Trefoil Factor Family (TFF) Peptides and Their Diverse Molecular Functions in Mucus Barrier Protection and More: Changing the Paradigm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Exocrine and Endocrine Secretion of TFF Peptides
1.2. Ectopic Expression of TFF Peptides during Inflammatory Conditions and in Tumors
1.3. Phenotypes of Tff-Deficient (TffKO) Animals
1.4. TFF Peptides Enhance Cell Migration: Implications for Mucosal Protection and Immune Responses
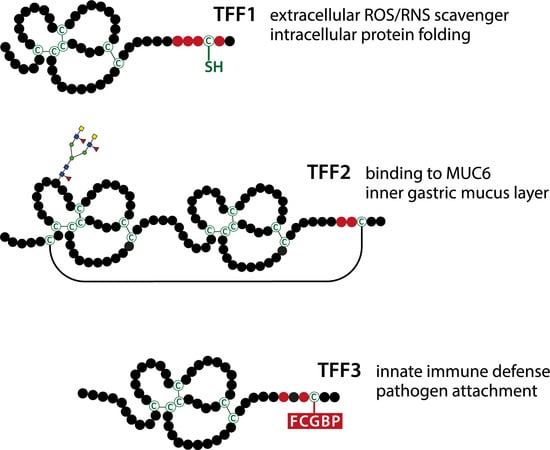
2. Molecular Forms of TFF Peptides and Their Interaction Partners: Functional Implications
2.1. TFF Domains Have Different Lectin Activities
2.2. Gastric TFF1 Mainly Occurs in a Monomeric Form with an Unusual Free Thiol Group: Possible Intracellular and Extracellular Functions in the Gastric Mucus Barrier and during Inflammation
2.3. TFF2 is a MUC6-Binding Lectin: Function for the Stabilization of the Inner Insoluble Layer of the Gastric Mucus–Bicarbonate Barrier and More
2.4. TFF3 Mainly Forms a Disulfide-linked Heteromer with FCGBP: Postulated Function in the Innate Immune Defense
3. Conclusions and Clinical Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DUOX | Dual oxidase |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FCGBP | IgG Fc binding protein |
| GKN | Gastrokine |
| NOX | NADPH oxidase |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SMC | Surface mucous cell |
| TFF | Trefoil factor family |
References
- Thim, L. Trefoil peptides: From structure to function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribieras, S.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. The pS2/TFF1 trefoil factor, from basic research to clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1378, F61–F77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W.; Jagla, W. Cell type specific expression of secretory TFF peptides: Colocalization with mucins and synthesis in the brain. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 147–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thim, L.; May, F.E. Structure of mammalian trefoil factors and functional insights. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2956–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellev, S. The trefoil factor family—Small peptides with multiple functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1350–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF peptides. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 2nd ed.; Kastin, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1338–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, F.; Roeben, C.; Hoffmann, W. xP2, a new member of the P-domain peptide family of potential growth factors, is synthesized in Xenopus laevis skin. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14451–14455. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.-B.; He, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, W.-H.; Qian, J.-Q.; Lai, R.; Jin, Y. A novel non-lens βγ-crystallin and trefoil factor complex from amphibian skin and its functional implications. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauser, F.; Gertzen, E.M.; Hoffmann, W. Expression of spasmolysin (FIM-A.1): An integumentary mucin from Xenopus laevis. Exp. Cell Res. 1990, 189, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, F.; Hoffmann, W. P-domains as shuffled cysteine-rich modules in integumentary mucin C.1 (FIM-C.1) from Xenopus laevis. Polydispersity and genetic polymorphism. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 24620–24624. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, W.; Hauser, F. Biosynthesis of frog skin mucins: Cysteine-rich shuffled modules, polydispersities and genetic polymorphism. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1993, 105, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Hoffmann, W. Porcine gastric TFF2 is a mucus constituent and differs from pancreatic TFF2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W.; Jagla, W.; Wiede, A. Molecular medicine of TFF-peptides: From gut to brain. Histol. Histopathol. 2001, 16, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madsen, J.; Nielsen, O.; Tornoe, I.; Thim, L.; Holmskov, U. Tissue localization of human trefoil factors 1, 2, and 3. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagla, W.; Wiede, A.; Dietzmann, K.; Rutkowski, K.; Hoffmann, W. Co-localization of TFF3 peptide and oxytocin in the human hypothalamus. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, T.; Stellmacher, A.; Znalesniak, E.B.; Dieterich, D.C.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Tff3 is expressed in neurons and microglial cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, H.G.; Dobrowolny, H.; Trubner, K.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B.; Hoffmann, W. Differential regional and cellular distribution of TFF3 peptide in the human brain. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, P.; Rickert, U.; Helmers, A.K.; Spreu, J.; Schneppenheim, J.; Lucius, R. Trefoil factor 3 shows anti-inflammatory effects on activated microglia. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, M.; Schwegler, H.; Chwieralski, C.E.; Laube, G.; Linke, R.; Pohle, W.; Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) expression in the mouse brain and pituitary: Changes in the developing cerebellum. Peptides 2004, 25, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.A.; Familari, M.; Thim, L.; Giraud, A.S. The trefoil peptides TFF2 and TFF3 are expressed in rat lymphoid tissues and participate in the immune response. FEBS Lett. 1999, 456, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baus-Lončar, M.; Kayademir, T.; Takaishi, S.; Wang, T. Trefoil factor family 2 deficiency and immune response. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Cao, L.; Sandor, F.