Anti-Inflammatory Potential of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Enriched Hen Eggs Consumption in Improving Microvascular Endothelial Function of Healthy Individuals—Clinical Trial
Abstract
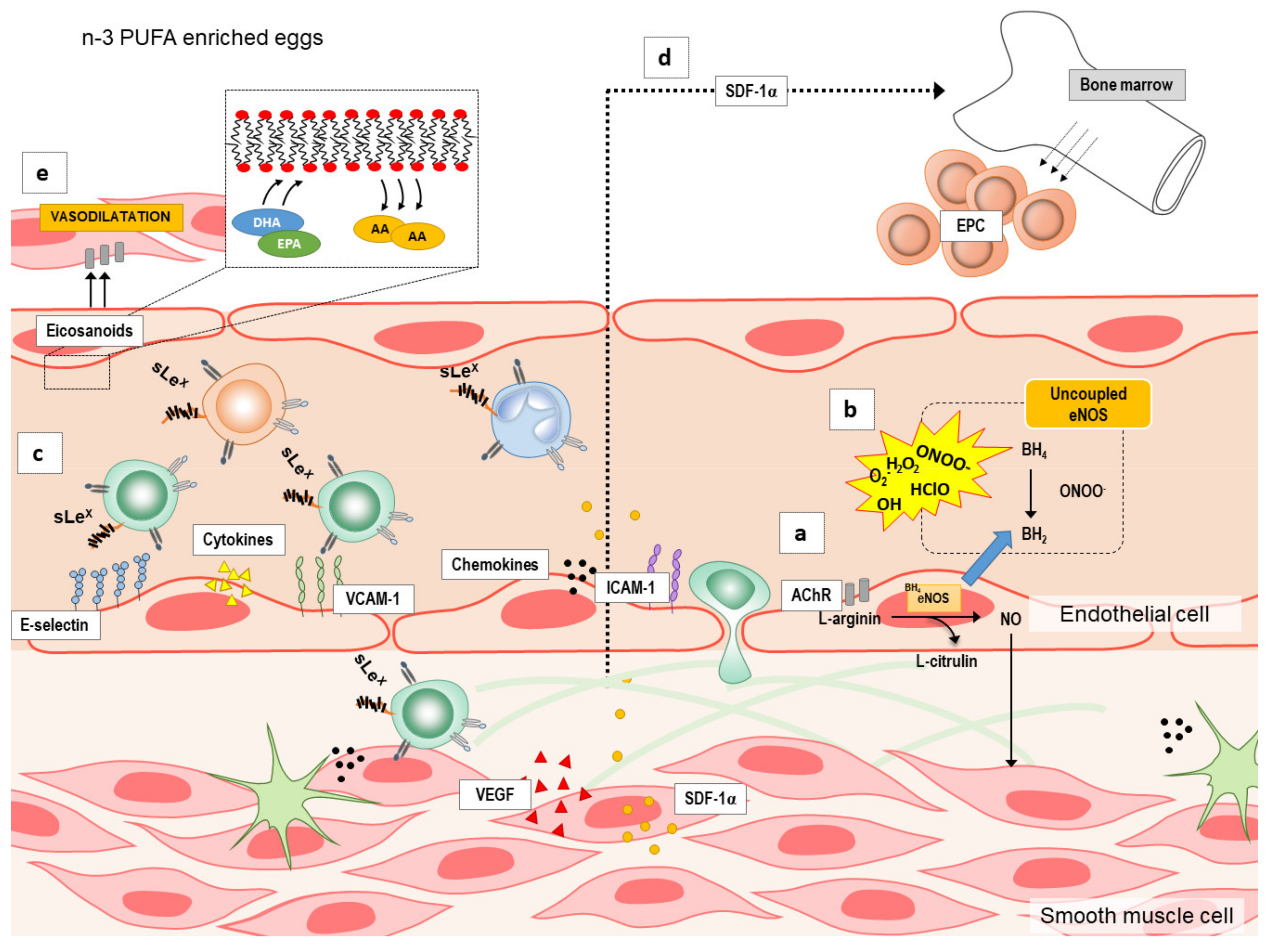
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Content of Fatty Acids in Chicken Feed Mixture and Edible Part of Eggs
2.2. Anthropometric, Hemodynamic, and Biochemical Parameters
2.3. Body Composition and Body Fluid Status
2.4. Serum Fatty Acids Profile
2.5. Forearm Skin Microvascular Endothelium-Dependent and Endothelium-Independent Vasodilation
2.6. Serum Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Soluble Cell Adhesion Molecules Protein Concentration
3. Discussion
3.1. n-3 PUFAs Enriched Hen Eggs and Serum Lipid Profile
3.2. n-3 PUFA Enriched Hen Eggs, Blood Pressure Level, Body Composition, and Body Fluid Status
3.3. n-3 PUFA Enriched Hen Eggs and Microvascular Endothelial Function
3.4. n-3 PUFAs Enriched Hen Eggs and Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Soluble Cell Adhesion Molecules
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Production of n-3 PUFAs Enriched Hen Eggs and Assessment of Fatty Acids Profile of Chicken Feed Mixtures and Edible Part of Eggs
4.3. Study Protocol
4.4. Anthropometric and Arterial Blood Pressure Measurements
4.5. Body Composition and Body Fluid Status Measurements
4.6. Venous Blood Samples Analysis
4.7. Analysis of Serum Fatty Acids Profile
4.8. Assessment of Microvascular Endothelium-Dependent and Endothelium-Independent Vasodilation
4.9. Measurement of Serum Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Soluble Cell Adhesion Molecules Protein Concentration
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CV | cardiovascular |
| n-3 PUFAs | n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| BP | blood pressure |
| EPA | eicosapentaenoic acid |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| ALA | alpha-linolenic acid |
| hsCRP | high-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| EPCs | endothelial progenitor cells |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| BMI | body mass index |
| HR | heart rate |
| SBP | systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| FFM% | Fat Free Mass% |
| Fat% | Fat Mass% |
| TBW% | Total Body Water% |
| ECW% | Extracellular Water% |
| ICW% | Intracellular Water% |
| PF | Plasma Fluid |
| IF | Interstitial Fluid |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| GC–MS/MS | gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| LDF | laser Doppler flowmetry |
| ACh | acetylcholine |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| SNP | sodium nitroprusside |
| INFγ | interferon gamma |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IL-17A | interleukin 17A |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-23 | Interleukin 23 |
| IL-9 | Interleukin 9 |
| IL-21 | Interleukin 21 |
| IL-22 | Interleukin 22 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| SDF-1α | stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha |
| LAP | latency associated peptide |
| VEGF-A | vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| VEGF-D | vascular endothelial growth factor D |
| sICAM-1 | soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| sVCAM-1 | soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| AChID | ACh-induced dilation |
| SNPID | SNP-induced dilation |
References
