β-Funaltrexamine Displayed Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects in Cells and Rat Model of Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
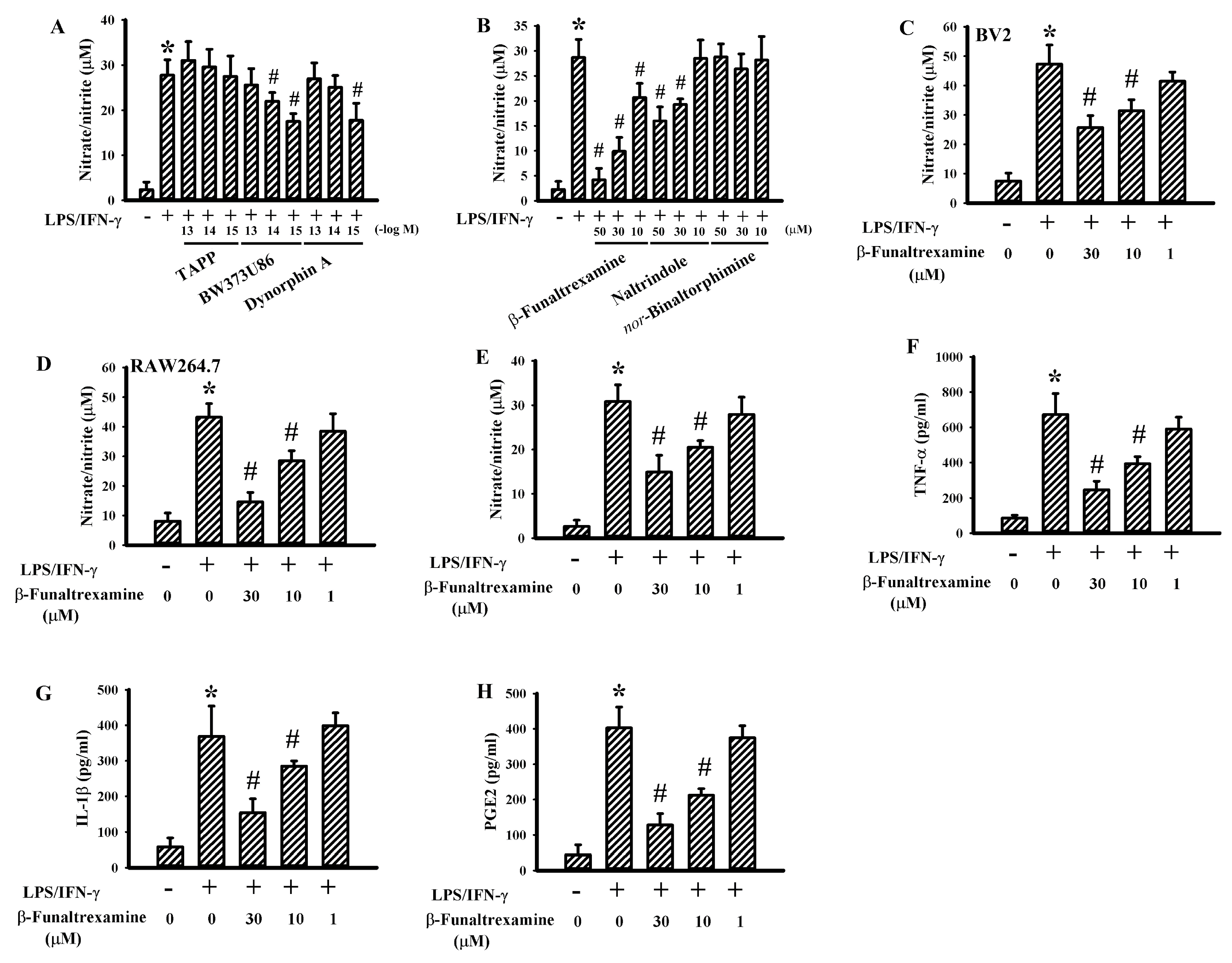
2.1. β-Funaltrexamine Alleviated Neurotoxic Cytokine Production
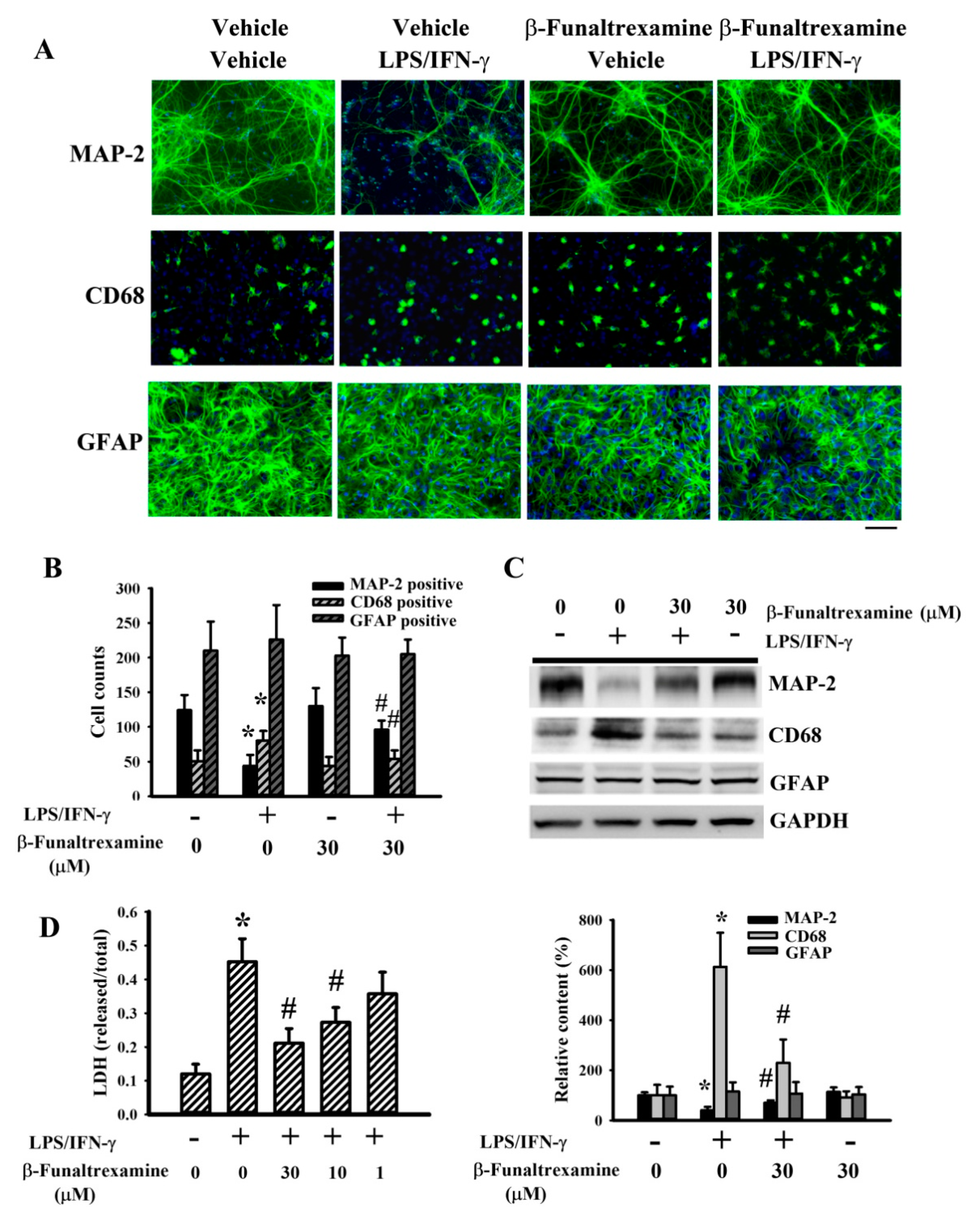
2.2. β-Funaltrexamine Alleviated Neuronal Cell Death
2.3. β-Funaltrexamine Alleviated Microglia Activation
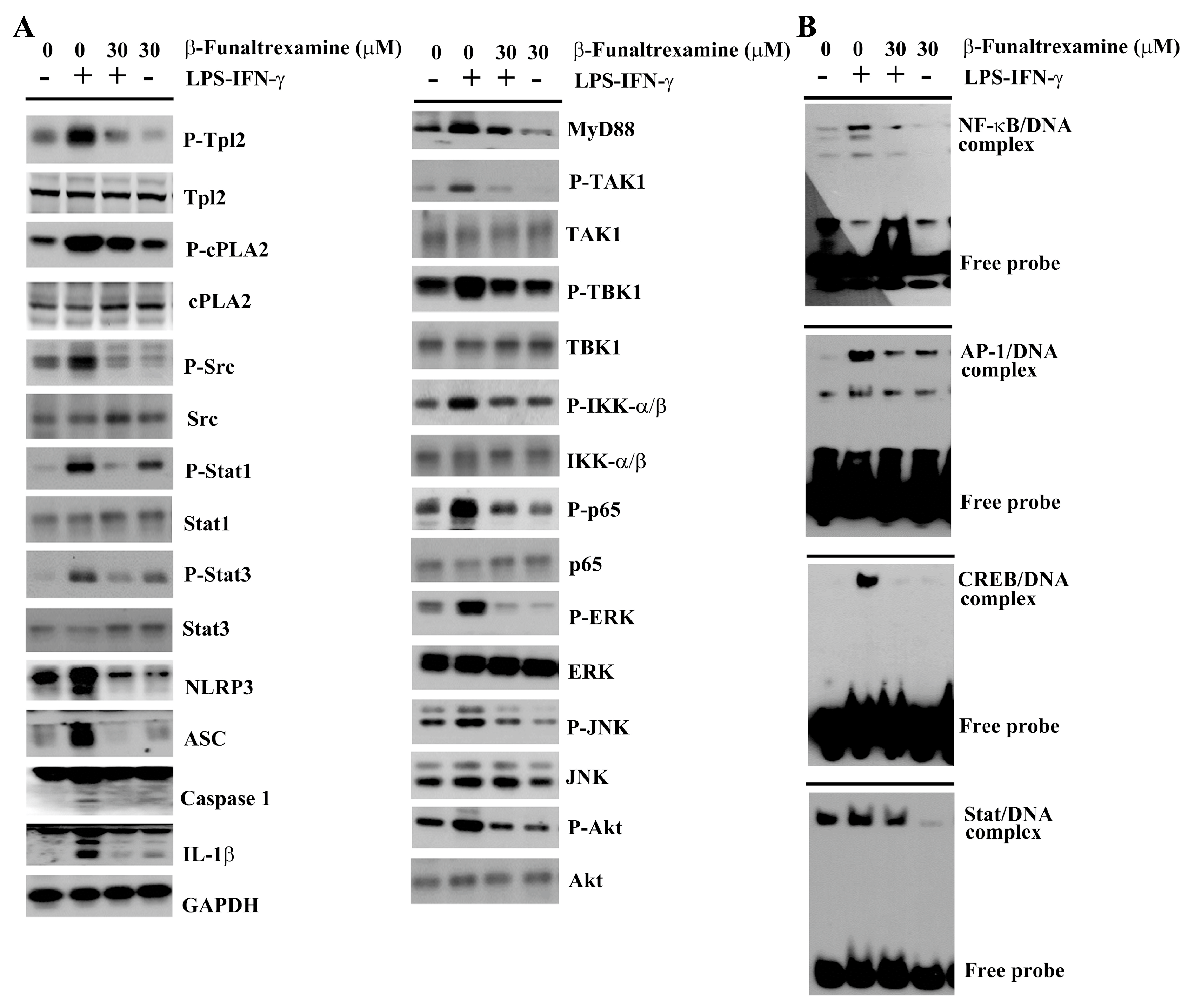
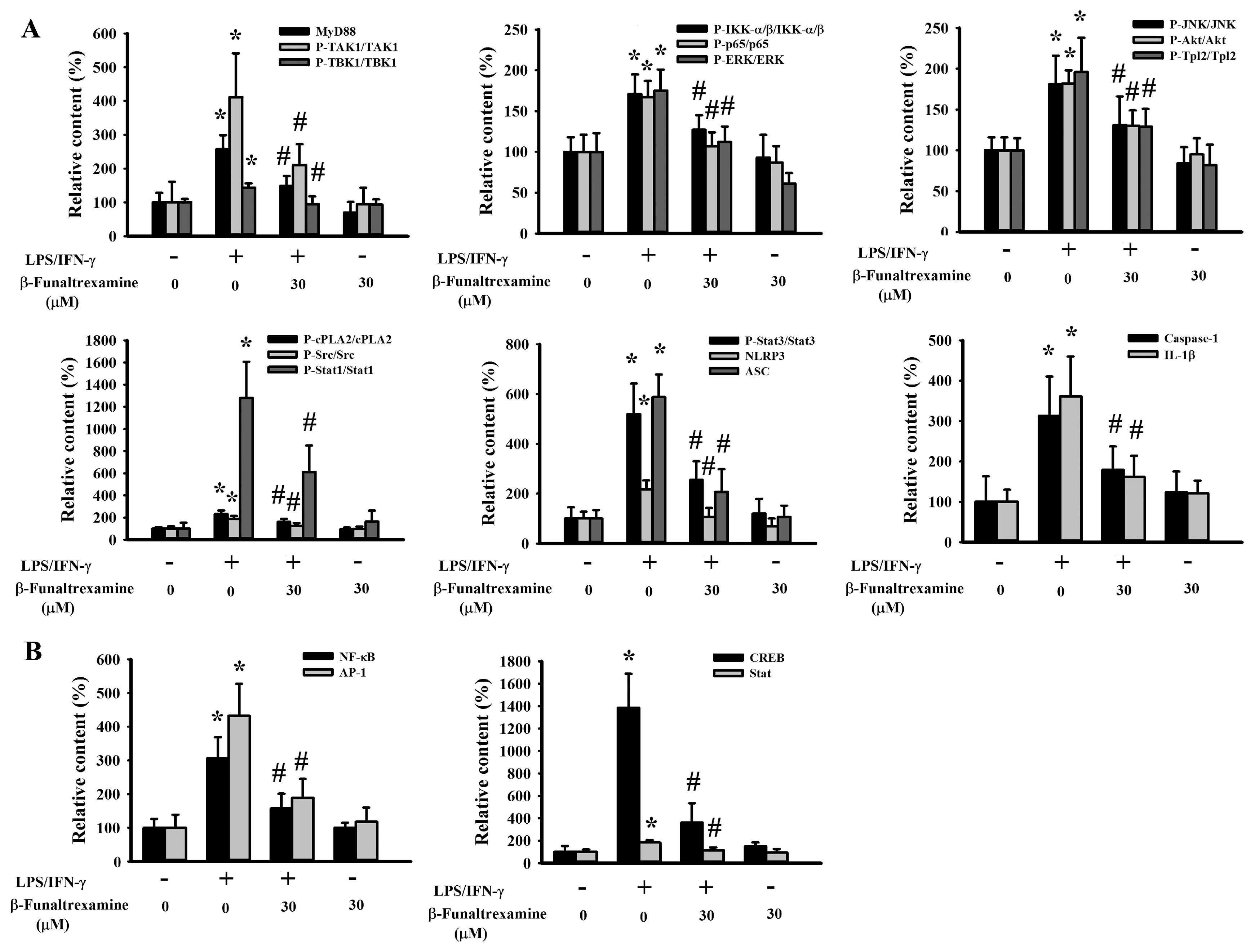
2.4. β-Funaltrexamine Alleviated Inflammatory Intracellular Signaling
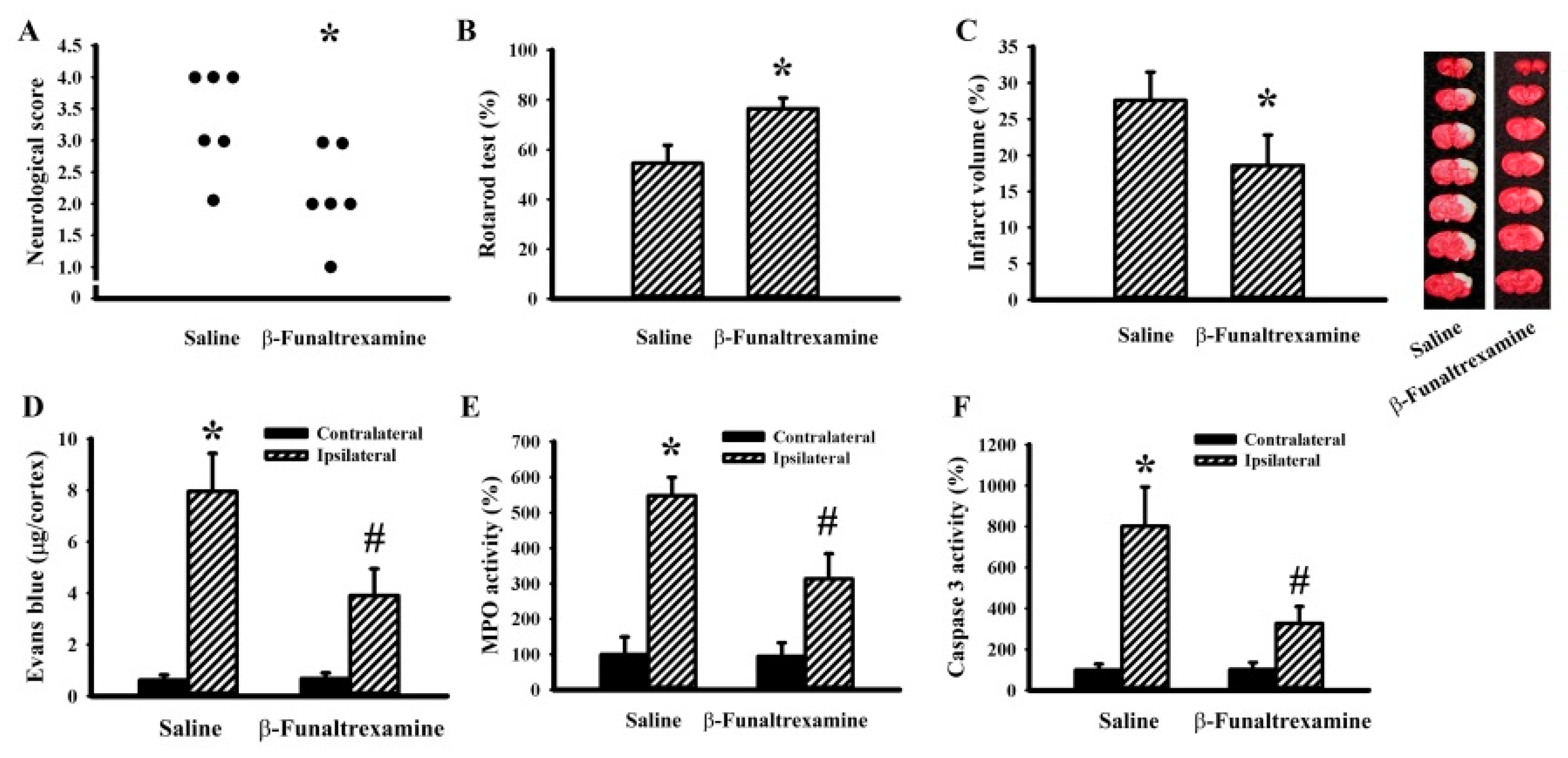
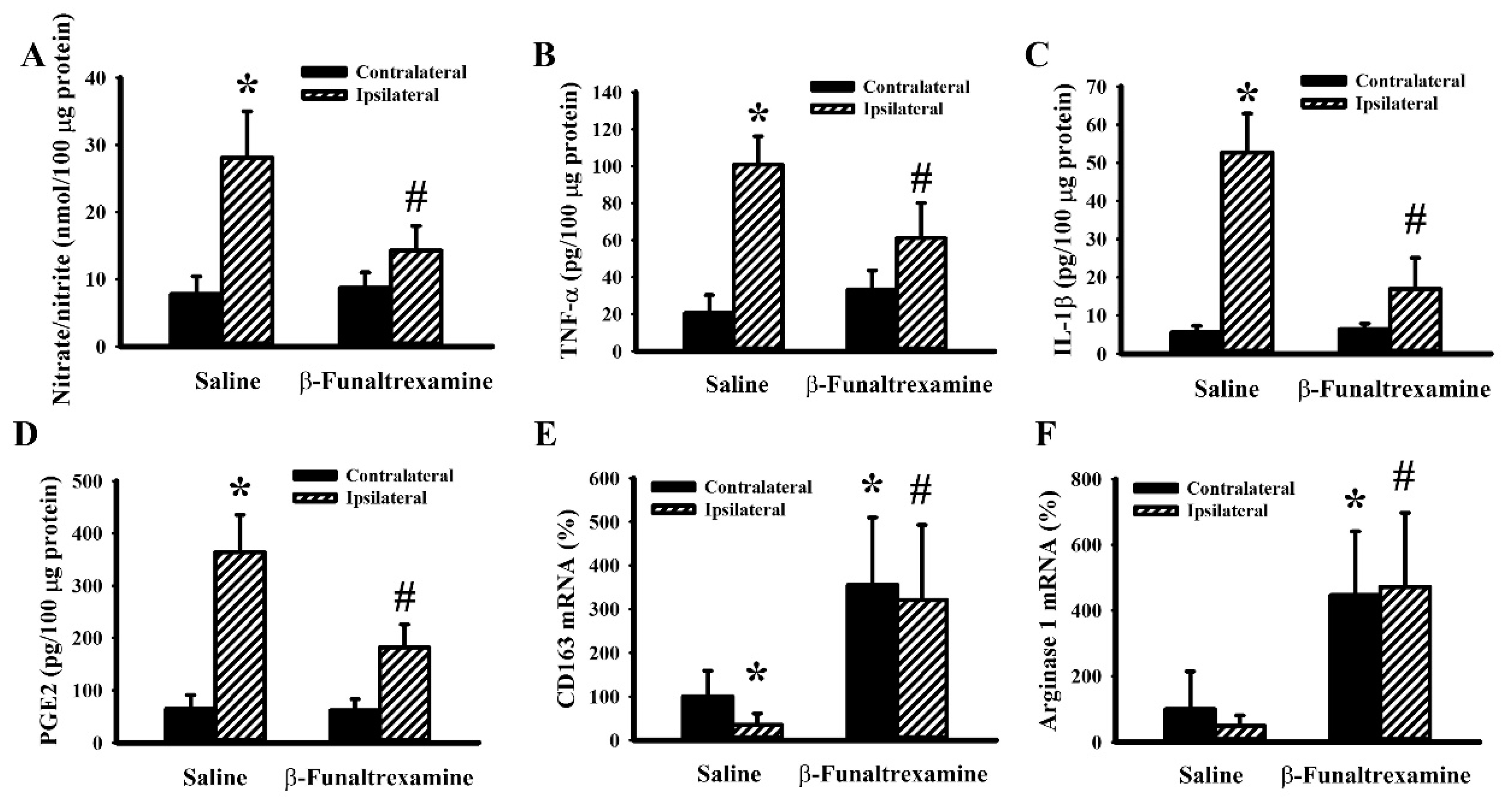
2.5. β-Funaltrexamine Alleviated Cerebral I/R Injury
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Cytotoxicity Assessment
4.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.7. Preparation of Nuclear Extracts and Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.8. Cerebral I/R
4.9. Quantification of Ischemic Infarction
4.10. Evans Blue Extravasation Assay
4.11. Neurological Evaluation
4.12. Rotarod Test
4.13. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity Assay
4.14. Caspase 3 Activity Assay
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASC | Apoptosis-Associated Speck-Like Protein Containing a CARD |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CCA | Common Carotid Arteries |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| cPLA2 | cytosolic Phospholipase A2 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EMSA | Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| FITC | Fluorescein Isothiocyanate |
| GADPH | Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IKK-α/β | IκB Kinase α/β |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| I/R | Ischemia/Reperfusion |
| IRF1 | Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal Kinase |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAP-2 | Microtubule-associated Protein 2 |
