PP2A Functions during Mitosis and Cytokinesis in Yeasts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
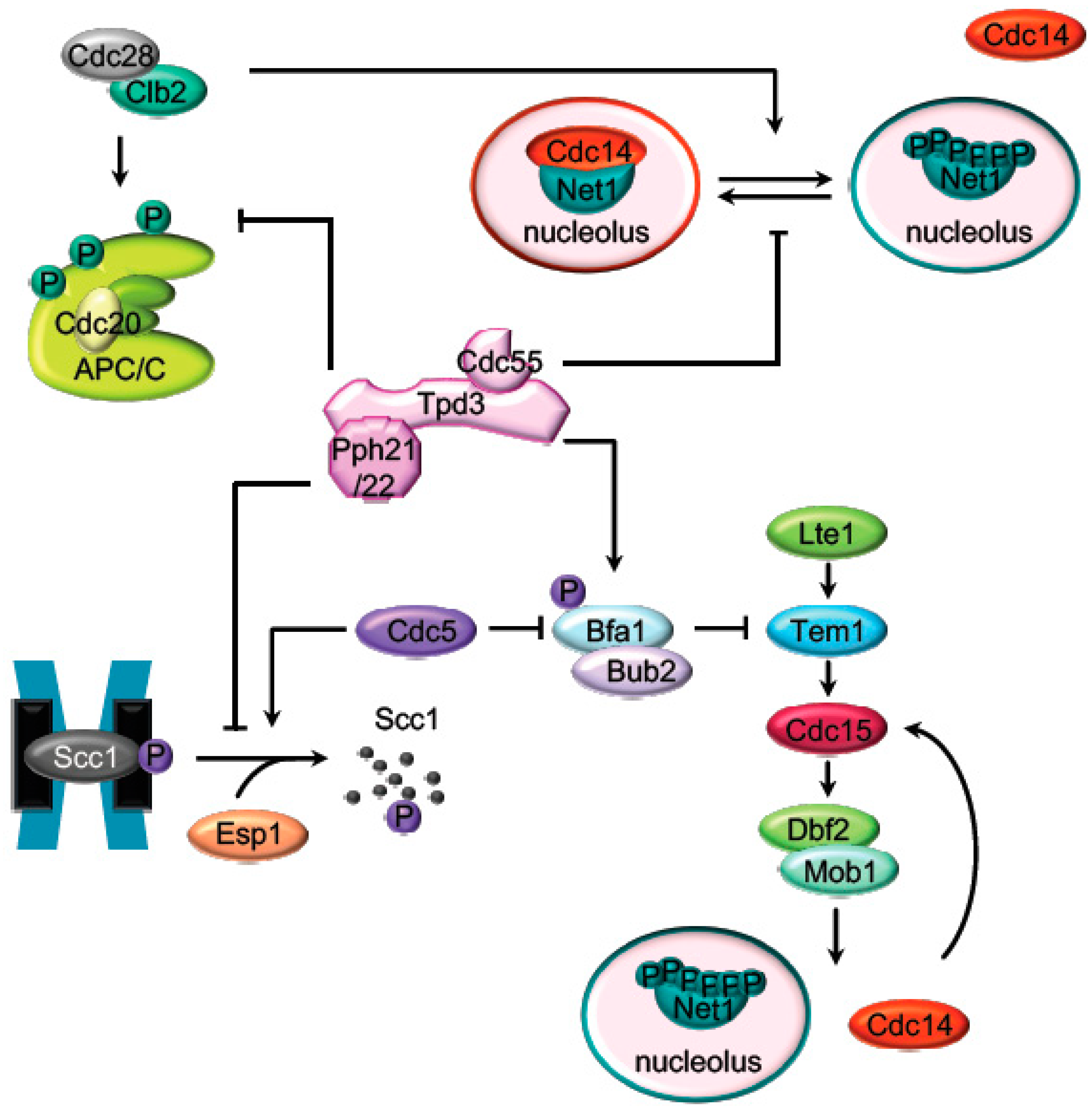
2. Mitosis Exit Regulation by PP2A
2.1. The APC Dephosphorylation by PP2ACdc55
2.2. The Regulation of the Cohesin Cleavage by PP2ACdc55
2.3. The FEAR-Cdc14 Release by PP2ACdc55
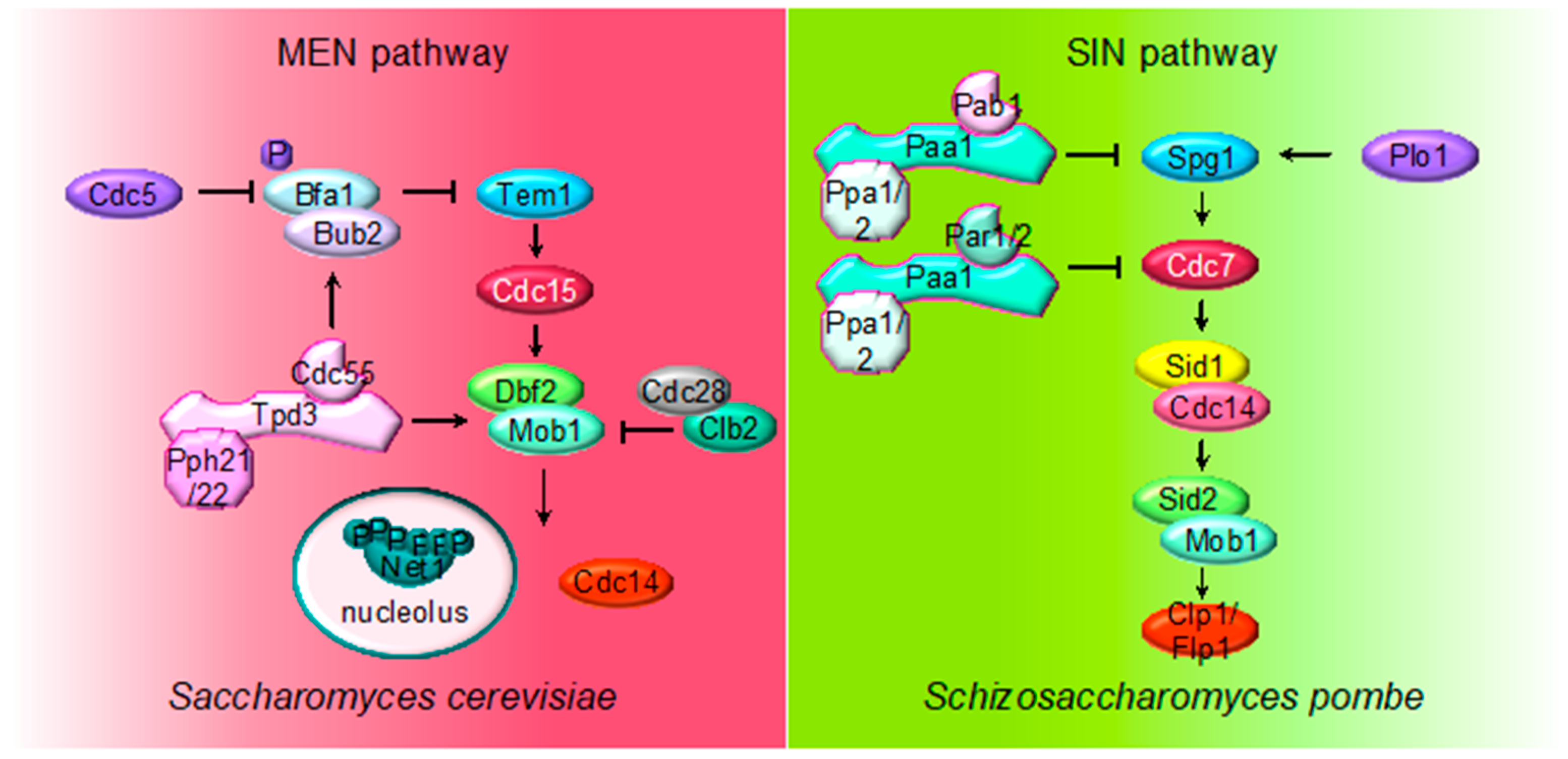
2.4. MEN (SIN) Regulation by PP2A
3. The Role of PP2A in Cytokinesis
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wlodarchak, N.; Xing, Y. PP2A as a master regulator of the cell cycle. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariño, J.; Velázquez, D.; Casamayor, A. Ser/Thr protein phosphatases in fungi: Structure, regulation and function. Microb. Cell (Graz, Austria) 2019, 6, 217–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, K.; Nemoto, T.; Nabeshima, K.; Kondoh, H.; Niwa, H.; Yanagida, M. The regulatory subunits of fission yeast protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) affect cell morphogenesis, cell wall synthesis and cytokinesis. Genes Cells 1996, 1, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, A.M.; Zolnierowicz, S.; Stapleton, A.E.; Goebl, M.; DePaoli-Roach, A.A.; Pringle, J.R. CDC55, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in cellular morphogenesis: Identification, characterization, and homology to the B subunit of mammalian type 2A protein phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5767–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Mui, M.Z.; Chan, F.; Roopchand, D.E.; Marcellus, R.C.; Blanchette, P.; Li, S.; Berghuis, A.M.; Branton, P.E. Genetic Analysis of B55 /Cdc55 Protein Phosphatase 2A Subunits: Association with the Adenovirus E4orf4 Protein. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Boguslawski, G.; Zitomer, R.S.; DePaoli-Roach, A.A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Homologs of Mammalian B and B’ Subunits of Protein Phosphatase 2A Direct the Enzyme to Distinct Cellular Functions. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 8256–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, Y.; Yang, H.; Hallberg, E.; Hallberg, R. Molecular genetic analysis of Rts1p, a B’ regulatory subunit of Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 2A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 3242–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gentry, M.S.; Hallberg, R.L. Localization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase 2A subunits throughout mitotic cell cycle. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 3477–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahoz, A.; Alcaide-Gavilan, M.; Daga, R.R.; Jimenez, J. Antagonistic roles of PP2A-Pab1 and Etd1 in the control of cytokinesis in fission yeast. Genetics 2010, 186, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Goff, X.; Buvelot, S.; Salimova, E.; Guerry, F.; Schmidt, S.; Cueille, N.; Cano, E.; Simanis, V. The protein phosphatase 2A B′-regulatory subunit par1p is implicated in regulation of the S. Pombe septation initiation network. FEBS Lett. 2001, 508, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Hallberg, R.L. Isolation and characterization of par1+ and par2+: Two schizosaccharomyces pombe genes encoding B’ subunits of protein phosphatase 2A. Genetics 2000, 154, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Tolstykh, T.; Lee, J.; Boyd, K.; Stock, J.B.; Broach, J.R. Carboxyl methylation of the phosphoprotein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit promotes its functional association with regulatory subunits in vivo. Embo J. 2000, 19, 5672–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.; Ashby, D.G.; Moreno, C.S.; Ogris, E.; Yeong, F.M.; Corbett, A.H.; Pallas, D.C. Carboxymethylation of the PP2A Catalytic Subunit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Is Required for Efficient Interaction with the B-type Subunits Cdc55p and Rts1p. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yabe, R.; Tsuji, S.; Mochida, S.; Ikehara, T.; Usui, T.; Ohama, T.; Sato, K. A stable association with PME-1 may be dispensable for PP2A demethylation–implications for the detection of PP2A methylation and immunoprecipitation. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabe, R.; Miura, A.; Usui, T.; Mudrak, I.; Ogris, E.; Ohama, T.; Sato, K. Protein phosphatase methyl-esterase PME-1 protects protein phosphatase 2A from ubiquitin/proteasome degradation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Játiva, S.; Calabria, I.; Moyano-Rodriguez, Y.; Garcia, P.; Queralt, E. Cdc14 activation requires coordinated Cdk1-dependent phosphorylation of Net1 and PP2A–Cdc55 at anaphase onset. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3601–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y. Regulation of the Cell Cycle by Protein Phosphatase 2A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Queralt, E.; Uhlmann, F. Cdk-counteracting phosphatases unlock mitotic exit. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008, 20, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stegmeier, F.; Amon, A. Closing mitosis: The functions of the Cdc14 phosphatase and its regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2004, 38, 203–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundell, M.J.; Hutter, L.H.; Bastos, R.N.; Poser, E.; Holder, J.; Mohammed, S.; Novak, B.; Barr, F.A. A PP2A-B55 recognition signal controls substrate dephosphorylation kinetics during mitotic exit. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, M.H.A.; Held, M.; Janssens, V.; Hutchins, J.R.A.; Hudecz, O.; Ivanova, E.; Goris, J.; Trinkle-Mulcahy, L.; Lamond, A.I.; Poser, I.; et al. Live-cell imaging RNAi screen identifies PP2A-B55alpha and importin-beta1 as key mitotic exit regulators in human cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manchado, E.; Guillamot, M.; de Cárcer, G.; Eguren, M.; Trickey, M.; García-Higuera, I.; Moreno, S.; Yamano, H.; Cañamero, M.; Malumbres, M. Targeting Mitotic Exit Leads to Tumor Regression In Vivo: Modulation by Cdk1, Mastl, and the PP2A/B55α,δ Phosphatase. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mochida, S.; Ikeo, S.; Gannon, J.; Hunt, T. Regulated activity of PP2A-B55 is crucial for controlling entry into and exit from mitosis in Xenopus egg extracts. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touati, S.A.; Hofbauer, L.; Jones, A.W.; Snijders, A.P.; Kelly, G.; Uhlmann, F. Cdc14 and PP2A Phosphatases Cooperate to Shape Phosphoproteome Dynamics during Mitotic Exit. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2105–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queralt, E.; Lehane, C.; Novak, B.; Uhlmann, F. Downregulation of PP2ACdc55 Phosphatase by Separase Initiates Mitotic Exit in Budding Yeast. Cell 2006, 125, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lianga, N.; Williams, E.C.; Kennedy, E.K.; Doré, C.; Pilon, S.; Girard, S.L.; Deneault, J.S.; Rudner, A.D. A wee1 checkpoint inhibits anaphase onset. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapata, J.; Dephoure, N.; Macdonough, T.; Yu, Y.; Parnell, E.J.; Mooring, M.; Gygi, S.P.; Stillman, D.J.; Kellogg, D.R. PP2ARts1 is a master regulator of pathways that control cell size. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peplowska, K.; Wallek, A.U.; Storchova, Z. Sgo1 Regulates Both Condensin and Ipl1/Aurora B to Promote Chromosome Biorientation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobbelaere, J.; Gentry, M.S.; Hallberg, R.L.; Barral, Y. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of septin dynamics during the cell cycle. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherwin, D.; Wang, Y. The Opposing Functions of Protein Kinases and Phosphatases in Chromosome Bipolar Attachment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Hsiao, J.Y.; Davey, N.E.; van Voorhis, V.A.; Foster, S.A.; Tang, C.; Morgan, D.O. Multiple mechanisms determine the order of APC/C substrate degradation in mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 207, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, M.; Morgan, D.O. Finishing mitosis, one step at a time. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Fix, O.; Peters, J.M.; Kirschner, M.W.; Koshland, D. Anaphase initiation in saccharomyces cerevisiae is controlled by the APC-dependent degradation of the anaphase inhibitor Pds1p. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilioti, Z.; Chung, Y.S.; Mochizuki, Y.; Hardy, C.F.J.; Cohen-Fix, O. The anaphase inhibitor Pds1 binds to the APC/C-associated protein Cdc20 in a destruction box-dependent manner. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, H.H.; Goh, P.Y.; Surana, U. Cdc20 is essential for the cyclosome-mediated proteolysis of both Pds1 and Clb2 during M phase in budding yeast. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, M.; Uhlmann, F. A non-proteolytic function of separase links the onset of anaphase to mitotic exit. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, F.; Wernic, D.; Poupart, M.A.; Koonin, E.V.; Nasmyth, K. Cleavage of cohesin by the CD clan protease separin triggers anaphase in yeast. Cell 2000, 103, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirchenko, L.; Uhlmann, F. Sli15INCENP dephosphorylation prevents mitotic checkpoint reengagement due to loss of tension at anaphase onset. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teichner, A.; Eytan, E.; Sitry-Shevah, D.; Miniowitz-Shemtov, S.; Dumin, E.; Gromis, J.; Hershko, A. p31comet Promotes disassembly of the mitotic checkpoint complex in an ATP-dependent process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3187–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossio, V.; Michimoto, T.; Sasaki, T.; Ohbayashi, I.; Kikuchi, Y.; Yoshida, S. Nuclear PP2A-Cdc55 prevents APC-Cdc20 activation during the spindle assembly checkpoint. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 4396–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yellman, C.M.; Burke, D.J. The role of Cdc55 in the spindle checkpoint is through regulation of mitotic exit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudner, A.D.; Murray, A.W. Phosphorylation by Cdc28 activates the Cdc20-dependent activity of the anaphase-promoting complex. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 1377–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vernieri, C.; Chiroli, E.; Francia, V.; Gross, F.; Ciliberto, A. Adaptation to the spindle checkpoint is regulated by the interplay between Cdc28/Clbs and PP2ACdc55. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Burke, D.J. Cdc55p, the B-type regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, has multiple functions in mitosis and is required for the kinetochore/spindle checkpoint in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ng, T.-Y.Y. Phosphatase 2A negatively regulates mitotic exit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokros, M.; Wang, Y. Spindle assembly checkpoint silencing and beyond. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1661–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaakov, G.; Thorn, K.; Morgan, D.O. Separase Biosensor Reveals that Cohesin Cleavage Timing Depends on Phosphatase PP2ACdc55 Regulation. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlmann, F.; Lottspeich, F.; Nasmyth, K.; Lottspelch, F.; Nasmyth, K.; Lottspeich, F.; Nasmyth, K. Sister-chromatid separation at anaphase onset is promoted by cleavage of the cohesin subunit Scc1. Nature 1999, 400, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakchuen, S.; Ishibashi, M.; Takakusagi, E.; Shirahige, K.; Sutani, T. Physical association of saccharomyces cerevisiae polo-like kinase cdc5 with chromosomal cohesin facilitates DNA damage response. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17228–17246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandru, G.; Uhlmann, F.; Mechtler, K.; Poupart, M.-A.A.; Nasmyth, K. Phosphorylation of the cohesin subunit Scc1 by Polo/Cdc5 kinase regulates sister chromatid separation in yeast. Cell 2001, 105, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornig, N.C.; Uhlmann, F. Preferential cleavage of chromatin-bound cohesin after targeted phosphorylation by Polo-like kinase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3144–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Wang, Y. Pds1/Esp1-dependent and -independent sister chromatid separation in mutants defective for protein phosphatase 2A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16290–16295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azzam, R.; Chen, S.L.; Shou, W.; Mah, A.S.; Alexandru, G.; Nasmyth, K.; Annan, R.S.; Carr, S.A.; Deshaies, R.J. Phosphorylation by cyclin B-Cdk underlies release of mitotic exit activator Cdc14 from the nucleolus. Science 2004, 305, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shou, W.; Azzam, R.; Chen, S.L.; Huddleton, M.J.; Baskerville, C.; Charbonneau, H.; Annan, R.S.; Carr, S.A.; Deshaies, R.J.; Huddleston, M.J.; et al. Cdc5 influences phosphorylation of Net1 and disassembly of the RENT complex. BMC Mol. Biol. 2002, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, J.A.; Moyano, Y.; Játiva, S.; Queralt, E. Mitotic Exit Function of Polo-like Kinase Cdc5 Is Dependent on Sequential Activation by Cdk1. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calabria, I.; Baro, B.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, J.-A.; Russiñol, N.; Queralt, E. Zds1 regulates PP2ACdc55 activity and Cdc14 activation during mitotic exit through its Zds_C motif. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De los Santos-Velázquez, A.I.; de Oya, I.G.; Manzano-López, J.; Monje-Casas, F. Late rDNA Condensation Ensures Timely Cdc14 Release and Coordination of Mitotic Exit Signaling with Nucleolar Segregation. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 3248–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queralt, E.; Uhlmann, F. Separase cooperates with Zds1 and Zds2 to activate Cdc14 phosphatase in early anaphase. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stegmeier, F.; Huang, J.; Rahal, R.; Zmolik, J.; Moazed, D.; Amon, A. The replication fork block protein Fob1 functions as a negative regulator of the FEAR network. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stegmeier, F.; Visintin, R.; Amon, A. Separase, Polo Kinase, the Kinetochore Protein Slk19, and Spo12 Function in a Network that Controls Cdc14 Localization during Early Anaphase. Cell 2002, 108, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomson, B.N.; Rahal, R.; Reiser, V.; Monje-Casas, F.; Mekhail, K.; Moazed, D.; Amon, A. Regulation of Spo12 phosphorylation and its essential role in the FEAR network. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nolt, J.K.; Rice, L.M.; Gallo-Ebert, C.; Bisher, M.E.; Nickels, J.T. PP2ACdc55 is required for multiple events during meiosis I. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1420–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerr, G.W.; Sarkar, S.; Tibbles, K.L.; Petronczki, M.; Millar, J.B.A.; Arumugam, P. Meiotic nuclear divisions in budding yeast require PP2A Cdc55-mediated antagonism of Net1 phosphorylation by Cdk. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bizzari, F.; Marston, A.L. Cdc55 coordinates spindle assembly and chromosome disjunction during meiosis. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.W.; Wong, J.H.; Arumugam, P. PP2ACdc55′s role in reductional chromosome segregation during achiasmate meiosis in budding yeast is independent of its FEAR function. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baro, B.; Queralt, E.; Monje-Casas, F. Regulation of mitotic exit in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1505, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, A.S.; Jang, J.; Deshaies, R.J. Protein kinase Cdc15 activates the Dbf2-Mob1 kinase complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7325–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visintin, R.; Amon, A. Regulation of the mitotic exit protein kinases Cdc15 and Dbf2. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 2961–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, S.; Toh-e, A. Regulation of the localization of Dbf2 and mob1 during cell division of saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Genet. Syst. 2001, 76, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baro, B.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, J.-A.; Calabria, I.; Hernáez, M.L.; Gil, C.; Queralt, E. Dual Regulation of the Mitotic Exit Network (MEN) by PP2A-Cdc55 Phosphatase. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geymonat, M.; Spanos, A.; Walker, P.A.; Johnston, L.H.; Sedgwick, S.G. In vitro regulation of budding yeast Bfa1/Bub2 GAP activity by Cdc5. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14591–14594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Qin, J.; Elledge, S.J. Regulation of the Bub2/Bfa1 GAP complex by Cdc5 and cell cycle checkpoints. Cell 2001, 107, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asakawa, K.; Yoshida, S.; Otake, F.; Toh-e, A. A novel functional domain of Cdc15 kinase is required for its interaction with Tem1 GTPase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 2001, 157, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Visintin, R.; Hwang, E.S.; Amon, A. Cfi 1 prevents premature exit from mitosis by anchoring Cdc14 phosphatase in the nucleolus. Nature 1999, 398, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohl, D.A.; Huddleston, M.J.; Collingwood, T.S.; Annan, R.S.; Deshaies, R.J. Dbf2-Mob1 drives relocalization of protein phosphatase Cdc14 to the cytoplasm during exit from mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- König, C.; Maekawa, H.; Schiebel, E.; Konig, C.; Maekawa, H.; Schiebel, E. Mutual regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase and the mitotic exit network. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruneberg, U.; Campbell, K.; Simpson, C.; Grindlay, J.; Schiebel, E. Nud1p links astral microtubule organization and the control of exit from mitosis. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6475–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cenamor, R.; Jiménez, J.; Cid, V.J.; Nombela, C.; Sanchez, M.; Jimenez, J.; Cid, V.J.; Nombela, C.; Sanchez, M.; Jiménez, J.; et al. The budding yeast Cdc 15 localizes to the spindle pole body in a cell-cycle-dependent manner. Mol. Cell. Biol. Res. Commun. 1999, 2, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspersen, S.L.; Morgan, D.O. Cdc14 activates cdc15 to promote mitotic exit in budding yeast. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.; Huang, H.K.; Kaiser, P.; Latterich, M.; Hunter, T. Phosphorylation and spindle pole body localization of the Cdc15p mitotic regulatory protein kinase in budding yeast. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menssen, R.; Neutzner, A.; Seufert, W. Asymmetric spindle pole localization of yeast Cdc15 kinase links mitotic exit and cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Aquino, K.E.; Monje-Casas, F.; Paulson, J.; Reiser, V.; Charles, G.M.; Lai, L.; Shokat, K.M.; Amon, A. The protein kinase Kin4 inhibits exit from mitosis in response to spindle position defects. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertazzi, D.T.; Kurtulmus, B.; Pereira, G. The cortical protein Lte1 promotes mitotic exit by inhibiting the spindle position checkpoint kinase Kin4. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falk, J.E.; Chan, L.Y.; Amon, A. Lte1 promotes mitotic exit by controlling the localization of the spindle position checkpoint kinase Kin4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12584–12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maekawa, H.; Priest, C.; Lechner, J.; Pereira, G.; Schiebel, E. The yeast centrosome translates the positional information of the anaphase spindle into a cell cycle signal. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, G.; Schiebel, E. Kin4 kinase delays mitotic exit in response to spindle alignment defects. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.Y.; Amon, A. The protein phosphatase 2A functions in the spindle position checkpoint by regulating the checkpoint kinase Kin4. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falk, J.E.; Campbell, I.W.; Joyce, K.; Whalen, J.; Seshan, A.; Amon, A. LTE1 promotes exit from mitosis by multiple mechanisms. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 3991–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simanis, V. Pombe’s thirteen - control of fission yeast cell division by the septation initiation network. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Hallberg, R.L. Correct regulation of the septation initiation network in Schizosaccharomyces pombe requires the activities of par1 and par2. Genetics 2001, 158, 1413–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.S.; Shao, N.; McLean, J.R.; Sevugan, M.; Ren, L.; Chew, T.G.; Bimbo, A.; Sharma, R.; Tang, X.; Gould, K.L.; et al. SIN-inhibitory phosphatase complex promotes Cdc11p dephosphorylation and propagates SIN asymmetry in fission yeast. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1968–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grallert, A.; Boke, E.; Hagting, A.; Hodgson, B.; Connolly, Y.; Griffiths, J.R.; Smith, D.L.; Pines, J.; Hagan, I.M. A PP1-PP2A phosphatase relay controls mitotic progression. Nature 2014, 517, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bardin, A.J.; Amon, A. Men and sin: What’s the difference? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meitinger, F.; Palani, S.; Pereira, G. The power of MEN in cytokinesis. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luca, F.C.; Mody, M.; Kurischko, C.; Roof, D.M.; Giddings, T.H.; Winey, M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mob1p Is Required for Cytokinesis and Mitotic Exit. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 6972–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frenz, L.M.; Lee, S.E.; Fesquet, D.; Johnston, L.H. The budding yeast Dbf2 protein kinase localises to the centrosome and moves to the bud neck in late mitosis. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 19, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Grenfell, T.Z.; Garfield, S.; Erikson, R.L.; Lee, K.S. Essential Function of the Polo Box of Cdc5 in Subcellular Localization and Induction of Cytokinetic Structures. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Q.-W.; Zhou, M.; Bimbo, A.; Balasubramanian, M.K.; McCollum, D. A role for the septation initiation network in septum assembly revealed by genetic analysis of sid2-250 suppressors. Genetics 2006, 172, 2101–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hachet, O.; Simanis, V. Mid1p/anillin and the septation initiation network orchestrate contractile ring assembly for cytokinesis. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 3205–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Yu, K.; Hao, Y.; Li, D.M.; Stewart, R.; Insogna, K.L.; Xu, T. LATS1 tumour suppressor affects cytokinesis by inhibiting LIMK1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palani, S.; Meitinger, F.; Boehm, M.E.; Lehmann, W.D.; Pereira, G. Cdc14-dependent dephosphorylation of Inn1 contributes to Inn1-Cyk3 complex formation. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3091–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, D.P.; Hall, H.; Chaparian, R.; Mara, M.; Mueller, A.; Hall, M.C.; Shannon, K.B. Dephosphorylation of Iqg1 by Cdc14 regulates cytokinesis in budding yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuilman, T.; Maiolica, A.; Godfrey, M.; Scheidel, N.; Aebersold, R.; Uhlmann, F. Identification of Cdk targets that control cytokinesis. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devrekanli, A.; Foltman, M.; Roncero, C.; Sanchez-Diaz, A.; Labib, K. Inn1 and Cyk3 regulate chitin synthase during cytokinesis in budding yeasts. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5453–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baro, B.; Játiva, S.; Calabria, I.; Vinaixa, J.; Bech-Serra, J.J.; De LaTorre, C.; Rodrigues, J.; Hernáez, M.L.; Gil, C.; Barceló-Batllori, S.; et al. SILAC-based phosphoproteomics reveals new PP2A-Cdc55-regulated processes in budding yeast. Gigascience 2018, 7, giy047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parnell, E.J.; Yu, Y.; Lucena, R.; Yoon, Y.; Bai, L.; Kellogg, D.R.; Stillman, D.J. The rts1 regulatory subunit of PP2A phosphatase controls expression of the ho endonuclease via localization of the Ace2 transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35431–35437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovacech, B.; Nasmyth, K.; Schuster, T. EGT2 gene transcription is induced predominantly by Swi5 in early G1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 3264–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Conalláin, C.; Doolin, M.T.; Taggart, C.; Thornton, F.; Butler, G. Regulated nuclear localisation of the yeast transcription factor Ace2p controls expression of chitinase (CTS1) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1999, 262, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, E.; Váchová, L.; Palková, Z. Cellular localization of Sun4p and its interaction with proteins in the yeast birth scar. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcaide-Gavilán, M.; Lahoz, A.; Daga, R.R.; Jimenez, J. Feedback regulation of SIN by Etd1 and Rho1 in fission yeast. Genetics 2014, 196, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, P.; Zheng, S.; Lu, L. Mitotic-spindle organizing protein MztA mediates septation signaling by suppressing the regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A-ParA in Aspergillus nidulans. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Pan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Sang, J. The PP2A regulatory subunits, Cdc55 and Rts1, play distinct roles in Candida albicans’ growth, morphogenesis, and virulence. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2019, 131, 103240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Han, Q.; Wang, N.; Yao, G.; Zeng, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Sang, J.; Wang, Y. Tpd3-Pph21 phosphatase plays a direct role in Sep7 dephosphorylation in Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Muñiz, J.M.; Renshaw, H.; Richards, A.D.; Waitt, G.; Soderblom, E.J.; Moseley, M.A.; Asfaw, Y.; Juvvadi, P.R.; Steinbach, W.J. Dephosphorylation of the Core Septin, AspB, in a Protein Phosphatase 2A-Dependent Manner Impacts Its Localization and Function in the Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, G.; Jiang, P.; Qiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Lu, L. Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulatory subunits ParA and PabA orchestrate septation and conidiation and are essential for PP2A activity in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moyano-Rodriguez, Y.; Queralt, E. PP2A Functions during Mitosis and Cytokinesis in Yeasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010264
Moyano-Rodriguez Y, Queralt E. PP2A Functions during Mitosis and Cytokinesis in Yeasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(1):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010264
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoyano-Rodriguez, Yolanda, and Ethel Queralt. 2020. "PP2A Functions during Mitosis and Cytokinesis in Yeasts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 1: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010264
APA StyleMoyano-Rodriguez, Y., & Queralt, E. (2020). PP2A Functions during Mitosis and Cytokinesis in Yeasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(1), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010264




