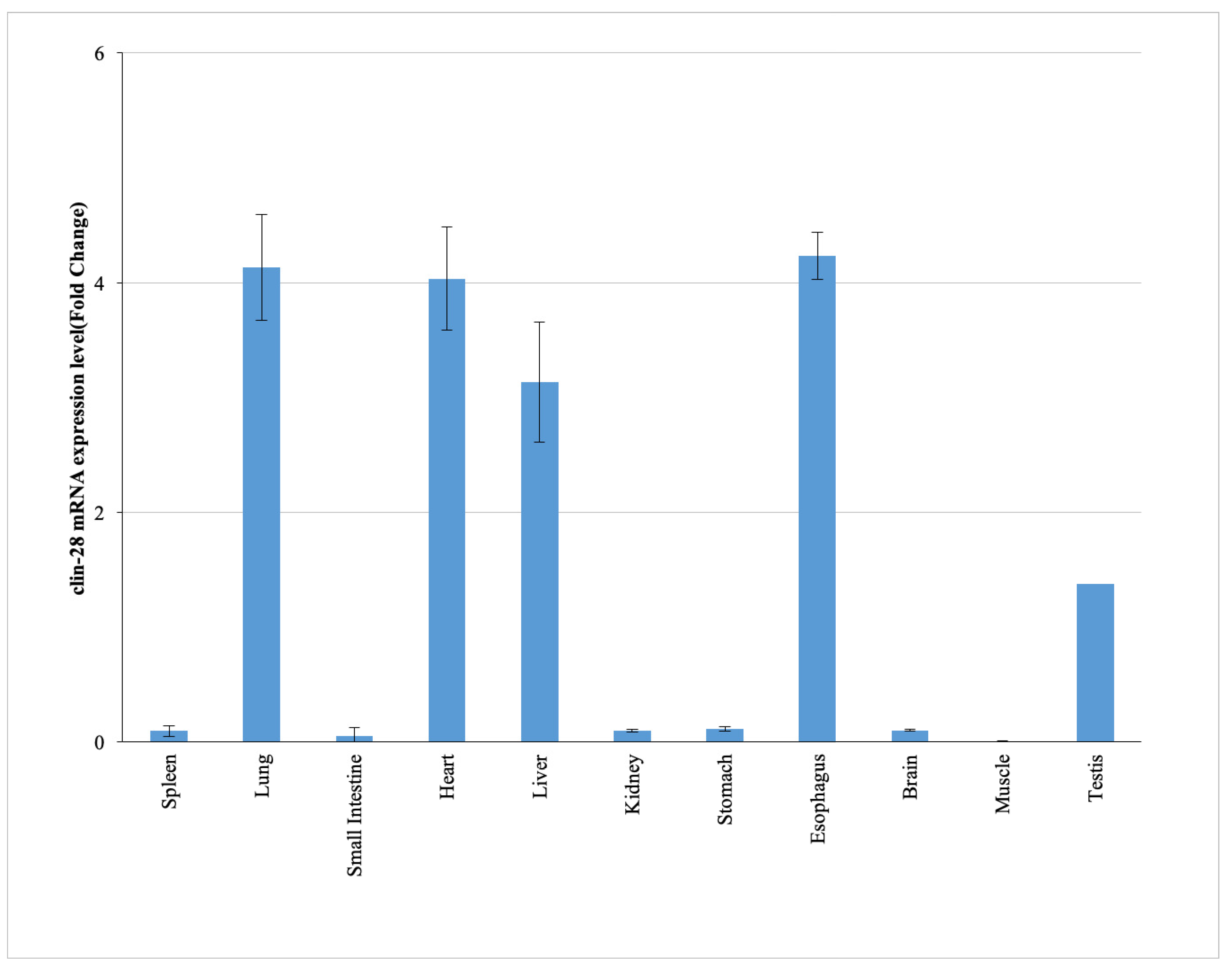
2.1. Tissue-Specific Expression Profile of cLin-28 mRNA
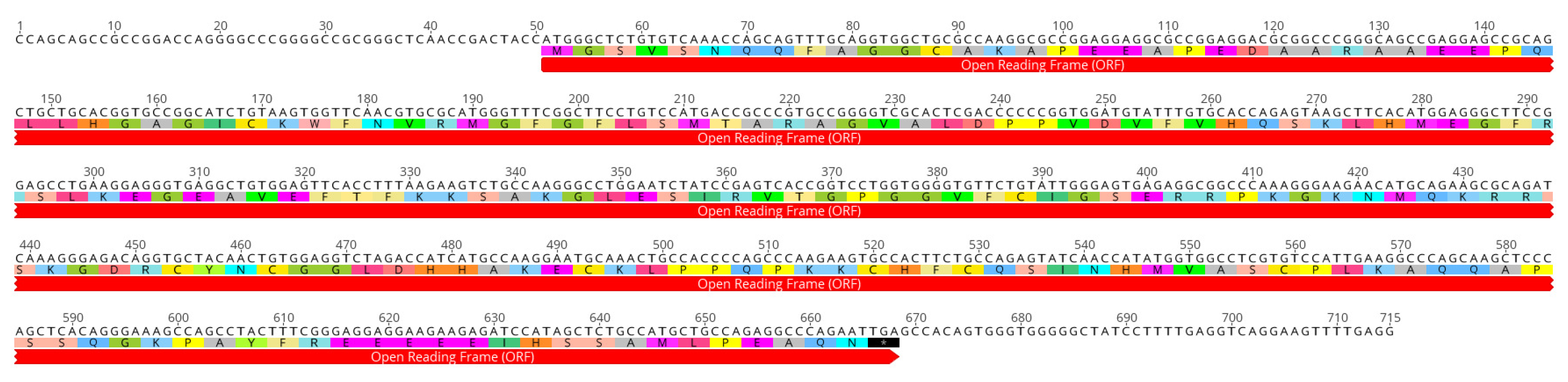
2.2. Characterization of the Full Coding cLin-28 Gene
2.3. Identification of cLin-28 Protein by Using Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Amino Acid Composition and Homology of cLin-28 Protein
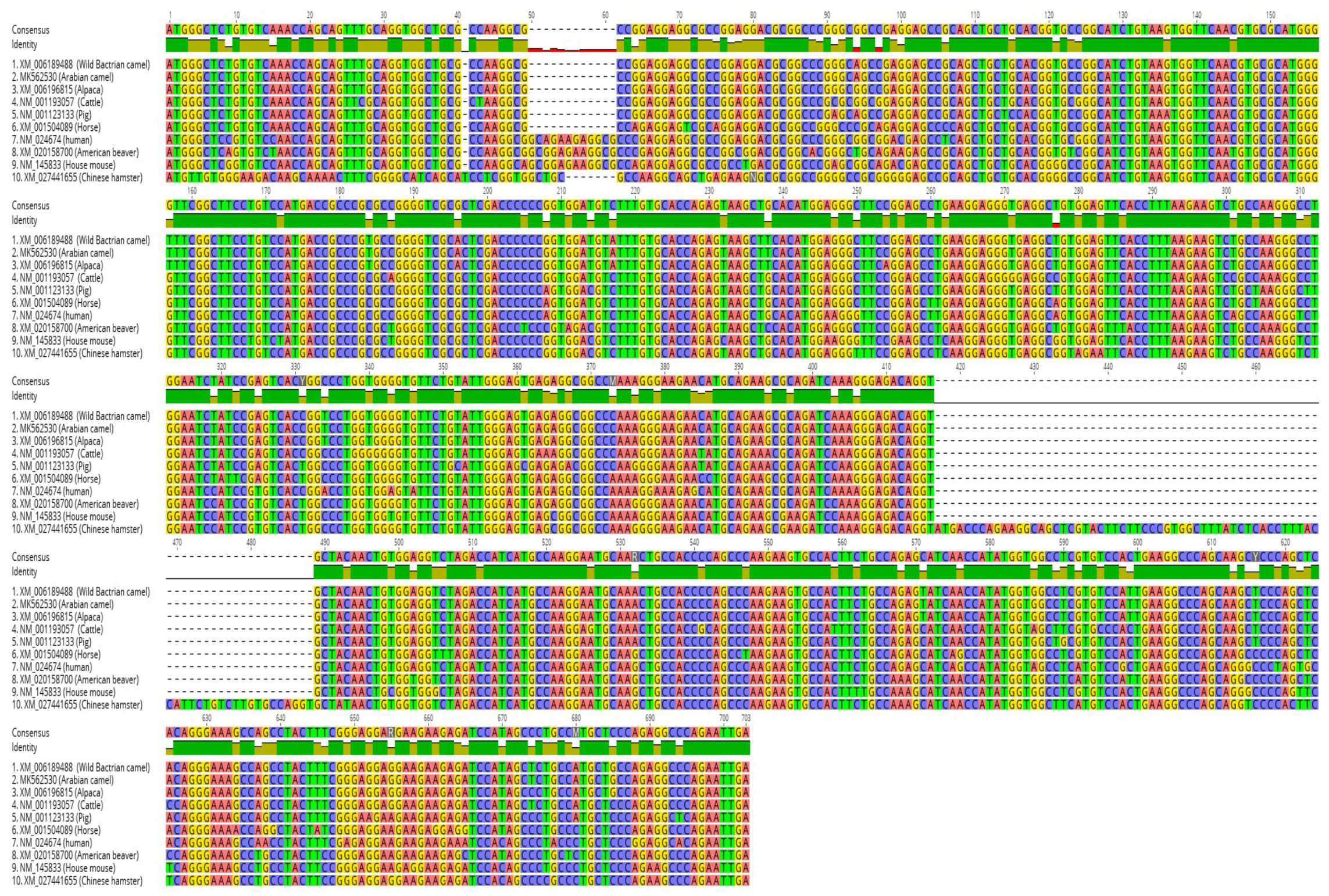
2.5. Multiple Sequence Alignment
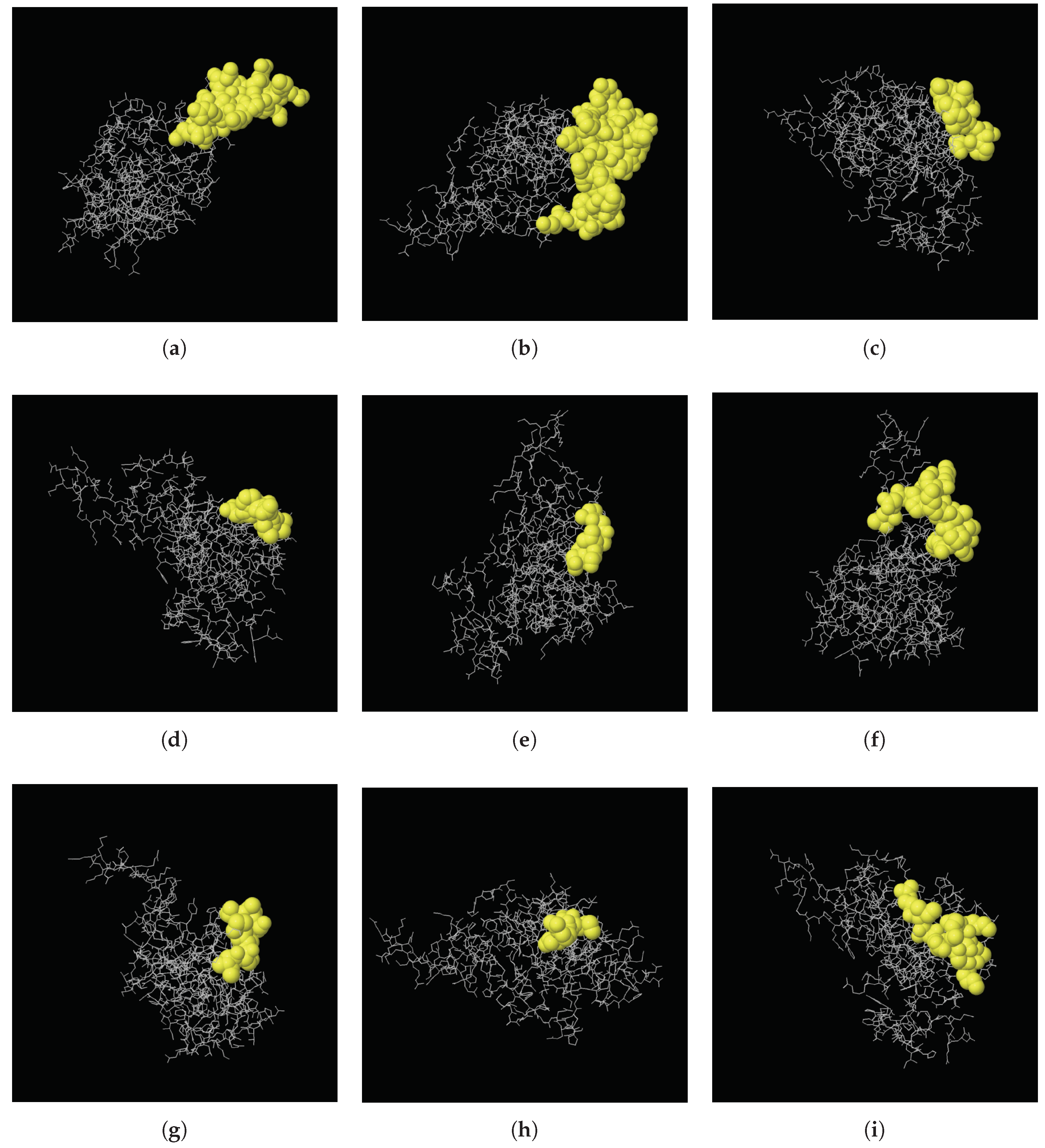
2.6. Secondary and 3D Structures of cLin-28 Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Isolation of RNA and Synthesis of cDNA
4.3. Examining Clin-28 Gene Expression by Using PCR and qRT-PCR
4.4. Protein Digestion and Mass Spectrometry
4.5. Structure Modeling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ORF | Open Reading Frame |
| RT-PCR | Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| CSD | Cold-Shock Domain |
| qPCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| PMF-MS | Peptide Mass Finger Print-Mass Spectrometry |
References
- Fowler, M. Medicine and Surgery of Camelids; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Manee, M.M.; Alharbi, S.N.; Algarni, A.T.; Alghamdi, W.M.; Altammami, M.A.; Alkhrayef, M.N.; Alnafjan, B.M. Molecular cloning, bioinformatics analysis, and expression of small heat shock protein beta-1 from Camelus dromedarius, Arabian camel. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alawad, A.; Alharbi, S.; Alhazzaa, O.; Alagrafi, F.; Alkhrayef, M.; Alhamdan, Z.; Alenazi, A.; Al-Johi, H.; Alanazi, I.O.; Hammad, M. Phylogenetic and Structural Analysis of the Pluripotency Factor Sex-Determining Region Y box2 Gene of Camelus dromedarius (cSox2). Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2016, 10, BBI-S39047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, E.G.; Tang, L. Conservation of the heterochronic regulator Lin-28, its developmental expression and microRNA complementary sites. Dev. Biol. 2003, 258, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darr, H.; Benvenisty, N. Genetic analysis of the role of the reprogramming gene LIN-28 in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsialikas, J.; Romer-Seibert, J. LIN28: Roles and regulation in development and beyond. Development 2015, 142, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, E.; Moss, E.G. Localization of the developmental timing regulator Lin28 to mRNP complexes, P-bodies and stress granules. RNA Biol. 2007, 4, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskounova, E.; Polytarchou, C.; Thornton, J.E.; LaPierre, R.J.; Pothoulakis, C.; Hagan, J.P.; Iliopoulos, D.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28A and Lin28B inhibit let-7 microRNA biogenesis by distinct mechanisms. Cell 2011, 147, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.A.; Thomson, J.M.; Hammond, S.M. Lin-28 interaction with the Let-7 precursor loop mediates regulated microRNA processing. Rna 2008, 14, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Yamanaka, K.; Inouye, M. Acquisition of double-stranded DNA-binding ability in a hybrid protein between Escherichia coli CspA and the cold shock domain of human YB-1. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasquinelli, A.E.; Ruvkun, G. Control of developmental timing by microRNAs and their targets. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 18, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, M.; Max, K.E.; Bandaru, P.; Morozov, P.; Gerstberger, S.; Brown, M.; Molina, H.; Tuschl, T. Identification of mRNAs bound and regulated by human LIN28 proteins and molecular requirements for RNA recognition. Rna 2013, 19, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thummel, C.S. Molecular mechanisms of developmental timing in C. elegans and Drosophila. Dev. Cell 2001, 1, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guruprasad, K.; Reddy, B.B.; Pandit, M.W. Correlation between stability of a protein and its dipeptide composition: a novel approach for predicting in vivo stability of a protein from its primary sequence. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1990, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopp, T.P.; Woods, K.R. A computer program for predicting protein antigenic determinants. Mol. Immunol. 