E8002 Inhibits Peripheral Nerve Adhesion by Enhancing Fibrinolysis of l-Ascorbic Acid in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Wound Healing Is Not Affected by E8002 Membrane
2.2. l-Ascorbic Acid-Containing E8002 Membrane Inhibits Formation of Nerve Adhesions
2.3. l-Ascorbic Acid-Containing E8002 Membrane Inhibits Scar Tissue Formation
2.4. E8002 Membrane Did Not Cause Neurological Adverse Effects in Rats Following Sciatic Nerve Adhesion
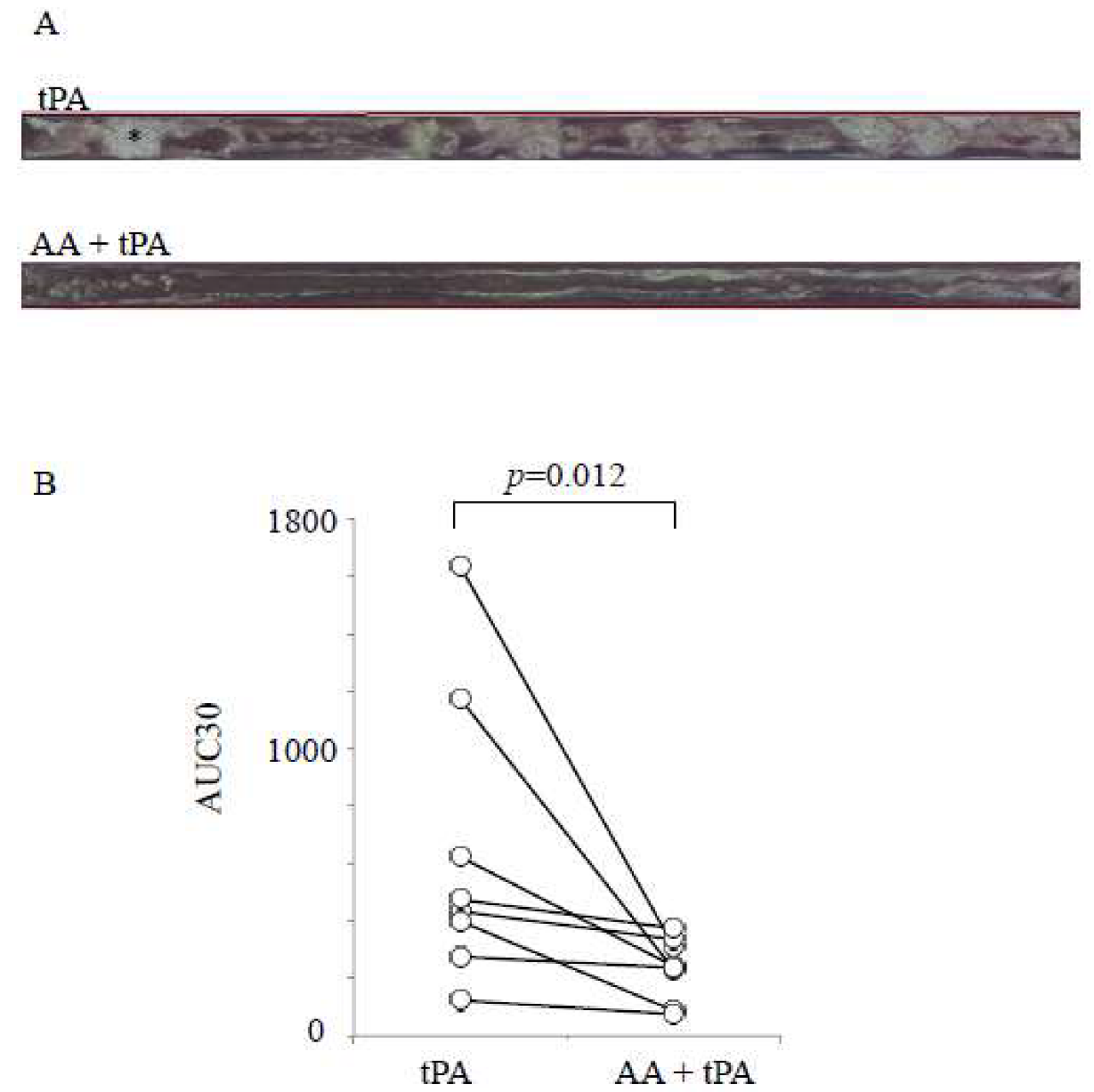
2.5. l-Ascorbic Acid Enhances Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Mediated Fibrinolysis
3. Discussion
Study Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Groups
4.2. Rat Sciatic Nerve Adhesion Model
4.3. Assessment of Neurological Adverse Events
4.4. Wound Healing Score
4.5. Nerve Adhesion Score
4.6. Histological Examination of Adhesions
4.7. Human Blood Samples
4.8. Assessment of Fibrinolysis Using the Total Thrombus-Formation Analysis System
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shintani, K.; Uemura, T.; Takamatsu, K.; Yokoi, T.; Onode, E.; Okada, M.; Nakamura, H. Protective effect of biodegradable nerve conduit against peripheral nerve adhesion after neurolysis. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsumi, H.; Hirata, H.; Nagakura, T.; Tsujii, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Horiuchi, T.; Nagao, M.; Nakashima, T.; Uchida, A. Enhancement of perineurial repair and inhibition of nerve adhesion by viscous injectable pure alginate sol. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngeow, W.C. Scar less: A review of methods of scar reduction at sites of peripheral nerve repair. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 109, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürgisser, G.M.; Buschmann, J. History and performance of implant materials applied as peritendinous antiadhesives. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yoshimoto, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Nakanishi, K. Interferon-gamma is a therapeutic target molecule for prevention of postoperative adhesion formation. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koninckx, P.R.; Gomel, V.; Ussia, A.; Adamyan, L. Role of the peritoneal cavity in the prevention of postoperative adhesions, pain, and fatigue. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Miwa, Y.; Nagasaki, Y. Design of high-performance anti-adhesion agent using injectable gel with an anti-oxidative stress function. Biomaterials 2015, 69, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.H.; Hart, G. In vitro oxidative damage to tissue-type plasminogen activator: A selective modification of the biological functions. Cardiovasc. Res. 1995, 30, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Setoyama, K.; Kawahara, K.I.; Nagasato, T.; Terashi, T.; Ueda, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Otsuka, S.; Miura, N.; Sameshima, H.; et al. Edaravone, a synthetic free radical scavenger, enhances alteplase-mediated thrombolysis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6873281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K.; Setoyama, K.; Tanaka, E.; Otsuka, S.; Terashi, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Takada, S.; Sakakima, H.; Ampawong, S.; Kawahara, K.; et al. Uric acid enhances alteplase-mediated thrombolysis as an antioxidant. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atilgan, R.; Kuloglu, T.; Ozkan, Z.S.; Kavak, S.B.; Kumbak, B.; Deveci, D.; Simsek, M.; Baspinar, M.; Sapmaz, E. Evaluation of vitamin C and vitamin E for prevention of postoperative adhesion: A rat uterine horn model study. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2015, 41, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K.; Setoyama, K.; Terashi, T.; Sumizono, M.; Tancharoen, S.; Otsuka, S.; Takada, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Ueda, K.; Sakakima, H.; et al. Application of a novel anti-adhesive membrane, E8002, in a rat laminectomy model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, T.; Kamitani, S.; Shimizu, T.; Fujino, M.; Tsutamoto, Y.; Endo, Y.; Hanasawa, K.; Tani, T. Development of a novel, nearly insoluble antiadhesive membrane. Eur. Surg. Res. 2011, 47, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Kondo, T.; Fukasawa, M.; Koide, T.; Maruyama, I.; Tanaka, K. A novel automated microchip flow-chamber system to quantitatively evaluate thrombus formation and antithrombotic agents under blood flow conditions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Woodcock-Mitchell, J.; Mitchell, J.; Sakamoto, T.; Marutsuka, K.; Sobel, B.E.; Fujii, S. Induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and type 1 collagen expression in rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cells by interleukin-1 and its dependence on oxygen-centered free radicals. Circulation 1998, 97, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Woodcock-Mitchell, J.; Marutsuka, K.; Mitchell, J.J.; Sobel, B.E.; Fujii, S. TNF-α and insulin, alone and synergistically, induce plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UMIN CTR. Randomized Controlled Trial on Efficacy and Safety of E8002. Available online: https://upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi-open-bin/ctr/ctr.cgi?function=brows&action=brows&recptno=R000032997&type=summary&language=J (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Otsuka, S.; Sakakima, H.; Sumizono, M.; Takada, S.; Terashi, T.; Yoshida, Y. The neuroprotective effects of preconditioning exercise on brain damage and neurotrophic factors after focal brain ischemia in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 15, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumizono, M.; Sakakima, H.; Otsuka, S.; Terashi, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Ueda, K.; Takada, S.; Kikuchi, K. The effect of exercise frequency on neuropathic pain and pain-related cellular reactions in the spinal cord and midbrain in a rat sciatic nerve injury model. J. Pain Res. 2018, 7, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kikuchi, K.; Setoyama, K.; Takada, S.; Otsuka, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Norimatsu, K.; Tani, A.; Sakakima, H.; Kawahara, K.-i.; Hosokawa, K.; et al. E8002 Inhibits Peripheral Nerve Adhesion by Enhancing Fibrinolysis of l-Ascorbic Acid in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113972
Kikuchi K, Setoyama K, Takada S, Otsuka S, Nakanishi K, Norimatsu K, Tani A, Sakakima H, Kawahara K-i, Hosokawa K, et al. E8002 Inhibits Peripheral Nerve Adhesion by Enhancing Fibrinolysis of l-Ascorbic Acid in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113972
Chicago/Turabian StyleKikuchi, Kiyoshi, Kentaro Setoyama, Seiya Takada, Shotaro Otsuka, Kazuki Nakanishi, Kosuke Norimatsu, Akira Tani, Harutoshi Sakakima, Ko-ichi Kawahara, Kazuya Hosokawa, and et al. 2020. "E8002 Inhibits Peripheral Nerve Adhesion by Enhancing Fibrinolysis of l-Ascorbic Acid in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113972
APA StyleKikuchi, K., Setoyama, K., Takada, S., Otsuka, S., Nakanishi, K., Norimatsu, K., Tani, A., Sakakima, H., Kawahara, K.-i., Hosokawa, K., Kiyama, R., Sumizono, M., Tancharoen, S., Maruyama, I., Hattori, G., Morioka, M., Tanaka, E., & Uchikado, H. (2020). E8002 Inhibits Peripheral Nerve Adhesion by Enhancing Fibrinolysis of l-Ascorbic Acid in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113972






