P-element Somatic Inhibitor Protein Binding a Target Sequence in dsx Pre-mRNA Conserved in Bombyx mori and Spodoptera litura
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Four KH_1 Motifs Play Important Roles in the Interaction Between BmPSI and CE1, Especially the KH_1-1 Motif and KH_1-2 Motif
2.2. Important Amino Acids in the KH_1-1 Motif of BmPSI Found in the Interaction between BmPSI and CE1
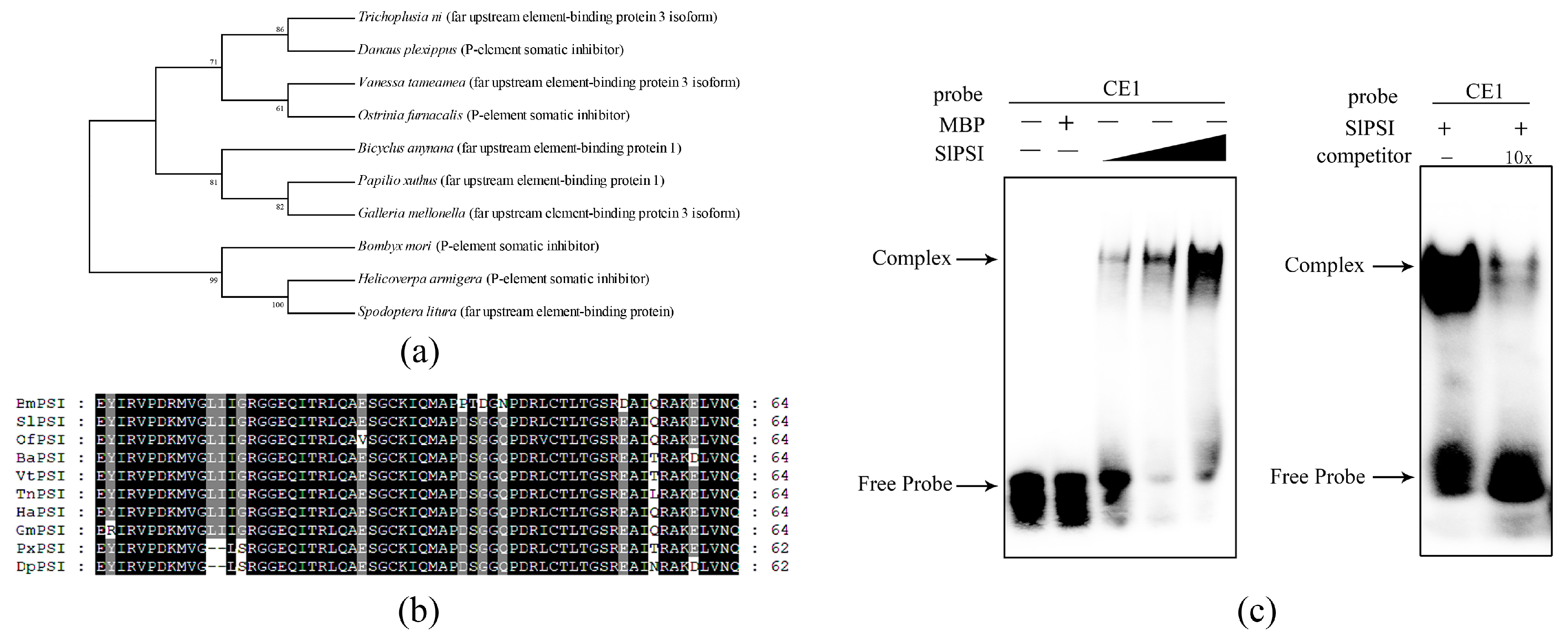
2.3. The Combination of PSI and CE1 is Conserved in Spodoptera Litura
2.4. Identifying a Key Amino Acid for the Combination of SlPSI and CE1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of Recombinant Expression Vectors
4.2. Preparation of Single Stranded RNA
4.3. The Overexpression and Purification of Different Kinds of Proteins
4.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.5. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
4.6. CD Wavelength Scans
4.7. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| dsx | Doublesex |
| PSI | P-element somatic inhibitor |
| CD | Circular dichroism |
| ITC | Isothermal titration calorimetry |
| EMSA | Electrophoretic mobility shift assay |
References
- Ohbayashi, F.; Suzuki, M.G.; Mita, K.; Okano, K.; Shimada, T. A homologue of the Drosophila doublesex gene is transcribed into sex-specific mRNA isoforms in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2001, 128, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.G.; Funaguma, S.; Kanda, T.; Tamura, T.; Shimada, T. Role of the male BmDSX protein in the sexual differentiation of Bombyx mori. Evol. Dev. 2005, 7, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaguma, S.; Suzuki, M.G.; Tamura, T.; Shimada, T. The Bmdsx transgene including trimmed introns is sex-specifically spliced in tissues of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Sci. 2005, 5, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.G.; Ohbayashi, F.; Mita, K.; Shimada, T. The mechanism of sex-specific splicing at the doublesex gene is different between Drosophila melanogaster and Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol Biol. 2001, 31, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.G.; Imanishi, S.; Dohmae, N.; Nishimura, T.; Shimada, T.; Matsumoto, S. Establishment of a novel in vivo sex-specific splicing assay system to identify a trans-acting factor that negatively regulates splicing of Bombyx mori dsx female exons. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Zeng, B.; James, A.A.; Tan, A.; Huang, Y. Bombyx mori P-element somatic inhibitor (BmPSI) is a key auxiliary factor for silkworm male sex determination. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi, S.; Bagni, C.; Castiglione Morelli, M.A.; Fraternali, F.; Musco, G.; Pastore, A. Novel RNA-binding motif: The KH module. Biopolymers 1999, 51, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternali, F.; Amodeo, P.; Musco, G.; Nilges, M.; Pastore, A. Exploring protein interiors: The role of a buried histidine in the KH module fold. Proteins 1999, 34, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, M.P.; Huang, S.; Black, D.L. Differentiation-induced colocalization of the KH-type splicing regulatory protein with polypyrimidine tract binding protein and the c-src pre-mRNA. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Art, J.; Besche, V.; Bros, M.; Li, H.; Handler, N.; Bauer, F.; Erker, T.; Behnke, F.; Monch, B.; Forstermann, U.; et al. Identification of the KH type splicing regulatory protein (KSRP) as a new important mediator of the anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol. N.-S. Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Chmiel, N.H.; Rio, D.C.; Doudna, J.A. Distinct contributions of KH domains to substrate binding affinity of Drosophila P-element somatic inhibitor protein. RNA 2006, 12, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zaysteva, O.; Nie, Z.; Mitchell, N.C.; Amanda Lee, J.E.; Ware, T.; Parsons, L.; Luwor, R.; Poortinga, G.; Hannan, R.D.; et al. Defining the essential function of FBP/KSRP proteins: Drosophila Psi interacts with the mediator complex to modulate MYC transcription and tissue growth. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7646–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labourier, E.; Blanchette, M.; Feiger, J.W.; Adams, M.D.; Rio, D.C. The KH-type RNA-binding protein PSI is required for Drosophila viability, male fertility, and cellular mRNA processing. Gene Dev. 2002, 16, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeyev, A.V.; Eastmond, D.L.; Liebhaber, S.A. Targeting a KH-domain protein with RNA decoys. RNA 2002, 8, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.X.; Xu, Y.J.; Liang, X.J.; Zeng, W.X. The biological function of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) and its roles in spermatogenisis. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 23, 661–670. [Google Scholar]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Kernya, L.; Lee, Y.H.; Goto, Y.; Refregiers, M.; Kardos, J. Accurate secondary structure prediction and fold recognition for circular dichroism spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3095–E3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arroyo-Maya, I.J.; McClements, D.J. Application of ITC in foods: A powerful tool for understanding the gastrointestinal fate of lipophilic compounds. BBA-Gen. Subjects 2016, 1860, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Manley, O.M.; Spuches, A.M.; Grossoehme, N.E. Dissecting ITC data of metal ions binding to ligands and proteins. BBA-Gen. Subjects 2016, 1860, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaoka, S.; Kadota, K.; Arai, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Fujii, T.; Abe, H.; Yasukochi, Y.; Mita, K.; Sugano, S.; Shimizu, K.; et al. The silkworm W chromosome is a source of female-enriched piRNAs. RNA 2011, 17, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hara, K.; Fujii, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugano, S.; Shimada, T.; Katsuma, S.; Kawaoka, S. Altered expression of testis-specific genes, piRNAs, and transposons in the silkworm ovary masculinized by a W chromosome mutation. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.G.; Imanishi, S.; Dohmae, N.; Asanuma, M.; Matsumoto, S. Identification of a male-specific RNA binding protein that regulates sex-specific splicing of Bmdsx by increasing RNA binding activity of BmPSI. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 5776–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, T.; Koga, H.; Kawamoto, M.; Shoji, K.; Sakai, H.; Arai, Y.; Ishihara, G.; Kawaoka, S.; Sugano, S.; Shimada, T.; et al. A single female-specific piRNA is the primary determiner of sex in the silkworm. Nature 2014, 509, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Wen, L.; Zheng, S.C.; Bi, H.L.; Huang, Y.P.; Feng, Q.L.; Liu, L. Identification and functional characterization of doublesex gene in the testis of Spodoptera litura. Insect Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashim, E.; Hujieda, T.; Moriizum, S. On expression of several characters affected by difference of sexes in silkworm. Jpn. J. Genet. 1967, 42, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Shabdini, A.; Seidavi, A.R.; Gharahveysi, S.; Mirhosseini, S.Z. Effects of sex, generation and genetic group on economic traits in three Iranian commercial silkworm pure lines. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, A.R.; Neves, L.A.; Valencio, C.R.; Roberto, G.F.; Zafalon, G.F.D. An approach for COFFEE objective function to global DNA multiple sequence alignment. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2018, 75, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nute, M.; Saleh, E.; Warnow, T. Evaluating statistical multiple sequence alignment in comparison to other alignment methods on protein data sets. Syst. Biol. 2018, 68, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Su, W.; Shi, W.; Zou, Q.; Peng, S. VCSRA: A fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment algorithm with a high degree of parallelism. J. Genet. Genomics 2018, 45, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkov, T.E.; Wahlstrom, J.M.; Hagiwara, K.; Finardi-Filho, F.; Kjemtrup, S.; Chrispeels, M.J. Evolutionary relationships among proteins in the phytohemagglutinin-arcelin-alpha-amylase inhibitor family of the common bean and its relatives. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1994, 26, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Q. Performance analysis of evolutionary algorithms for steiner tree problems. Evol. Comput. 2017, 25, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, L.M.; Fried, M.G. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) for detecting protein-nucleic acid interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, D.; Agnew, J.; Patton, W.F.; Hendrickson, J.; Beechem, J.M. A sensitive two-color electrophoretic mobility shift assay for detecting both nucleic acids and protein in gels. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fillebeen, C.; Wilkinson, N.; Pantopoulos, K. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) for the study of RNA-protein interactions: The IRE/IRP example. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 94, e52230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.B.; Mortensen, K.; Pavan, G.M.; Kasimova, M.R.; Jensen, D.K.; Gadzhyeva, V.; Nielsen, H.M.; Foged, C. Molecular characterization of the interaction between siRNA and PAMAM G7 dendrimers by SAXS, ITC, and molecular dynamics simulations. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3571–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Molecule | ΔH (cal/mol) | ΔS (cal/mol/deg) | n | K (M−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BmPSI | −3.3 × 104 ± 269.2 | −77.9 | 1.02 | 1.74 × 107 |
