Apelin Controls Angiogenesis-Dependent Glioblastoma Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
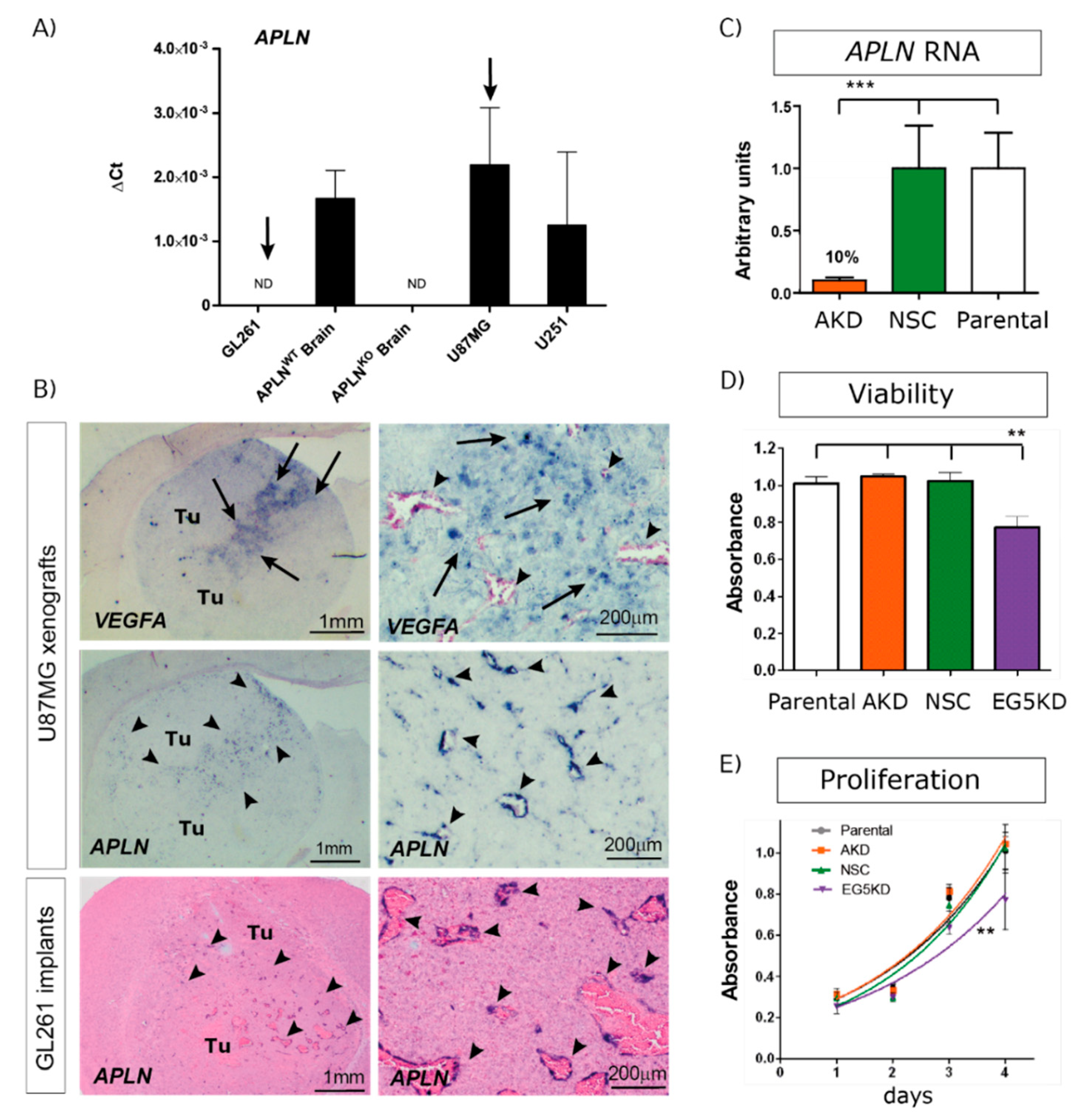
2.1. APLN Is Expressed at Variable Levels in GBM Cells and Upregulated in the Pathologic Neo-Vasculature
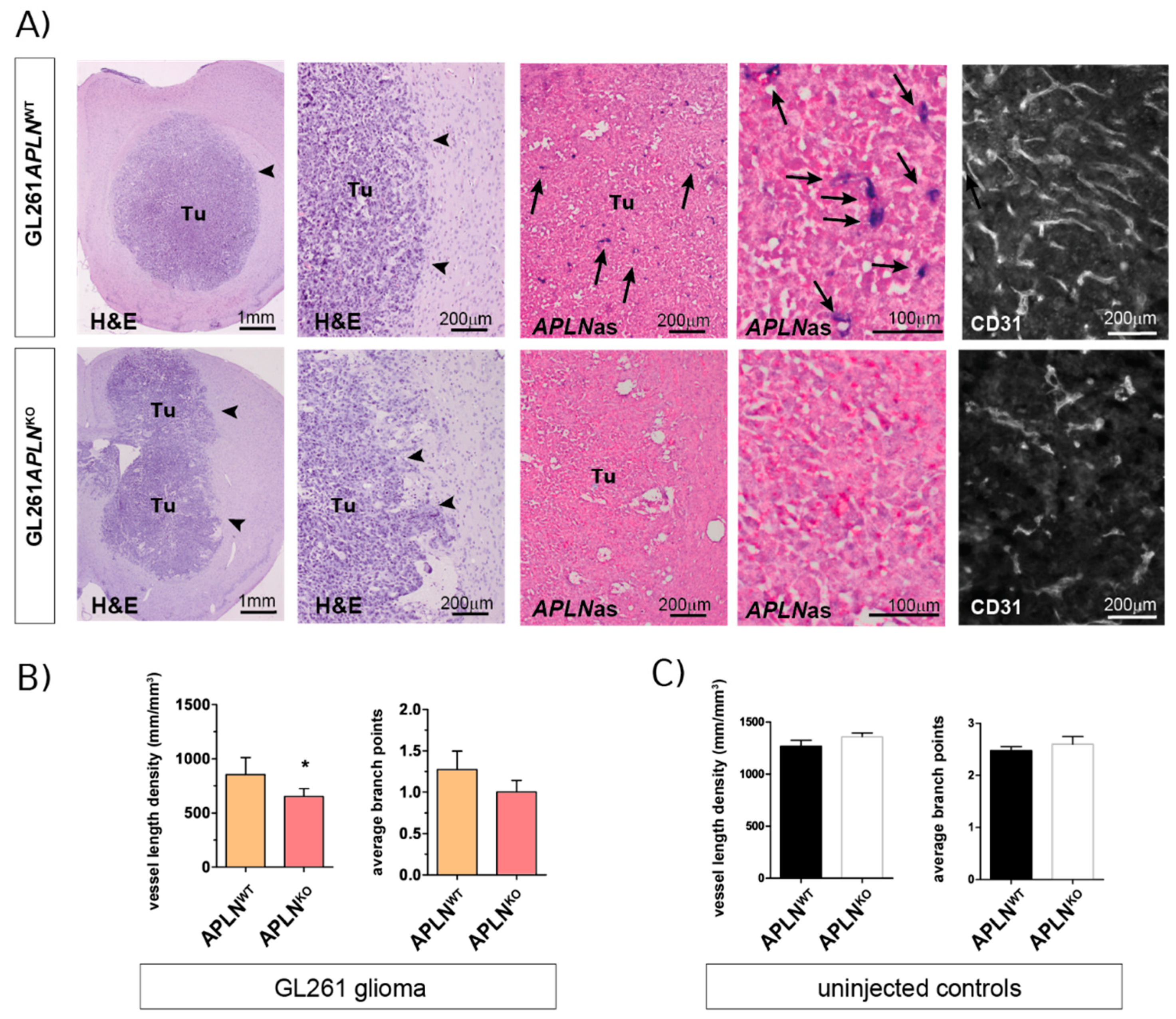
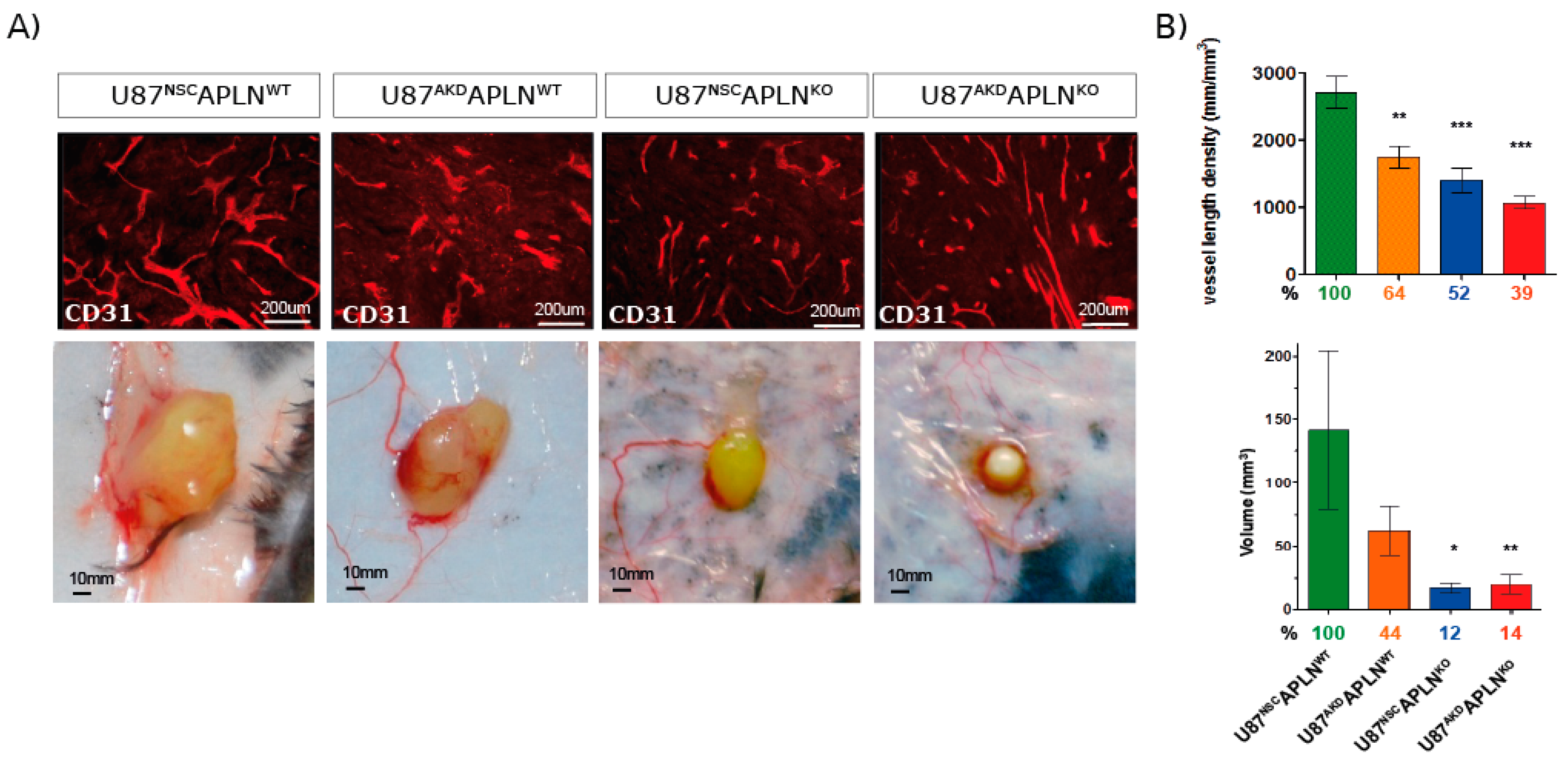
2.2. APLN Expression Is Required for the Formation of the GBM Neo-Vasculature
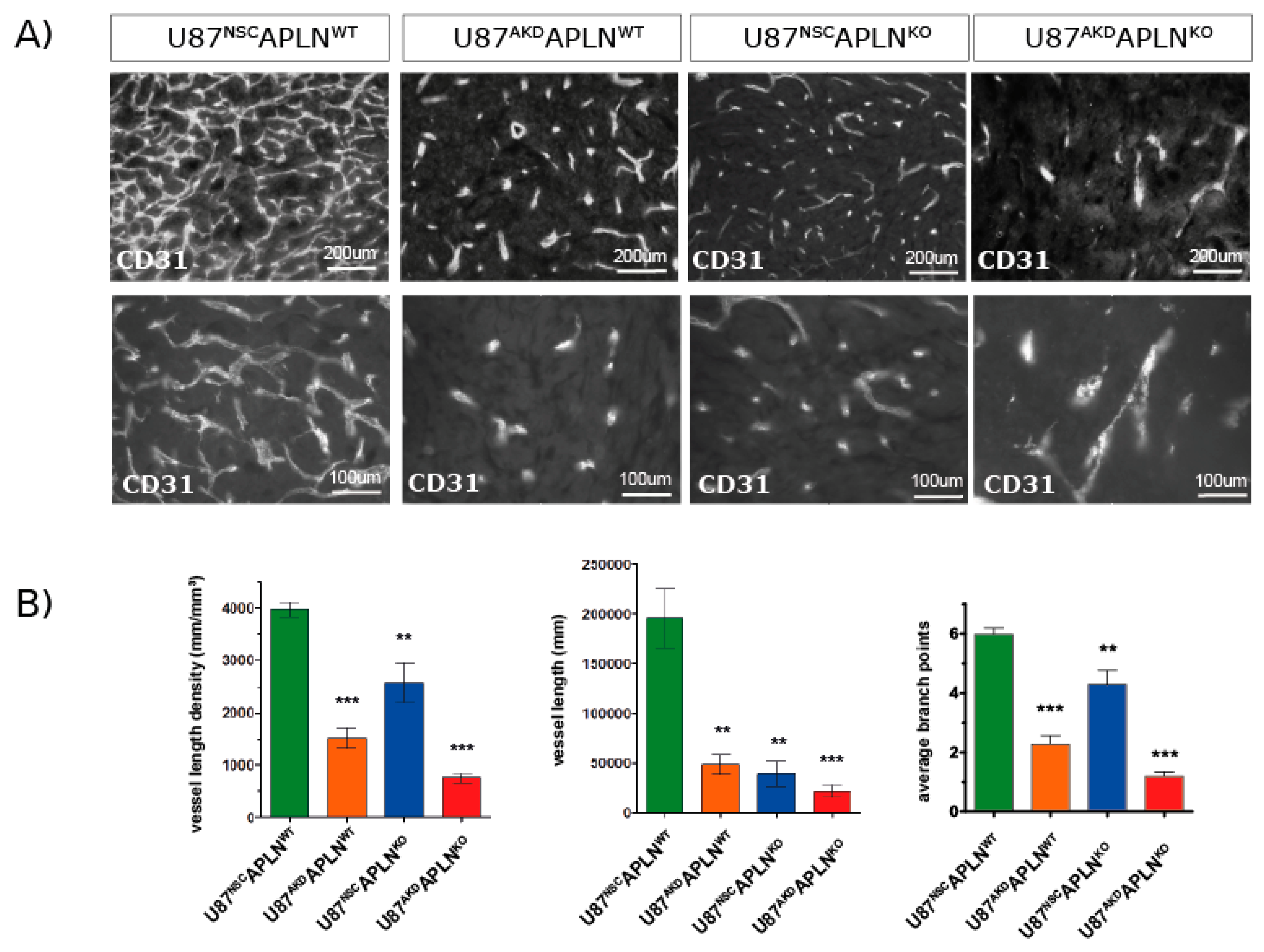
2.3. Paracrine and Autocrine APLN Signaling Controls GBM Angiogenesis
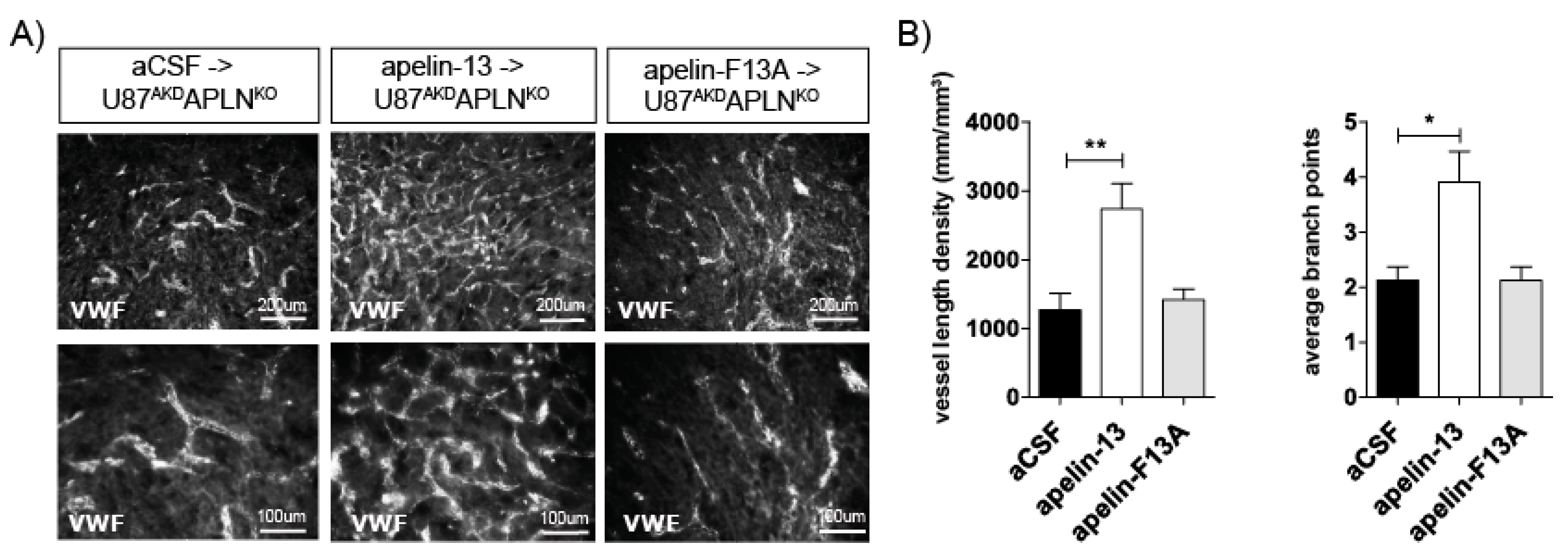
2.4. Apelin-13 Specifically Controls Vessel Density in the GBM Neo-Vasculature
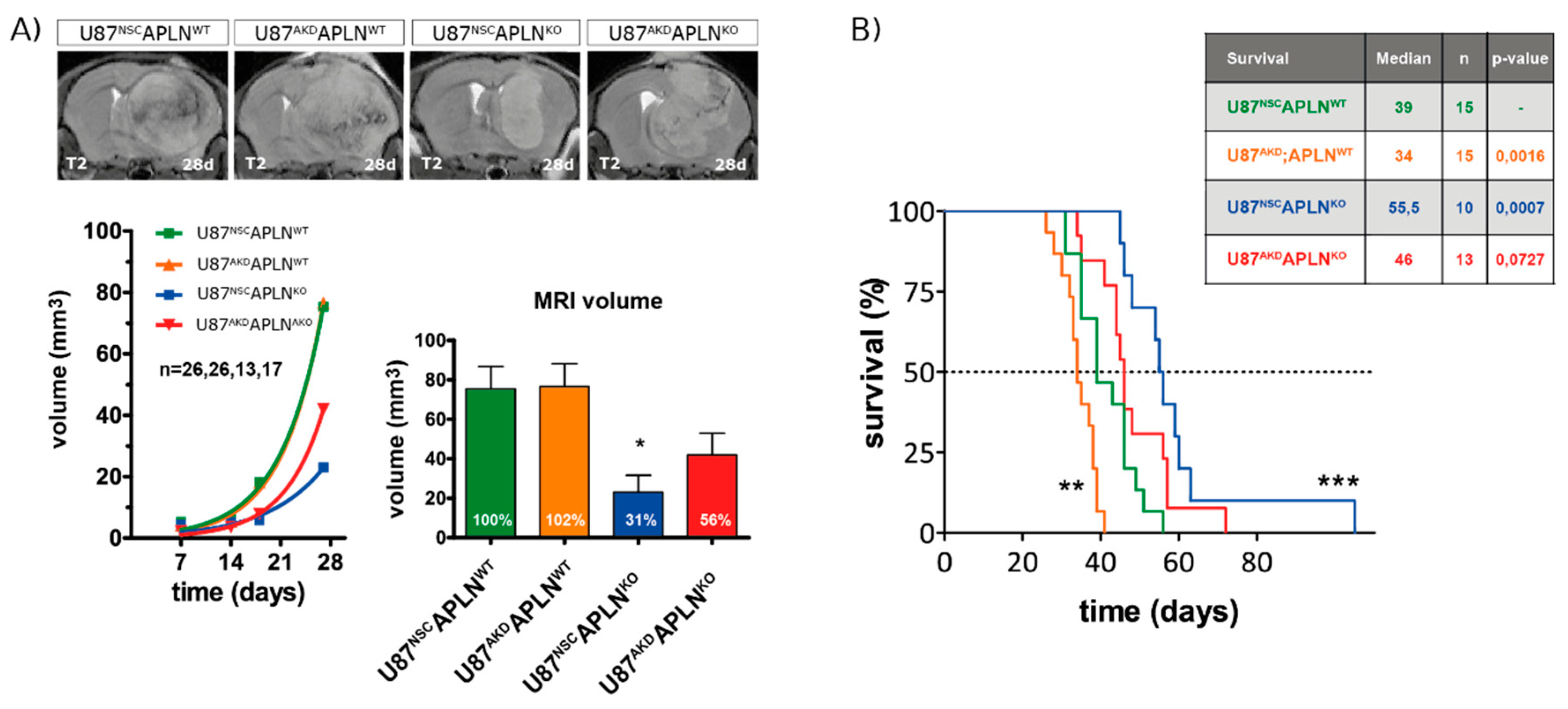
2.5. Loss of APLN Reduces Angiogenesis-Dependent Tumor Growth
2.6. Loss-of-APLN Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment Increases Survival of Glioma-Bearing Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Transduction
4.3. Animals
4.4. Tumor Implantation
4.5. Intracerebral Drug Application
4.6. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
4.7. HE Tumor Volume Analysis
4.8. Quantitative PCR
4.9. Viability and Proliferation Assays
4.10. In Situ Hybridization
4.11. Immunofluorescence and Vessel Density Quantification
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABP | Average branch points |
| aCSF | Artificial cerebrospinal fluid |
| AKD | Apelin knock-down |
| APLNKO | Apelin knock-out |
| APLNWT | Apelin wildtype |
| APLN | Apelin |
| APLNR | Apelin Receptor |
| dpi | days post implantation |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| NSC | Non-silencing control |
| VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor-A |
| VLD | Vessel length density |
| VWF | von Willebrand factor |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- Kleihues, P.; Cavenee, W.K. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Nervous System; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; van den Bent, M.; Tonn, J.C.; Stupp, R.; Preusser, M.; Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal, E.; Henriksson, R.; Le Rhun, E.; Balana, C.; Chinot, O.; et al. European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of adult astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e315–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W.; et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; van den Bent, M.J.; Hegi, M.E. Optimal role of temozolomide in the treatment of malignant gliomas. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2005, 5, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N.; Henzel, W.J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 161, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Li, B.; Winer, J.; Armanini, M.; Gillett, N.; Phillips, H.S.; Ferrara, N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Novotny, W.; Cartwright, T.; Hainsworth, J.; Heim, W.; Berlin, J.; Baron, A.; Griffing, S.; Holmgren, E.; et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinot, O.L.; Wick, W.; Mason, W.; Henriksson, R.; Saran, F.; Nishikawa, R.; Carpentier, A.F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Kavan, P.; Cernea, D.; et al. Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.R.; Dignam, J.J.; Armstrong, T.S.; Wefel, J.S.; Blumenthal, D.T.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Colman, H.; Chakravarti, A.; Pugh, S.; Won, M.; et al. A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holash, J.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; Compton, D.; Boland, P.; Alexander, C.R.; Zagzag, D.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Wiegand, S.J. Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 1999, 284, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.V.; Bergers, G. Mechanisms of evasive resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in glioblastoma. CNS Oncol. 2013, 2, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiero, M.; Simoes, F.C.; Han, H.D.; Snell, C.; Peterkin, T.; Bridges, E.; Mangala, L.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Pradeep, S.; Li, D.; et al. A core human primary tumor angiogenesis signature identifies the endothelial orphan receptor ELTD1 as a key regulator of angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dowd, B.F.; Heiber, M.; Chan, A.; Heng, H.H.; Tsui, L.C.; Kennedy, J.L.; Shi, X.; Petronis, A.; George, S.R.; Nguyen, T. A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene 1993, 136, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, K.; Hosoya, M.; Habata, Y.; Fujii, R.; Kakegawa, T.; Zou, M.X.; Kawamata, Y.; Fukusumi, S.; Hinuma, S.; Kitada, C.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamata, Y.; Habata, Y.; Fukusumi, S.; Hosoya, M.; Fujii, R.; Hinuma, S.; Nishizawa, N.; Kitada, C.; Onda, H.; Nishimura, O.; et al. Molecular properties of apelin: Tissue distribution and receptor binding. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1538, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kälin, R.E.; Kretz, M.P.; Meyer, A.M.; Kispert, A.; Heppner, F.L.; Brändli, A.W. Paracrine and autocrine mechanisms of apelin signaling govern embryonic and tumor angiogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2007, 305, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Ishida, J.; Yamamoto, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Asada, S.; Kasuya, Y.; Mochizuki, N.; Fukamizu, A. G protein-coupled APJ receptor signaling induces focal adhesion formation and cell motility. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya, M.; Kawamata, Y.; Fukusumi, S.; Fujii, R.; Habata, Y.; Hinuma, S.; Kitada, C.; Honda, S.; Kurokawa, T.; Onda, H.; et al. Molecular and functional characteristics of APJ. Tissue distribution of mRNA and interaction with the endogenous ligand apelin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21061–21067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.M.; D’Agostino, S.L.; Miller, M.K.; Heimark, R.L.; Krieg, P.A. Apelin, the ligand for the endothelial G-protein-coupled receptor, APJ, is a potent angiogenic factor required for normal vascular development of the frog embryo. Dev. Biol. 2006, 296, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, A.; Shintani, N.; Oda, M.; Kakuda, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Matsuda, T.; Hinuma, S.; Baba, A. Apelin is a novel angiogenic factor in retinal endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 325, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samura, M.; Morikage, N.; Suehiro, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Nishimoto, A.; Ueno, K.; Hosoyama, T.; Hamano, K. Combinatorial Treatment with Apelin-13 Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of a Preconditioned Cell-Based Therapy for Peripheral Ischemia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Ye, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, L. Elabela-apelin receptor signaling pathway is functional in mammalian systems. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berta, J.; Hoda, M.A.; Laszlo, V.; Rozsas, A.; Garay, T.; Torok, S.; Grusch, M.; Berger, W.; Paku, S.