- Versari, D.; Daghini, E.; Virdis, A.; Ghiadoni, L.; Taddei, S. Endothelial Dysfunction as a Target for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zehr, K.R.; Walker, M.K. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids improve endothelial function in humans at risk for atherosclerosis: A review. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018, 134, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thies, F.; Garry, J.M.; Yaqoob, P.; Rerkasem, K.; Williams, J.; Shearman, C.P.; Gallagher, P.J.; Calder, P.C.; Grimble, R.F. Association of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with stability of atherosclerotic plaques: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schacky, C.; Angerer, P.; Kothny, W.; Theisen, K.; Mudra, H. The effect of dietary omega-3 fatty acids on coronary atherosclerosis. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolecek, T.A. Epidemiological evidence of relationships between dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and mortality in the multiple risk factor intervention trial. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1992, 200, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daviglus, M.L.; Stamler, J.; Orencia, A.J.; Dyer, A.R.; Liu, K.; Greenland, P.; Walsh, M.K.; Morris, D.; Shekelle, R.B. Fish Consumption and the 30-Year Risk of Fatal Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupin, M.; Kibel, A.; Stupin, A.; Selthofer-Relatić, K.; Matić, A.; Mihalj, M.; Mihaljević, Z.; Jukić, I.; Drenjančević, I. The Physiological Effect of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (n-3 PUFAs) Intake and Exercise on Hemorheology, Microvascular Function, and Physical Performance in Health and Cardiovascular Diseases; Is There an Interaction of Exercise and Dietary n-3 PUFA I. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulu, A.; Stephen Lee, K.S.; Miyabe, C.; Yang, J.; Hammock, B.G.; Dong, H.; Hammock, B.D. An Omega-3 Epoxide of Docosahexaenoic Acid Lowers Blood Pressure in Angiotensin-II–Dependent Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 64, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.E.; Van Elswyk, M.; Alexander, D.D. Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid and Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Hypertens. 2014, 27, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renier, G.; Skamene, E.; DeSanctis, J.; Radzioch, D. Dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids prevent the development of atherosclerotic lesions in mice. Modulation of macrophage secretory activities. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1993, 13, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calder, P.C. n−3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorlaksdottir, A.Y.; Skuladottir, G.V.; Petursdottir, A.L.; Tryggvadottir, L.; Ogmundsdottir, H.M.; Eyfjord, J.E.; Jonsson, J.J.; Hardardottir, I. Positive association between plasma antioxidant capacity and n-3 PUFA in red blood cells from women. Lipids 2006, 41, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenjančević, I.; Kralik, G.; Kralik, Z.; Mihalj, M.; Stupin, A.; Novak, S.; Grčević, M. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Cardiovascular Health: Revealing Potentials of Functional Food. In Superfood and Functional Food-The Development of Superfoods and Their Roles as Medicine, 1st ed.; Naofumi, S., Ed.; InTechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fraeye, I.; Bruneel, C.; Lemahieu, C.; Buyse, J.; Muylaert, K.; Foubert, I. Dietary enrichment of eggs with omega-3 fatty acids: A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki Van, E.; McCarthy, S.; Veith, H.; Ingram, H.; Calaguas, D. Lipid Responses in Mildly Hypertriglyceridemic Men and Women to Consumption of Docosahexaenoic Acid-Enriched Eggs. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2003, 73, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, N.M.; Schalch, K.; Scheideler, S.E. Serum Lipid Response to n-3 Fatty Acid Enriched Eggs in Persons with Hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2000, 100, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Heart Association News. Fish oil supplements provide some benefit after heart attack, heart failure. Available online: www.heart.org/en/news/2018/05/01/fish-oil-supplements-provide-some-benefit-after-heart-attack-heart-failure (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Bovet, P.; Faeh, D.; Madeleine, G.; Viswanathan, B.; Paccaud, F. Decrease in blood triglycerides associated with the consumption of eggs of hens fed with food supplemented with fish oil. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 17, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupin, A.; Rasic, L.; Matic, A.; Stupin, M.; Kralik, Z.; Kralik, G.; Grcevic, M.; Drenjancevic, I. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids-enriched hen eggs consumption enhances microvascular reactivity in young healthy individuals. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 43, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajianfar, H.; Paknahad, Z.; Bahonar, A. The effect of omega-3 supplements on antioxidant capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, S234–S238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Todd, S.; Yaqoob, P. Fish-oil supplementation alters numbers of circulating endothelial progenitor cells and microparticles independently of eNOS genotype. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ander, B.P.; Dupasquier, C.M.; Prociuk, M.A.; Pierce, G.N. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their effects on cardiovascular disease. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2003, 8, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Omura, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Mizukami, Y.; Mogami, K.; Todoroki-Ikeda, N.; Miyake, T.; Matsuzaki, M. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) induces Ca(2+)-independent activation and translocation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Febs Lett. 2001, 487, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirafuji, M.; Machida, T.; Tsunoda, M.; Miyamoto, A.; Minami, M. Docosahexaenoic acid potentiates interleukin-1β induction of nitric oxide synthase through mechanism involving p44/42 MAPK activation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiest, E.F.; Walsh-Wilcox, M.T.; Walker, M.K. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Protect against Cigarette Smoke-Induced Oxidative Stress and Vascular Dysfunction. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 156(1), 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caterina, R.; Cybulsky, M.I.; Clinton, S.K.; Gimbrone, M.A.; Libby, P. The omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoate reduces cytokine-induced expression of proatherogenic and proinflammatory proteins in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1994, 14, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Sheu, W.H.-H.; Chiang, A.-N. Docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid suppress adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells via differential mechanisms. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Elsen, L.; Garssen, J.; Willemsen, L. Long chain N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the prevention of allergic and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2375–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, S.; Ziouzenkova, O.; Ni, H.; Wagner, D.D.; Plutzky, J.; Mayadas, T.N. Oxidized omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil inhibit leukocyte-endothelial interactions through activation of PPARα. Blood 2002, 100, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bobetić, B. Challenges and expectations of the eu and croatian poultry in the medium term by 2030. In Proceedings of the Zbornik; 2019; Volume 12, p. 18. Available online: https://bib.irb.hr/datoteka/1001168.Zbornik_-_Proceedings_2019.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Jacobson, T.A.; Ito, M.K.; Maki, K.C.; Orringer, C.E.; Bays, H.E.; Jones, P.H.; McKenney, J.M.; Grundy, S.M.; Gill, E.A.; Wild, R.A.; et al. National Lipid Association recommendations for patient-centered management of dyslipidemia: Part 1 – executive summary. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S.; Appel, L.J. Fish Consumption, Fish Oil, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, M.A.; Cohen, D.J.A.; Liddle, D.M.; Robinson, L.E.; Ma, D.W.L. A review of the effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on blood triacylglycerol levels in normolipidemic and borderline hyperlipidemic individuals. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.Y.; Ryue, J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Bell, D.E. Eggs enriched in ω-3 fatty acids and alterations in lipid concentrations in plasma and lipoproteins and in blood pressure. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns-Whitmore, B.; Haddad, E.; Sabaté, J.; Rajaram, S. Effects of supplementing n-3 fatty acid enriched eggs and walnuts on cardiovascular disease risk markers in healthy free-living lacto-ovo-vegetarians: A randomized, crossover, free-living intervention study. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appel, L.J.; Miller, E.R.; Seidler, A.J.; Whelton, P.K. Does supplementation of diet with “fish oil” reduce blood pressure? A meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, H.R.; FitzGerald, G.A. The Antihypertensive Effects of Fish Oil. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bønaa, K.H.; Bjerve, K.S.; Straume, B.; Gram, I.T.; Thelle, D. Effect of Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acids on Blood Pressure in Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestin, M.; Clifton, P.; Belling, G.B.; Nestel, P.J. n-3 fatty acids of marine origin lower systolic blood pressure and triglycerides but raise LDL cholesterol compared with n-3 and n-6 fatty acids from plants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, B.M.; Vessby, B.; Uusitupa, M.; Berglund, L.; Pedersen, E.; Riccardi, G.; Rivellese, A.A.; Tapsell, L.; Hermansen, K. Effects of dietary saturated, monounsaturated, and n−3 fatty acids on blood pressure in healthy subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prabodh Shah, A.; Ichiuji, A.M.; Han, J.K.; Traina, M.; El-Bialy, A.; Kamal Meymandi, S.; Yvonne Wachsner, R. Cardiovascular and Endothelial Effects of Fish Oil Supplementation in Healthy Volunteers. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 12, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieger, J.A.; Miller, M.D.; Cobiac, L. Investigation of the effects of a high fish diet on inflammatory cytokines, blood pressure, and lipids in healthy older Australians. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 58, 20369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hlais, S.; El-Bistami, D.; El Rahi, B.; Mattar, M.A.; Obeid, O.A. Combined Fish Oil and High Oleic Sunflower Oil Supplements Neutralize their Individual Effects on the Lipid Profile of Healthy Men. Lipids 2013, 48, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, M.; Collier, S.R.; Zwetsloot, K.A.; West, K.L.; McGinn, M.C. A randomized trial of fish oil omega-3 fatty acids on arterial health, inflammation, and metabolic syndrome in a young healthy population. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Victoria, E.; Yago, M.D. Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and body weight. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bender, N.; Portmann, M.; Heg, Z.; Hofmann, K.; Zwahlen, M.; Egger, M. Fish or n3-PUFA intake and body composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, D.J. Enrichment of hen eggs with n-3 long-chain fatty acids and evaluation of enriched eggs in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: From molecules to man. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Taylor, C.G.; Zahradka, P. Modulation of endothelial cell responses and vascular function by dietary fatty acids. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F. The effects of dietary fatty acid supplementation on endothelial function and vascular tone in healthy subjects. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 59, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, F.; López-Miranda, J.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; Jiménez, Y.; Marín, C.; Gómez, P.; Fernández, J.M.; Caballero, J.