Flutamide Alters the Expression of Chemerin, Apelin, and Vaspin and Their Respective Receptors in the Testes of Adult Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of Adipokines and Their Receptor Genes in Rat Testes, Effect of Flutamide
2.1.1. Immunolocalisation of Adipokines and Their Receptors
2.1.2. Expression Levels of Adipokine and Adipokine Receptor Proteins
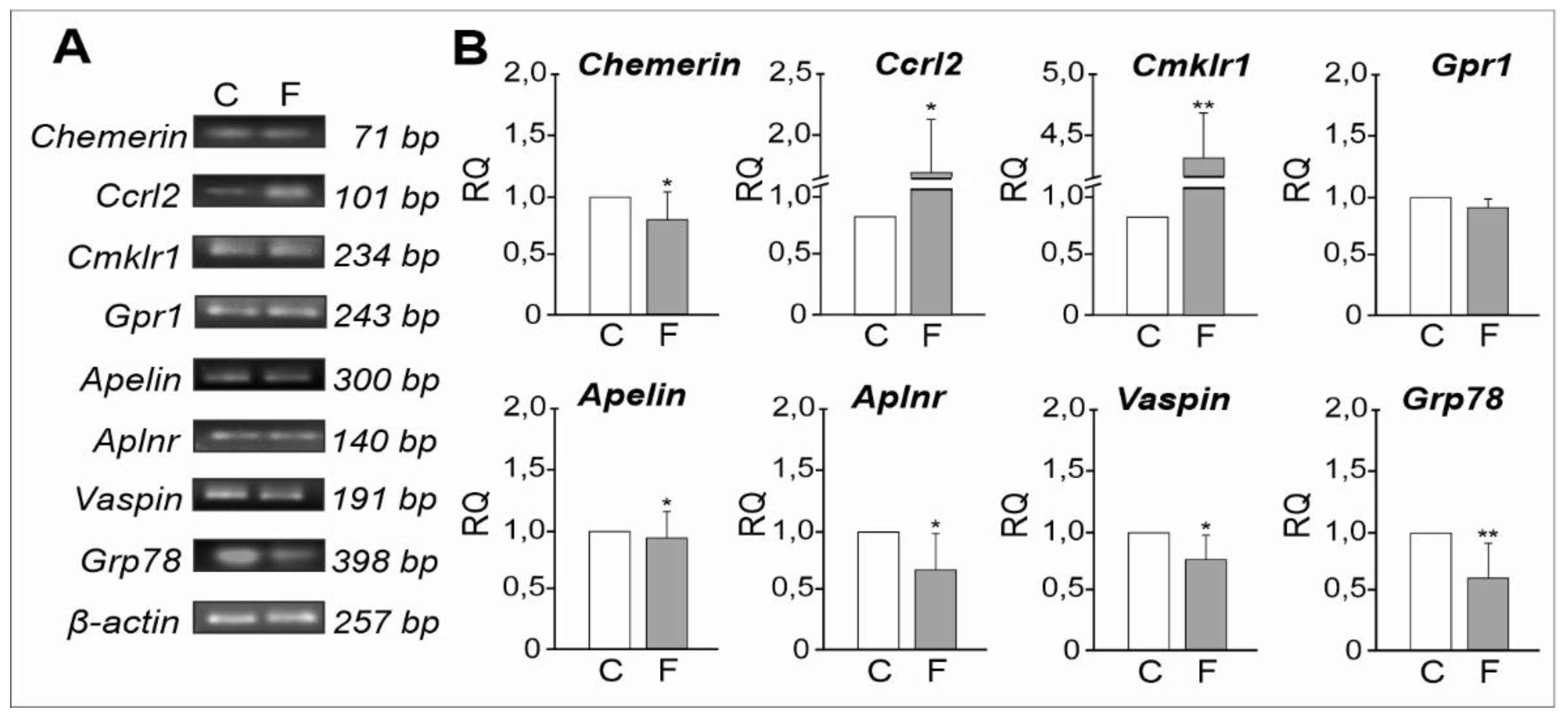
2.1.3. mRNA Expression Levels of Adipokines and Their Receptors
2.2. Plasma Concentrations of Adipokines, Effect of Flutamide
2.3. Testosterone Blood Plasma Concentration, Effects of Flutamide
2.4. Plasma Cholesterol Content, Effects of Flutamide
2.5. Expression of PLIN1 and TSPO Genes in Rat Testes, Effect of Flutamide
2.6. Expression of Nectin2 and Afadin Genes in Rat Testes, Effect of Flutamide
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Tissue Preparation
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription
4.5. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Analysis
4.7. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ranjan, A. Adipokines as a modulator of reproductive function. J. Sci. Res. 2017, 61, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ashima, R.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Obesity 2006, 14, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, F.; Gomez, R.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Dieguez, C.C.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines as novel modulators of lipid metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estienne, A.; Bongrani, A.; Reverchon, M.; Ramé, C.; Ducluzeau, P.-H.; Froment, P.; Dupont, J. Involvement of novel adipokines, chemerin, visfatin, resistin and apelin in reproductive functions in normal and pathological conditions in humans and animal models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chehab, F.F.; Mounzih, K.; Lu, R.; Lim, M.E. Early onset of reproductive function in normal female mice treated with leptin. Science 1997, 275, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barash, I.A.; Cheung, C.C.; Weigle, D.S.; Ren, H.; Kabigting, E.B.; Kuijper, J.K.; Clifton, D.K.; Steiner, R.A. Leptin is a metabolic signal to the reproductive system. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 3144–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Garrido, M.A.; Tena-Sempere, M. Metabolic control of puberty: Roles of leptin and kisspeptins. Horm. Behav. 2013, 64, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, A.; Mellouk, N.; Froment, P.; Dupont, J. Adiponectin and resistin: Potential metabolic signals affecting hypothalamo-pituitary gonadal axis in females and males of different species. Reproduction 2017, 153, R215–R226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbe, A.; Bongrani, A.; Mellouk, N.; Estienne, A.; Kurowska, P.; Grandhaye, J.; Elfassy, Y.; Levy, R.; Rak, A.; Froment, P.; et al. Mechanisms of adiponectin action in fertility: An overview from gametogenesis to gestation in humans and animal models in normal and pathological conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeger, J.; Ziegelmeier, M.; Bachmann, A.; Lössner, U.; Kratzsch, J.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M. Serum levels of the adipokine vaspin in relation to metabolic and renal parameters. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trujillo, M.E.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue-derived factors: Impact on health and disease. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 627, 762–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Choubey, M.; Bora, P.; Krishna, A. Adiponectin and chemerin: Contrary adipokines in regulating reproduction and metabolic disorders. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 10, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, N.O.; Bakos, H.W.; Fullston, T.; Lane, M. Impact of obesity on male fertility, sperm function and molecular composition. Spermatogenesis 2012, 2, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syriou, V.; Papanikolaou, D.; Kozyraki, A.; Goulis, D.G. Cytokines and male infertility. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2018, 29, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, I.V.; Yango, P.; Svechnikov, K.; Tran, N.D.; Soder, O. Adipocytokines may delay pubertal maturation of human Sertoli cells. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2019, 31, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tena-Sempere, M.; Barreiro, M.L. Leptin in male reproduction: The testis paradigm. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 188, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarrow, J.F.; Beggs, L.A.; Conover, C.F.; McCoy, S.C.; Beck, D.T.; Borst, S.E. Influence of androgens on circulating adiponectin in male and female rodents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, F.F.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Impaired steroidogenesis in the testis of leptin-deficient mice (ob/ob -/-). Acta Histochem. 2017, 119, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena-Sempere, M.; Manna, P.R.; Zhang, F.P.; Pinilla, L.; González, L.C.; Diéguez, C.; Huhtaniemi, I.; Aguilar, E. Molecular mechanisms of leptin action in adult rat testis: Potential targets for leptin-induced inhibition of steroidogenesis and pattern of leptin receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression. J Endocrinol. 2001, 170, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Silva, P.; Furriel, A.; Costa, W.S.; Sampaio, F.J.B.; Gregorio, B.M. Metabolic and testicular effects of the long-term administration of different high-fat diets in adult rats. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2015, 41, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ocon-Grove, O.M.; Krzysik-Walker, S.M.; Maddineni, S.R.; Hendricks, G.L.; Ramachandran, R. Adiponectin and its receptors are expressed in the chicken testis: Influence of sexual maturation on testicular ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2 mRNA abundance. Reproduction 2008, 136, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfaehler, A.; Nanjappa, M.K.; Coleman, E.S.; Mansour, M.; Wanders, D.; Plaisance, E.P.; Judd, R.L.; Akingbemi, B.T. Regulation of adiponectin secretion by soy isoflavones has implication for endocrine function of the testis. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 209, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choubey, M.; Ranjan, A.; Bora, P.S.; Baltazar, F.; Martin, L.C.; Krishna, A. Role of adiponectin as a modulator of testicular function during aging in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeremy, M.; Gurusubramanian, G.; Roy, V.K. Localization pattern of visfatin (NAMPT) in d-galactose induced aged rat testis. Ann. Anat. 2017, 211, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocon-Grove, O.M.; Krzysik-Walker, S.M.; Maddineni, S.R.; Hendricks, G.L.; Ramachandran, R. NAMPT (visfatin) in the chicken testis: Influence of sexual maturation on cellular localization, plasma levels and gene and protein expression. Reproduction 2010, 139, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogueiras, R.; Barreiro, M.L.; Caminos, J.E.; Gaytan, F.; Suominen, J.S.; Navarro, V.M.; Casanueva, F.F.; Aguilar, E.; Toppari, J.; Dieguez, C.; et al. Novel expression of resistin in rat testis: Functional role and regulation by nutritional status and hormonal factors. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hameed, W.; Yousaf, I.; Latif, R.; Aslam, M. Effect of visfatin on testicular steroidogenesis in purified Leydig cells. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2012, 24, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Riammer, S.; Garten, A.; Schaab, M.; Grunewald, S.; Kiess, W.; Kratzsch, J.; Paasch, U. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase production in human spermatozoa influenced by maturation stage. Andrology 2016, 4, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duliban, M.; Gorowska-Wojtowicz, E.; Tworzydlo, W.; Rak, A.; Brzoskwinia, M.; Krakowska, I.; Wolski, J.K.; Kotula-Balak, M.; Płachno, B.J.; Bilinska, B. Interstitial Leydig cell tumorigenesis –leptin and adiponectin signaling in relation to aromatase expression in the human testis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, R.; Moriya, J.; Yamakawa, J.; Sumino, H.; Kanda, T.; Takahashi, T. A novel adipocytokine, visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor (vaspin) and obesity. J. Int. Med. Res. 2008, 36, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandal, S.; Tekin, S.; Seker, F.B.; Beytur, A.; Vardi, N.; Colak, C.; Tapan, T.; Yildiz, S.; Yilmaz, B. The effects of intracerebroventricular infusion of apelin-13 on reproductive function in male rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 602, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, W.J.; Millar, M.R.; Sharpe, R.M.; Saunders, P.T. Immunohistochemical localization of androgen receptors in the rat testis: Evidence for stage-dependent expression and regulation by androgens. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labrie, F. Mechanism of action and pure antiandrogenic properties of flutamide. Cancer 1993, 72, 3816–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejmej, A.; Bilinska, B. The effects of flutamide on cellular junctions in the testis and epididymis and prostate. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 304, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilagan, R.; Zhang, L.J.; Pottratz, J.; Le, K.; Salas, S.; Iyer, M.; Wu, L.; Gambhir, S.S.; Carey, M. Imaging androgen receptor function during flutamide treatment in the LAPC9 xenograft model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kassim, N.M.; McDonald, S.W.; Reid, O.; Bennett, N.K.; Gilmore, D.P.; Payne, A.P. The effects of pre- and postnatal exposure to the nonsteroidal antiandrogen flutamide on testis descent and morphology in the Albino Swiss rat. J. Anat. 1997, 190, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, B.S.; Barlow, N.J.; Foster, P.M. Androgen-mediated development in male rat offspring exposed to flutamide in utero: Permanence and correlation of early postnatal changes in anogenital distance and nipple retention with malformations in androgen-dependent tissues. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 62, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopera, I.; Durlej, M.; Hejmej, A.; Knapczyk-Stwora, K.; Duda, M.; Slomczynska, M.; Bilinska, B. Differential expression of connexin 43 in adult pig testes during normal spermatogenic cycle and after flutamide treatment. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2011, 46, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio, L.R.; Cordeiro, R.S.; Taboga, S.R.; Goes, R.M. Short-term antiandrogen flutamide treatment causes structural alterations in somatic cells associated with premature detachment of spermatids in the testis of pubertal and adult guinea pigs. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 45, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Hejmej, A.; Zarzycka, M.; Tworzydlo, W.; Bilinski, S.; Pardyak, L.; Kaminska, A.; Bilinska, B. Flutamide induces alterations in the cell-cell junction ultrastructure and reduces the expression of Cx43 at the blood-testis barrier with no disturbance in the rat seminiferous tubule histology. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2016, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wei, S.; Li, L.; Su, X.; Du, C.; Li, F.; Geng, B.; Liu, P.; Xu, G. Proteomic analysis of murine testes lipid droplets. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulos, V.; Fan, J.; Zirkin, B. Translocator protein (18 kDa): An update on its function in steroidogenesis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, A.H.; Hales, D.B. Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 947–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorini, C.; Tilloy-Ellul, A.; Chevalier, S.; Charuel, C.; Pointis, G. Sertoli cell junctional proteins as early targets for different classes of reproductive toxicants. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 18, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzycka, M.; Chojnacka, K.; Mruk, D.D.; Górowska, E.; Hejmej, A.; Kotula-Balak, M.; Pardyak, L.; Bilinska, B. Flutamide alters distribution of c-Src and affects cell adhesion function in the adult rat seminiferous epithelium. Andrology 2015, 3, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; Yanase, T.; Nomura, M.; Okabe, T.; Goto, K.; Sato, T.; Kawano, H.; Kato, S.; Nawata, H. Androgen receptor null male mice develop late-onset obesity caused by decreased energy expenditure and lipolytic activity but show normal insulin sensitivity with high adiponectin secretion. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Shi, H. Sex hormones and their receptors regulate liver energy homeostasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 294278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Kratzsch, D.; Schaab, M.; Scholz, M.; Grunewald, S.; Thiery, J.; Paasch, U.; Kratzsch, J. Seminal plasma adipokine levels are correlated with functional characteristics of spermatozoa. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 99, 1256–1263.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J. Implications of adiponectin in linking metabolism to testicular function. Endocrine 2014, 46, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverchon, M.; Ramé, C.; Bertoldo, M.; Dupont, J. Adipokines and the female reproductive tract. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 232454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, P.; Huang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Xiao, T.; Ren, P.G.; Zabel, B.A.; Zhang, J.V. Expression of chemerin and its receptors in rat testes and its action on testosterone secretion. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, P.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Zabel, B.A.; Zhang, J.V. Chemerin-derived peptide C-20 suppressed gonadal steroidogenesis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014, 71, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Yan, D.; Xiang, L.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Xiao, T.; et al. Chemokine-like receptor 1 deficiency leads to lower bone mass in male mice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminos, J.E.; Nogueiras, R.; Gaytán, F.; Pineda, R.; González, C.R.; Barreiro, M.L.; Castaño, J.P.; Malagón, M.M.; Pinilla, L.; Toppari, J.; et al. Novel expression and direct effects of adiponectin in the rat testis. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3390–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chabrolle, C.; Tosca, L.; Crochet, S.; Tesseraud, S.; Dupont, J. Expression of adiponectin and its receptors (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) in chicken ovary: Potential role in ovarian steroidogenesis. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2007, 33, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, D.; Colangelo, C.; Williams, K.; Gerstein, M. Comparing protein abundance and mRNA expression levels on a genomic scale. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koiou, E.; Tziomalos, K.; Dinas, K.; Katsikis, I.; Kalaitzakis, E.; Delkos, D.; Kandaraki, E.A.; Panidis, D. The effect of weight loss and treatment with metformin on serum vaspin levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocr. J. 2011, 58, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viguier-Martinez, M.C.; Hochereau de Reviers, M.T.; Barenton, B.; Perreau, C. Endocrinological and histological changes induced by flutamide treatment on the hypothalamo-hypophyseal testicular axis of the adult male rat and their incidences on fertility. Acta Endocrinol. (Copenh) 1983, 104, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarrabay, A.; Hilmi, C.; Tinwell, H.; Schorsch, F.; Pallardy, M.; Bars, R.; Rouquié, D. Low dose evaluation of the antiandrogen flutamide following a mode of action approach. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirkin, B.R.; Papadopoulos, V. Leydig cells: Formation, function, and regulation. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, J.R.; Harris, L.-A.; Shew, T.M.; Abumrad, N.A.; Wolins, N.E. Perilipin 1 moves between the fat droplet and the endoplasmic reticulum. Adipocyte 2013, 2, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tasci, I.; Dogru, T.; Naharci, I.; Erdem, G.