Hyperoside Induces Breast Cancer Cells Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
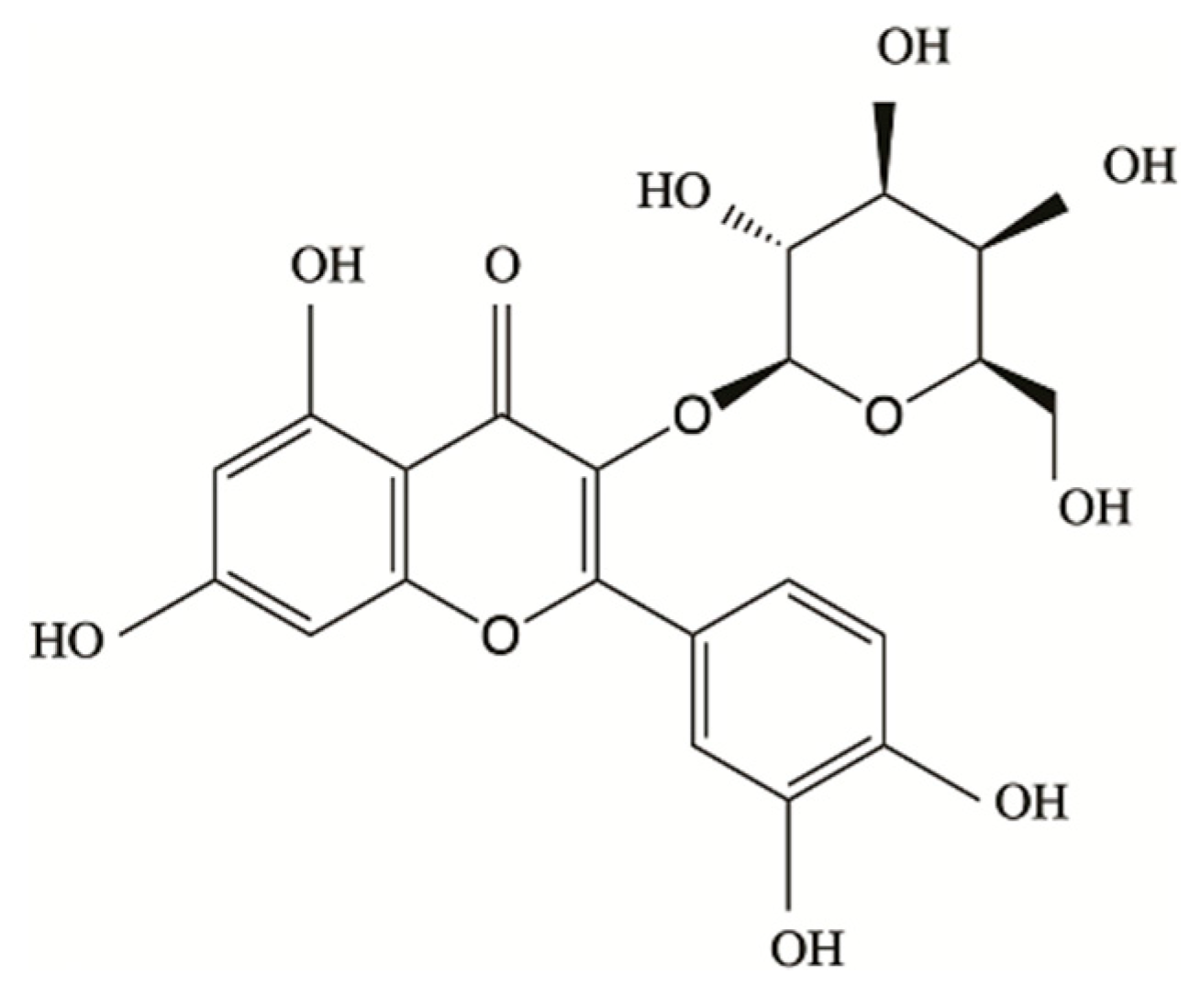
1. Introduction
2. Results
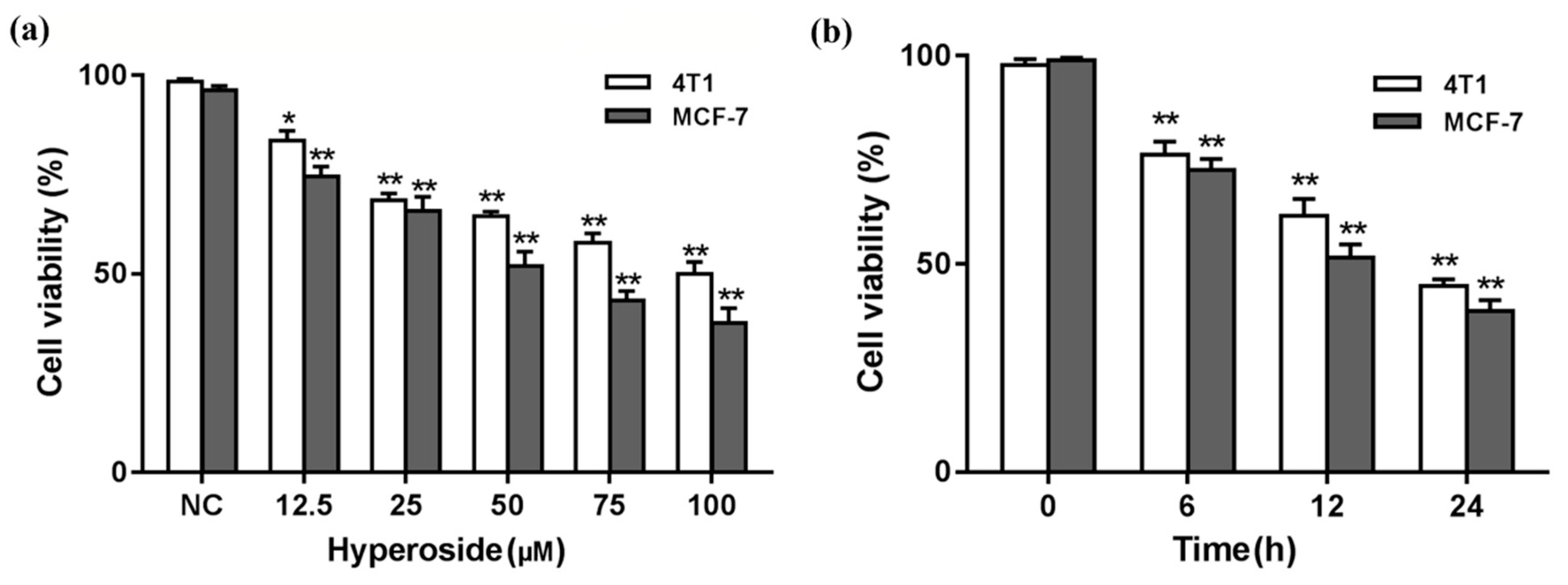
2.1. Effects of Hyperoside on Cell Viability
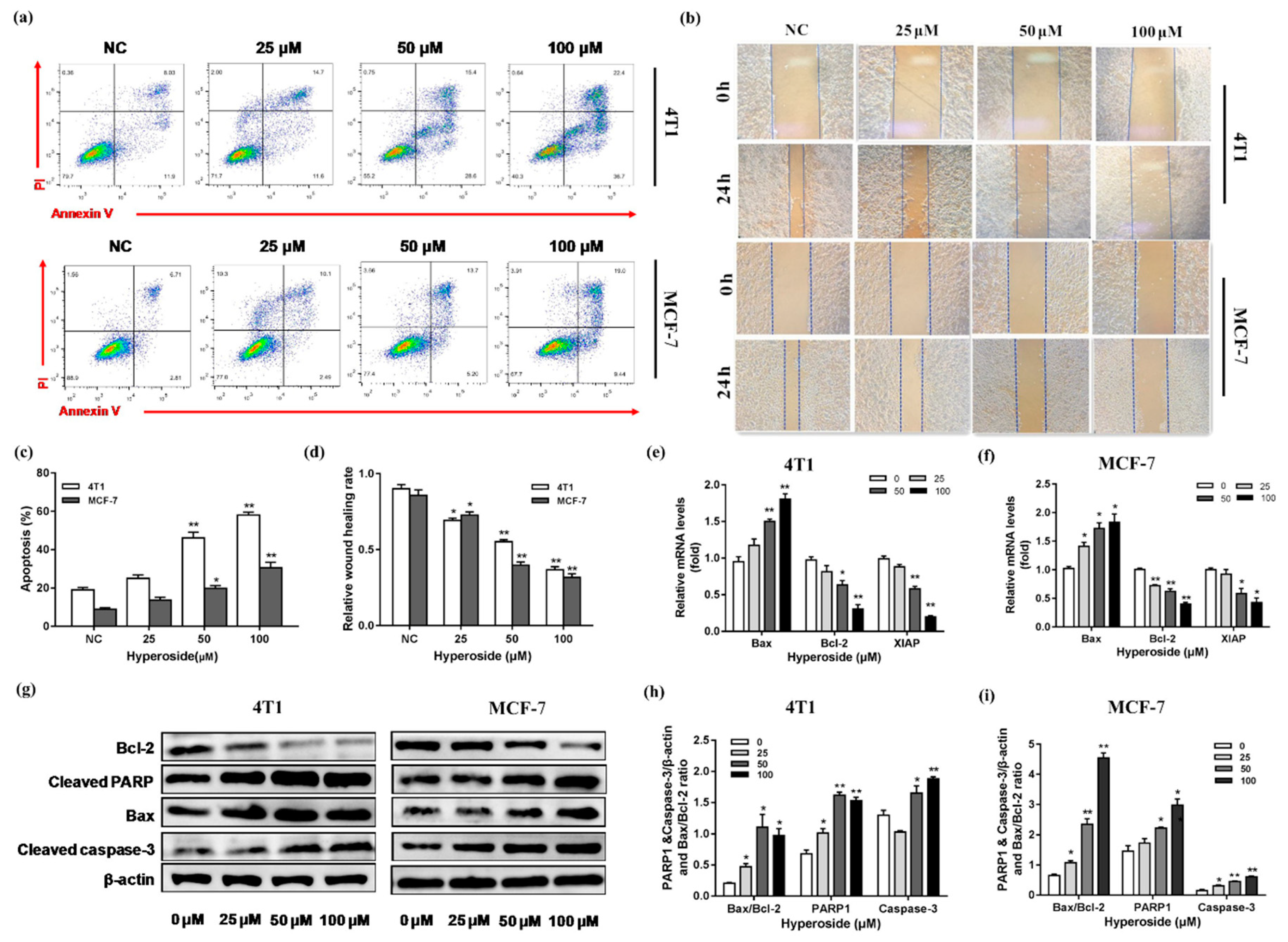
2.2. Hyperoside Can Cause Apoptosis on Breast Cancer Cells
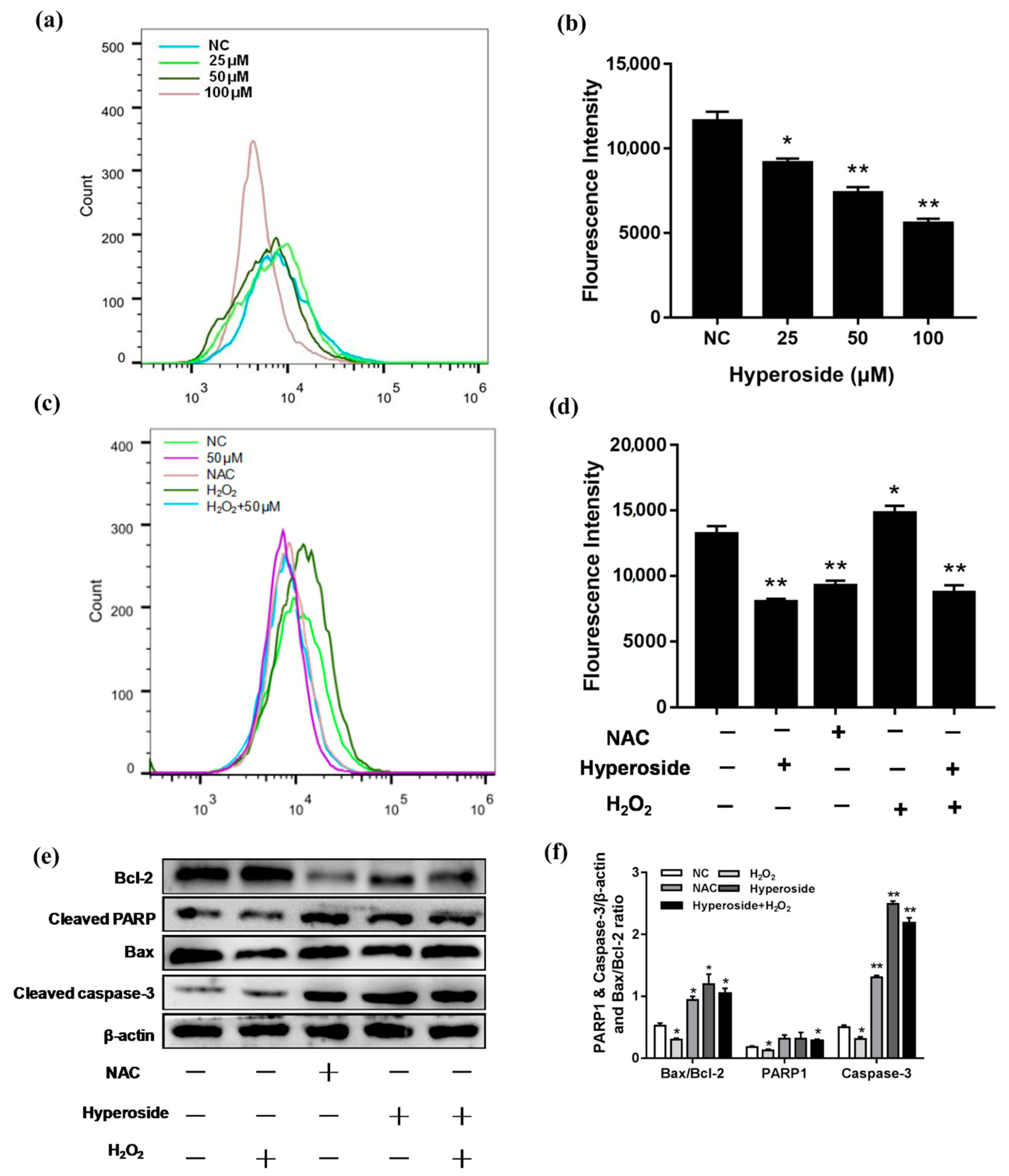
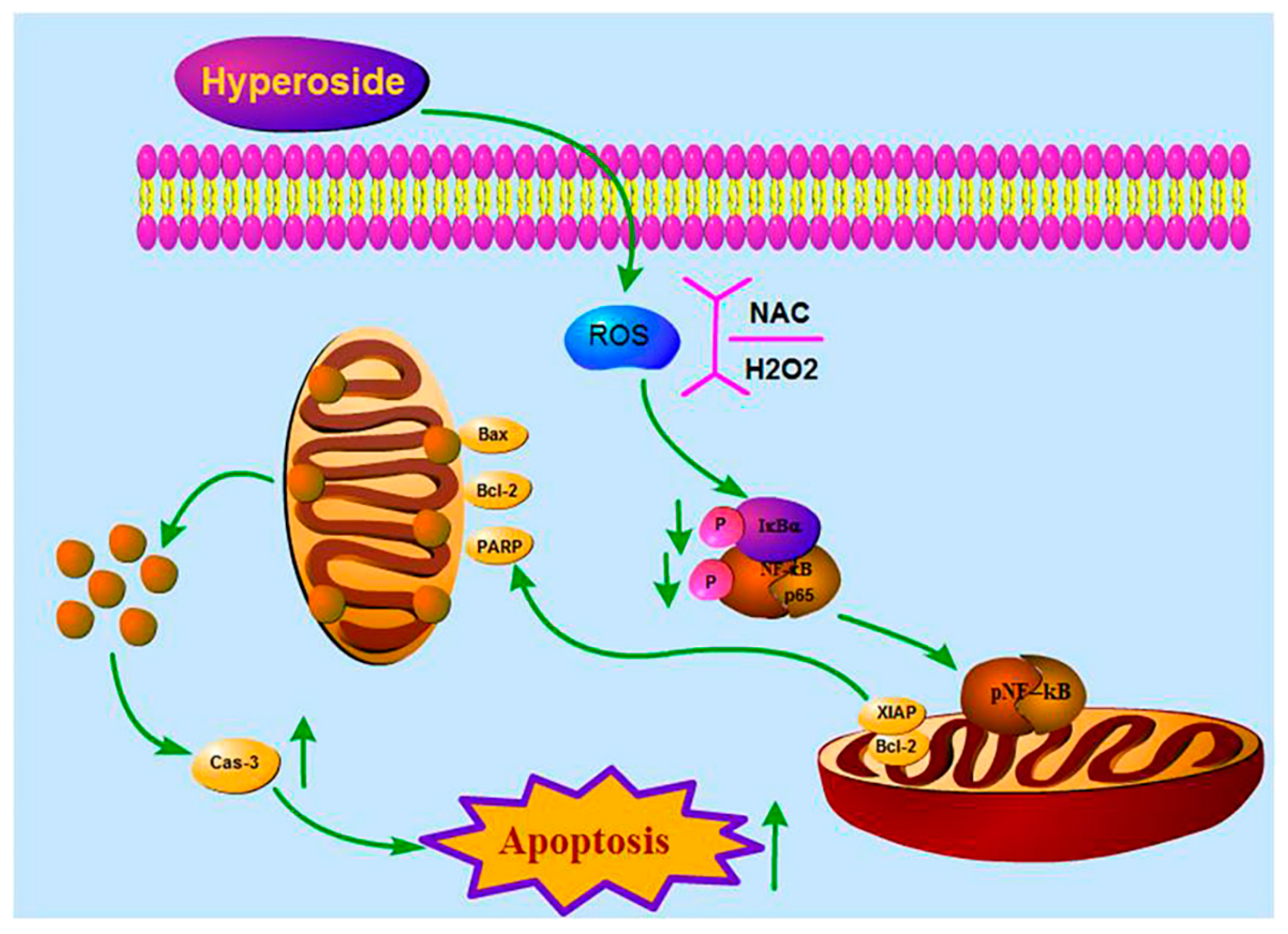
2.3. Hyperoside Induces Apoptosis by Reducing Intracellular ROS Levels
2.4. Hyperoside Inhibits NF-κB Signaling Pathway via ROS
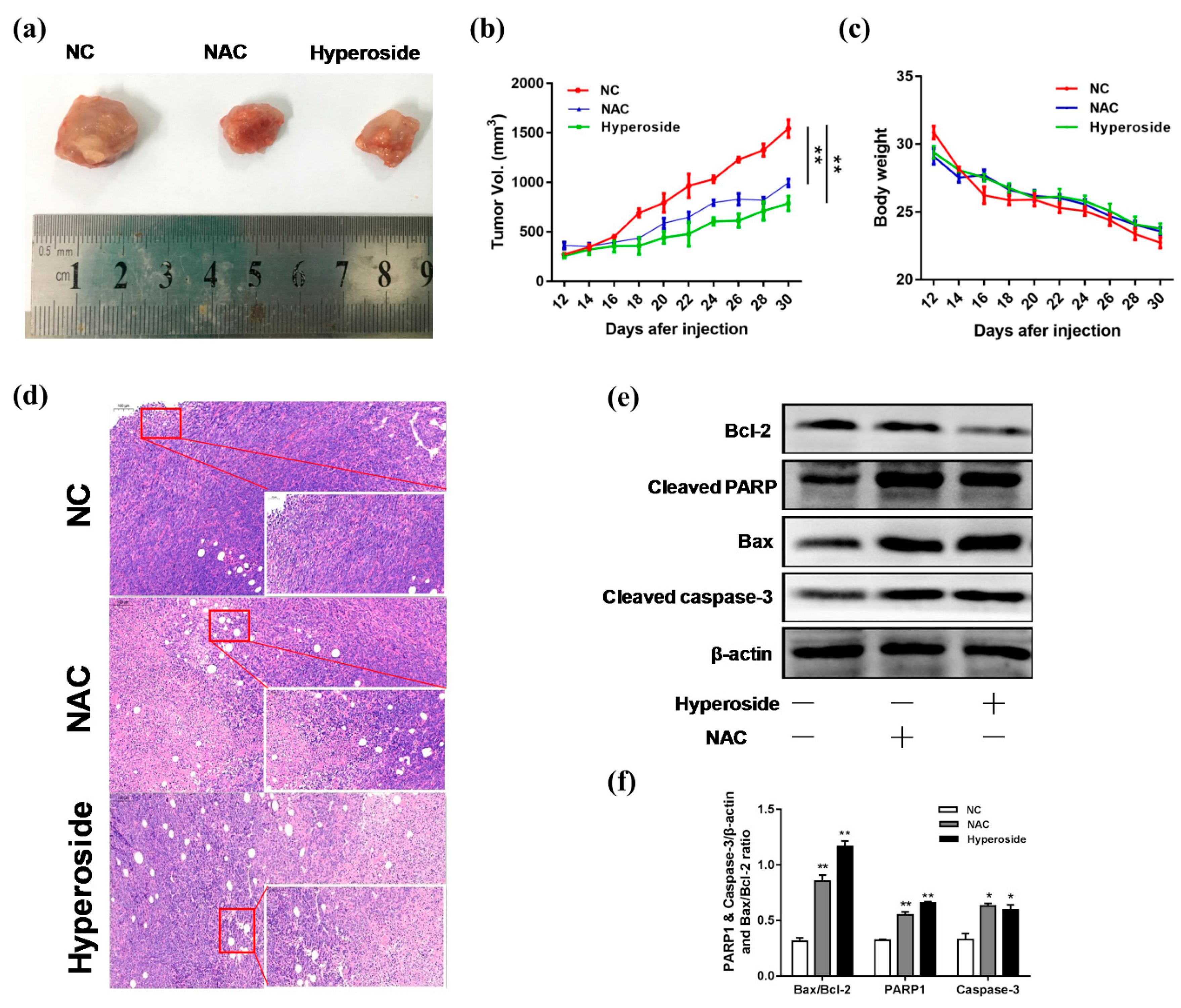
2.5. Hyperoside Can Inhibit the Growth of Breast Tumor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Intracellular ROS Assay
4.5. Apoptosis Assay
4.6. Wound-Healing Migration Assay
4.7. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. In Vivo Experiment
4.11. Histopathological Assessment
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bcl-2 | B cell lymphoma-2 |
| MCF-7 | Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 |
| PI | Propidine iodide |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| NAC | N-acetyl-l-cysteine |
| XIAP | X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time PCR |
| NF-κB | Nuclear transcription factor-κB |
| NC | normal control |
| ERK | extracellular regulated protein kinase |