| MCA | Middle Cerebral Artery |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| NLRP3 | NLR Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| P2X4R | P2X purinoceptor 4 |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| RT-PCR | Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| Stat1 | Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription 1 |
| TAK1 | Transforming Growth Factor β-Activated Kinase-1 |
| TBK1 | TANK-binding Kinase 1 |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic Acid |
| TLR | Toll-Like Receptor |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| Tpl2 | Tumor Progression Locus 2 |
References
- Stein, C. Opioid receptors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentino, R.J.; Volkow, N.D. Untangling the complexity of opioid receptor function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anttila, J.E.; Albert, K.; Wires, E.S.; Mätlik, K.; Loram, L.C.; Watkins, L.R.; Rice, K.C.; Wang, Y.; Harvey, B.K.; Airavaara, M. Post-stroke intranasal (+)-naloxone delivery reduces microglial activation and improves behavioral recovery from ischemic injury. eNeuro 2018, 5, ENEURO.0395-17.2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissonnette, S.; Vaillancourt, M.; Hébert, S.S.; Drolet, G.; Samadi, P. Striatal pre-enkephalin overexpression improves Huntington’s disease symptoms in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, S.; Muratot, S.; Vernoux, N.; Bezeau, F.; Calon, F.; Hébert, S.S.; Samadi, P. The effect of striatal pre-enkephalin overexpression in the basal ganglia of the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 2406–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, H.; Dauphin, F.; MacKenzie, E.T.; Jauzac, P. Differential time-course decreases in nonselective, mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke 1999, 30, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.R.; Li, B.; Wang, M.G.; Meng, F.G.; Yu, J.J.; Guo, F.; Li, Y. Activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway promotes neuroprotection of the d-opioid receptor agonist against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat models. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 93, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Siegel, C.S.; Sekine-Konno, T.; Cafferty, W.B.J.; Strittmatter, S.M. The nociceptin receptor inhibits axonal regeneration and recovery from spinal cord injury. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaao4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Huang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhi, F.; Tian, X.; Wen, G.; Ding, G.; Xia, T.C.; Hua, F.; Xia, Y. Neuroprotection against hypoxic/ischemic injury: D-opioid receptors and BDNF-TrkB pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xu, H.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, H. Neuroprotection by the kappa-opioid receptor agonist, BRL52537, is mediated via up-regulating phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.K.; Ou, Y.C.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Chiang, A.N.; Chen, C.J. Opioids modulate post-ischemic progression in a rat model of stroke. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.N.; Ortiz, G.M.; Angel, T.E.; Jacobs, J.M.; Gritsenko, M.; Chan, E.Y.; Purdy, D.E.; Murnane, R.D.; Larsen, K.; Palermo, R.E.; et al. Morphine produces immunosuppressive effects in nonhuman primates at the proteomic and cellular levels. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Chou, K.Y.; Shen, C.H.; Chien, C.C.; Tsai, W.Y.; Huang, Y.N.; Tao, P.L.; Lin, Y.S.; Wong, C.S. Resveratrol regulates n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor expression and suppresses neuroinflammation in morphine-tolerant rats. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 944e52. [Google Scholar]
- Aceves, M.; Terminel, M.N.; Okoreeh, A.; Aceves, A.R.; Gong, Y.M.; Polanco, A.; Sohrabji, F.; Hook, M.A. Morphine increases macrophages at the lesion site following spinal cord injury: Protective effects of minocycline. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 79, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Bencivenni, S.; Fazzi, D.