Elastography Techniques for the Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
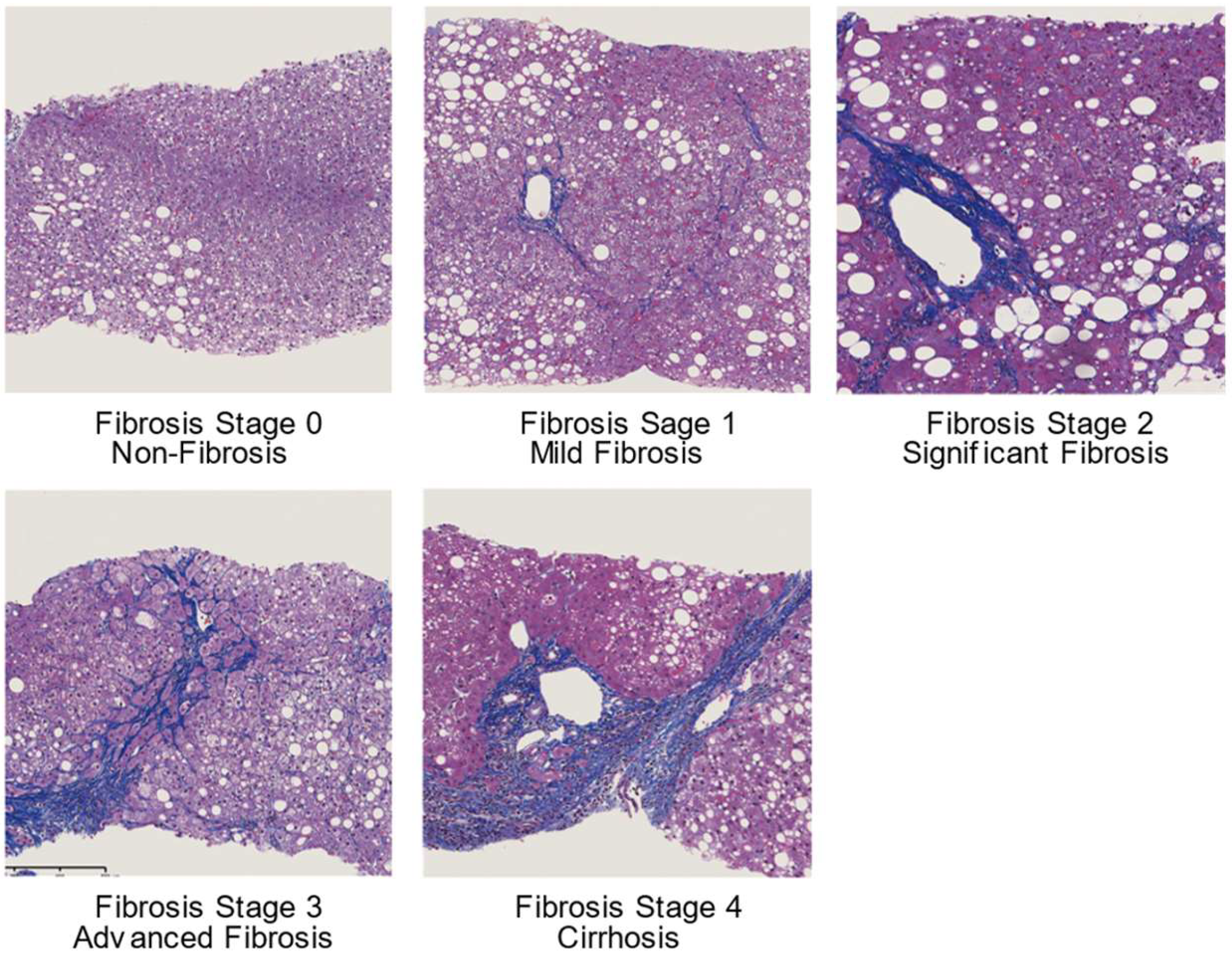
1. Introduction
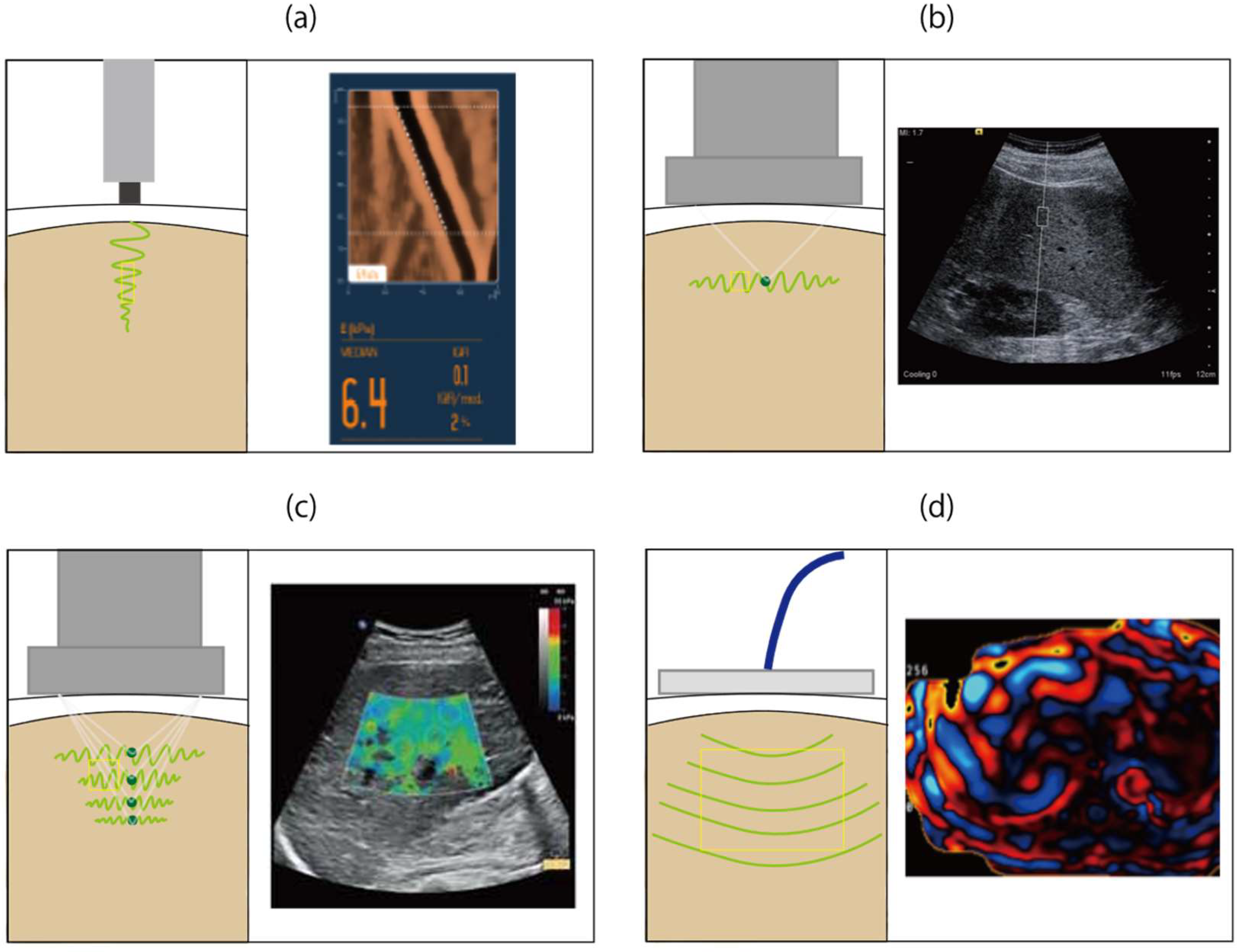
2. Vibration-Controlled Transient Elastography
3. Point Shear Wave Elastography
4. Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography
5. Magnetic Resonance Elastography
6. Comparison of Elastography Techniques in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Keonig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999–2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.P.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Cortez-Pinto, H. Hepatic histology in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milic, S.; Lulic, D.; Stimac, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity: Biochemical, metabolic and clinical presentations. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9330–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Ye, L.; Wen, S.W.; Deng, J.; Wu, X.; Lai, Z. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Ekstedt, M.; Hammar, U.; Stål, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Kechagias, S. Fibrosis stage but not NASH predicts mortality and time to development of severe liver disease in biopsy-proven NAFLD. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Eng. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedossa, P.; Carrat, F. Liver biopsy: The best, not the gold standard. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Itoh, Y. Limitations of liver biopsy and non-invasive diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwalkar, J.A. Elastography for detecting hepatic fibrosis: Options and considerations. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sandrin, L.; Tanter, M.; Gennisson, J.L.; Catheline, S.; Fink, M. Shear elasticity probe for soft tissues with 1-D transient elastography. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2002, 49, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Wong, V.W.; Castera, L.; Berzigotti, A.; Sporea, I.; Dietrich, C.F.; Choi, B.I.; Wilson, S.R.; Kudo, M.; Barr, R.G. Liver ultrasound elastography: An update to the world federation for ultrasound in medicine and biology guidelines and recommendations. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2419–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Fujita, K.; Inamori, M.; Nakajima, A.; Yoneda, M.; Tamano, M.; Hiraishi, H. Transient elastography in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Gut 2007, 56, 1330–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for Study of Liver. EASL Clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 392–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarajah, S.K.; Chan, W.K.; Nik Mustapha, N.R.; Mahadeva, S. Repeated liver stiffness measurement compared with paired liver biopsy in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, A.; Yoneda, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Kessoku, T.; Honda, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tomeno, W.; Imajo, K.; Kirikoshi, H.; et al. Assessment of 10-year changes in liver stiffness using vibration-controlled transient elastography in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, A.W.; Shu, S.S.; Chan, C.K.; Leung, J.K.; Choi, P.C.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W. Repeating measurements by transient elastography in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with high liver stiffness. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, K.H.; Lai, L.L.; Vethakkan, S.R.; Nik Mustapha, N.R.; Mahadeva, S.; Chan, W.K. Liver stiffness measurement in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Two is better than one. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraquelli, M.; Rigamonti, C.; Casazza, G.; Conte, D.; Donato, M.F.; Ronchi, G.; Colombo, M. Reproducibility of transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut 2007, 56, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ledinghen, V.; Vergniol, J. Transient elastography (FibroScan). Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2008, 32, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, L.; Foucher, J.; Bernard, P.H.; Carvalho, F.; Allaix, D.; Merrouche, W.; Couzigou, P.; de Ledinghen, V. Pitfalls of liver stiffness measurement: A 5-year prospective study of 13,369 examinations. Hepatology 2010, 51, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirli, R.; Sporea, I.; Bota, S.; Jurchis, A. Factors influencing reliability of liver stiffness measurements using transient elastography (M-probe)-monocentric experience. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e313–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Vergniol, J.; Wong, G.L.; Foucher, J.; Chan, H.L.; Le Bail, B.; Choi, P.C.; Kowo, M.; Chan, A.W.; Merrouche, W.; et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Tse, Y.K.; Wong, G.L.; Ha, Y.; Lee, A.U.; Ngu, M.C.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease--the role of transient elastography and plasma cytokeratin-18 fragments. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Huang, S.; Teng, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, M.; Zhou, X.; Ran, H. Diagnostic accuracy of point shear wave elastography and transient elastography for staging hepatic fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e021787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, G. Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Robertis, R.; D’Onofrio, M.; Demozzi, E.; Crosara, S.; Canestrini, S.; Pozzi Mucelli, R. Noninvasive diagnosis of cirrhosis: A review of different imaging modalities. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7231–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Labyed, Y.; Sy, E.Z.; Boehringer, A.S.; Andre, M.P.; Erdman, J.W., Jr.; Loomba, R.; Sirlin, C.B.; O’Brien, W.D., Jr. Inter-sonographer reproducibility of quantitative ultrasound outcomes and shear wave speed measured in the right lobe of the liver in adults with known or suspected non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4992–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bota, S.; Sporea, I.; Sirli, R.; Popescu, A.; Danila, M.; Costachescu, D. Intra- and interoperator reproducibility of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography—Preliminary results. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, M.; Souza, F.; Munoz, C.; Augustin, S.; Loo, N.; Deng, Y.; Ciarleglio, M.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Liver and spleen stiffness measurements by point shear wave elastography via acoustic radiation force impulse: Intraobserver and interobserver variability and predictors of variability in a US population. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Tinelli, C.; Lissandrin, R.; Zicchetti, M.; Bernuzzi, S.; Salvaneschi, L.; Filice, C. Ultrasound point shear wave elastography assessment of liver and spleen stiffness: Effect of training on repeatability of measurements. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, J.; Hong, R.; Liu, L.; Li, F. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for the non-invasive evaluation of hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A systematic review & meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fu, J.; Hong, R.; Liu, L.; Li, F. The diagnostic accuracy of liver fibrosis in non-viral liver diseases using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercoff, J.; Tanter, M.; Fink, M. Supersonic shear imaging: A new technique for soft tissue elasticity mapping. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2004, 51, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavu, E.; Gennisson, J.L.; Couade, M.; Bercoff, J.; Mallet, V.; Fink, M.; Badel, A.; Vallet-Pichard, A.; Nalpas, B.; Tanter, M.; et al. Noninvasive in vivo liver fibrosis evaluation using supersonic shear imaging: A clinical study on 113 hepatitis C virus patients. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2011, 37, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinotto, C.; Boursier, J.; de Ledinghen, V.; Lebigot, J.; Lapuyade, B.; Cales, P.; Hiriart, J.B.; Michalak, S.; Bail, B.L.; Cartier, V.; et al. Liver stiffness in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comparison of supersonic shear imaging, FibroScan, and ARFI with liver biopsy. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporea, I.; Bota, S.; Jurchis, A.; Sirli, R.; Gradinaru-Tascau, O.; Popescu, A.; Ratiu, I.; Szilaski, M. Acoustic radiation force impulse and supersonic shear imaging versus transient elastography for liver fibrosis assessment. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Tinelli, C.; Zicchetti, M.; Above, E.; Poma, G.; Di Gregorio, M.; Filice, C. Reproducibility of real-time shear wave elastography in the evaluation of liver elasticity. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3102–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, W.; Cho, B.; Choi, B.I. Comparison of the reliability of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging and supersonic shear imaging in measurement of liver stiffness. Radiology 2015, 277, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthupillai, R.; Lomas, D.J.; Rossman, P.J.; Greenleaf, J.F.; Manduca, A.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science 1995, 269, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.K.; Yin, M.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography of liver: Technique, analysis, and clinical applications. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.G.; Ferraioli, G.; Palmeri, M.L.; Goodman, Z.D.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Rubin, J.; Garra, B.; Myers, R.P.; Wilson, S.R.; Rubens, D.; et al. Elastography assessment of liver fibrosis: Society of radiologists in ultrasound consensus conference statement. Radiology 2015, 276, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Babu, A.; Wells, M.L.; Teytelboym, O.M.; Mackey, J.E.; Miller, F.H.; Yeh, B.M.; Ehman, R.L.; Venkatesh, S.K. Elastography in chronic liver disease: Modalities, techniques, limitations, and future directions. Radiographics 2016, 36, 1987–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, S.K.; Talwalkar, J.A. When and how to use magnetic resonance elastography for patients with liver disease in clinical practice. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, J.A.; Navasa, M.; Forns, X. MR elastography to assess liver fibrosis. Radiology 2008, 247, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.G. Elastography in clinical practice. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 52, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Venkatesh, S.K. Magnetic resonance elastography and other magnetic resonance imaging techniques in chronic liver disease: Current status and future directions. Gut Liver 2016, 10, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Cui, J.; Wolfson, T.; Haufe, W.; Hooker, J.; Szeverenyi, N.; Ang, B.; Bhatt, A.; Wang, K.; Aryafar, H.; et al. Novel 3D magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in NAFLD: A prospective study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Glaser, K.J.; Manduca, A.; Grimm, R.C.; Rossman, P.; Fidler, J.L.; Ehman, R.L. Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1207–1213.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, C.D.; Bley, T.A.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Reeder, S.B. Repeatability of magnetic resonance elastography for quantification of hepatic stiffness. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shire, N.J.; Yin, M.; Chen, J.; Railkar, R.A.; Fox-Bosetti, S.; Johnson, S.M.; Beals, C.R.; Dardzinski, B.J.; Sanderson, S.O.; Talwalkar, J.A.; et al. Test-retest repeatability of MR elastography for noninvasive liver fibrosis assessment in hepatitis C. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 34, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, A.T.; Serai, S.; Mahley, A.D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Dillman, J.R. Liver stiffness measurements with MR elastography: Agreement and repeatability across imaging systems, field strengths, and pulse sequences. Radiology 2016, 281, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasar, T.K.; Wagner, M.; Bane, O.; Besa, C.; Babb, J.S.; Kannengiesser, S.; Fung, M.; Ehman, R.L.; Taouli, B. Interplatform reproducibility of liver and spleen stiffness measured with MR elastography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 43, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Loomba, R.; Wang, Z.; Sirlin, C.; Chen, J.; Yin, M.; Miller, F.H.; Low, R.N.; Hassanein, T.; et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 440–451.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Glaser, K.J.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Chen, J.; Manduca, A.; Ehman, R.L. Dynamic postprandial hepatic stiffness augmentation assessed with MR elastography in patients with chronic liver disease. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Loomba, R.; Wang, Z.; Sirlin, C.; Chen, J.; Yin, M.; Miller, F.H.; Low, R.N.; Hassanein, T.; et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A diagnostic accuracy systematic review and individual participant data pooled analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bota, S.; Sporea, I.; Sirli, R.; Popescu, A.; Danila, M.; Jurchis, A.; Gradinaru-Tascau, O. Factors associated with the impossibility to obtain reliable liver stiffness measurements by means of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography—Analysis of a cohort of 1,031 subjects. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, L. Noninvasive methods to assess liver disease in patients with hepatitis B or C. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1293–1302.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.K.; Wells, M.L.; Miller, F.H.; Jhaveri, K.S.; Silva, A.C.; Taouli, B.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography: Beyond liver fibrosis-a case-based pictorial review. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 1590–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.L.; Wong, V.W.; Chim, A.M.; Yiu, K.K.; Chu, S.H.; Li, M.K.; Chan, H.L. Factors associated with unreliable liver stiffness measurement and its failure with transient elastography in the Chinese population. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.P.; Pomier-Layrargues, G.; Kirsch, R.; Pollett, A.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Wong, D.; Beaton, M.; Levstik, M.; Crotty, P.; Elkashab, M. Feasibility and diagnostic performance of the FibroScan XL probe for liver stiffness measurement in overweight and obese patients. Hepatology 2012, 55, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Wen, H.; Chen, S.; Chen, X. The influence of hepatic steatosis on the evaluation of fibrosis with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by acoustic radiation force impulse. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Seogwipo, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 2988–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.K.; Kim, W.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.; Lee, K.L.; Chang, M.S.; Jung, Y.J.; So, Y.H.; Lee, M.S.; et al. Steatosis severity affects the diagnostic performances of noninvasive fibrosis tests in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeda, S.; Takahashi, H.; Imajo, K.; Seko, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Moriguchi, M.; Yoneda, M.; Anzai, K.; Aishima, S.; Kage, M.; et al. Accuracy of liver stiffness measurement and controlled attenuation parameter using FibroScan((R)) M/XL probes to diagnose liver fibrosis and steatosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicenter prospective study. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppalanchi, R.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Van Natta, M.L.; Hallinan, E.; Brandman, D.; Kowdley, K.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Dasarathy, S.; Abdelmalek, M.; et al. Performance characteristics of vibration-controlled transient elastography for evaluation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddowes, P.J.; Sasso, M.; Allison, M.; Tsochatzis, E.; Anstee, Q.M.; Sheridan, D.; Guha, I.N.; Cobbold, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Paradis, V.; et al. Accuracy of FibroScan controlled attenuation parameter and liver stiffness measurement in assessing steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajo, K.; Kessoku, T.; Honda, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Ogawa, Y.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Taguri, M.; Hyogo, H.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging more accurately classifies steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease than transient elastography. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 626–637.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Ang, B.; Haufe, W.; Hernandez, C.; Verna, E.C.; Sirlin, C.B.; Loomba, R. Comparative diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance elastography vs. eight clinical prediction rules for non-invasive diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Heba, E.; Hernandez, C.; Haufe, W.; Hooker, J.; Andre, M.P.; Valasek, M.A.; Aryafar, H.; Sirlin, C.B.; Loomba, R. Magnetic resonance elastography is superior to acoustic radiation force impulse for the Diagnosis of fibrosis in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study. Hepatology 2016, 63, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.C.; Nguyen, P.; Hernandez, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Ramirez, K.; Fortney, L.; Hooker, J.; Sy, E.; Savides, M.T.; Alquiraish, M.H.; et al. Magnetic resonance elastography vs. transient elastography in detection of fibrosis and noninvasive measurement of steatosis in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 598–607.