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; et al. Apelin promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4426–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Li, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, H.; Cao, J.; Liu, M.; Wu, D.; He, L.; et al. PAK1-cofilin phosphorylation mediates human lung adenocarcinoma cells migration induced by apelin-13. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Toro, R.; Prahst, C.; Mathivet, T.; Siegfried, G.; Kaminker, J.S.; Larrivee, B.; Breant, C.; Duarte, A.; Takakura, N.; Fukamizu, A.; et al. Identification and functional analysis of endothelial tip cell-enriched genes. Blood 2010, 116, 4025–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, A.; Shintani, N.; Kato, H.; Matsuda, S.; Gomi, F.; Haba, R.; Hashimoto, H.; Kakuda, M.; Tano, Y.; Baba, A. Retardation of retinal vascular development in apelin-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidoya, H.; Ueno, M.; Yamada, Y.; Mochizuki, N.; Nakata, M.; Yano, T.; Fujii, R.; Takakura, N. Spatial and temporal role of the apelin/APJ system in the caliber size regulation of blood vessels during angiogenesis. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, G.A.; Kaminker, J.S.; Tessier-Lavigne, M. Microarray analysis of retinal endothelial tip cells identifies CXCR4 as a mediator of tip cell morphology and branching. Blood 2010, 115, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hu, T.; He, L.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; He, L.; Pu, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; et al. Genetic targeting of sprouting angiogenesis using Apln-CreER. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, A.Y.; Chun, H.J.; Glassford, A.J.; Kundu, R.K.; Kutschka, I.; Ardigo, D.; Hendry, S.L.; Wagner, R.A.; Chen, M.M.; Ali, Z.A.; et al. F genetic profiling and cellular localization of apelin reveals a hypoxia-sensitive, endothelial-centered pathway activated in ischemic heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H88–H98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, K.; Zhang, L.; Imai, Y.; Arab, S.; Chen, M.; Maekawa, Y.; Leschnik, M.; Leibbrandt, A.; Markovic, M.; Schwaighofer, J.; et al. Impaired heart contractility in Apelin gene-deficient mice associated with aging and pressure overload. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, e32–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidoya, H.; Naito, H.; Takakura, N. Apelin induces enlarged and nonleaky blood vessels for functional recovery from ischemia. Blood 2010, 115, 3166–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charo, D.N.; Ho, M.; Fajardo, G.; Kawana, M.; Kundu, R.K.; Sheikh, A.Y.; Finsterbach, T.P.; Leeper, N.J.; Ernst, K.V.; Chen, M.M.; et al. Endogenous regulation of cardiovascular function by apelin-APJ. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H1904–H1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plate, K.H.; Breier, G.; Weich, H.A.; Risau, W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 1992, 359, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, D.; Garcon, L.; Harper, M.; Dumenil, D.; Dautry, F.; Kress, M. Targeting the kinesin Eg5 to monitor siRNA transfection in mammalian cells. Biotechniques 2002, 33, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machein, M.R.; Renninger, S.; de Lima-Hahn, E.; Plate, K.H. Minor contribution of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitors to the vascularization of murine gliomas. Brain Pathol. 2003, 13, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, D.S.; Vinnakota, K.; Chirasani, S.; Synowitz, M.; Raguet, H.; Stock, K.; Sliwa, M.; Lehmann, S.; Kälin, R.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Gliomas induce and exploit microglial MT1-MMP expression for tumor expansion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12530–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockery, P.; Fraher, J. The quantification of vascular beds: A stereological approach. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 82, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokkegaard, A.; Nyengaard, J.R.; West, M.J. Stereological estimates of number and length of capillaries in subdivisions of the human hippocampal region. Hippocampus 2001, 11, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, P.R.; Gokhale, A.M.; Ward, N.L.; West, M.J. Stereological length estimation using spherical probes. J. Microsc. 2002, 206, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, S.; Gama Sosa, M.A.; English, D.F.; Oler, E.; Oung, T.; Janssen, W.G.; De Gasperi, R.; Schmeidler, J.; Dickstein, D.L.; Schmitz, C.; et al. Novel cerebrovascular pathology in mice fed a high cholesterol diet. Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walchli, T.; Mateos, J.M.; Weinman, O.; Babic, D.; Regli, L.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Gerhardt, H.; Schwab, M.E.; Vogel, J. Quantitative assessment of angiogenesis, perfused blood vessels and endothelial tip cells in the postnatal mouse brain. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Saldivia, V.R.; Nguyen, T.; Cheng, R.; George, S.R.; O’Dowd, B.F. Modification of the terminal residue of apelin-13 antagonizes its hypotensive action. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Gerber, H.P.; Novotny, W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berta, J.; Kenessey, I.; Dobos, J.; Tovari, J.; Klepetko, W.; Jan Ankersmit, H.; Hegedus, B.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; Varga, J.; Lorincz, Z.; et al. Apelin expression in human non-small cell lung cancer: Role in angiogenesis and prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2010, 5, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorli, S.C.; Le Gonidec, S.; Knibiehler, B.; Audigier, Y. Apelin is a potent activator of tumour neoangiogenesis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7692–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson-Welsh, L. What is normal? Apelin and VEGFA, drivers of tumor vessel abnormality. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribesalgo, I.; Hoffmann, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kavirayani, A.; Lazovic, J.; Berta, J.; Novatchkova, M.; Pai, T.P.; Wimmer, R.A.; Laszlo, V.; et al. Apelin inhibition prevents resistance and metastasis associated with anti-angiogenic therapy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kälin, S.; Kälin, R.E. Adipocitokines, Energy Balance and Cancer—Energy Balance and Cancer; Reizes, O., Berger, N.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 137–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, D.; Cai, C.; Sims, M.M.; He Yang, C.; Thomas, M.; Cheng, J.; Saad, A.G.; Pfeffer, L.M. APELA Expression in Glioma, and Its Association with Patient Survival and Tumor Grade. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chng, S.C.; Ho, L.; Tian, J.; Reversade, B. Elabela: A hormone essential for heart development signals via the apelin receptor. Dev. Cell 2013, 27, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, A.; Norris, M.L.; Valen, E.; Chew, G.L.; Gagnon, J.A.; Zimmerman, S.; Mitchell, A.; Ma, J.; Dubrulle, J.; Reyon, D.; et al. Toddler: An embryonic signal that promotes cell movement via apelin receptors. Science 2014, 343, 