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S. The activation of m-opioid receptor potentiates LPS-induced NF-kB promoting an inflammatory phenotype in microglia. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2813–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, L. Morphine enhances IL-1b release through toll-like receptor 4-mediated endocytic pathway in microglia. Purinergic Signal. 2016, 12, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Fazzi, D.; Stefanelli, A.; Borea, P.A. Morphine mediates a proinflammatory phenotype via μ-opioid receptor-PKCε-Akt-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in activated microglial cells. Biochem. Pharm. 2013, 86, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Cheng, Y.C.; Wong, C.S. (+)-Naloxone inhibits morphine-induced chemotaxis via prevention of heat shock protein 90 cleavage in microglia. J. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 446–455. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.L.; Buck, D.J.; Saffarian, N.; Stevens, C.W. The opioid antagonist, beta-funaltrexamine, inhibits chemokine expression in human astroglial cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 186, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Cabrera, M.A.; Chastain, L.G.; Boyadjieva, N.I.; Jabbar, S.; Franklin, T.; Sarkar, D.K. Mu-opioid receptor and delta-opioid receptor differentially regulate microglial inflammatory response to control proopiomelanocortin neuronal apoptosis in the hypothalamus: Effects of neonatal alcohol. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Wu, C.Y.; Burton, F.H.; Loh, H.H.; Wei, L.N. b-arrestin protects neurons by mediating endogenous opioid arrest of inflammatory microglia. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Dai, H.; Tan, S.; Mao, X.; Chen, Z. Dynorphin activation of kappa opioid receptor promotes microglial polarization toward M2 phenotype via TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; Mao, X.F.; Tang, X.Q.; Ali, U.; Apryani, E.; Liu, H.