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulai, P.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Loomba, R. MRI and MRE for non-invasive quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in NAFLD and NASH: Clinical trials to clinical practice. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmera, V.H.; Liu, A.; Singh, S.; Yachoa, G.; Ramey, M.; Bhargava, M.; Zamani, A.; Lopez, S.; Mangla, N.; Bettencourt, R.; et al. Clinical utility of an increase in magnetic resonance elastography in predicting fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2020, 71, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, M.; Beaugrand, M.; de Ledinghen, V.; Douvin, C.; Marcellin, P.; Poupon, R.; Sandrin, L.; Miette, V. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP): A novel VCTE™ guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: Preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Sasso, M.; Deeks, J.J.; Paredes, A.; Boursier, J.; Chan, W.K.; Yilmaz, Y.; Czernichow, S.; Zheng, M.H.; Wong, V.W.; et al. FibroScan-AST (FAST) score for the non-invasive identification of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with significant activity and fibrosis: A prospective derivation and global validation study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, S.B.; Robson, P.M.; Yu, H.; Shimakawa, A.; Hines, C. DG.; McKenzie, C.A.; Brittain, J.H. Quantification of hepatic steatosis with MRI: The effects of accurate fat spectral modeling. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 29, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permutt, Z.; Le, T.-A.; Peterson, M.R.; Seki, E.; Brenner, D.A.; Sirlin, C.; Loomba, R. Correlation between liver histology and novel magnetic resonance imaging in adult patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—MRI accurately quantifies hepatic steatosis in NAFLD. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Imajo, K.; Nakajima, A. Non-invasive diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1409–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castera, L.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Loomba, R. Noninvasive assessment of liver disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1264–1281.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Goh, G.B.; Fan, J.G.; Song, M.J.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Duseja, A.; Dan, Y.Y.; Imajo, K.; Nakajima, A.; et al. Optimizing use of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis score, fibrosis-4 score, and liver stiffness measurement to identify patients with advanced fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2570–2580.e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Nik Mustapha, N.R.; Mahadeva, S. A novel 2-step approach combining the NAFLD fibrosis score and liver stiffness measurement for predicting advanced fibrosis. Hepatol. Int. 2015, 9, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Vanni, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Di Marco, V.; Cammà, C.; Cabibi, D.; Mezzabotta, L.; Craxì, A. The combination of liver stiffness measurement and NAFLD fibrosis score improves the noninvasive diagnostic accuracy for severe liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver International 2015, 35, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Cammà, C.; Hiriart, J.