The Influence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Digestive and Extra-Intestinal Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Relationships between SIBO and Other Diseases
2.1. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
2.2. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
2.3. Celiac Disease
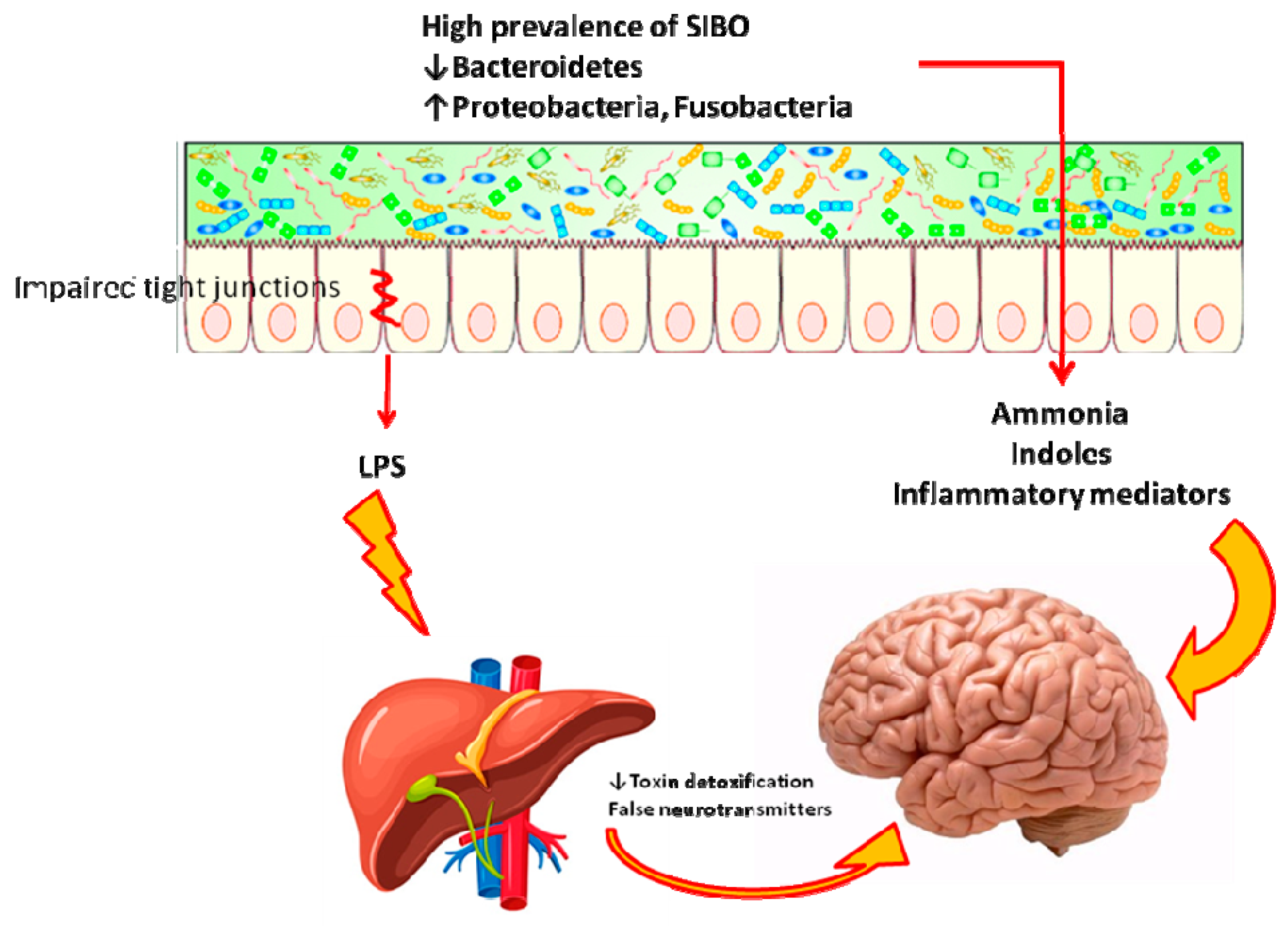
2.4. Hepatic Encephalopathy
2.5. Obesity and Related Diseases
2.6. Rheumatologic Diseases
2.7. Dermatologic Diseases
2.8. Parkinson Disease
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bures, J.; Cyrany, J.; Kohoutova, D.; Förstl, M.; Rejchrt, S.; Kvetina, J.; Vorisek, V.; Kopacova, M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebye, E. The pathogenesis of gastrointestinal bacterial overgrowth. Chemotherapy 2005, 51 (Suppl. 1), 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibiino, G.; Ianiro, G.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A. The gut microbiota: Its anatomy and physiology over a lifetime. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2017, 63, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaie, A.; Pimentel, M.; Rao, S.S. How to test and treat small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: An evidence-based approach. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losurdo, G.; Leandro, G.; Ierardi, E.; Perri, F.; Barone, M.; Principi, M.; Di Leo, A. Breath Tests for the Non-invasive Diagnosis of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gasbarrini, A.; Corazza, G.R.; Gasbarrini, G. Methodology and indications of H2-breath testing in gastrointestinal diseases: The Rome Consensus Conference. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29 (Suppl. 1), 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, J.; Sinha, S.K.; Singh, K. Comparison of lactulose and glucose breath test for diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Digestion 2012, 85, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpellini, E.; Giorgio, V.; Gabrielli, M.; Lauritano, E.C.; Pantanella, A.; Fundarò, C.; Gasbarrini, A. Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in children with irritable bowel syndrome: A case-control study. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Yu, J.H.; Lim, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, Y.H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.I. Usefulness of lactulose breath test for the prediction of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 56, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lupascu, A.; Gabrielli, M.; Lauritano, E.C.; Scarpellini, E.; Santoliquido, A.; Cammarota, G.; Flore, R.; Tondi, P.; Pola, P.; Gasbarrini, G.; et al. Hydrogen glucose breath test to detect small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: A prevalence case-control study in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Talley, N.J.; Jones, M.; Kendall, B.J.; Koloski, N.; Walker, M.M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddymasu, S.C.; Sostarich, S.; McCallum, R.W. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in irritable bowel syndrome: Are there any predictors? BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.V.; Toskes, P.P. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth: Presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2004, 7, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Srivastava, D.; Ghoshal, U.; Misra, A. Breath tests in the diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with irritable bowel syndrome in comparison with quantitative upper gut aspirate culture. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, B.M.; Chey, W.D.; Chang, L. Bacterial overgrowth and irritable bowel syndrome: Unifying hypothesis or a spurious consequence of proton pump inhibitors? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2972–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choung, R.S.; Ruff, K.C.; Malhotra, A.; Herrick, L.; Locke, G.R., 3rd; Harmsen, W.S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Talley, N.J.; Saito, Y.A. Clinical predictors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth by duodenal aspirate culture. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasbarrini, A.; Scarpellini, E.; Gabrielli, M.; Tortora, A.; Purchiaroni, F.; Ojetti, V. Clinical predictors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth by duodenal aspirate culture. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1378–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haderstorfer, B.; Psycholgin, D.; Whitehead, W.E.; Schuster, M.M. Intestinal gas production from bacterial fermentation of undigested carbohydrate in irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1989, 84, 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Pimentel, M.; Lembo, A.; Chey, W.D.; Zakko, S.; Ringel, Y.; Yu, J.; Mareya, S.M.; Shaw, A.L.; Bortey, E.; Forbes, W.P. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatta, L.; Scarpignato, C. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Rifaximin is effective and safe for the treatment of small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Morrison, M.; Burger, D.; Martin, N.; Rich, J.; Jones, M.; Koloski, N.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.; Holtmann, G.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Malik, A.; Kaur, J.; Prasad, K.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Singh, K. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and orocecal transit time in patients of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 2594–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Mekelburg, S.; Tafesh, Z.; Coburn, E.; Weg, R.; Malik, N.; Webb, C.; Hammad, H.; Scherl, E.; Bosworth, B.P. Testing and Treating Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Reduces Symptoms in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chachu, K.A.; Osterman, M.T. How to Diagnose and Treat IBD Mimics in the Refractory IBD Patient Who Does Not Have IBD. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricci, J.E.R.; Chebli, L.A.; Ribeiro, T.C.d.R.; Castro, A.C.S.; Gaburri, P.D.; Pace, F.H.d.L.; Barbosa, K.V.B.D.; Ferreira, L.E.V.V.d.C.; Passos, M.d.C.F.; Malaguti, C.; et al. Small-Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth is Associated with Concurrent Intestinal Inflammation But Not with Systemic Inflammation in Crohn’s Disease Patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Colombel, J.F.; Shin, A.; Gibson, P.R. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 380–390.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Brignolo, P.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Reggiani, S.; Sguazzini, C.; Smedile, A.; Pellicano, R.; Resegotti, A.; Astegiano, M.; et al. Glucose breath test and Crohn’s disease: Diagnosis of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and evaluation of therapeutic response. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Catassi, C. Clinical practice. Celiac disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, E.; Losurdo, G.; Iannone, A.; Piscitelli, D.; Amoruso, A.; Barone, M.; Principi, M.; Pisani, A.; Di Leo, A. Lymphocytic duodenitis or microscopic enteritis and gluten-related conditions: What needs to be explored? Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.M.; Kelleher, D. Refractory celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, K.D.; Meyer, R.L.; Lee, E.L. The prevalence and causes of chronic diarrhea in patients with celiac sprue treated with a gluten-free diet. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassotti, G.; Castellucci, G.; Betti, C.; Fusaro, C.; Cavalletti, M.L.; Bertotto, A.; Spinozzi, F.; Morelli, A.; Pelli, M.A. Abnormal gastrointestinal motility in patients with celiac sprue. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1994, 39, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraquelli, M.; Bardella, M.T.; Peracchi, M.; Cesana, B.M.; Bianchi, P.A.; Conte, D. Gallbladder emptying and somatostatin and cholecystokinin plasma levels in celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardella, M.T.; Fraquelli, M.; Peracchi, M.; Cesana, B.M.; Bianchi, P.A.; Conte, D. Gastric emptying and plasma neurotensin levels in untreated celiac patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Remes-Troche, J.M.; Adames, K.; Castillo-Rodal, A.I.; Ramírez, T.; Barreto-Zuñiga, R.; López-Vidal, Y.; Uscanga, L.F. Intraepithelial gammadelta+ lymphocytes: A comparative study between celiac disease, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, and irritable bowel syndrome. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2007, 41, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.D.; Jia, L.; Edelblum, K.L. Policing the intestinal epithelial barrier: Innate immune functions of intraepithelial lymphocytes. Curr. Pathobiol Rep. 2018, 6, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, A.; Brandimarte, G.; Giorgetti, G. High prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in celiac patients with persistence of gastrointestinal symptoms after gluten withdrawal. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Ghoshal, U.; Misra, A.; Choudhuri, G. Partially responsive celiac disease resulting from small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and lactose intolerance. BMC Gastroenterol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdulkarim, A.S.; Burgart, L.J.; See, J.; Murray, J.A. Etiology of nonresponsive celiac disease: Results of a systematic approach. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2016–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, P.D.; Evans, K.E.; Sanders, D.S. Letter: Coeliac disease and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth--is dysmotility the missing link? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Barton, S.H.; Rosenblatt, J.E.; Murray, J.A. Prevalence of small intestine bacterial overgrowth diagnosed by quantitative culture of intestinal aspirate in celiac disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, M.S.; Minaya, M.T.; Cheng, J.; Connor, B.A.; Lewis, S.K.; Green, P.H. Double-blind randomized controlled trial of rifaximin for persistent symptoms in patients with celiac disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasa, J.S.; Zubiaurre, I.; Fanjul, I.; Olivera, P.; Soifer, L. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth prevalence in celiac disease patients is similar in healthy subjects and lower in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2015, 80, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Losurdo, G.; Marra, A.; Shahini, E.; Girardi, B.; Giorgio, F.; Amoruso, A.; Pisani, A.; Piscitelli, D.; Barone, M.; Principi, M.; et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and celiac disease: A systematic review with pooled-data analysis. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017, 29, e13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Shahini, E.; Iannone, A.; Viggiani, M.T.; Corvace, V.; Principi, M.; Di Leo, A. Critical Flicker Frequency Test Predicts Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy and Survival in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharidou, E.; Dhar, A.; Patch, D. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders and Their Clinical Implications in Cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 8270310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, D.W.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, O.Y.; Chae, J.D.; Son, B.K.; Kim, S.H.; Jo, Y.J.; Park, Y.S. Association Between Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Peripheral Bacterial DNA in Cirrhotic Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, C.; Kumar, A.; Sarin, S.K. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in cirrhosis is related to the severity of liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thiel, D.H.; Fagiuoli, S.; Wright, H.I.; Chien, M.C.; Gavaler, J.S. Gastrointestinal Transit in Cirrhotic Patients: Effect of Hepatic Encephalopathy and Its Treatment. Hepatology 1994, 19, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dhiman, R.K.; Kumari, S.; Rana, S.; Agarwal, R.; Duseja, A.; Chawla, Y. Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Delayed Gastrointestinal Transit Time in Cirrhotic Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, N.M.; Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.; Poordad, F.; Neff, G.; Leevy, C.B.; Sigal, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Beavers, K.; Frederick, T.; et al. Rifaximin Treatment in Hepatic Encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cao, B.; Tian, Q. Effects of sibo and rifaximin therapy on mhe caused by hepatic cirrhosis. Int. J. Clin Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 2954–2957. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Schütte, K.; Reisener, N.; Voss, J.; Kandulski, A.; Malfertheiner, P. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Not Associated with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Endosc. 2016, 1, 1001. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Ridlon, J.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Heuman, D.M.; Smith, S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Linkage of Gut Microbiome with Cognition in Hepatic Encephalopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G168–G75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Ridlon, J.M.; Heuman, D.M.; Daita, K.; White, M.B.; Monteith, P.; Noble, N.A.