| Z. bungeanum | Zanthoxylum bungeanum |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohme, S.; Simmons, R.L.; Tsung, A. Surgery for Cancer: A Trigger for Metastases. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bogaard, V.A.B.; van Luijk, P.; Hummel, Y.M.; van der Meer, P.; Schuit, E.; Boerman, L.M.; Maass, S.; Nauta, J.F.; Steggink, L.C.; Gietema, J.A.; et al. Cardiac Function After Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Briaux, A.; Becette, V.; Benoist, C.; Boulai, A.; Chemlali, W.; Schnitzler, A.; Baulande, S.; Rivera, S.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; et al. Molecular profiling of hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancers from patients treated with neoadjuvant endocrine therapy in the CARMINA 02 trial (UCBG-0609). J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J.M.; Peer, D. Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. The role of Chinese medicine in clinical oncology. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checker, R.; Gambhir, L.; Sharma, D.; Kumar, M.; Sandur, S.K. Plumbagin induces apoptosis in lymphoma cells via oxidative stress mediated glutathionylation and inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases (MKP1/2). Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, K.; Wu, H.; Deng, G.; Qiu, C. Sodium selenite induces apoptosis via ROS-mediated NF-kappaB signaling and activation of the Bax-caspase-9-caspase-3 axis in 4T1 cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, J.N.; Cotter, T.G. ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 80, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.H.; Siraj, S.; Arshad, A.; Waheed, U.; Aldakheel, F.; Alduraywish, S.; Arshad, M. ROS-modulated therapeutic approaches in cancer treatment. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1789–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; DeGuzman, A.; Bucana, C.D.; Fidler, I.J. Nuclear factor-kappaB activity correlates with growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis of human melanoma cells in nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Maeda, S. Targeting NF-kappaB for colorectal cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Dai, J.; Keller, E.T.; Giordano, T.; Gu, K.; Shah, V.; Pei, L.; Zarbo, R.J.; et al. NF-kappaB in breast cancer cells promotes osteolytic bone metastasis by inducing osteoclastogenesis via GM-CSF. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, J.; Rychahou, P.G.; Qiu, S.; Evers, B.M.; Zhou, B.P. Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell. 2009, 15, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q.; Gong, C.; Yao, Y.; Lv, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, H.; Su, F.; Li, D.; et al. A cytoplasmic NF-kappaB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IkappaB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2015, 27, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E., Jr.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wei, D. Antioxidant activity of a flavonoid-rich extract of Hypericum perforatum L. in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5032–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Liao, X.H.; Xiang, Y.; Yao, A.; Song, R.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Huang, F.; Dai, Z.T.; Zhang, T.C. Hyperoside and let-7a-5p synergistically inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation via inducing G1/S phase arrest. Gene 2018, 679, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukes, G.J.; van de Venter, M. The apoptotic and autophagic properties of two natural occurring prodrugs, hyperoside and hypoxoside, against pancreatic cancer cell lines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.Q.; Liu, M.; Li, W.; Che, J.P.; Wang, G.C.; Zheng, J.H. Combination of quercetin and hyperoside inhibits prostate cancer cell growth and metastasis via regulation of microRNA21. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Inhibitory effect of hyperoside isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum leaves on SW620 human colorectal cancer cells via induction of the p53 signaling pathway and apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P. Inhibitory effects of hyperoside on lung cancer by inducing apoptosis and suppressing inflammatory response via caspase-3 and NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 82, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Li, S. The effects of hyperoside on apoptosis and the expression of Fas/FasL and survivin in SW579 human thyroid squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ji, M.; Han, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, W.; Gao, F.