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Pérez-Jiménez, F. Chronic effects of a high-fat diet enriched with virgin olive oil and a low-fat diet enriched with α-linolenic acid on postprandial endothelial function in healthy men. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbins, C.L.; Stice, J.P.; Hart, C.M.; Mbai, F.N.; Knowlton, A.A. Effects of Dietary Decosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) on eNOS in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 13, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agbor, L.N.; Wiest, E.F.; Rothe, M.; Schunck, W.-H.; Walker, M.K. Role of CYP1A1 in Modulating the Vascular and Blood Pressure Benefits of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, E.J.; Yusof, M.H.; Yaqoob, P.; Miles, E.A.; Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and leukocyte-endothelium adhesion: Novel anti-atherosclerotic actions. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 64, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holm, P.W.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Tio, R.A. Atherosclerotic plaque development and instability: A dual role for VEGF. Ann. Med. 2009, 41, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Huerta, O.D.; Aguilera, C.M.; Mesa, M.D.; Gil, A. Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation on inflammatory biomakers: A systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eschen, O.; Christensen, J.; Decaterina, R.; Schmidt, E. Soluble adhesion molecules in healthy subjects: A dose-response study using n-3 fatty acids. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2004, 14, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, H.M.; Miles, E.A.; Calder, P. Influence of very long-chain n-3 fatty acids on plasma markers of inflammation in middle-aged men. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2008, 78, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thies, F.; Miles, E.A.; Nebe-von-Caron, G.; Powell, J.R.; Hurst, T.L.; Newsholme, E.A.; Calder, P.C. Influence of dietary supplementation with long-chain n−3 or n−6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on blood inflammatory cell populations and functions and on plasma soluble adhesion molecules in healthy adults. Lipids 2001, 36, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzola, R.; Russo-Volpe, S.; Miles, E.A.; Rees, D.; Banerjee, T.; Roynette, C.E.; Wells, S.J.; Goua, M.; Wahle, K.W.J.; Calder, P.C.; et al. Age- and dose-dependent effects of an eicosapentaenoic acid-rich oil on cardiovascular risk factors in healthy male subjects. Atherosclerosis 2007, 193, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, M.C.; Andrade, A.M.; Andrade, M.L.; Morais, M.G.; Kiely, M.; Parra, D.; Martinéz, J.A.; Thorsdottir, I.; Bandarra, N.M. Influence of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on soluble cellular adhesion molecules as biomarkers of cardiovascular risk in young healthy subjects. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundblad, A.; Holven, K.B.; Bruheim, I.; Myhrstad, M.C.; Ulven, S.M. Effects of fish and krill oil on gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and circulating markers of inflammation: A randomised controlled trial. J. Nutr. Sci. 2018, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sierra, S.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Comalada, M.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J. Dietary eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid equally incorporate as decosahexaenoic acid but differ in inflammatory effects. Nutrition 2008, 24, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Bi, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhao, A.Z. Therapeutic Potential of ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Human Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Csapó, J.; Sugár, L.; Horn, A.; Kiss, C. Chemical composition of milk from red deer roe and fallow deer kept in captivit. Acta Agron Hung. 1987, 36, 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Summerhill, K.; Rodriguez-Canas, C.; Mather, I.; Patel, P.; Eiden, M.; Young, S.; Forouhi, N.G.; Koulman, A. Development and validation of a robust automated analysis of plasma phospholipid fatty acids for metabolic phenotyping of large epidemiological studies. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barić, L.; Drenjančević, I.; Mihalj, M.; Matić, A.; Stupin, M.; Kolar, L.; Mihaljević, Z.; Mrakovčić-Šutić, I.; Šerić, V.; Stupin, A. Enhanced Antioxidative Defense by Vitamins C and E Consumption Prevents 7-Day High-Salt Diet-Induced Microvascular Endothelial Function Impairment in Young Healthy Individuals. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stupin, M.; Stupin, A.; Rasic, L.; Cosic, A.; Kolar, L.; Seric, V.; Lenasi, H.; Izakovic, K.; Drenjancevic, I. Acute exhaustive rowing exercise reduces skin microvascular dilator function in young adult rowing athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barić, L.; Drenjančević, I.; Matić, A.; Stupin, M.; Kolar, L.; Mihaljević, Z.; Lenasi, H.; Šerić, V.; Stupin, A. Seven-Day Salt Loading Impairs Microvascular Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation without Changes in Blood Pressure, Body Composition and Fluid Status in Healthy Young Humans. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Parameter | Control | n-3 PUFAs |
|---|---|---|
| N (W/M) | 21 (10/11) | 19 (10/9) |
| Age (years) | 24 ± 3 | 24 ± 2 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.3 ± 3.1 | 23.3 ± 3.6 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 117 ± 10 | 115 ± 11 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 77 ± 8 | 77 ± 8 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 90 ± 7 | 90 ± 7 |
| HR (beats per min) | 77 ± 11 | 78 ± 13 |
| erythrocytes (× 10E12/L) | 4.8 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.4 |
| hemoglobin (g/L) | 140 ± 11 | 142 ± 13 |
| hematocrit (%) | 41.0 ± 2.8 | 41.5 ± 3.4 |
| leukocytes (× 10E9/L) | 6.2 ± 1.4 | 6.3 ± 1.4 |
| thrombocytes (× 10E9/L) | 256 ± 66 | 225 ± 36 |
| urea (mmol/L) | 5.3 ± 1.3 | 5.7 ± 1.3 |
| creatinine (µmol/L) | 79 ± 17 | 83 ± 18 |
| sodium (mmol/L) | 138 ± 2 | 138 ± 2 |
| potassium (mmol/L) | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 4.2 ± 0.2 |
| glucose (mmol/L) | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 0.8 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 1.6 ± 2.2 | 1.3 ± 1.2 |
| cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.2 ± 0.9 | 4.6 ± 0.9 |
| triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 1.0 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 3.1 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.6 |
| Fatty Acid | Feeding Mixture (n = 3) | Eggs (n = 10) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/100 g Total Fatty Acids) | (mg/100 g Egg 1) | |||
| Control | n-3 PUFAs | Control | n-3 PUFAs | |
| ∑SFA | 16.6 ± 0.2 | 16.8 ± 0.2 | 2082.6 ± 83.1 | 2162.1 ± 52.6 |
| ∑MUFA | 26.5 ± 0.1 | 25.9 ± 0.1 | 2669.6 ± 84.8 | 2917.5 ± 137.9 * |
| ∑n-6 PUFA | 51.9 ± 0.1 * | 23.4 ± 0.2 | 1417.7 ± 119.3 * | 1182.6 ± 111.9 |
| LA | 51.9 ± 0.1 * | 23.2 ± 0.2 | 1274.4 ± 127.3 | 1106.6 ± 108.6 |
| AA | N/F | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 125.4 ± 6.1 * | 67.1 ± 3.6 |
| ∑N-3 PUFA | 5.05 ± 0.04 | 33.9 ± 0.3 * | 138.2 ± 28.4 | 585.2 ± 77.1 * |
| ALA | 5.05 ± 0.04 | 28.5 ± 0.2 * | 59.9 ± 16.1 | 384.2 ± 64.0 * |
| EPA | N/F | 1.87 ± 0.03 | N/F | 25.2 ± 3.2 |
| DHA | N/F | 3.54 ± 0.07 | 78.3 ± 13.8 | 175.8 ± 25.9 * |
| ∑n-6/n-3 PUFA | 10.3 * | 0.69 | 10.3 * | 2.02 |
| Parameter | Control | n-3 PUFAs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.3 ± 3.1 | 23.0 ± 6.1 | 23.3 ± 3.6 | 21.9 ± 6.8 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 117 ± 10 † | 112 ± 11 | 115 ± 11 | 112 ± 11 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 77 ± 8 | 73 ± 8 | 77 ± 8 | 74 ± 8 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 90 ± 7 † | 86 ± 8 | 90 ± 7 | 87 ± 8 |