1983, 20, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, P.; Schulz, G. Prediction of chain flexibility in proteins. Naturwissenschaften 1985, 72, 212–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaskar, A.; Tongaonkar, P.C. A semi-empirical method for prediction of antigenic determinants on protein antigens. FEBS Lett. 1990, 276, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emini, E.A.; Hughes, J.V.; Perlow, D.; Boger, J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J. Virol. 1985, 55, 836–839. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, P.; Fasman, G. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv. Enzymol. 1978, 47, 45–148. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Dosztányi, Z.; Mészáros, B.; Simon, I. ANCHOR: Web server for predicting protein binding regions in disordered proteins. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2745–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T. Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 292, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskounova, E.; Viswanathan, S.R.; Janas, M.; LaPierre, R.J.; Daley, G.Q.; Sliz, P.; Gregory, R.I. Determinants of microRNA processing inhibition by the developmentally regulated RNA-binding protein Lin28. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21310–21314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Oldfield, C.J.; Van, Y.Y.; Dunker, A.K.; Uversky, V.N. Protein intrinsic disorder and induced pluripotent stem cells. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongbao, M.; Young, J.; Shen, C. RNA, DNA and protein isolation using TRI Zol reagent. Nat. Sci. 2008, 6, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havli, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]

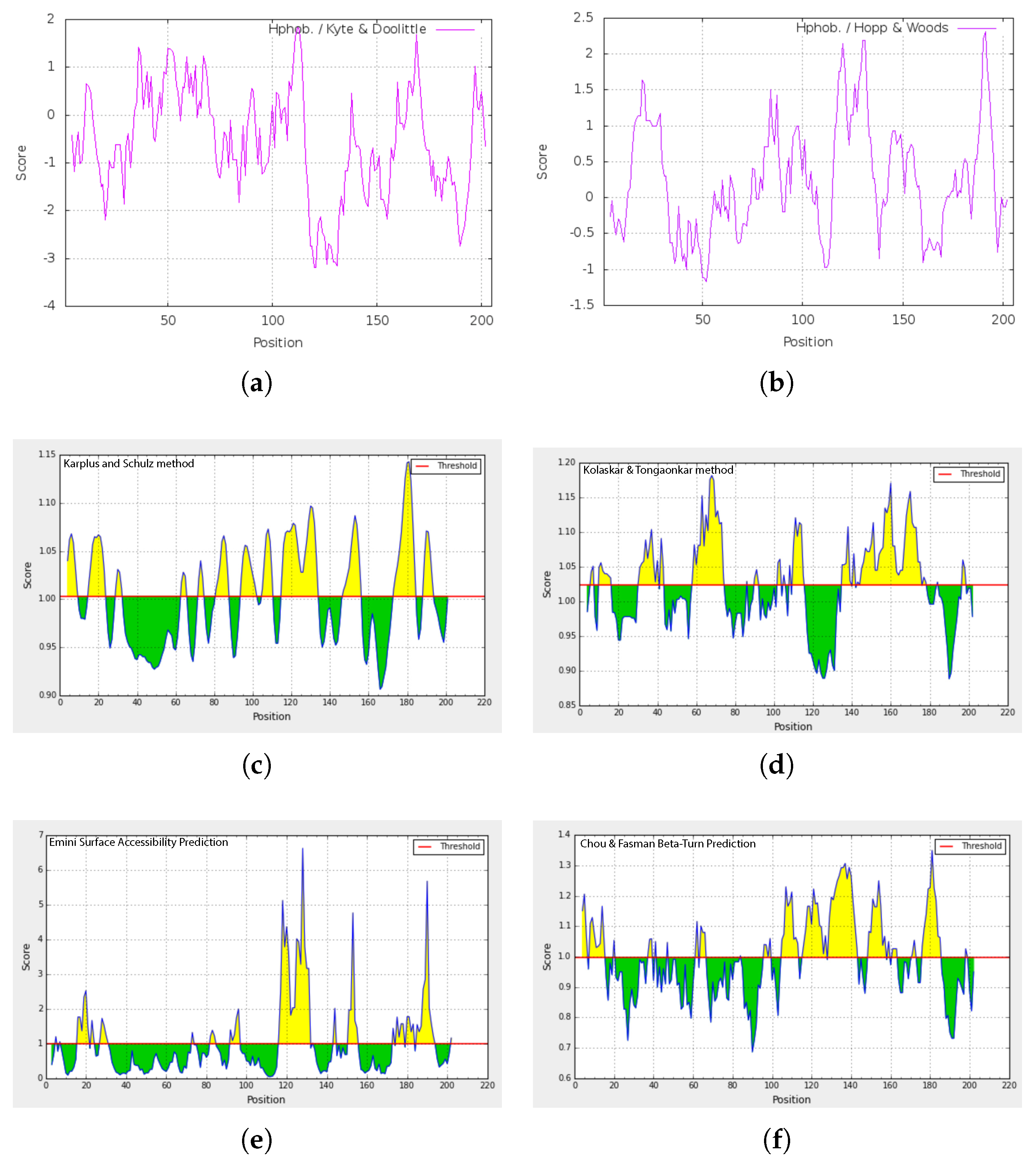


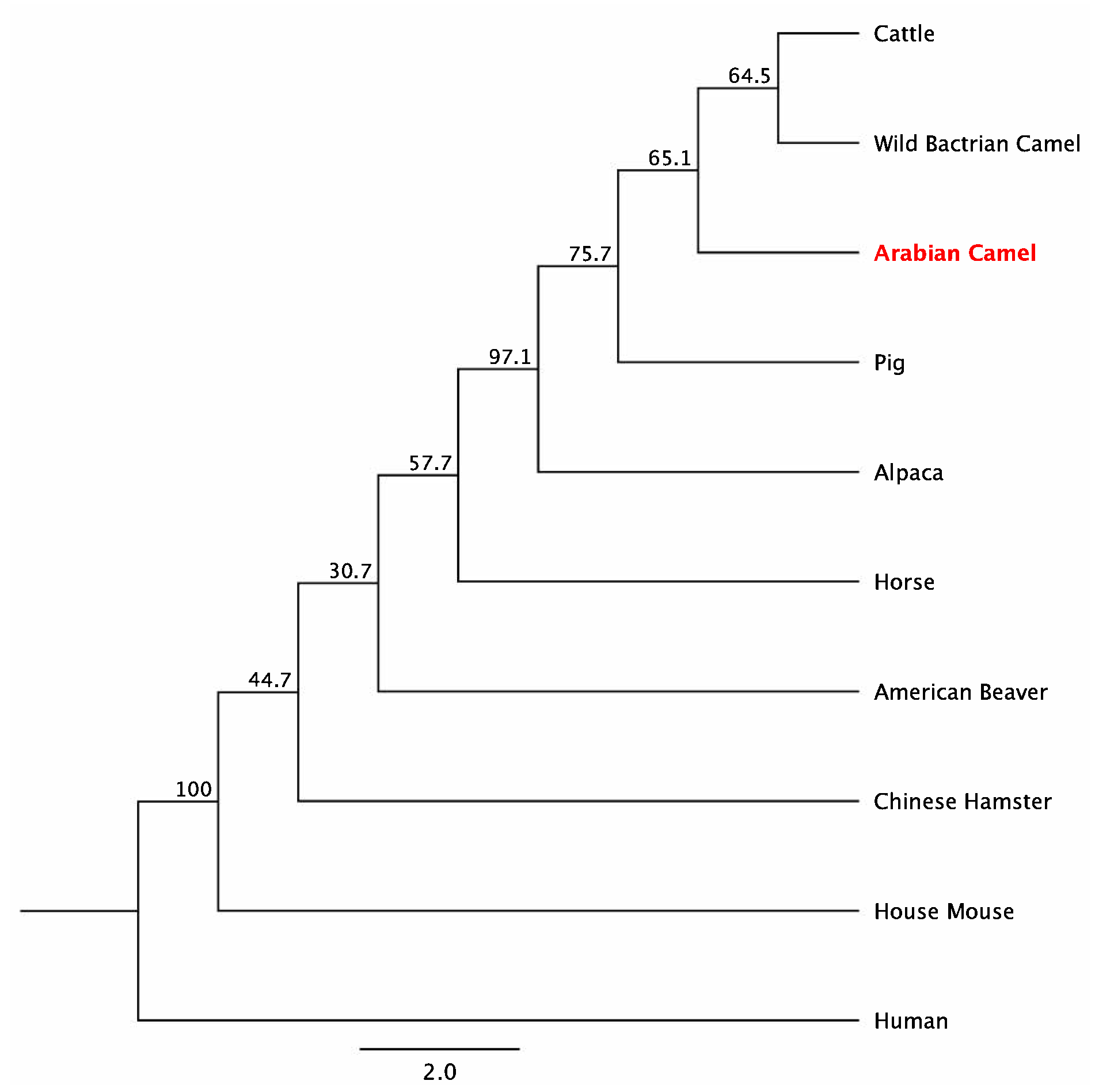
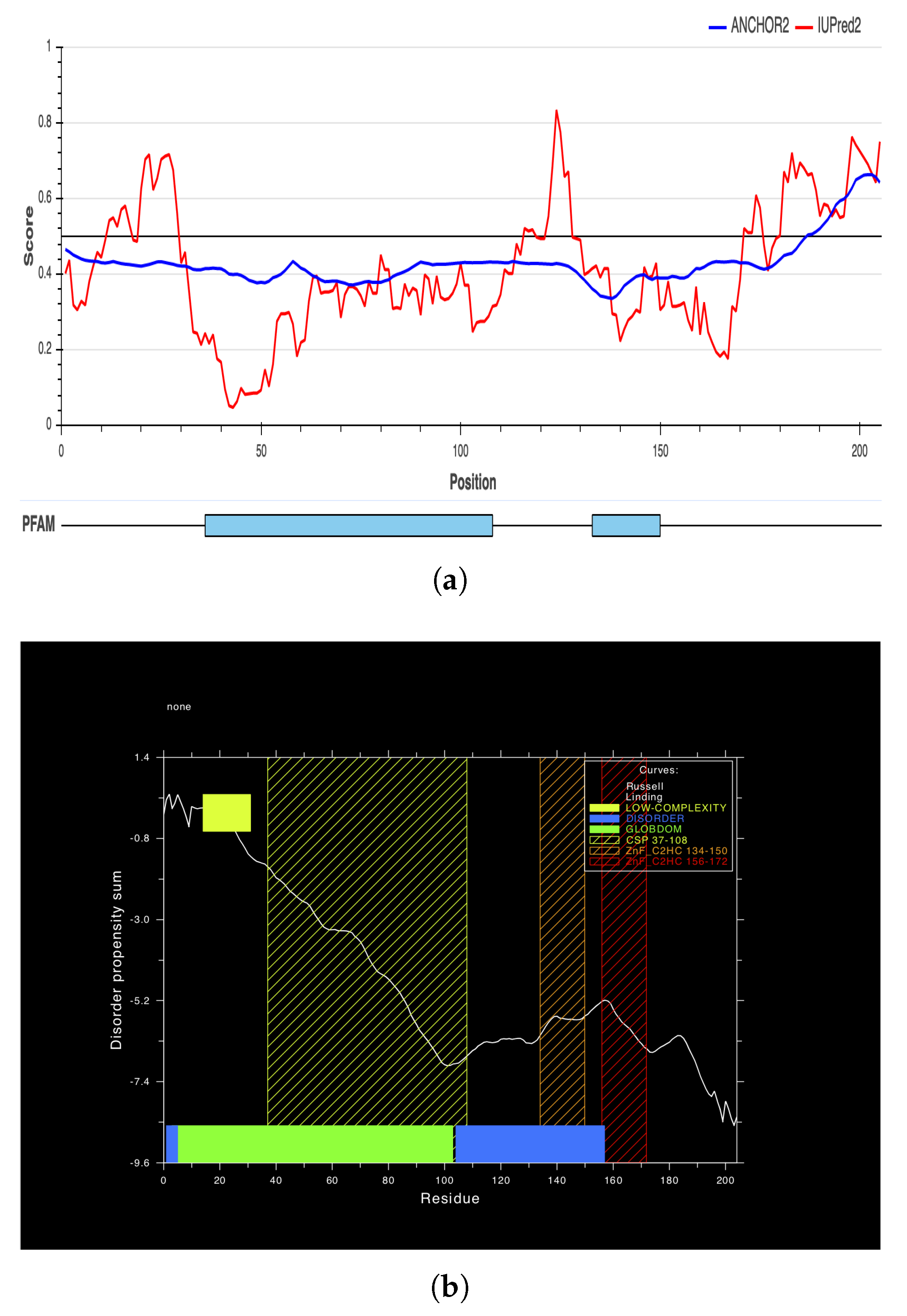
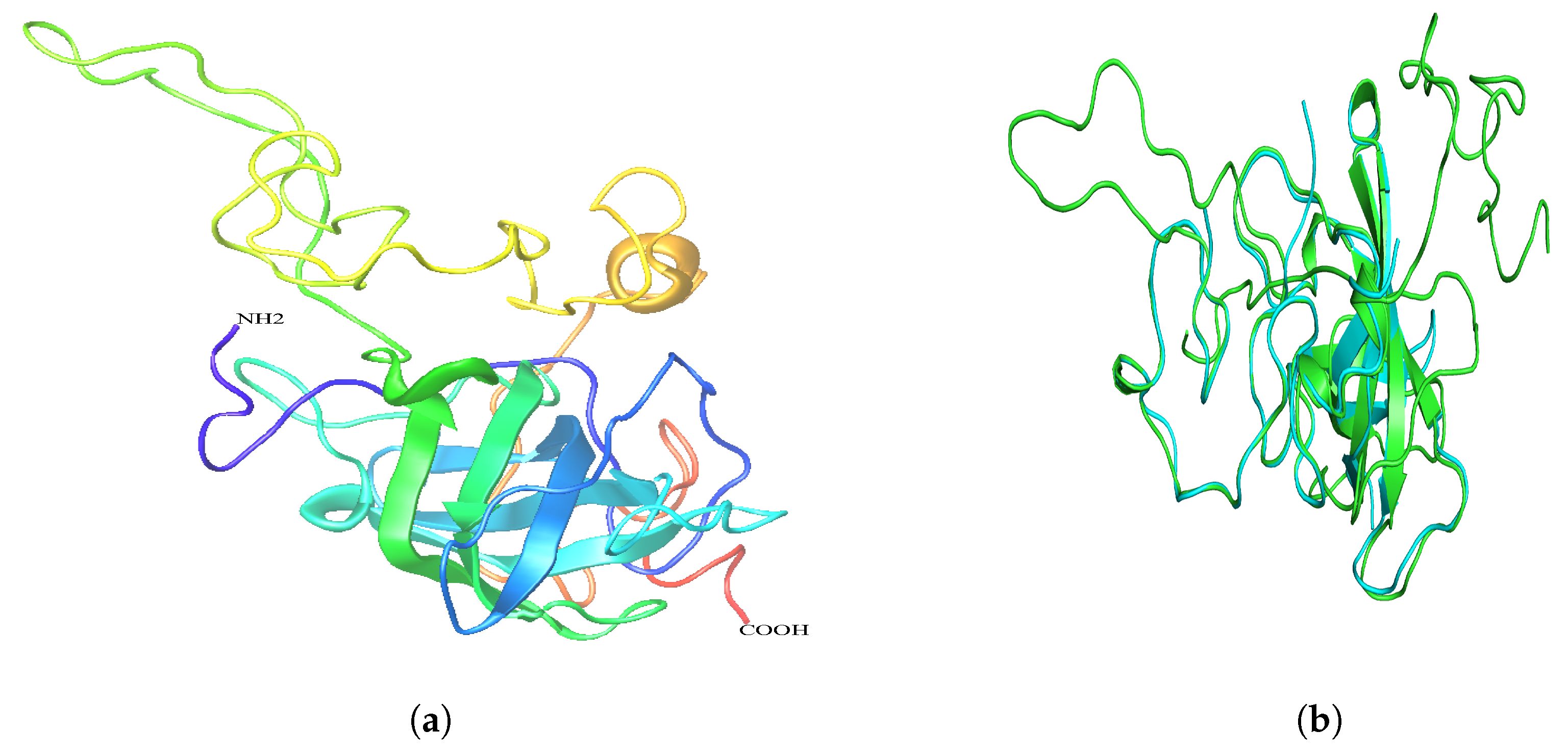
| Usage | Primer Name | Primer Sequence 5 → 3 | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ORF-PCR | cLin-28-F | ACTACCATGGGCTCTGTGTC | 636 |
| cLin-28-R | ACCCACTGTGGCTCAATTCT | ||
| GAPDH-F | CTGGGAAGATGTGGCGTGAT | 190 | |
| GAPDH-R | AAGGCCATGCCAGTTAGCTT | ||
| qRT-PCR | cLin-28-qF | AAAGCCAGCCTACTTTCGGG | 101 |
| cLin-28-qR | CAAAAGGATAGCCCCCACCC | ||
| -Actin-F | CCCATTGAGCATGGCATCGT | 80 | |
| -Actin-R | GTAGATGGGCACAGTGTGAG |
| Amino Acid Positions | [M + H]+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Start-End | B | Calculated (m/z) | Peptide Sequence |
| 2–15 | 1353.6800 | 1353.4608 | MGSVSNQQFAGGCAKA |
| 16–26 | 1155.5100 | 1155.1723 | KAPEEAPEDAARA |
| 27–41 | 1537.5300 | 1536.7512 | RAAEEPQLLHGAGICKW |