-B.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Vergniol, J.; Chan, A.W.-H.; Di Marco, V.; Merrouche, W.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; et al. Serial combination of non-invasive tools improves the diagnostic accuracy of severe liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Technique | Author | Year | Reference No. | No. of Patients | No. of Studies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCTE M probe | Kwok et al. | 2014 | 26 | 854 | 8 | Fibrosis Stage | Range | |||
| Cut-off (kPa) | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUROC | |||||||
| ≥2 | 6.65–7.7 | 0.67–0.94 | 0.61–0.84 | 0.79–0.87 | ||||||
| ≥3 | 8.0–10.4 | 0.65–1.00 | 0.75–0.97 | 0.76–0.98 | ||||||
| ≥4 | 10.3–17.5 | 0.78–1.00 | 0.82–0.98 | 0.91–0.99 | ||||||
| Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||||||||
| Sensitivity | Specificity | |||||||||
| ≥2 | 0.79 | 0.75 | ||||||||
| ≥3 | 0.85 | 0.85 | ||||||||
| ≥4 | 0.92 | 0.92 | ||||||||
| Xiao et al. | 2017 | 28 | 2495 | 16 | Fibrosis Stage | Range | ||||
| Cut-off (kPa) | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||||||
| ≥2 | 5.8 | 0.90–0.94 | 0.42–0.80 | |||||||
| 6.65–7 | 0.58–1.00 | 0.45–0.84 | ||||||||
| 7.25–11 | 0.53–0.84 | 0.70–0.93 | ||||||||
| ≥3 | 6.95–7.25 | 0.67–0.70 | 0.65–0.68 | |||||||
| 7.6–8 | 0.65–1.00 | 0.66–0.90 | ||||||||
| 8.7–9 | 0.76–0.88 | 0.63–0.88 | ||||||||
| 9.6–11.4 | 0.69–1.00 | 0.84–0.97 | ||||||||
| ≥4 | 7.9–8.4 | 0.93–1.00 | 0.76–0.79 | |||||||
| 10.3–11.3 | 0.78–1.00 | 0.82–0.90 | ||||||||
| 11.5–11.95 | 0.69–0.90 | 0.85–0.91 | ||||||||
| 13.4–22.3 | 0.41–1.00 | 0.76–0.98 | ||||||||
| Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||||||||
| AUROC (95% CI) | ||||||||||
| ≥2 | 0.83 (0.79–0.86) | |||||||||
| ≥3 | 0.87 (0.83–0.90) | |||||||||
| ≥4 | 0.92 (0.90–0.94) | |||||||||
| Jiang et al. | 2018 | 27 | 1753 | 11 | Fibrosis Stage | Range | ||||
| Cut-off (kPa) | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUROC | |||||||
| ≥2 | 6.7–11.0 | 0.60–0.94 | 0.61–1.00 | 0.79–0.88 | ||||||
| ≥3 | 8.0–12.5 | 0.57–1.00 | 0.76–0.97 | 0.76–0.99 | ||||||
| ≥4 | 10.4–17.5 | 0.65–1.00 | 0.76–0.98 | 0.87–0.99 | ||||||
| Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||||||||
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) | ||||||||
| ≥2 | 0.77 (0.70–0.84) | 0.80 (0.74–0.84) | 0.85 (0.82–0.88) | |||||||
| ≥3 | 0.79 (0.69–0.87) | 0.89 (0.84–0.92) | 0.92 (0.89–0.94) | |||||||
| ≥4 | 0.90 (0.73–0.97) | 0.91 (0.87–0.94) | 0.94 (0.93–0.97) | |||||||
| VCTE XL probe | Xiao et al. | 2017 | 28 | 318 | 3 | Fibrosis Stage | Range | |||
| Cut-off (kPa) | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||||||
| ≥2 | 4.8–8.2 | 0.57–0.92 | 0.37–0.90 | |||||||
| ≥3 | 5.7–9.3 | 0.57–0.91 | 0.54–0.90 | |||||||
| ≥4 | 7.2–16 | 0.71–1.00 | 0.70–0.91 | |||||||
| Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||||||||
| AUROC (95% CI) | ||||||||||
| ≥2 | 0.82 (0.75–0.89) | |||||||||
| ≥3 | 0.86 (0.78–0.94) | |||||||||
| ≥4 | 0.94 (0.88–0.99) | |||||||||
| pSWE | Liu et al. | 2015 | 34 | 723 | 7 | Fibrosis Stage | Range | |||
| Cut-off (m/s) | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||||||
| ≥2 | 1.165–1.79 | 0.71–0.90 | 0.67–0.90 | |||||||
| ≥3 | 1.45–2.20 | 0.75–1.00 | 0.68–0.95 | |||||||
| ≥4 | 1.61–2.90 | 0.74–1.00 | 0.67–0.96 | |||||||
| Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||||||||
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) | ||||||||
| ≥2 | 0.80 (0.76–0.84) | 0.85 (0.81–0.89) | 0.90 | |||||||