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X. Spinal interleukin-10 produces antinociception in neuropathy through microglial b-endorphin expression, separated from antineuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 504–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Raung, S.L.; Chen, C.J. Neuroprotection of naloxone against ischemic injury in rats: Role of mu receptor antagonism. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 345, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyravian, N.; Dikici, E.; Deo, S.; Toborek, M.; Daunert, S. Opioid antagonists as potential therapeutics for ischemic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 182, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Z.J.; Wu, J.L.; Quan, W.Q.; Xiao, W.D.; Chew, H.; Jiang, C.M.; Li, D. Naloxone attenuates ischemic brain injury in rats through suppressing the NIK/IKKa/NF-kB and neuronal apoptotic pathways. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2019, 40, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Buck, D.J.; Saffarian, N.; Mohan, S.; DeSilva, U.; Fernando, S.C.; Stevens, C.W. Beta-funaltrexamine inhibits inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression in human astroglial cells. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2008, 3, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Das, S.; Buck, D.J.; Stevens, C.W. β-funaltrexamine inhibits chemokine (CXCL10) expression in normal human astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.L.; Das, S.; Thomas Curtis, J.; Stevens, C.W. The opioid antagonist, β-funaltrexamine, inhibits NF-κB signaling and chemokine expression in human astrocytes and in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 2015, 762, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.L.; Stevens, C.W.; Thomas Curtis, J. The opioid antagonist, b-funaltrexamine, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and reduces sickness behavior in mice. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 173, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Li, J.R.; Wang, J.D.; Wu, C.C.; Kuan, Y.H.; Liao, S.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Chen, C.J. Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of fungal immunomodulatory protein involving microglial inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, E3678. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mamun, A.; Chauhan, A.; Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Sharmeen, R.; Liu, F. Interferon regulatory factor 4/5 signaling impacts on microglial activation after ischemic stroke in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, I.; Zambusi, L.; Finardi, A.; Bodini, A.; Provini, L.; Furlan, R.; Morara, S. Calcitonin gene-related peptide decreases IL-1beta, IL-6 as well as Ym1, Arg1, CD163 expression in a brain tissue context-dependent manner while ameliorating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 323, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.J.; Raung, S.L.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, S.Y. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by baicalein in endotoxin/cytokine-stimulated microglia. Biochem. Pharm. 2004, 67, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.Y.; Jong, Y.J.; Lin, Y.T.; Tseng, Y.T.; Hsu, S.H.; Lo, Y.C. Nanomolar naloxone attenuates neurotoxicity induced by oxidative stress and survival motor neuron protein deficiency. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 25, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Guo, J.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Wu, G.; Xia, Y. d-Opioid receptor activation rescues the functional TrkB receptor and protects the brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, T.Y.; Kirsch, J.R.; Toung, T.J.; Traystman, R.J.; Koehler, R.C.; Hurn, P.D.; Bhardwaj, A. Kappa-opioid receptor selectivity for ischemic neuroprotection with BRL 52537 in rats. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 97, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, E.; Chung, Y.C.; Kim, K.S.; Baik, H.H.; Shin, W.H.; Jin, B.K. Modulation of M1/M2 polarization by capsaicin contributes to the survival of dopaminergic neurons in the lipopolysaccharide-lesioned substantia nigra in vivo. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Kuan, Y.H.; Li, J.R.; Chen, W.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Pan, H.C.; Liao, S.L.; Raung, S.L.; Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.J. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces cellular inflammatory response following permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślusarczyk, J.; Trojan, E.; Głombik, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Budziszewska, B.; Kubera, M.; Popiołek-Barczyk, K.; Lasoń, W.; Mika, J.; Basta-Kaim, A. Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome-related pathways via tianeptine treatment-suppressed microglia polarization to the M1 phenotype in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2018, 19, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Velagapudi, R.; Jamshaid, F.; Lepiarz, I.; Katola, F.O.; Hemming, K.; Olajide, O.A. The tiliroside derivative, 3-O-[(E)-(2-oxo-4-(p-tolyl) but-3-en-1-yl] kaempferol produced inhibition of neuroinflammation and activation of AMPK and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways in BV-2 microglia. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.K.; Chang, C.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Kuan, Y.H.; Pan, H.C.; Liao, S.L.; Li, G.Z.; Chen, C.J. Tetramethylpyrazine reduces cellular inflammatory response following permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 247, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaserer, T.; Lantero, A.; Schmidhammer, H.; Spetea, M.; Schuster, D. m Opioid receptor: Novel antagonists and structural modeling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangherlini, G.; Kalinin, D.V.; Schepmann, D.; Che, T.; Mykicki, N.; Ständer, S.; Loser, K.; Wünsch, B. Development of novel quinoxaline-based κ-opioid receptor agonists for the treatment of neuroinflammation. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Muo, C.H.; Liang, J.A.; Sung, F.C.; Kao, C.H. Association of intensive morphine treatment and increased stroke incidence in prostate cancer patients: A population-based nested case-control study. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 43, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.K.; Ou, Y.C.; Kuo, J.S.; Chen, W.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Wu, C.W.; Chen, C.J.; Ling, N.N.; Zhang, Y.H.; Peng, W.H. Neuroprotection by tetramethylpyrazine against ischemic brain injury in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 166–176. [Google Scholar]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Shih, K.-C.; Hung, C.-J.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, W.-Y.; Kuan, Y.-H.; Liao, S.-L.; Wang, W.-Y.; et al. β-Funaltrexamine Displayed Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects in Cells and Rat Model of Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113866
Wu C-C, Chang C-Y, Shih K-C, Hung C-J, Wang Y-Y, Lin S-Y, Chen W-Y, Kuan Y-H, Liao S-L, Wang W-Y, et al. β-Funaltrexamine Displayed Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects in Cells and Rat Model of Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113866
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chih-Cheng, Cheng-Yi Chang, Kuei-Chung Shih, Chih-Jen Hung, Ya-Yu Wang, Shih-Yi Lin, Wen-Ying Chen, Yu-Hsiang Kuan, Su-Lan Liao, Wen-Yi Wang, and et al. 2020. "β-Funaltrexamine Displayed Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects in Cells and Rat Model of Stroke" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113866
APA StyleWu, C.-C., Chang, C.-Y., Shih, K.-C., Hung, C.-J., Wang, Y.-Y., Lin, S.-Y., Chen, W.-Y., Kuan, Y.-H., Liao, S.-L., Wang, W.-Y., & Chen, C.-J. (2020). β-Funaltrexamine Displayed Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects in Cells and Rat Model of Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113866