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Nambiar, P.R.; Cerny, A.; Bowen, G.; Yan, J.; Takaishi, S.; et al. Trefoil family factor 2 is expressed in murine gastric and immune cells and controls both gastrointestinal inflammation and systemic immune responses. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kont, V.; Laan, M.; Kisand, K.; Merits, A.; Scott, H.S.; Peterson, P. Modulation of Aire regulates the expression of tissue-restricted antigens. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubeykovskaya, Z.; Si, Y.; Chen, X.; Worthley, D.L.; Renz, B.W.; Urbanska, A.M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Xu, T.; Westphalen, C.B.; Dubeykovskiy, A.; et al. Neural innervation stimulates splenic TFF2 to arrest myeloid cell expansion and cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackerott, M.; Lee, Y.C.; Møllgård, K.; Kofod, H.; Jensen, J.; Rohleder, S.; Neubauer, N.; Gaarn, L.W.; Lykke, J.; Dodge, R.; et al. Trefoil factors are expressed in human and rat endocrine pancreas: Differential regulation by growth hormone. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 5752–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takano, T.; Miyauchi, A.; Yoshida, H.; Kuma, K.; Amino, N. High-throughput differential screening of mRNAs by serial analysis of gene expression: Decreased expression of trefoil factor 3 mRNA in thyroid follicular carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vestergaard, E.M.; Brynskov, J.; Ejskjaer, K.; Clausen, J.T.; Thim, L.; Nexø, E.; Poulsen, S.S. Immunoassays of human trefoil factors 1 and 2: Measured on serum from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab Investig. 2004, 64, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.A. Aspects of the biology of regeneration and repair in the human gastrointestinal tract. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1998, 353, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rio, M.-C.; Chenard, M.P.; Wolf, C.; Marcellin, L.; Tomasetto, C.; Lathe, R.; Bellocq, J.P.; Chambon, P. Induction of pS2 and hSP genes as markers of mucosal ulceration of the digestive tract. Gastroenterology 1991, 100, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsom, R.; Wright, N.A. Trefoil peptides: A newly recognized family of epithelial mucin-associated molecules. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, G205–G213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, M.P.A.; Hoffmann, J.; Haeckel, C.; Rutkowski, K.; Schmid, R.M.; Wagner, M.; Adler, G.; Schulz, H.U.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W.; et al. Induction of TFF1 gene expression in pancreas overexpressing transforming growth factor α. Gut 1999, 45, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viby, N.E.; Nexø, E.; Kissow, H.; Andreassen, H.; Clementsen, P.; Thim, L.; Poulsen, S.S. Trefoil factors (TFFs) are increased in bronchioalveolar lavage fluid from patients with chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD). Peptides 2015, 63, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longman, R.J.; Poulsom, R.; Corfield, A.P.; Warren, B.F.; Wright, N.A.; Thomas, M.G. Alterations in the composition of the supramucosal defense barrier in relation to disease severity of ulcerative colitis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Chwieralski, C.E.; Bälder, R.; Hinz, M.; Braun, A.; Krug, N.; Hoffmann, W. Induced trefoil factor family 1 expression by trans-differentiating Clara cells in a murine asthma model. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Guttek, K.; Händel, U.; Reinhold, D.; Hoffmann, W. Increased Cerebral Tff1 Expression in Two Murine Models of Neuroinflammation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Salm, F.; Händel, U.; Hoffmann, W. Transcriptional Responses in the Murine Spleen after Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Inflammasome and Mucus-Associated Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldenring, J.R.; Nam, K.T.; Wang, T.C.; Mills, J.C.; Wright, N.A. Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia and intestinal metaplasia: Time for reevaluation of metaplasias and the origins of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2207–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, M. Trefoil factors and human gastric cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 12, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalo, G.; Wright, N.A.; Machado, J.C. Trefoil factors: From ulceration to neoplasia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2910–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.S.; Oh, R.R.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.H. Somatic mutations of the trefoil factor family 1 gene in gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckler, A.D.; Roche, J.K.; Harper, J.C.; Petroni, G.; Frierson, H.F., Jr.; Moskaluk, C.A.; El-Rifai, W.; Powell, S.M. Decreased abundance of trefoil factor 1 transcript in the majority of gastric carcinomas. Cancer 2003, 98, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, O.; Chenard, M.P.; Masson, R.; Linares, J.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Wendling, C.; Tomasetto, C.; Chambon, P.; Rio, M.-C. Gastric mucosa abnormalities and tumorigenesis in mice lacking the pS2 trefoil protein. Science 1996, 274, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. Pleiotropic effects of Trefoil Factor 1 deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Fox, J.G.; Gonda, T.; Worthley, D.L.; Muthupalani, S.; Wang, T.C. Mouse models of gastric cancer. Cancers 2013, 5, 92–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Salm, F.; Hoffmann, W. Molecular Alterations in the Stomach of Tff1-Deficient Mice: Early Steps in Antral Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karam, S.M.