| Name | Primers |
|---|---|
| Bmpsi | 5′-cgcggatccatgagtgattattcttctat-3′, |
| 5′-ccgctcgagtcactgctggtggtcggagc-3′ | |
| ΔKH_1-1 | 5′-cgatcagagcatcaatattgtgaatcatcgaggaa-3′ |
| 5′-ttcctcgatgattcacaatattgatgctctgatcg-3′ | |
| ΔKH_1-2 | 5′-ccaggccctaatgcaatgctcctcgccaacaagga-3′ |
| 5′-tccttgttggcgaggagcattgcattagggcctgg-3′ | |
| ΔKH_1-3 | 5′-aacggactcgccaccactcttatatctagtgtcaa-3′ |
| 5′-ttgacactagatataagagtggtggcgagtccgtt-3′ | |
| ΔKH_1-4 | 5′-gaccgaccagagatgcgcaaagttggtgggcctgt-3′ |
| 5′-acaggcccaccaactttgcgcatctctggtcggtc-3′ | |
| I116G | 5′-gttggactaggaattggacgtggt-3′ |
| 5′-accacgtccaattcctagtccaac-3′ | |
| L127G | 5′-atcaccagagggcaagcagaatcc-3′ |
| 5′-ggattctgcttgccctctggtgat-3′ | |
| K134G, | 5′-tccggttgcgggatacaaatggca-3′ |
| 5′-tgccatttgtatcccgcaaccgga-3′ | |
| A161G | 5′-atacagagaggtaaagaattagtg-3′ |
| 5′-cactaattctttacctctctgtat-3′ | |
| L164G | 5′-gctaaagaaggagtgaaccaaatt-3′ |
| 5′-aatttggttcactccttctttagc-3′ | |
| V165G | 5′-aaagaattagggaaccaaattgtg-3′ |
| 5′-cacaatttggttccctaattcttt-3′ | |
| IGGI 117, 118, 121, 124 AAAA | 5′-ggactaatagctgcacgtggtgga-3′ |
| 5′-tccaccacgtgcagctattagtcc-3′, | |
| 5′-cacgtggtgcagaacaagccaccagactgca-3′ | |
| 5′-tgcagtctggtggcttgttctgcaccacgtg-3′, | |
| 5′- gcagaacaagccaccagactgcaa-3′ | |
| 5′-ttgcagtctggtggcttgttctgc-3′ |
| Name | Primers |
|---|---|
| Slpsi | 5′- cgggatccatgagtgattattcttctatggc-3′ |
| 5′-ggaattcctattgatgatggtcggg-3′ | |
| I116G | 5′-atggttggactcggaattgggcgcggc-3′ |
| 5′-gccgcgcccaattccgagtccaaccat-3′ | |
| L127G | 5′-atcacacgcgggcaggcggagtca-3′ |
| 5′-tgactccgcctgcccgcgtgtgat-3′ | |
| IGGI 117, 118, 121, 124 AAAA | 5′-ggactcatagctgggcgcggcggtgag-3′ |
| 5′-ctcaccgccgcgcccagctatgagtcc-3′, | |
| 5′-ggactcatagctgcacgcggcggtgag-3′ | |
| 5′-ctcaccgccgcgtgcagctatgagtcc-3′, | |
| 5′-gcacgcggcgcagagcaggccacacgc-3′ | |
| 5′-gcgtgtggcctgctctgcgccgcgtgc-3′ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wan, Q.-X.; Wang, K.-X.; Zha, X.-F. P-element Somatic Inhibitor Protein Binding a Target Sequence in dsx Pre-mRNA Conserved in Bombyx mori and Spodoptera litura. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092361
Wang Y, Zhao Q, Wan Q-X, Wang K-X, Zha X-F. P-element Somatic Inhibitor Protein Binding a Target Sequence in dsx Pre-mRNA Conserved in Bombyx mori and Spodoptera litura. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092361
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yao, Qin Zhao, Qiu-Xing Wan, Kai-Xuan Wang, and Xing-Fu Zha. 2019. "P-element Somatic Inhibitor Protein Binding a Target Sequence in dsx Pre-mRNA Conserved in Bombyx mori and Spodoptera litura" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092361
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhao, Q., Wan, Q. -X., Wang, K. -X., & Zha, X. -F. (2019). P-element Somatic Inhibitor Protein Binding a Target Sequence in dsx Pre-mRNA Conserved in Bombyx mori and Spodoptera litura. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092361