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C. PGRMC1-dependent autophagy by hyperoside induces apoptosis and sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin treatment. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Han, X.; Piao, M.J.; Oh, M.C.; Fernando, P.M.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Jung, U.; Kim, I.G.; Hyun, J.W. Hyperoside Induces Endogenous Antioxidant System to Alleviate Oxidative Stress. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 21, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xin, W. Matrine inhibiting pancreatic cells epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion through ROS/NF-kappaB/MMPs pathway. Life Sci. 2018, 192, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosiek, T. Systemic treatment of early breast cancer-current state of knowledge after the conference St Gallen 2017. Pol. Merkur. Lekarski. 2017, 43, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Bonofiglio, D.; Giordano, C.; De Amicis, F.; Lanzino, M.; Ando, S. Natural Products as Promising Antitumoral Agents in Breast Cancer: Mechanisms of Action and Molecular Targets. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tantai, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, C.; Li, Z. Effect of hyperoside on the apoptosis of A549 human nonsmall cell lung cancer cells and the underlying mechanism. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6483–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, Y. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in apoptosis: Apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells 1998, 3, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi-Marjaneh, R.; Hassanian, S.M.; Mehramiz, M.; Rezayi, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Khazaei, M.; Avan, A. Reactive oxygen species in colorectal cancer: The therapeutic impact and its potential roles in tumor progression via perturbation of cellular and physiological dysregulated pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 10072–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, F.D.; Zhou, L.; Gong, X.G.; Han, Q.F. Proliferative and anti-proliferative effects of thymosin alpha1 on cells are associated with manipulation of cellular ROS levels. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 180, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fang, L.; Wang, X.; Lan, R.; Wang, M.; Du, G.; Guan, W.; Liu, J.; Brennan, M.; Guo, H.; et al. Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Dietary Flavonoid Hyperoside Using Saccharomyces Cerevisiae as a Model. Molecules 2019, 24, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Liu, J.C.; Hu, J.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, S.W.; Yi, D.H.; Zhao, M.G. Protective effects of hyperoside against human umbilical vein endothelial cell damage induced by hydrogen peroxide. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatoniene, J.