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. Amplification and invasiveness of epithelial progenitors during gastric carcinogenesis in trefoil factor 1 knockout mice. Cell Prolif. 2008, 41, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutto, M.; Belkhiri, A.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Schneider, B.G.; Peng, D.; Jiang, A.; Washington, M.K.; Kokoye, Y.; Crowe, S.E.; Zaika, A.; et al. Loss of TFF1 is associated with activation of NF-κB-mediated inflammation and gastric neoplasia in mice and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saukkonen, K.; Tomasetto, C.; Narko, K.; Rio, M.-C.; Ristimaki, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and effect of celecoxib in gastric adenomas of trefoil factor 1-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3032–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Karam, S.M.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. Trefoil factor 1 is required for the commitment programme of mouse oxyntic epithelial progenitors. Gut 2004, 53, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buache, E.; Etique, N.; Alpy, F.; Stoll, I.; Muckensturm, M.; Reina-San-Martin, B.; Chenard, M.P.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Deficiency in trefoil factor 1 (TFF1) increases tumorigenicity of human breast cancer cells and mammary tumor development in TFF1-knockout mice. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3261–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tebbutt, N.C.; Giraud, A.S.; Inglese, M.; Jenkins, B.; Waring, P.; Clay, F.J.; Malki, S.; Alderman, B.M.; Grail, D.; Hollande, F. Reciprocal regulation of gastrointestinal homeostasis by SHP2 and STAT-mediated trefoil gene activation in gp130 mutant mice. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.C.; Goldenring, J.R. Inflammation intersection: gp130 balances gut irritation and stomach cancer. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, J.J.; Taupin, D.; Koh, T.J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C.-M.; Podolsky, D.K.; Wang, T.C. TFF2/SP-deficient mice show decreased gastric proliferation, increased acid secretion, and increased susceptibility to NSAID injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baus-Loncar, M.; Schmid, J.; Lalani, E.-N.; Rosewell, I.; Goodlad, R.A.; Stamp, G.W.H.; Blin, N.; Kayademir, T. Trefoil factor 2 (Tff2) deficiency in murine digestive tract influences the immune system. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 16, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Ge, Z.; Ohtani, M.; Jones, E.K.; Wang, T.C. Accelerated progression of gastritis to dysplasia in the pyloric antrum of TFF2 -/- C57BL6 x Sv129 Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, A.A.; Mihalj, M.; Ratkay, I.; Lubka-Pathak, M.; Balogh, P.; Klingel, K.; Bohn, E.; Blin, N.; Baus-Lončar, M. Increased susceptibility to Yersinia enterocolitica Infection of Tff2 deficient mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.M.; Chalinor, H.V.; Walduck, A.; Pavlic, D.I.; Dabritz, J.; Dubeykovskaya, Z.; Wang, T.C.; Menheniott, T.R.; Giraud, A.S. TFF2 deficiency exacerbates weight loss and alters immune cell and cytokine profiles in DSS colitis, and this cannot be rescued by wild-type bone marrow. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G12–G24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Birchenough, G.M.H.; Taylor, P.W. Loss of Trefoil Factor 2 Sensitizes Rat Pups to Systemic Infection with the Neonatal Pathogen Escherichia coli K1. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00878-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birchenough, G.M.; Johansson, M.E.; Stabler, R.A.; Dalgakiran, F.; Hansson, G.C.; Wren, B.W.; Luzio, J.P.; Taylor, P.W. Altered innate defenses in the neonatal gastrointestinal tract in response to colonization by neuropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mashimo, H.; Wu, D.C.; Podolsky, D.K.; Fishman, M.C. Impaired defense of intestinal mucosa in mice lacking intestinal trefoil factor. Science 1996, 274, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.L.; Wong, J.F.; Li, Y.; Swaminathan, S.; Xavier, R.J.; Devaney, K.L.; Podolsky, D.K. Chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-induced intestinal damage is regulated by intestinal trefoil factor. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, K. Vergleichende neurobiologische Untersuchungen von TFF3-defizienten Mäusen und Wildtyptieren. M.D. Thesis, Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dignass, A.; Lynch-Devaney, K.; Kindon, H.; Thim, L.; Podolsky, D.K. Trefoil peptides promote epithelial migration through a transforming growth factor β-independent pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Playford, R.J.; Marchbank, T.; Chinery, R.; Evison, R.; Pignatelli, M.; Boulton, R.A.; Thim, L.; Hanby, A.M. Human spasmolytic polypeptide is a cytoprotective agent that stimulates cell migration. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göke, M.N.; Cook, J.R.; Kunert, K.S.; Fini, M.E.; Gipson, I.K.; Podolsky, D.K. Trefoil peptides promote restitution of wounded corneal epithelial cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 2001, 264, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, U.; Hampel, U.; Sel, S.; Contreras-Ruiz, L.; Schicht, M.; Dieckow, J.; Diebold, Y.; Paulsen, F. Trefoil factor family peptide 3 (TFF3) is upregulated under experimental conditions similar to dry eye disease and supports corneal wound healing effects in vitro. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 3037–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graness, A.; Chwieralski, C.E.; Reinhold, D.; Thim, L.; Hoffmann, W. Protein kinase C and ERK activation are required for TFF-peptide-stimulated bronchial epithelial cell migration and tumor necrosis factor-α-induced interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-8 secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18440–18446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, T.