| HR (beats per min) | 77 ± 11 | 73 ± 11 | 78 ± 13 | 76 ± 11 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 1.6 ± 2.2 | 1.8 ± 2.6 | 1.3 ± 1.2 | 1.8 ± 2.1 |
| cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.2 ± 0.9 | 5.3 ± 1.0 * | 4.6 ± 0.9 | 4.7 ± 0.7 |
| triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 0.6 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.4 * | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 3.1 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.8 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 2.8 ± 0.4 |
| Parameter | Control | n-3 PUFAs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | |
| Fat Free Mass (%) | 79.1 ± 8.6 * | 75.7 ± 8.4 | 77.7 ± 6.9 | 77.8 ± 6.7 |
| Fat (%) | 20.9 ± 8.6 * | 24.3 ± 8.4 | 22.3 ± 6.9 | 22.2 ± 6.7 |
| Total Body Water (%) | 56.7 ± 5.4 * | 54.2 ± 5.8 | 56.6 ± 6.2 | 55.5 ± 4.8 |
| Extracellular Water (%) | 43.0 ± 4.1 | 42.8 ± 4.4 | 41.4 ± 1.2 | 41.3 ± 1.4 |
| Intracellular Water (%) | 57.0 ± 4.1 | 57.2 ± 4.4 | 58.6 ± 1.2 | 58.7 ± 1.4 |
| Plasma Fluid (L) | 3.64 ± 0.68 | 3.56 ± 0.72 | 3.46 ± 0.96 | 3.34 ± 0.89 |
| Interstitial Fluid (L) | 12.73 ± 2.36 | 12.44 ± 2.51 | 12.11 ± 3.38 | 11.68 ± 3.12 |
| Body Density (kg/L) | 1.051 ± 0.020 | 1.044 ± 0.018 | 1.048 ± 0.015 | 1.048 ± 0.014 |
| Parameter | Control | n-3 PUFAs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | ||
| SFA (μmol/L) | |||||
| C4:0 Butyric acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C6:0 Caproic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C8:0 Caprylic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C10:0 Capric acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C11:0 Undecylic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C12:0 Lauric acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| C13:0 Tridecylic acid | N/F | N/F | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| C14:0 Myristic acid | 35.0 ± 14.5 | 25.5 ± 5.6 | 42.0 ± 12.3 | 32.7 ± 5.2 | |
| C15:0 Pentadecylic acid | 12,70 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 10,90 | |
| C16:0 Palmitic Acid | 825.4 ± 127.6 † | 767.1 ± 185.1 | 515.2 ± 170.5 | 552.7 ± 253.8 | |
| C17:0 Margaric acid | 9,91 | <LOQ | 10,80 | 10.3 ± 0.8 | |
| C18:0 Stearic acid | 224.9 ± 40.2 † | 213.8 ± 36.4 | 153.1 ± 61.0 | 161.1 ± 78.6 | |
| C20:0 Arachidic acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| C21:0 Heneicosanoic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C22:0 Behenic acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| C23:0 Tricosanoic acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| C24:0 Lignoceric acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| PUFA (μmol/L) | |||||
| n-5 | |||||
| C14:1[cis-9] Myristoleic acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | 13,7 | <LOQ | |
| C15:1[cis-10] Cis-10-Pentadecenoic acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| n-7 | |||||
| C16:1[cis-9] Palmitoleic acid | 61.9 ± 26.5 | 53.7 ± 22.2 | 47.9 ± 19.3 | 45.5 ± 19.1 | |
| C17:1[cis-10] cis-10-Heptadecenoic acid | 8,90 | <LOQ | 5,50 | <LOQ | |
| n-9 | |||||
| C18:1[trans-9] Elaidic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C18:1[cis-9] Oleic acid | 562.0 ± 108.2 † | 507.1 ± 151.2 | 372.4 ± 152.7 | 383.6 ± 235.4 | |
| C20:1[cis-11] 11-Eicosenoic acid | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| C22:1[cis-13] Erucic acid | N/F | N/F | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| C24:1[cis-15] Nervonic acid | N/F | N/F | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| n-6 | |||||
| C18:2[trans-9,12] Linoelaidic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C18:2[cis-9,12] Linoleic acid | 1065.4 ± 136.8 | 961.0 ± 95.1 | 849.1 ± 291.6 | 889.3 ± 363.8 | |
| C18:3[cis-6,9,12] gamma-Linolenic acid | 21.0 ± 5.2 | 16.9 ± 4.1 | 18.2 ± 5.0 | 16.4 ± 6.6 | |