| 27–46 | 2240.1300 | 2239.5544 | RAAEEPQLLHGAGICKWFNVRM |
| 42–46 | 721.4700 | 720.8185 | KWFNVRM |
| 75–81 | 889.4300 | 889.0332 | KLHMEGFRS |
| 85–94 | 1157.6300 | 1156.2416 | KEGEAVEFTFKK |
| 105–118 | 1378.8600 | 1378.5532 | RVTGPGGVFCIGSERR |
| 122–127 | 705.3800 | 704.8391 | KGKNMQKR |
| 150–156 | 807.5000 | 806.9923 | KLPPQPKKC |
| 174–183 | 1001.2400 | 1001.0520 | KAQQAPSSQGKP |
| Amino Acid | Number Count | % By Weight | % By Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ala (A) | 21 | 6.67 | 10.24 | |
| Cys (C) | 9 | 4.15 | 4.39 | |
| Asp (D) | 5 | 2.57 | 2.44 | |
| Glu (E) | 18 | 10.38 | 8.78 | |
| Phe (F) | 11 | 7.23 | 5.37 | |
| Gly (G) | 20 | 5.10 | 9.76 | |
| His (H) | 8 | 4.90 | 3.90 | |
| Ile (I) | 5 | 2.56 | 5.37 | |
| lys (K) | 17 | 9.73 | 8.29 | |
| Leu (L) | 11 | 5.56 | 5.37 | |
| Met (M) | 7 | 4.10 | 3.41 | |
| Asn (N) | 6 | 3.06 | 2.93 | |
| Pro (P) | 14 | 6.07 | 6.83 | |
| Gln (Q) | 11 | 6.30 | 5.37 | |
| Arg (R) | 11 | 7.67 | 5.37 | |
| Ser (S) | 15 | 5.83 | 7.32 | |
| Thr (T) | 3 | 1.35 | 1.46 | |
| Val (V) | 10 | 4.43 | 4.88 | |
| Trp (W) | 1 | 0.88 | 0.49 | |
| Tyr (Y) | 2 | 1.46 | 0.98 |
| No. | Start | End | Peptide | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 16 | AGGCAKA | 7 |
| 2 | 31 | 40 | PQLLHGAGIC | 10 |
| 3 | 58 | 74 | AGVALDPPVDVFVHQSK | 17 |
| 4 | 110 | 115 | GVFCIG | 6 |
| 5 | 143 | 175 | HHAKECKLPPQPKKCHFCQSINHMVASCPLKAQ | 33 |