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Colonic Mucosal Microbiome Differs from Stool Microbiome in Cirrhosis and Hepatic Encephalopathy and Is Linked To Cognition and Inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G675–G685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.M.; Lin, Y.F.; Chen, K.F.; Ke, H.M.; Huang, H.Y.; Gong, Y.N.; Tsai, W.S.; You, J.F.; Lu, M.J.; Cheng, H.T.; et al. Predicting Clinical Outcomes of Cirrhosis Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy from the Fecal Microbiome. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 301–318.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shawcross, D.L.; Wright, G.; Olde Damink, S.W.; Jalan, R. Role of ammonia and inflammation in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2007, 22, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawcross, D.L.; Sharifi, Y.; Canavan, J.B.; Yeoman, A.D.; Abeles, R.D.; Taylor, N.J.; Auzinger, G.; Bernal, W.; Wendon, J.A. Infection and Systemic Inflammation, Not Ammonia, Are Associated with Grade 3/4 Hepatic Encephalopathy, But Not Mortality in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijls, K.E.; Jonkers, D.M.; Elamin, E.E.; Masclee, A.A.; Koek, G.H. Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function in Liver Cirrhosis: An Extensive Review of the Literature. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T.M.; Schwacha, H.; Steinbrückner, B.; Brinkmann, F.E.; Ditzen, A.K.; Aponte, J.J.; Pelz, K.; Berger, D.; Kist, M.; Blum, H.E. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Human Cirrhosis Is Associated with Systemic Endotoxemia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, K.; Saikawa, S.; Takaya, H.; Fujinaga, Y.; Furukawa, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Ozutsumi, T.; Kaya, D.; Tsuji, Y.; Sawada, Y.; et al. Rifaximin alleviates endotoxemia with decreased serum levels of soluble CD163 and mannose receptor and partial modification of gut microbiota in cirrhotic patients. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres-Fuentes, C.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiota-gut-brain axis in obesity. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aversa, F.; Tortora, A.; Ianiro, G.; Ponziani, F.R.; Annicchiarico, B.E.; Gasbarrini, A. Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8 (Suppl. 1), S11–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, E.; Losurdo, G.; Sorrentino, C.; Giorgio, F.; Rossi, G.; Marinaro, A.; Romagno, K.R.; Di Leo, A.; Principi, M. Macronutrient intakes in obese subjects with or without small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: An alimentary survey. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, B.C.; Lee, D.; Miller, L.S.; Vegesna, A.; Yolken, R.; Severance, E.; Prandovszky, E.; Zheng, X.E.; Mullin, G.E. Obesity increases the risk of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, A.P.; Fisberg, M.; Morais, M.B. Macronutrient intakes in overweight adolescents with or without small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.E.; Joo, N.S.; Han, K.S.; Kim, K.N. Obesity Is Inversely Related to Hydrogen-Producing Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Non-Constipation Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, A.M.; Poniachik, J.; Quera, R.; Defilippi, C. Small intestinal clustered contractions and bacterial overgrowth: A frequent finding in obese patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Werlang, M.E.; Watthanasuntorn, K.; Panjawatanan, P.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Gomez, V.; Lukens, F.J.; Ungprasert, P. Obesity and Risk of Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianiro, G.; Bibbò, S.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G. Therapeutic modulation of gut microbiota: Current clinical applications and future perspectives. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Cho, D.Y.; Joo, N.S.; Kim, K.N. Effect of eradicating hydrogen-forming small intestinal bacterial overgrowth with rifaximin on body weight change. Medicine 2019, 98, e18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, K.; Kalantzis, C.; Papadopoulos, A.A.; Apostolopoulos, P.; Rokkas, T.; Kalantzis, N.; Ladas, S.D. Video-capsule endoscopy gastric and small bowel transit time and completeness of the examination in patients with diabetes mellitus. Dig. Liver Dis. 2007, 39, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.V.; Malik, A.; Bhadada, S.K.; Sachdeva, N.; Morya, R.K.; Sharma, G. Malabsorption, Orocecal Transit Time and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Connection. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 32, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, S.; Bhansali, A.; Bhadada, S.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, J.; Singh, K. Orocecal transit time and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in type 2 diabetes patients from North India. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2011, 13, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietz, B.; Lock, G.; Straub, R.H.; Braun, B.; Schölmerich, J.; Palitzsch, K.D. Small-bowel bacterial overgrowth in diabetic subjects is associated with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1200–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.A.; Baker, J.R.; Wamsteker, E.J.; Saad, R.; DiMagno, M.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Common in Chronic Pancreatitis and Associates with Diabetes, Chronic Pancreatitis Severity, Low Zinc Levels, and Opiate Use. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kurdi, B.; Babar, S.; El Iskandarani, M.; Bataineh, A.; Lerch, M.M.; Young, M.; Singh, V.P. Factors That Affect Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Chronic Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubinstein, E.; Mark, Z.; Haspel, J.; Ben-Ari, G.; Dreznik, Z.; Mirelman, D.; Tadmor, A. Antibacterial activity of the pancreatic fluid. Gastroenterology 1985, 88, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virally-Monod, M.; Tielmans, D.; Kevorkian, J.P.; Bouhnik, Y.; Flourie, B.; Porokhov, B.; Ajzenberg, C.; Warnet, A.; Guillausseau, P.J. Chronic diarrhoea and diabetes mellitus: Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Diabetes Metab. 1998, 24, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuoco, L.; Montalto, M.; Jorizzo, R.A.; Santarelli, L.; Arancio, F.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, G. Eradication of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and oro-cecal transit in diabetics. Hepatogastroenterology 2002, 49, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.U.; Cusi, K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyn, M.; Grys, I.; Kukla, M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Mascianà, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Duseja, A.; Sharma, B.K.; Singla, B.; Chakraborti, A.; Das, A.; Ray, P.; Dhiman, R.K.; Chawla, Y. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and toll-like receptor signaling in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domper Bardají, F.; Gil Rendo, A.; Illescas Fernández-Bermejo, S.; Patón Arenas, R.; Hernández Albújar, A.; Martín Dávila, F.; Murillo Lázaro, C.; Sánchez, M.A.; Serrano, M.D.; Sobrino, A.L.; et al. An assessment of bacterial overgrowth and translocation in the non-alcoholic fatty liver of patients with morbid obesity. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2019, 111, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, A.; Fialho, A.; Thota, P.; McCullough, A.J.; Shen, B. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Is Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2016, 25, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Baba, C.S.; Ghoshal, U.; Alexander, G.; Misra, A.; Saraswat, V.A.; Choudhuri, G. Low-grade small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is common in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis on quantitative jejunal aspirate culture. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 36, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belei, O.; Olariu, L.; Dobrescu, A.; Marcovici, T.; Marginean, O. The relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth among overweight and obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 30, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangarapu, V.; Ince, A.T.; Baysal, B.; Kayar, Y.; Kılıç, U.; Gök, Ö.; Uysal, Ö.; Şenturk, H. Efficacy of rifaximin on circulating endotoxins and cytokines in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razik, A.; Mousa, N.; Shabana, W.; Refaey, M.; Elzehery, R.; Elhelaly, R.; Zalata, K.; Abdelsalam, M.; Eldeeb, A.A.; Awad, M.; et al. Rifaximin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Hit multiple targets with a single shot. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbold, J.F.L.; Atkinson, S.; Marchesi, J.R.; Smith, A.; Wai, S.N.; Stove, J.; Shojaee-Moradie, F.; Jackson, N.; Umpleby, A.M.; Fitzpatrick, J.; et al. Rifaximin in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: An open-label pilot study. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adike, A.; DiBaise, J.K. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Nutritional Implications, Diagnosis, and Management. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.; Siwiec, R.M.; Wo, J.M. Diagnosis and management of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2013, 28, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.C. Gastric and enteric involvement in progressive systemic sclerosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, M.; Avouac, J.; Benahmed, A.; Barbot, L.; Coustet, B.; Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Prevalence and predictors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. 86), S82–S87. [Google Scholar]
- Polkowska-Pruszyńska, B.; Gerkowicz, A.; Szczepanik-Kułak, P.; Krasowska, D. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis: A review of the literature. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2019, 311, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawadpanich, K.; Soison, P.; Chunlertrith, K.; Mairiang, P.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Sangchan, A.; Suttichaimongkol, T.; Foocharoen, C. Prevalence and associated factors of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth among systemic sclerosis patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Fransen, K.; Avouac, J.; Becker, M.; Kulak, A.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Clements, P.; Cutolo, M.; Czirjak, L.; et al. Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pittman, N.; Rawn, S.M.; Wang, M.; Masetto, A.; Beattie, K.A.; Larché, M. Treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis: A systematic review. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaye, S.A.; Lim, S.G.; Taylor, M.; Patel, S.; Gillespie, S.; Black, C.M. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth in systemic sclerosis: Detection using direct and indirect methods and treatment outcome. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 34, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, A.; Sessarego, M.; Greco, A.; Bazzica, M.; Filaci, G.; Setti, M.; Savarino, E.; Indiveri, F.; Savarino, V.; Ghio, M. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients suffering from scleroderma: Clinical effectiveness of its eradication. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Collinot, G.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Martínez-Bencomo, M.; Carranza-Muleiro, R.A.; Jara, L.J.; Vera-Lastra, O.; Montes-Cortes, D.H.; Medina, G.; Cruz-Domínguez, M.P. Effectiveness of Saccharomyces boulardii and Metronidazole for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Systemic Sclerosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosania, R.; Giorgio, F.; Principi, M.; Amoruso, A.; Monno, R.; Di Leo, A.; Ierardi, E. Effect of probiotic or prebiotic supplementation on antibiotic therapy in the small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: A comparative evaluation. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criteria for Diagnosis of Behçet’s Disease. International Study Group for Behçet’s Disease. Lancet 1990, 335, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Hisamatsu, T.; Ueno, F.; Matsumoto, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Koganei, K.; Kunisaki, R.; Hirai, F.; Nagahori, M.; Matsushita, M.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. The 2nd edition of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet’s disease: Indication of anti-TNFα monoclonal antibodies. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, W.H. Rediscover the clinical value of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with intestinal Behçet’s disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorizzo, J.L.; Apisarnthanarax, P.; Subrt, P.; Hebert, A.A.; Henry, J.C.; Raimer, S.S.; Dinehart, S.M.; Reinarz, J.A. Bowel-bypass syndrome without bowel bypass. Bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome. Arch. Intern. Med. 1983, 143, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Shi, W.; Luo, H.; Duan, L.; You, Y.; Li, Y.; Zuo, X. Is it bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome induced by small intestinal bacteria overgrowth? Springerplus 2016, 13, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polkowska-Pruszynska, B.; Gerkowicz, A.; Krasouska, D. The gut microbiome alterations in allergic and inflammatory skin diseases—An update. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, I.; Ramser, A.; Isham, N.; Ghannoum, M.A. The Gut Microbiome as a Major Regulator of the Gut-Skin Axis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 10, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Ortonne, J.P.; Wilhelm, K.; Marticou, L.; Baltas, E.; Rivier, M.; Petit, L.; Martel, P. An observational cross-sectional survey of rosacea: Clinical associations and progression between subtypes. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Paolino, S.; Greco, A.; Drago, F.; Mansi, C.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A.; Savarino, V. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in rosacea: Clinical effectiveness of its eradication. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, L.B.; Steinhoff, M. Rosacea and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: Prevalence and response to rifaximin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 875–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; De Col, E.; Agnoletti, A.F.; Schiavetti, I.; Savarino, V.; Rebora, A.; Paolino, S.; Cozzani, E.; Parodi, A. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in rosacea: A 3-year follow-up. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, e113–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Parodi, A. Effects of the treatment for small intestine bacterial overgrowth on rosacea. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeberg, A.; Weinstock, L.B.; Thyssen, E.P.; Gislason, G.H.; Thyssen, J.P. Rosacea and gastrointestinal disorders: A population-based cohort study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, A.; Federico, A.; Ruocco, E.; Lo Schiavo, A.; Masarone, M.; Tuccillo, C.; Peccerillo, F.; Miranda, A.; Romano, L.; de Sio, C.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection but not small intestinal bacterial overgrowth may play a pathogenic role in rosacea. United European Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fowler, E.; Maderal, A. Pyoderma faciale in a patient with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, e152–e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago, F.; Ciccarese, G.; Indemini, E.; Savarino, V.; Parodi, A. Psoriasis and small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfeiffer, R.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, S.M.; Dobbs, R.J.; Weller, C.; Charlett, A.; Augustin, A.; Taylor, D.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Bjarnason, I. Peripheral aetiopathogenic drivers and mediators of Parkinson’s disease and co-morbidities: Role of gastrointestinal microbiota. J. Neurovirol. 2016, 22, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, A.H.; Mahadeva, S.; Thalha, A.M.; Gibson, P.R.; Kiew, C.K.; Yeat, C.M.; Ng, S.W.; Ang, S.P.; Chow, S.K.; Tan, C.T.; et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Bove, F.; Gabrielli, M.; Petracca, M.; Zocco, M.A.; Ragazzoni, E.; Barbaro, F.; Piano, C.; Fortuna, S.; Tortora, A.; et al. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, R.J.; Charlett, A.; Dobbs, S.M.; Weller, C.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Iguodala, O.; Smee, C.; Plant, J.M.; Lawson, A.J.; Taylor, D.; et al. Leukocyte-subset counts in idiopathic parkinsonism provide clues to a pathogenic pathway involving small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. A surveillance study. Gut Pathog. 2012, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Losurdo, G.; D’Abramo, F.S.; Indellicati, G.; Lillo, C.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A. The Influence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Digestive and Extra-Intestinal Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103531
Losurdo G, D’Abramo FS, Indellicati G, Lillo C, Ierardi E, Di Leo A. The Influence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Digestive and Extra-Intestinal Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103531
Chicago/Turabian StyleLosurdo, Giuseppe, Fulvio Salvatore D’Abramo, Giuseppe Indellicati, Chiara Lillo, Enzo Ierardi, and Alfredo Di Leo. 2020. "The Influence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Digestive and Extra-Intestinal Disorders" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103531
APA StyleLosurdo, G., D’Abramo, F. S., Indellicati, G., Lillo, C., Ierardi, E., & Di Leo, A. (2020). The Influence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Digestive and Extra-Intestinal Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103531