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. TFF1 is differentially expressed in stationary and migratory rat gastric epithelial cells (RGM-1) after in vitro wounding: Influence of TFF1 RNA interference on cell migration. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storesund, T.; Hayashi, K.; Kolltveit, K.M.; Bryne, M.; Schenck, K. Salivary trefoil factor 3 enhances migration of oral keratinocytes. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2008, 116, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guppy, N.J.; El-Bahrawy, M.E.; Kocher, H.M.; Fritsch, K.; Qureshi, Y.A.; Poulsom, R.; Jeffery, R.E.; Wright, N.A.; Otto, W.R.; Alison, M.R. Trefoil factor family peptides in normal and diseased human pancreas. Pancreas 2012, 41, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prest, S.J.; May, F.E.; Westley, B.R. The estrogen-regulated protein, TFF1, stimulates migration of human breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwieralski, C.E.; Schnurra, I.; Thim, L.; Hoffmann, W. Epidermal growth factor and trefoil factor family 2 synergistically trigger chemotaxis on BEAS-2B cells via different signaling cascades. Am. J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinery, R.; Playford, R.J. Combined intestinal trefoil factor and epidermal growth factor is prophylactic against Indomethacin-Induced gastric damage in the rat. Clin. Sci. 1995, 88, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Van Aken, E.; Van Bocxlaer, S.; Attoub, S.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Bruyneel, E.; Westley, B.R.; May, F.E.; Thim, L.; Mareel, M.; et al. Trefoil peptides as proangiogenic factors in vivo and in vitro: Implication of cyclooxygenase-2 and EGF receptor signaling. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lalani, E.N.; Williams, R.; Jayaram, Y.; Gilbert, C.; Chaudhary, K.S.; Siu, L.S.; Koumarianou, A.; Playford, R.; Stamp, G.W. Trefoil factor-2, human spasmolytic polypeptide, promotes branching morphogenesis in MCF-7 cells. Lab. Investig. 1999, 79, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taupin, D.R.; Kinoshita, K.; Podolsky, D.K. Intestinal trefoil factor confers colonic epithelial resistance to apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bossenmeyer-Pourié, C.; Kannan, R.; Ribieras, S.; Wendling, C.; Stoll, I.; Thim, L.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. The trefoil factor 1 participates in gastrointestinal cell differentiation by delaying G1-S phase transition and reducing apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 157, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, L.S.; Romanska, H.; Abel, P.D.; Baus-Lončar, M.; Kayademir, T.; Stamp, G.W.; Lalani, E.-N. TFF2 (trefoil family factor2) inhibits apoptosis in breast and colorectal cancer cell lines. Peptides 2004, 25, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösler, S.; Haase, T.; Claassen, H.; Schulze, U.; Schicht, M.; Riemann, D.; Brandt, J.; Wohlrab, D.; Müller-Hilke, B.; Goldring, M.B.; et al. Trefoil factor 3 is induced during degenerative and inflammatory joint disease, activates matrix metalloproteinases, and enhances apoptosis of articular cartilage chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Klemke, R.L. Extracellular-regulated kinase activation and CAS/Crk coupling regulate cell migration and suppress apoptosis during invasion of the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taupin, D.; Podolsky, D.K. Trefoil factors: Initiators of mucosal healing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 4, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factors TFF (trefoil factor family) peptide-triggered signals promoting mucosal restitution. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, K.; Hans, W.; Van Huysse, J.; Neirynck, S.; Demetter, P.; Remaut, E.; Rottiers, P.; Steidler, L. Active delivery of trefoil factors by genetically modified Lactococcus lactis prevents and heals acute colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolsky, D.K.; Gerken, G.; Eyking, A.; Cario, E. Colitis-associated variant of TLR2 causes impaired mucosal repair because of TFF3 deficiency. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, W.R.; Thim, L. Trefoil factor family-interacting proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thim, L.; Mørtz, E. Isolation and characterization of putative trefoil peptide receptors. Regul. Pept. 2000, 90, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.; Sorensen, G.L.; Nielsen, O.; Tornøe, I.; Thim, L.; Fenger, C.; Mollenhauer, J.; Holmskov, U. A variant form of the human deleted in malignant brain tumor 1 (DMBT1) gene shows increased expression in inflammatory bowel diseases and interacts with dimeric trefoil factor 3 (TFF3). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leito, J.T.; Ligtenberg, A.J.; van Houdt, M.; van den Berg, T.K.; Wouters, D. The bacteria binding glycoprotein salivary agglutinin (SAG/gp340) activates complement via the lectin pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 49, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubeykovskaya, Z.; Dubeykovskiy, A.; Solal-Cohen, J.; Wang, T.C. Secreted trefoil factor 2 activates the CXCR4 receptor in epithelial and lymphocytic cancer cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3650–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieckow, J.; Brandt, W.; Hattermann, K.; Schob, S.; Schulze, U.; Mentlein, R.; Ackermann, P.; Sel, S.; Paulsen, F.P. CXCR4 and CXCR7 mediate TFF3-Induced cell migration independently from the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Investig. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2016, 57, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and chemokine receptors: A promising relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6505–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, K.A.; Hanyu, H.; Matthis, A.L.; Zhang, T.; Frey, M.R.; Oshima, Y.; Aihara, E.; Montrose, M.H. Trefoil factor 2 activation of CXCR4 requires calcium mobilization to drive epithelial repair in gastric organoids. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2673–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, J.; Lee, W.; Zhang, Y. Activation of protease-activated receptor (PAR) 1 by frog trefoil factor (TFF) 2 and PAR4 by human TFF2. Cell. Mol. Live Sci. 2011, 68, 3771–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera Roa, G.J.; Sanchez Tortolero, G.S. Trefoil factor 3 (TFF3) from human breast milk activates PAR-2 receptors, of the intestinal epithelial cells HT-29, regulating cytokines and defensins. Bratisl. Med. J. 2016, 117, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riemer, J.; Bulleid, N.; Herrmann, J.M. Disulfide formation in the ER and mitochondria: Two solutions to a common process. Science 2009, 324, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchbank, T.; Westley, B.R.; May, F.E.B.; Calnan, D.P.; Playford, R.J. Dimerization of human pS2 (TFF1) plays a key role in its protective/healing effects. J. Pathol. 1998, 185, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calnan, D.P.; Westley, B.R.; May, F.E.B.; Floyd, D.N.; Marchbank, T.; Playford, R.J. The trefoil peptide TFF1 inhibits the growth of the human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line AGS. J. Pathol. 1999, 188, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Taupin, D.R.; Itoh, H.; Podolsky, D.K. Distinct pathways of cell migration and antiapoptotic response to epithelial injury: Structure-function analysis of human intestinal trefoil factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4680–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reeves, E.P.; Ali, T.; Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; O’Kennedy, R.; May, F.E.B.; Westley, B.R.; Josenhans, C.; Rust, M.; Suerbaum, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide interacts with TFF1 in a pH-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westley, B.R.; Griffin, S.M.; May, F.E.B. Interaction between TFF1, a gastric tumor suppressor trefoil protein, and TFIZ1, a brichos domain-containing protein with homology to SP-C. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7967–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, T.K.; Laubinger, W.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.-G.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Human intestinal TFF3 forms disulfide-linked heteromers with the mucus-associated FCGBP protein and is released by hydrogen sulfide. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, T.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Different Forms of TFF3 in the Human Saliva: Heterodimerization with IgG Fc Binding Protein (FCGBP). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heuer, J.; Heuer, F.; Stürmer, R.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Braga Emidio, N.; Muttenthaler, M.; Jechorek, D.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. The Tumor Suppressor TFF1 Occurs in Different Forms and Interacts with Multiple Partners in the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: Indications for Diverse Protective Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dolan, B.; Naughton, J.; Tegtmeyer, N.; May, F.E.B.; Clyne, M. The interaction of Helicobacter pylori with the adherent mucus gel layer secreted by polarized HT29-MTX-E12 cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braga Emidio, N.; Baik, H.; Lee, D.; Stürmer, R.; Heuer, J.; Elliott, A.G.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Haupenthal, K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Hoffmann, W.; et al. Chemical synthesis of human trefoil factor 1 (TFF1) and its homodimer provides novel insights into their mechanisms of action. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6420–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Laubinger, W.; Kalbacher, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W. Biosynthesis of gastrokine-2 in the human gastric mucosa: Restricted spatial expression along the antral gland axis and differential interaction with TFF1, TFF2 and mucins. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanisch, F.-G.; Bonar, D.; Schloerer, N.; Schroten, H. Human trefoil factor 2 is a lectin that binds α-GlcNAc-capped mucin glycans with antibiotic activity against Helicobacter pylori. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27363–27375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF2, a MUC6-binding lectin stabilizing the gastric mucus barrier and more. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stürmer, R.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Hoffmann, W. Commercial porcine gastric mucin preparations, also used as artificial saliva, are a rich source for the lectin TFF2: In vitro binding studies. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, F.; Stürmer, R.; Heuer, J.; Kalinski, T.; Lemke, A.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Different Forms of TFF2, A Lectin of the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: In Vitro Binding Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stürmer, R.; Reising, J.; Hoffmann, W. Trefoil Factor Family (TFF) Modules Are Characteristic Constituents of Separate Mucin Complexes in the Xenopus laevis Integumentary Mucus: In Vitro Binding Studies with FIM-A. 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacchettini, J.C.; Baum, L.G.; Brewer, C.F. Multivalent protein-carbohydrate interactions. A new paradigm for supermolecular assembly and signal transduction. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 3009–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, G.A.; Toscano, M.A.; Jackson, S.S.; Vasta, G.R. Functions of cell surface galectin-glycoprotein lattices. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newton, J.; Allen, A.; Westley, B.R.; May, F.E.B. The human trefoil peptide, TFF1, is present in different molecular forms that are intimately associated with mucus in normal stomach. Gut 2000, 46, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stürmer, R.; Reising, J.; Hoffmann, W. The TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 Appear in Distinctive Forms in the Xenopus laevis Gastric Mucosa: Indications for Different Protective Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, H.; Hoffmann, W. Subcellular Localization of the TFF Peptides xP1 and xP4 in the Xenopus laevis Gastric/Esophageal Mucosa: Different Secretion Modes Reflecting Diverse Protective Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Self-renewal of the human gastric epithelium: New insights from expression profiling using laser microdissection. Mol. BioSyst. 2011, 7, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fra, A.M.; Fagioli, C.; Finazzi, D.; Sitia, R.; Alberini, C.M. Quality control of ER synthesized proteins: An exposed thiol group as a three-way switch mediating assembly, retention and degradation. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 4755–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Sparvoli, A.; Fagioli, C.; Fassina, G.; Sitia, R. Formation of reversible disulfide bonds with the protein matrix of the endoplasmic reticulum correlates with the retention of unassembled Ig light chains. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.F. Molecular and cellular aspects of thiol-disulfide exchange. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 1990, 63, 69–172. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, L.B. The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, W.; Hauser, F. The P-domain or trefoil motif: A role in renewal and pathology of mucous epithelia? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1993, 18, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.-F.; Karam, S.M.; Wendling, C.; Chenard, M.-P.; Kershenobich, D.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. Trefoil factor 1 (TFF1/pS2) deficiency activates the unfolded protein response. Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindquist, J.A.; Hämmerling, G.J.; Trowsdale, J. ER60/ERp57 forms disulfide-bonded intermediates with MHC class I heavy chain. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1448–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishkin, S.; Eremina, L.; Kovalev, L.; Kovaleva, M. AGR2, ERp57/GRP58, and some other human protein disulfide isomerases. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 1415–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, G.I.; Jacob, C. Reactive sulfur species: An emerging concept in oxidative stress. Biol. Chem. 2002, 383, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Clavreul, N.; Sethuraman, M.; Adachi, T.; Cohen, R.A. Thiol oxidation in signaling and response to stress: Detection and quantification of physiological and pathophysiological thiol modifications. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colovic, M.B.; Vasic, V.M.; Djuric, D.M.; Krstic, D.Z. Sulphur-containing amino acids: Protective role against free radicals and heavy metals. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Mogami, S.; Hibi, T. Roles of oxidative stress in stomach disorders. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 50, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, W. Current status on stem cells and cancers of the gastric epithelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19153–19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, M.; Atuma, C.; Henriksnas, J.; Holm, L. The importance of mucus layers and bicarbonate transport in preservation of gastric juxtamucosal pH. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G211–G219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.S.; Choi, M.K.; Lee, W.J. Dual oxidase in mucosal immunity and host-microbe homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasberger, H.; El-Zaatari, M.; Dang, D.T.; Merchant, J.L. Dual oxidases control release of hydrogen peroxide by the gastric epithelium to prevent Helicobacter felis infection and inflammation in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.-H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björne, H.; Petersson, J.; Phillipson, M.; Weitzberg, E.; Holm, L.; Lundberg, J.O. Nitrite in saliva increases gastric mucosal blood flow and mucus thicknes. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, M.W.; McMahon, T.J.; Stamler, J.S. S-nitrosylation in health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugrin, J.; Rosenblatt-Velin, N.; Parapanov, R.; Liaudet, L. The role of oxidative stress during inflammatory processes. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Kaul, M.; Yan, B.; Kridel, S.J.; Cui, J.; Strongin, A.; Smith, J.W.; Liddington, R.C.; Lipton, S.A. S-nitrosylation of matrix metalloproteinases: Signaling pathway to neuronal cell death. Science 2002, 297, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosco, A.; Monti, M.C.; Fontanella, B.; Montefusco, S.; D’Andrea, L.; Ziaco, B.; Baldantoni, D.; Rio, M.