| C21:2[cis-11,14] Eicosadienoic acid | 7.1 ± 0.5 | 7,40 | 8,10 | 7,8 | |
| C20:3[cis-8,11,14] Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid | 55.4 ± 15.9 † | 45.5 ± 10.8 | 29.8 ± 8.3 | 32.1 ± 11.1 | |
| C20:4[cis-5,8,11,14] Arachidonic acid | 355.2 ± 91.4 † | 363.8 ± 74.6 † | 231.9 ± 92.1 | 236.8 ± 106.2 | |
| C22:2[cis-13,16] 13,16-Docosadienoic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| n-3 | |||||
| C18:3[cis-9,12,15] alpha-Linolenic acid | 10.3 ± 2.2 | 10.5 ± 3.4 | 11.9 ± 1.6 | 19.3 ± 6.2 † | |
| C20:3[cis-11,14,17] 11,14,17-Eicosatrienoic acid | N/F | N/F | N/F | N/F | |
| C20:4[cis-5,8,11,14] Eicosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoic acid | 9.2 ± 2.4 | 10.7 ± 4.5 | 10.4 ± 1.7 | 16.0 ± 6.5 | |
| C22:6[cis-4,7,10,13,16,19] cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid | 39.1 ± 11.1 | 50.8 ± 14.1 | 33.7 ± 11.4 | 52.8 ± 28.0 * | |
| n-6/n-3 PUFAs | 14.9 | 12.5 | 13.1 | 9.3 | |
| Parameter | Control | n-3 PUFAs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Βefore | After | Βefore | After | |
| IFNγ (pg/mL) | 14.3 ± 8.7 | 16.6 ± 9.9 | 31.9 ± 31.9 † | 12.2 ± 5.5 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 11.1 ± 4.4 | 13.8 ± 6.1 | 9.1 ± 3.0 | 17.9 ± 16.4 |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | 7.3 ± 4.8 | 9.7 ± 4.7 † | 6.63 ± 2.57 | 9.2 ± 8.9 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 32.4 ± 12.9 | 38.8 ± 17.1 | 32.6 ± 13.3 | 45.8 ± 28.5 |
| IL-21 (pg/mL) | 42.3 ± 30.1 | 46.8 ± 30.5 | 51.6 ± 48.2 | 80.7 ± 47.4 |
| IL-22 (pg/mL) | 31.6 ± 21.8 | 41.2 ± 34.3 | 36.5 ± 47.3 | 76.2 ± 59.2 |
| IL-23 (pg/mL) | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 3.50 ± 0.31 | 4.0 ± 1.1 |
| IL-9 (pg/mL) | 4.9 ± 4.7 | 5.9 ± 5.2 | 4.0 ± 2.1 | 7.6 ± 11.7 |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 2.6 ± 1.1 | 3.2 ± 1.3 † | 2.7 ± 1.5 | 6.7 ± 4.6 *,† |
| SDF-1α (ng/mL) | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 0.8 ± 0.4 |
| LAP (ng/mL) | 32.5 ± 16.8 | 27.4 ± 11.1 | 30.3 ± 11.8 | 29.4 ± 15.9 |
| VEGF-A (pg/mL) | 611.5 ± 480.9 | 684.3 ± 465.9 † | 527.8 ± 331.9 | 705.1 ± 602.6 |
| VEGF-D (pg/mL) | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 * | 0.5 ± 0.3 |
| sICAM-1 (ng/mL) | 91.5 ± 51.2 | 95.2 ± 50.2 | 103.2 ± 46.5 | 107.0 ± 49.6 |
| sVCAM-1 (ng/mL) | 50.7 ± 17.7 | 48.2 ± 18.7 | 53.0 ± 23.1 | 55.1 ± 21.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stupin, A.; Mihalj, M.; Kolobarić, N.; Šušnjara, P.; Kolar, L.; Mihaljević, Z.; Matić, A.; Stupin, M.; Jukić, I.; Kralik, Z.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Enriched Hen Eggs Consumption in Improving Microvascular Endothelial Function of Healthy Individuals—Clinical Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114149
Stupin A, Mihalj M, Kolobarić N, Šušnjara P, Kolar L, Mihaljević Z, Matić A, Stupin M, Jukić I, Kralik Z, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Enriched Hen Eggs Consumption in Improving Microvascular Endothelial Function of Healthy Individuals—Clinical Trial. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114149
Chicago/Turabian StyleStupin, Ana, Martina Mihalj, Nikolina Kolobarić, Petar Šušnjara, Luka Kolar, Zrinka Mihaljević, Anita Matić, Marko Stupin, Ivana Jukić, Zlata Kralik, and et al. 2020. "Anti-Inflammatory Potential of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Enriched Hen Eggs Consumption in Improving Microvascular Endothelial Function of Healthy Individuals—Clinical Trial" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114149
APA StyleStupin, A., Mihalj, M., Kolobarić, N., Šušnjara, P., Kolar, L., Mihaljević, Z., Matić, A., Stupin, M., Jukić, I., Kralik, Z., Grčević, M., Kralik, G., Šerić, V., & Drenjančević, I. (2020). Anti-Inflammatory Potential of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Enriched Hen Eggs Consumption in Improving Microvascular Endothelial Function of Healthy Individuals—Clinical Trial. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114149