| Species | Common Name | Protein(Accession no.) | Protein Length (bp) | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Human | EAX07815.1 | 360 | 80 |
| Mus musculus | House Mouse | AAH68304.1 | 209 | 95.7 |
| Sus scrofa | Pig | ADK26463.1 | 205 | 98.1 |
| Camelus bactrianus | Wild Bactrian Camel | EPY77519.1 | 232 | 88.6 |
| Camelus dromedarius | Arabian Camel | XP_010992036 | 205 | 100 |
| Vicugna pacos | Alpaca | XP_006196877.1 | 205 | 98.6 |
| Bos taurus | Cattle | NP_001179986.1 | 205 | 98.1 |
| Equus przewalskii | Horse | XP_001504139.1 | 205 | 94.6 |
| Cricetulus griseus | Chinese hamster | ERE84162.1 | 209 | 96.2 |
| Castor canadensis | American beaver | XP_020014289.1 | 209 | 96.2 |
| Start | End | Peptide | Length | Score | 3D Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 117 | 134 | ERRPKGKNMQKRRSKGDR | 18 | 0.803 | A |
| 173 | 205 | KAQQAPSSQGKPAYFREEEEEIHSSAMLPEAQN | 33 | 0.785 | B |
| 57 | 65 | RAGVALDPP | 9 | 0.709 | C |
| 29 | 35 | EEPQLLH | 7 | 0.702 | D |
| 1 | 6 | MGSVSN | 6 | 0.622 | E |
| 141 | 156 | LDHHAKECKLPPQPKK | 16 | 0.617 | F |
| 163 | 170 | INHMVASC | 8 | 0.574 | G |
| 45 | 48 | VRMG | 4 | 0.556 | H |
| 94 | 104 | KKSAKGLESIR | 11 | 0.518 | I |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, S.N.; Alduhaymi, I.S.; Alqahtani, L.; Altammaami, M.A.; Alhoshani, F.M.; Alrabiah, D.K.; Alyemni, S.O.; Alsulami, K.A.; Alghamdi, W.M.; Fallatah, M. Molecular Characterization, Bioinformatic Analysis, and Expression Profile of Lin-28 Gene and Its Protein from Arabian Camel (Camelus dromedarius). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092291