| Jiang et al. | 2018 | 27 | 982 | 9 | Fibrosis Stage | Range | ||||
| Cut-off (m/s) | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUROC | |||||||
| ≥2 | 1.16–1.32 | 0.56–0.85 | 0.78–0.91 | 0.71–0.94 | ||||||
| ≥3 | 1.34–1.77 | 0.59–1.00 | 0.74–0.96 | 0.76–0.99 | ||||||
| ≥4 | 1.40–2.48 | 0.44–1.00 | 0.74–1.00 | 0.84–0.98 | ||||||
| Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||||||||
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) | ||||||||
| ≥2 | 0.70 (0.59–0.79) | 0.84 (0.79–0.88) | 0.86 (0.83–0.89) | |||||||
| ≥3 | 0.89 (0.73–0.96) | 0.88 (0.82–0.92) | 0.94 (0.91–0.95) | |||||||
| ≥4 | 0.89 (0.60–0.98) | 0.91 (0.82–0.95) | 0.95 (0.93–0.97) | |||||||
| Lin et al. | 2020 | 35 | 1147 | 13 | Fibrosis Stage | Summary | ||||
| Cut-off (m/s) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) | |||||||
| ≥2 | 1.3 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.89 (0.85–0.91) | ||||||
| ≥3 | 2.06 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.94 (0.91–0.96) | ||||||
| ≥4 | 1.89 | 0.9 | 0.95 | 0.94 (0.92–0.95) | ||||||
| MRE | Singh et al. | 2016 | 58 | 232 | 9 | Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||
| Cut-off (kPa) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | AUROC (95% CI) | |||||||
| ≥1 | 2.88 | 0.75 (0.68–0.87) | 0.77 (0.65–0.88) | 0.86 (0.82–0.90) | ||||||
| ≥2 | 3.54 | 0.79 (0.76–0.90) | 0.81 (0.72–0.91) | 0.87 (0.82–0.93) | ||||||
| ≥3 | 3.77 | 0.83 (0.53–0.90) | 0.86 (0.81–0.96) | 0.90 (0.84–0.94) | ||||||
| ≥4 | 4.09 | 0.88 (0.82–1.00) | 0.87 (0.77–0.97) | 0.91 (0.76–0.95) | ||||||
| Xiao et al. | 2017 | 28 | 628 | 5 | Fibrosis Stage | Range | ||||
| Cut-off (kPa) | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||||||||
| ≥2 | 3.4–3.62 | 65.7–97.3 | 85.0–95.7 | |||||||
| ≥3 | 3.62–4.8 | 74.5–92.2 | 86.9–93.3 | |||||||
| ≥4 | 4.15–6.7 | 80.0–90.9 | 91.4–94.5 | |||||||
| Fibrosis Stage | Summary | |||||||||
| AUROC (95% CI) | ||||||||||
| ≥2 | 0.88 (0.83–0.92) | |||||||||
| ≥3 | 0.93 (0.90–0.97) | |||||||||
| ≥4 | 0.92 (0.80–1.00) | |||||||||
| US-Based | MR-Based | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCTE | pSWE | 2D-SWE | MRE | ||
| M Probe | XL Probe | ||||
| Confounder | Obesity | Obesity | Obesity | ||
| Inflammation | Inflammation | Inflammation | Inflammation | ||
| Ascites | Ascites | ||||
| Iron Overload | |||||
| Cholestasis, Hepatic Congestion | |||||
| Sampling Volume of Liver | Little | Large | |||
| Technical Failure | 6.7–29.2% | ~2% | ~5% | ~5% | |
| Cost | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Availability | Good | Limited | |||
| HCC Screening | Blind technique | US Exam | US Exam | MRI Exam | |
| Evaluation of Liver Fat Accumulation | CAP | - | - | PDFF | |
| Guideline Recommendation | AASLD, EASL | - | - | AASLD | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honda, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Imajo, K.; Nakajima, A. Elastography Techniques for the Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114039
Honda Y, Yoneda M, Imajo K, Nakajima A. Elastography Techniques for the Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114039
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonda, Yasushi, Masato Yoneda, Kento Imajo, and Atsushi Nakajima. 2020. "Elastography Techniques for the Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114039
APA StyleHonda, Y., Yoneda, M., Imajo, K., & Nakajima, A. (2020). Elastography Techniques for the Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 4039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114039