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Sonmez, A.; Bingol, N.; Kilic, S.; Bingol, S.; Erikci, S. Plasma apelin is lower in patients with elevated LDL-cholesterol. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2007, 115, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoraszczuk, E.; Słupecka, M.; Wolinski, J.; Hejmej, A.; Bilinska, B.; Fiedor, E.; Piwnicka, N.; Rak, A. Maternal high-fat diet during pregnancy and lactation had gender difference effect on adiponectin in rat offspring. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rak, A.; Hejmej, A.; Słupecka-Ziemilska, M.; Wolinski, J.; Fiedor, E.; Bilinska, B.; Gregoraszczuk, E.L. Maternal high-fat diet during pregnancy and lactation has opposite effects on gonadal expression of leptin and leptin receptor in rat dams and their offspring. Horm. Metab. Res. 2017, 49, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milon, A.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Pawlicki, P.; Bilinska, B.; Duliban, M.; Gorowska-Wojtowicz, E.; Tworzydlo, W.; Kotula-Balak, M. Do estrogens regulate lipid status in testicular steroidogenic Leydig cell? Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, Y.; Nakanishi, H. Nectin and afadin: Novel organizers of intercellular junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouchard, M.J.; Dong, Y.; McDermott, B.M., Jr.; Lam, D.-H.; Brown, K.; Shelanski, M.; Bellvé, A.R.; Racaniello, V.R. Defects in nuclear and cytoskeletal morphology and mitochondrial localization in spermatozoa of mice lacking nectin-2, a component of cell-cell adherens junctions. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozaki-Kuroda, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Ohta, H.; Tanaka, H.; Kurihara, H.; Mueller, S.; Irie, K.; Ikeda, W.; Sakai, T.; Wimmer, E.; et al. Nectin couples cell-cell adhesion and the actin scaffold at heterotypic testicular junctions. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, E.W.; Yan, H.H.; Mruk, D.D. Regulation of spermatogenesis in the microenvironment of the seminiferous epithelium: New insights and advances. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 315, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurowska, P.; Mlyczynska, E.; Barbe, A.; Staub, C.; Gregoraszczuk, E.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. Vaspin in the pig ovarian follicles: Expression and regulation by different hormones. Reproduction 2019, 158, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gye, M.C.; Ohsako, S. Effects of flutamide in the rat testis on the expression of occludin, an integral member of the tight junctions. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 143, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilinska, B.; Hejmej, A.; Kotula-Balak, M. Preparation of testicular samples for histology and immunohistochemistry. In Sertoli Cells; Alves, M.G., Oliveira, P.F., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, A.J. Image analytic techniques for quantification of immunocytochemical staining in the nervous system. In Methods in Neurosciences; Conn, P.M., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 208–229. [Google Scholar]
- Hejmej, A.; Kopera, I.; Kotula-Balak, M.; Lydka, M.; Lenartowicz, M.; Bilinska, B. Are expression and localization of tight and adherens junction proteins in testes of adult boar affected by fetal and neonatal exposure to flutamide? Int. J. Androl. 2012, 35, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorowska, E.; Chojnacka, K.; Zarzycka, M.; Bilinska, B.; Hejmej, A. Postnatal exposure to flutamide affects CTNNB1 and CDH1 gene expression in adult pig epididymis and prostate and alters metabolism of testosterone. Andrology 2014, 2, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svec, D.; Tichopad, A.; Novosadova, V.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Kubista, M. How good is a PCR efficiency estimate: Recommendations for precise and robust qPCR efficiency assessments. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2015, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Control | Flutamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemerin | 12.736 ± 0.650 ng/mL | 13.346 ± 1.116 ng/mL |