Alharbi SN, Alduhaymi IS, Alqahtani L, Altammaami MA, Alhoshani FM, Alrabiah DK, Alyemni SO, Alsulami KA, Alghamdi WM, Fallatah M. Molecular Characterization, Bioinformatic Analysis, and Expression Profile of Lin-28 Gene and Its Protein from Arabian Camel (Camelus dromedarius). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092291
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Sultan N., Ibtehal S. Alduhaymi, Lama Alqahtani, Musaad A. Altammaami, Fahad M. Alhoshani, Deema K. Alrabiah, Saleh O. Alyemni, Khulud A. Alsulami, Waleed M. Alghamdi, and Mohannad Fallatah. 2019. "Molecular Characterization, Bioinformatic Analysis, and Expression Profile of Lin-28 Gene and Its Protein from Arabian Camel (Camelus dromedarius)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092291
APA StyleAlharbi, S. N., Alduhaymi, I. S., Alqahtani, L., Altammaami, M. A., Alhoshani, F. M., Alrabiah, D. K., Alyemni, S. O., Alsulami, K. A., Alghamdi, W. M., & Fallatah, M. (2019). Molecular Characterization, Bioinformatic Analysis, and Expression Profile of Lin-28 Gene and Its Protein from Arabian Camel (Camelus dromedarius). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092291