1248636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidoya, H.; Kunii, N.; Naito, H.; Muramatsu, F.; Okamoto, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Takakura, N. The apelin/APJ system induces maturation of the tumor vasculature and improves the efficiency of immune therapy. Oncogene 2011, 31, 3254–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrella, G.; Hou, M.; Li, M.; Stoecklein, V.M.; Zdouc, N.; Volmar, M.N.M.; Miletic, H.; Reinhard, S.; Herold-Mende, C.C.; Kleber, S.; et al. Targeting APLN/APLNR Improves Antiangiogenic Efficiency and Blunts Proinvasive Side Effects of VEGFA/VEGFR2 Blockade in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2298–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunkel, P.; Ulbricht, U.; Bohlen, P.; Brockmann, M.A.; Fillbrandt, R.; Stavrou, D.; Westphal, M.; Lamszus, K. Inhibition of glioma angiogenesis and growth in vivo by systemic treatment with a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6624–6628. [Google Scholar]
- Lamszus, K.; Kunkel, P.; Westphal, M. Invasion as limitation to anti-angiogenic glioma therapy. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2003, 88, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Keunen, O.; Johansson, M.; Oudin, A.; Sanzey, M.; Rahim, S.A.; Fack, F.; Thorsen, F.; Taxt, T.; Bartos, M.; Jirik, R.; et al. Anti-VEGF treatment reduces blood supply and increases tumor cell invasion in glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3749–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford-Wright, E.; Andre-Gregoire, G.; Jacobs, K.A.; Treps, L.; Le Gonidec, S.; Leclair, H.M.; Gonzalez-Diest, S.; Roux, Q.; Guillonneau, F.; Loussouarn, D.; et al. Pharmacological targeting of apelin impairs glioblastoma growth. Brain 2017, 140, 2939–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, H.R.; Camelo-Piragua, S.; Kurian, K.M. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in adult and pediatric gliomas: Toward personalized treatment. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Sung, H.J.; Li, H.Y.; Yoo, C.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, U.L.; Nam, B.H.; Kim, E.O.; et al. Hypoxia-induced up-regulation of apelin is associated with a poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuurbier, L.; Rahman, A.; Cordes, M.; Scheick, J.; Wong, T.J.; Rustenburg, F.; Joseph, J.C.; Dynoodt, P.; Casey, R.; Drillenburg, P.; et al. Apelin: A putative novel predictive biomarker for bevacizumab response in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 42949–42961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tian, X.