| Apelin | 176.386 ± 41.236 pg/mL | 192.110 ± 67.429 pg/mL |
| Vaspin | 452.349 ± 15.379 pg/mL | 488.864 ± 36.916 pg/mL |
| Antibody | Host Species | Vendor | Cat. Number | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-chemerin | Rabbit | Abcam | ab103153 | 1:500 (WB) 1:200 (IHC) |
| Anti-CCRL2 | Rabbit | Sigma-Aldrich | SAB2100371 | 1:1000 (WB) 1:200 (IHC) |
| Anti-CKMLR1 | Rabbit | Abcam | ab64881 | 1:500 (WB) 1:200 (IHC) |
| Anti-GPR1 | Goat | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-48178 | 1:200 (WB) 1:200 (IHC) |
| Anti-apelin | Mouse | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-293441 | 1:1000 (WB) 1:200 (IHC) |
| Anti-APLNR | Mouse | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-73713 | 1:500 (WB) 1:200 (IHC) |
| Anti-vaspin | Rabbit | ThermoFisher Scientific | PA5-30989 | 1:500 (WB) 1:500 (IHC) |
| Anti-GRP78 | Rabbit | ThermoFisher Scientific | PA5-19503 | 1:500 (WB) 1:500 (IHC) |
| Anti-PLIN1 | Goat | Abcam | ab61682 | 1:300 (WB) 1:400 (IHC) |
| Anti-TSPO | Rabbit | Bioassay Technology Laboratory | BT-AP06962 | 1:400 (WB) 1:200 (IHC) |
| Anti-nectin-2 | Rabbit | Bioassay Technology Laboratory | BT-AP04642 | 1:1000 (WB) 1:100 (IHC) |
| Anti-afadin | Rabbit | Bioassay Technology Laboratory | BT-AP06988 | 1:500 (WB) 1:100 (IHC) |
| Anti-β-actin | Mouse | Sigma-Aldrich | A2228 | 1:500 (WB) |
| Genes | Primers (5’–3´) | Product Size (bp) | Annealing Temp. (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemerin | 5′-TGTGCAGTGGGCCTTCCA-3′ 5′-CAAAGGTGCCAGCTGAGAAGA-3′ | 71 | 55 |
| Ccrl2 | 5′-TGTGTTTCCTGCTTCCCCTG-3′ 5′-CGAGGAGTGGAGTCCGACAA-3′ | 101 | 60 |
| Ckmlr1 | 5′-CAAGCAAACAGCCACTACCA-3′ 5′-TAGATGCCGGAGTCGTTGTAA-3′ | 234 | 52 |
| Gpr1 | 5′-GGAGCTCAGCATTCATCACA-3′ 5′-GACAGGCTCTTGGTTTCAGC-3′ | 243 | 53 |
| Apelin | 5′-AGACCCCGGAGGCTAAGGAGTT-3′ 5′-TCCGTCATAGTGTCCTCCATCA-3′ | 300 | 62 |
| Aplnr | 5′-GGACTCCGAATTCCCTTCTC-3′ 5′-CTTGTGCAAGGTCAACCTCA-3′ | 140 | 53 |
| Vaspin | 5′-CTGAAACTGGCTAAGAACT-3′ 5′-CACCTGCCTTGAAAGTAAAT-3′ | 191 | 47 |
| Grp78 | 5′-CTGGGTACATTTGATCTGACTGG-3′ 5′-GCATCCTGGTGGCTTTCCAGCCATTC-3′ | 398 | 64 |
| Plin1 | 5′-TGCGCAAGAAGAGCTGAGTA-3′ 5′-AGAGGCCAACCTGAAGGAGT-3′ | 128 | 53 |
| Tspo | 5′-GCTGGACACTCGCTCCCA-3′ 5′-CATACCCCATGGCCGAATAC-3′ | 51 | 54 |
| Nectin2 | 5′-CGGAACTGTCACTGTCACCA-3′ 5′-GACACTTCAGGAGGGTAGCG-3′ | 150 | 57 |
| Afadin | 5′-CCGACATCATCCACCACTGG-3′ 5′-CAGCATTCGCATATCAGGTCG-3′ | 218 | 60 |
| β-actin | 5′-AAGTACCCCATTGAACACGG-3′ 5′-ATCACAATGCCAGTGGTACG-3′ | 257 | 52 |
| Gapdh | 5′-ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC-3′ 5′-TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA-3′ | 452 | 55 |
| Rpl13a | 5′-CATTCGAACGTCTGCCCTAT-3′ 5′-GTTTCTCAGGCTCCCTCTCC-3′ | 128 | 56 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brzoskwinia, M.; Pardyak, L.; Rak, A.; Kaminska, A.; Hejmej, A.; Marek, S.; Kotula-Balak, M.; Bilinska, B. Flutamide Alters the Expression of Chemerin, Apelin, and Vaspin and Their Respective Receptors in the Testes of Adult Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124439
Brzoskwinia M, Pardyak L, Rak A, Kaminska A, Hejmej A, Marek S, Kotula-Balak M, Bilinska B. Flutamide Alters the Expression of Chemerin, Apelin, and Vaspin and Their Respective Receptors in the Testes of Adult Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124439
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrzoskwinia, Malgorzata, Laura Pardyak, Agnieszka Rak, Alicja Kaminska, Anna Hejmej, Sylwia Marek, Malgorzata Kotula-Balak, and Barbara Bilinska. 2020. "Flutamide Alters the Expression of Chemerin, Apelin, and Vaspin and Their Respective Receptors in the Testes of Adult Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124439
APA StyleBrzoskwinia, M., Pardyak, L., Rak, A., Kaminska, A., Hejmej, A., Marek, S., Kotula-Balak, M., & Bilinska, B. (2020). Flutamide Alters the Expression of Chemerin, Apelin, and Vaspin and Their Respective Receptors in the Testes of Adult Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124439