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Jakstas, V.; Majiene, D.; Baniene, R.; Kursvietiene, L.; Masteikova, R.; Savickas, A.; Toleikis, A.; Trumbeckaite, S. The effect of Leonurus cardiaca herb extract and some of its flavonoids on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in the heart. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guon, T.E.; Chung, H.S. Hyperoside and rutin of Nelumbo nucifera induce mitochondrial apoptosis through a caspase-dependent mechanism in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2463–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Kong, R.; Pan, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Hyperoside induces apoptosis and inhibits growth in pancreatic cancer via Bcl-2 family and NF-kappaB signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 7345–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakar, A.L.; Tannis, L.L.; Zeindler, C.; Russo, M.P.; Jobin, C.; Park, D.S.; MacPherson, S.; Barker, P.A. Constitutive nuclear factor-kappa B activity is required for central neuron survival. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8466–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarugi, A. Characterization of the molecular events following impairment of NF-kappaB-driven transcription in neurons. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 109, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.A.; Park, D.W.; Sohn, E.H.; Lee, S.R.; Kang, S.C. Hyperoside suppresses tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated vascular inflammatory responses by downregulating mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 294, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′): Forward and Reverse | GenBank Accession Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CAGCTACTCGCGGCTTTAC CCCTGCTTATCCAGTCCTAGC | NM_008084.3 |
| Bax | CTGGATCCAAGACCAGGGTG CCTTTCCCCTTCCCCCATTC | NM_007527.3 |
| Bcl-2 | TCTTTGAGTTCGGTGGGGTC AGTTCCACAAAGGCATCCCAG | NM_009741.5 |
| XIAP | CTGGCCGGACTATGCTCATT CACGATCACAGGGTTCCCAA | NM_001301639.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Ju, B.; Zhou, T.; Deng, G.; Qiu, C. Hyperoside Induces Breast Cancer Cells Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010131
Qiu J, Zhang T, Zhu X, Yang C, Wang Y, Zhou N, Ju B, Zhou T, Deng G, Qiu C. Hyperoside Induces Breast Cancer Cells Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(1):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010131
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Jinxia, Tao Zhang, Xinying Zhu, Chao Yang, Yaxing Wang, Ning Zhou, Bingxin Ju, Tianhong Zhou, Ganzhen Deng, and Changwei Qiu. 2020. "Hyperoside Induces Breast Cancer Cells Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 1: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010131
APA StyleQiu, J., Zhang, T., Zhu, X., Yang, C., Wang, Y., Zhou, N., Ju, B., Zhou, T., Deng, G., & Qiu, C. (2020). Hyperoside Induces Breast Cancer Cells Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010131