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Pu, W.; Liu, Q.; Tang, J.; Wu, J.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Apj (+) Vessels Drive Tumor Growth and Represent a Tractable Therapeutic Target. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoozgar, Z.; Jain, R.K.; Duda, D.G. Role of Apelin in Glioblastoma Vascularization and Invasion after Anti-VEGF Therapy: What Is the Impact on the Immune System? Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2104–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Kingdom Co-Ordinating Committee on Cancer. Guidelines for the welfare of animals in experimental neoplasia. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989, 8, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkai, Y.; Rathbun, G.; Lam, K.P.; Oltz, E.M.; Stewart, V.; Mendelsohn, M.; Charron, J.; Datta, M.; Young, F.; Stall, A.M.; et al. RAG-2-deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell 1992, 68, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, T.M.; Mwamengele, G.L.; Dantzer, V. Stereological and allometric studies on mammalian cerebral cortex with implications for medical brain imaging. J. Anat. 1996, 189, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frisch, A.; Kälin, S.; Monk, R.; Radke, J.; Heppner, F.L.; Kälin, R.E. Apelin Controls Angiogenesis-Dependent Glioblastoma Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114179
Frisch A, Kälin S, Monk R, Radke J, Heppner FL, Kälin RE. Apelin Controls Angiogenesis-Dependent Glioblastoma Growth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(11):4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114179
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrisch, Anne, Stefanie Kälin, Raymond Monk, Josefine Radke, Frank L. Heppner, and Roland E. Kälin. 2020. "Apelin Controls Angiogenesis-Dependent Glioblastoma Growth" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 11: 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114179
APA StyleFrisch, A., Kälin, S., Monk, R., Radke, J., Heppner, F. L., & Kälin, R. E. (2020). Apelin Controls Angiogenesis-Dependent Glioblastoma Growth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(11), 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114179




