Studies on the Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Heparin- and Hyaluronan-Containing Multilayer Coatings—Targeting NF-κB Signalling Pathway
Abstract
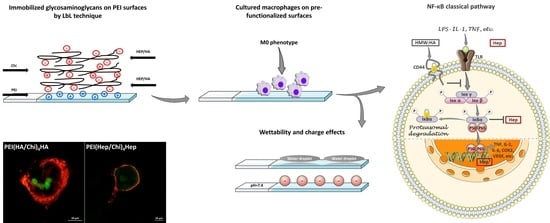
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Physical Properties of Coatings
2.2. Adhesion of Macrophages and Multinucleated Giant Cell Formation
2.3. IL-1β Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining of NF-κB in Macrophages
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Association of GAG with Macrophages Studied by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.7. Association of FITC-Labelled GAG with Macrophages Studied by Flow Cytometry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals for Surface Modification
4.2. Substrates and Polyelectrolyte (PEL) Preparation
4.3. Polyelectrolyte Multilayers (PEMs) Formation
4.4. Characterization of Surface Properties and Multilayer Formation
4.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4.2. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4.4.3. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
4.4.4. Measurement of Multilayer Thickness by Ellipsometry
4.5. Studies with THP-1 Derived Macrophages
4.5.1. Cell Culture
4.5.2. Cell Adhesion Studies
4.5.3. Analysis of Multinucleated Giant Cells (MNGCs) Formation
4.5.4. IL-1β Production Measurement
4.5.5. Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining of NF-kB
4.5.6. Cell Lysis for Immunoblotting (IB)
4.5.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.5.8. Association of FITC-GAG with Macrophages Studied by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
4.5.9. Uptake of FITC-GAG by Macrophages Studied with Flow Cytometry
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, L.; Eaton, J.W. Inflammatory responses to biomaterials. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 103, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M. In vitro and in vivo monocyte, macrophage, foreign body giant cell, and lymphocyte interactions with biomaterials. In Biological Interactions on Materials Surfaces; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 225–244. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, E.; Lisignoli, G.; Borzì, R.M.; Pulsatelli, L. Biomaterials: Foreign bodies or tuners for the immune response? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, R.J.; Parisi-Amon, A.; Reichert, W.M. Cytokine profiling using monocytes/macrophages cultured on common biomaterials with a range of surface chemistries. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2009, 88, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wynn, T.A.; Barron, L. Macrophages: Master regulators of inflammation and fibrosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fialkow, L.; Wang, Y.; Downey, G.P. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as signaling molecules regulating neutrophil function. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, D.M.; Goodridge, H.S. Information processing during phagocytosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Z.; Triffitt, J.T. A review on macrophage responses to biomaterials. Biomed. Mater. 2006, 1, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serini, G.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.-L.; Ropraz, P.; Geinoz, A.; Borsi, L.; Zardi, L.; Gabbiani, G. The fibronectin domain ED-A is crucial for myofibroblastic phenotype induction by transforming growth factor-β1. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barron, L.; Wynn, T.A. Fibrosis is regulated by Th2 and Th17 responses and by dynamic interactions between fibroblasts and macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratner, B.D.; Bryant, S.J. Biomaterials: Where we have been and where we are going. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.D.; Manjoo, A.; Fierlinger, A.; Niazi, F.; Nicholls, M. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: A systematic review. Bmc Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franz, S.; Rammelt, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Simon, J.C. Immune responses to implants–a review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6692–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroman, L.; Adams, A.; Fischer, G.; Munoz, P. Interaction of high molecular weight kininogen, factor XII, and fibrinogen in plasma at interfaces. Blood 1980, 55, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suarez, P.; Rojo, L.; Gonzalez-Gomez, A.; Roman, J.S. Self-assembling gradient copolymers of vinylimidazol and (acrylic)ibuprofen with anti-inflammatory and zinc chelating properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khoury, H.; Espinosa-Cano, E.; Aguilar, M.a.R.; Romaán, J.S.; Syrowatka, F.; Schmidt, G.; Groth, T. Anti-inflammatory Surface Coatings Based on Polyelectrolyte Multilayers of Heparin and Polycationic Nanoparticles of Naproxen-Bearing Polymeric Drugs. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.; Mano, J.F. Molecular interactions driving the layer-by-layer assembly of multilayers. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8883–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkirane-Jessel, N.; Schwinte, P.; Falvey, P.; Darcy, R.; Haïkel, Y.; Schaaf, P.; Voegel, J.C.; Ogier, J. Build-up of polypeptide multilayer coatings with anti-inflammatory properties based on the embedding of piroxicam–cyclodextrin complexes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wen, C.; Xuan, M.; Zhang, H.; Frueh, J.; Wan, M.; Gao, L.; He, Q. Polyelectrolyte multilayer-cushioned fluid lipid bilayers: A parachute model. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 2008–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKhoury, H.; Hautmann, A.; Erdmann, F.; Zhou, G.; Stojanovic, S.; Najman, S.; Groth, T. Study on the potential mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of covalently immobilized hyaluronan and heparin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Altgärde, N.; Svedhem, S.; Michanetzis, G.; Missirlis, Y.; Groth, T. Tuning Cell Adhesion and Growth on Biomimetic Polyelectrolyte Multilayers by Variation of p H During Layer-by-L ayer Assembly. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.B.; Besner, G.E. Inhibition of NF-κB activation and its target genes by heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 6014–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, A.; Schinzel, R.; Palm, D.; Riederer, P.; Münch, G. High molecular weight hyaluronic acid inhibits advanced glycation endproduct-induced NF-κB activation and cytokine expression. FEBS Lett. 1999, 453, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-κB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-κB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenoso, A.; D’Ascola, A.; Scuruchi, M.; Mandraffino, G.; Calatroni, A.; Saitta, A.; Campo, S.; Campo, G.M. Hyaluronan in the experimental injury of the cartilage: Biochemical action and protective effects. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R.; Bedi, A.; Manjoo, A.; Niazi, F.; Shaw, P.; Mease, P. Anti-inflammatory effects of intra-articular hyaluronic acid: A systematic review. Cartilage 2019, 10, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, D.; Nedvetzki, S.; Walmsley, M.; Yayon, A.; Turley, E.A.; Golan, I.; Caspi, D.; Sebban, L.E.; Zick, Y.; Garin, T. CD44 involvement in autoimmune inflammations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1110, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Seo, G.H.; Kim, C.H.; Ahn, Y.S. Heparin inhibits NF-κB activation and increases cell death in cerebral endothelial cells after oxygen-glucose deprivation. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2007, 32, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köwitsch, A.; Zhou, G.; Groth, T. Medical application of glycosaminoglycans: A review. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e23–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Niepel, M.S.; Saretia, S.; Groth, T. Reducing the inflammatory responses of biomaterials by surface modification with glycosaminoglycan multilayers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2016, 104, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolasinska, M.; Krastev, R.; Warszynski, P. Characteristics of polyelectrolyte multilayers: Effect of PEI anchoring layer and posttreatment after deposition. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 305, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Loppnow, H.; Groth, T. A macrophage/fibroblast co-culture system using a cell migration chamber to study inflammatory effects of biomaterials. Acta Biomater 2015, 26, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacakova, L.; Filova, E.; Parizek, M.; Ruml, T.; Svorcik, V. Modulation of cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation on materials designed for body implants. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 739–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Al-Khoury, H.; Groth, T. Covalent immobilization of glycosaminoglycans to reduce the inflammatory effects of biomaterials. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2016, 39, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Montelongo, J.; Nascimento, V.F.; Murillo, D.; Taketa, T.B.; Sahoo, P.; de Souza, A.A.; Beppu, M.M.; Cotta, M.A. Nanofilms of hyaluronan/chitosan assembled layer-by-layer: An antibacterial surface for Xylella fastidiosa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Brooks, P.; Barzilay, O.; Fine, N.; Glogauer, M. Macrophages, foreign body giant cells and their response to implantable biomaterials. Materials 2015, 8, 5671–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, Y.-D.; Choi, C.-H.; Bark, H.; Son, H.-Y.; Park, H.-H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.-W.; Park, E.-K.; Shin, H.-I.; Kim, S.-H. Quercetin inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in HMC-1 human mast cell line. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, T.S.; Blackwell, T.R.; Christman, J.W. Impaired activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in endotoxin-tolerant rats is associated with down-regulation of chemokine gene expression and inhibition of neutrophilic lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 5934–5940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Altankov, G.; Grabiec, U.; Bennett, M.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M.; Dehghani, F.; Groth, T. Molecular composition of GAG-collagen I multilayers affects remodeling of terminal layers and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2016, 41, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E. The anti-inflammatory effects of heparin and related compounds. Thromb. Res. 2008, 122, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, E.; Venner, T.; Ribau, J.; Shaughnessy, S.; Hirsh, J.; Podor, T.J. The binding of unfractionated heparin and low molecular weight heparin to thrombin-activated human endothelial cells. Thromb. Res. 1999, 96, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, S.M.; Hawn, T.R.; Arrigoni, A.; Wight, T.N.; Bollyky, P.L. Tissue integrity signals communicated by high-molecular weight hyaluronan and the resolution of inflammation. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neuman, M.G.; Nanau, R.M.; Oruña, L.; Coto, G. In vitro anti-inflammatory effects of hyaluronic acid in ethanol-induced damage in skin cells. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 14, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knudson, W.; Chow, G.; Knudson, C.B. CD44-mediated uptake and degradation of hyaluronan. Matrix Biol. 2002, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zang, Y.C.; Halder, J.B.; Hong, J.; Rivera, V.M.; Zhang, J.Z. Regulatory effects of estriol on T cell migration and cytokine profile: Inhibition of transcription factor NF-κB. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 124, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köwitsch, A.; Abreu, M.J.; Chhalotre, A.; Hielscher, M.; Fischer, S.; Mäder, K.; Groth, T. Synthesis of thiolated glycosaminoglycans and grafting to solid surfaces. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macek, M. A review cf advanced wet cleaning. Inf. Midem 1993, 23, 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Noursadeghi, M.; Tsang, J.; Haustein, T.; Miller, R.F.; Chain, B.M.; Katz, D.R. Quantitative imaging assay for NF-κB nuclear translocation in primary human macrophages. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 329, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkhoury, H.; Hautmann, A.; Fuhrmann, B.; Syrowatka, F.; Erdmann, F.; Zhou, G.; Stojanović, S.; Najman, S.; Groth, T. Studies on the Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Heparin- and Hyaluronan-Containing Multilayer Coatings—Targeting NF-κB Signalling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103724
Alkhoury H, Hautmann A, Fuhrmann B, Syrowatka F, Erdmann F, Zhou G, Stojanović S, Najman S, Groth T. Studies on the Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Heparin- and Hyaluronan-Containing Multilayer Coatings—Targeting NF-κB Signalling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103724
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkhoury, Hala, Adrian Hautmann, Bodo Fuhrmann, Frank Syrowatka, Frank Erdmann, Guoying Zhou, Sanja Stojanović, Stevo Najman, and Thomas Groth. 2020. "Studies on the Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Heparin- and Hyaluronan-Containing Multilayer Coatings—Targeting NF-κB Signalling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103724
APA StyleAlkhoury, H., Hautmann, A., Fuhrmann, B., Syrowatka, F., Erdmann, F., Zhou, G., Stojanović, S., Najman, S., & Groth, T. (2020). Studies on the Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Heparin- and Hyaluronan-Containing Multilayer Coatings—Targeting NF-κB Signalling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103724