-C.; Marzullo, L. Copper binds the carboxy-terminus of trefoil protein 1 (TFF1), favoring its homodimerization and motogenic activity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, N.A.; Poulsom, R.; Stamp, G.; Van Noorden, S.; Sarraf, C.; Elia, G.; Ahnen, D.; Jeffery, R.; Longcroft, J.; Pike, C. Trefoil peptide gene expression in gastrointestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1993, 104, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Hayama, M.; Momose, M.; El-Zimaity, H.M.; Matsuda, K.; Sano, K.; Maruta, F.; Okumura, N.; Katsuyama, T. Co-localization of TFF2 with gland mucous cell mucin in gastric mucous cells and in extracellular mucous gel adherent to normal and damaged gastric mucosa. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 126, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oinuma, T.; Ide, S.; Kawano, J.; Suganuma, T. Purification and immunohistochemistry of Griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin-II-binding mucus glycoprotein in rat stomach. Glycobiology 1994, 4, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, K.; Kurihara, M.; Goso, Y.; Urata, T.; Ota, H.; Katsuyama, T.; Hotta, K. Peripheral α -linked N-acetylglucosamine on the carbohydrate moiety of mucin derived from mammalian gastric gland mucous cells: Epitope recognized by a newly characterized monoclonal antibody. Biochem. J. 1996, 318, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.; Klasson, S.; Larsson, E.; Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C.; Samuelsson, T. Searching the Evolutionary Origin of Epithelial Mucus Protein Components-Mucins and FCGBP. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakubo, M.; Ito, Y.; Okimura, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sakura, K.; Kasama, S.; Fukuda, M.N.; Fukuda, M.; Katsuyama, T.; Nakayama, J. Natural antibiotic function of a human gastric mucin against Helicobacter pylori infection. Science 2004, 305, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Wang, P.; Hoshino, H.; Ito, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Nakayama, J.; Seeberger, P.H.; Fukuda, M. α1,4GlcNAc-capped mucin-type O-glycan inhibits cholesterol α-glucosyltransferase from Helicobacter pylori and suppresses H. pylori growth. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van den Brink, G.R.; Tytgat, K.M.A.J.; Van der Hulst, R.W.M.; Van der Loos, C.M.; Einerhand, A.W.; Büller, H.A.; Dekker, J. H pylori colocalises with MUC5AC in the human stomach. Gut 2000, 46, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, F.; Shiota, A.; Goso, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sato, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Fujiwara, M.; Yokosawa, S.; Muraki, T.; Miyagawa, S. Essential role of gastric gland mucin in preventing gastric cancer in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanisch, F.-G.; Ragge, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Human gastric TFF2 peptide contains an N-linked fucosylated N,N’-diacetyllactosediamine (LacdiNAc) oligosaccharide. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semple, J.I.; Newton, J.L.; Westley, B.R.; May, F.E.B. Dramatic diurnal variation in the concentration of the human trefoil peptide TFF2 in gastric juice. Gut 2001, 48, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossez, Y.; Gosset, P.; Boneca, I.G.; Magalhães, A.; Ecobichon, C.; Reis, C.A.; Cieniewski-Bernard, C.; Joncquel Chevalier Curt, M.; Léonard, R.; Maes, E. The lacdiNAc-specific adhesin LabA mediates adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric mucosa. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillipson, M.; Johansson, M.E.; Henriksnas, J.; Petersson, J.; Gendler, S.J.; Sandler, S.; Persson, A.E.; Hansson, G.C.; Holm, L. The gastric mucus layers: Constituents and regulation of accumulation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G806–G812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, S.B.; Takamura, K.; Anway, R.; Shekels, L.L.; Toribara, N.W.; Ota, H. The adherent gastric mucous layer is composed of alternating layers of MUC5AC and MUC6 mucin proteins. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, J.A.; Lee, L.S.; Wu, B.; Repas, K.; Banks, P.A.; Conwell, D.L.; Steen, H. Proteomic analysis of endoscopically (ePFT) collected gastroduodenal fluid using in-gel tryptic digestion followed by LC-MS/MS. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thim, L.; Madsen, F.; Poulsen, S.S. Effect of trefoil factors on the viscoelastic properties of mucus gels. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menheniott, T.R.; O’Connor, L.; Chionh, Y.T.; Däbritz, J.; Scurr, M.; Rollo, B.N.; Ng, G.Z.; Jacobs, S.; Catubig, A.; Kurklu, B. Loss of gastrokine-2 drives premalignant gastric inflammation and tumor progression. J. Cin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1383–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, N.; Iijima, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshida, T.; Brown, W.R.; Hibi, T.; Oshima, A.; Morikawa, M. Human IgGFc binding protein (FcγBP) in colonic epithelial cells exhibits mucin-like structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 15232–15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.; Ogata, H.; Morikawa, M.; Iijima, S.; Harada, N.; Yoshida, T.; Brown, W.; Inoue, N.; Hamada, Y.; Ishii, H. Distribution and partial characterisation of IgG Fc binding protein in various mucin producing cells and body fluids. Gut 2002, 51, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Gerlach, K.L.; Zahl, C.; Hoffmann, W. Expression analysis of human salivary glands by laser microdissection: Differences between submandibular and labial glands. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, R.; Su, B.; Luo, Y.; Terhune, J.; Beck, B.; Peatman, E. Evasion of mucosal defenses during Aeromonas hydrophila infection of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) skin. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Song, H.; Tang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, X. FcGBP was upregulated by HPV infection and correlated to longer survival time of HNSCC patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86503–86514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.L. Fcgbp—A Potential Viral Trap in RV144. Open AIDS J. 2014, 8, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhen, G.; Park, S.W.; Nguyenvu, L.T.; Rodriguez, M.W.; Barbeau, R.; Paquet, A.C.; Erle, D.J. IL-13 and epidermal growth factor receptor have critical but distinct roles in epithelial cell mucin production. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilek, A.; Mollay, C.; Tippelt, C.; Grassi, J.; Mignogna, G.; Müllegger, J.; Sander, V.; Fehrer, C.; Barra, D.; Kreil, G. Biosynthesis of a D-amino acid in peptide linkage by an enzyme from frog skin secretions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4235–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nieuw Amerongen, A.V.; Veerman, E.C. Saliva—The defender of the oral cavity. Oral Dis. 2002, 8, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossez, Y.; Coddeville, B.; Elass, E.; Quinchon, J.F.; Vidal, O.; Corfield, A.P.; Gosset, P.; Lacroix, J.M.; Michalski, J.C.; Robbe-Masselot, C. Interaction between DMBT1 and galectin 3 is modulated by the structure of the oligosaccharides carried by DMBT1. Biochimie 2011, 93, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.; Thomsson, K.A.; Hansson, G.C. Proteomic analyses of the two mucus layers of the colon barrier reveal that their main component, the Muc2 mucin, is strongly bound to the Fcgbp protein. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3549–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Sjoberg, K.E.; Petersson, J.; Holm, L.; Sjovall, H.; Hansson, G.C. Bacteria penetrate the inner mucus layer before inflammation in the dextran sulfate colitis model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gäbel, G.; Northoff, B.H.; Weinzierl, I.; Ludwig, S.; Hinterseher, I.; Wilfert, W.; Teupser, D.; Doderer, S.A.; Bergert, H.; Schönleben, F.; et al. Molecular Fingerprint for Terminal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lieleg, O.; Lieleg, C.; Bloom, J.; Buck, C.B.; Ribbeck, K. Mucin biopolymers as broad-spectrum antiviral agents. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braga Emidio, N.; Hoffmann, W.; Brierley, S.M.; Muttenthaler, M. Trefoil Factor Family: Unresolved Questions and Clinical Perspectives. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, S.A.; Haddad, R.I.; Cilli, F.; Sonis, S.T.; Colevas, A.D.; Brennan, M.T.; Hu, K.S.; Murphy, B.A. Phase 1b, multicenter, single blinded, placebo-controlled, sequential dose escalation study to assess the safety and tolerability of topically applied AG013 in subjects with locally advanced head and neck cancer receiving induction chemotherapy. Cancer 2013, 119, 4268–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.E.; Barker, N.P.; Akhmadullina, L.I.; Rodionova, I.; Sherman, N.Z.; Davidenko, I.S.; Rakovskaya, G.N.; Gotovkin, E.A.; Shinkarev, S.A.; Kopp, M.V.; et al. Phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of recombinant human intestinal trefoil factor oral spray for prevention of oral mucositis in patients with colorectal cancer who are receiving fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 27, 4333–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-M.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Chong, Q.-Y.; Poh, H.-M.; Tan, T.-Z.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, T.; Pandey, V.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of TFF3 Enhances Sensitivity of CMS4 Colorectal Carcinoma to 5-Fluorouracil through Inhibition of p44/42 MAPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Vliet, M.; Harmsen, H.J.; de Bont, E.S.; Tissing, W.J. The role of intestinal microbiota in the development and severity of chemotherapy-induced mucositis. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caballero, G.G.; Kaltner, H.; Kutzner, T.J.; Ludwig, A.-K.; Manning, J.C.; Schmidt, S.; Sinowatz, F.; Gabius, H.-J. How galectins have become multifunctional proteins. Histol. Histopathol. 2020, 35, 509–539. [Google Scholar]


| TFF Peptides | Exocrine Secretion (Major/Minor) | Endocrine Secretion |
|---|---|---|
| TFF1 | Stomach, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, salivary glands, lung, urogenitary tract | CNS |
| TFF2 | Stomach, Brunner’s glands, salivary glands | CNS, lymphoid tissues |
| TFF3 | Intestine, salivary glands, lung, uterus, vagina, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, inner ear, esophagus, stomach, gallbladder, Vater’s ampulla, urinary tract | CNS, thyroid, lymphoid tissues, endocrine pancreas |
| TFFs | Structures | Expression Sites | Natural Forms (Major/Minor) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TFF1 |  | Stomach | TFF1mono TFF1-FCGBP TFF1-X (60 k) TFF1-GKN2 TFF1-TFF1 |
| TFF2 |  | Stomach | TFF2/MUC6 TFF2 |
| TFF3 |  | Intestine, salivary glands | TFF3-FCGBP TFF3-TFF3 TFF3mono |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoffmann, W. Trefoil Factor Family (TFF) Peptides and Their Diverse Molecular Functions in Mucus Barrier Protection and More: Changing the Paradigm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124535
Hoffmann W. Trefoil Factor Family (TFF) Peptides and Their Diverse Molecular Functions in Mucus Barrier Protection and More: Changing the Paradigm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124535
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoffmann, Werner. 2020. "Trefoil Factor Family (TFF) Peptides and Their Diverse Molecular Functions in Mucus Barrier Protection and More: Changing the Paradigm" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124535
APA StyleHoffmann, W. (2020). Trefoil Factor Family (TFF) Peptides and Their Diverse Molecular Functions in Mucus Barrier Protection and More: Changing the Paradigm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124535