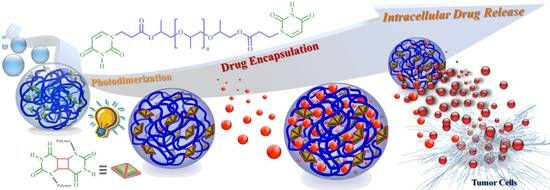
Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
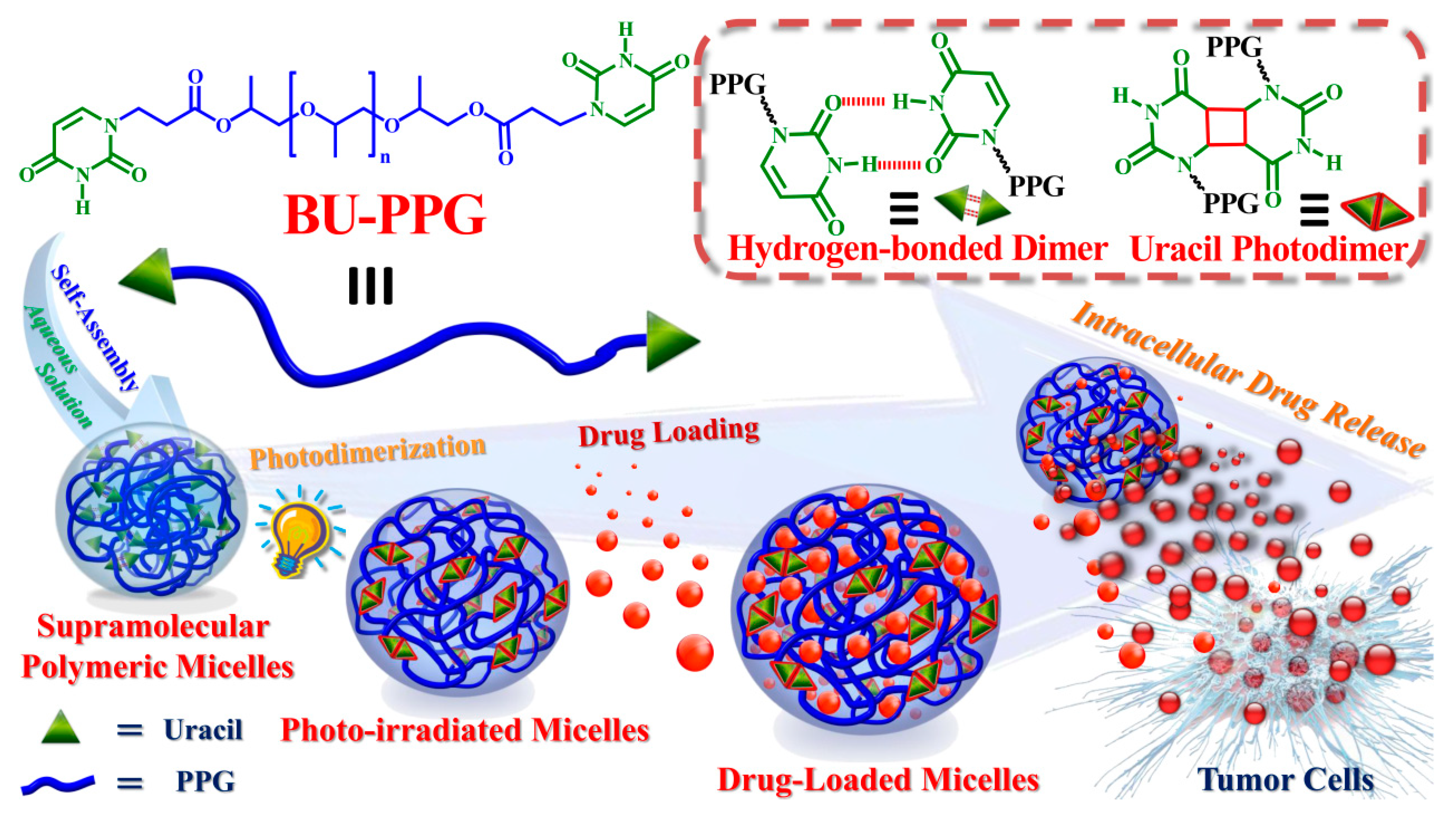
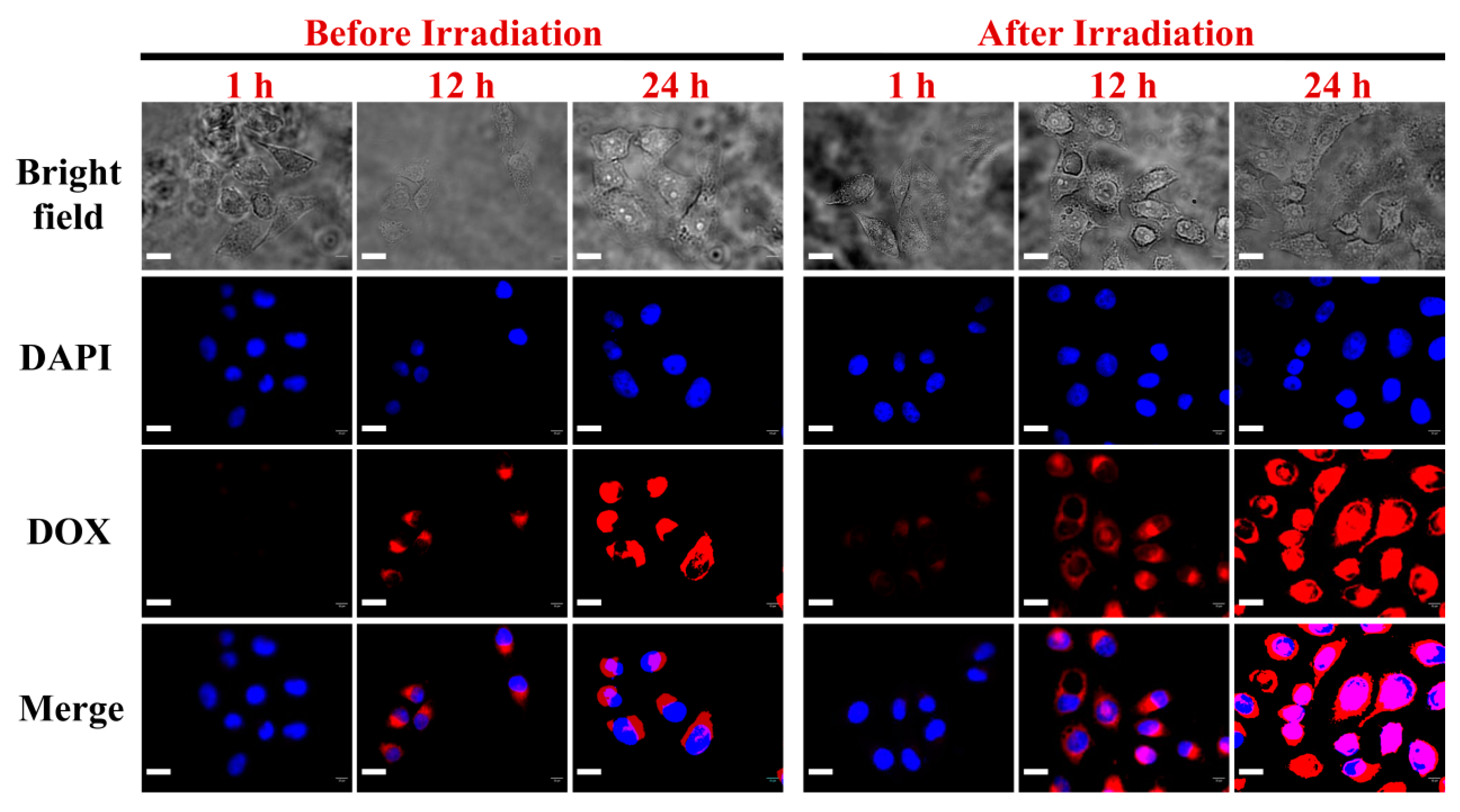
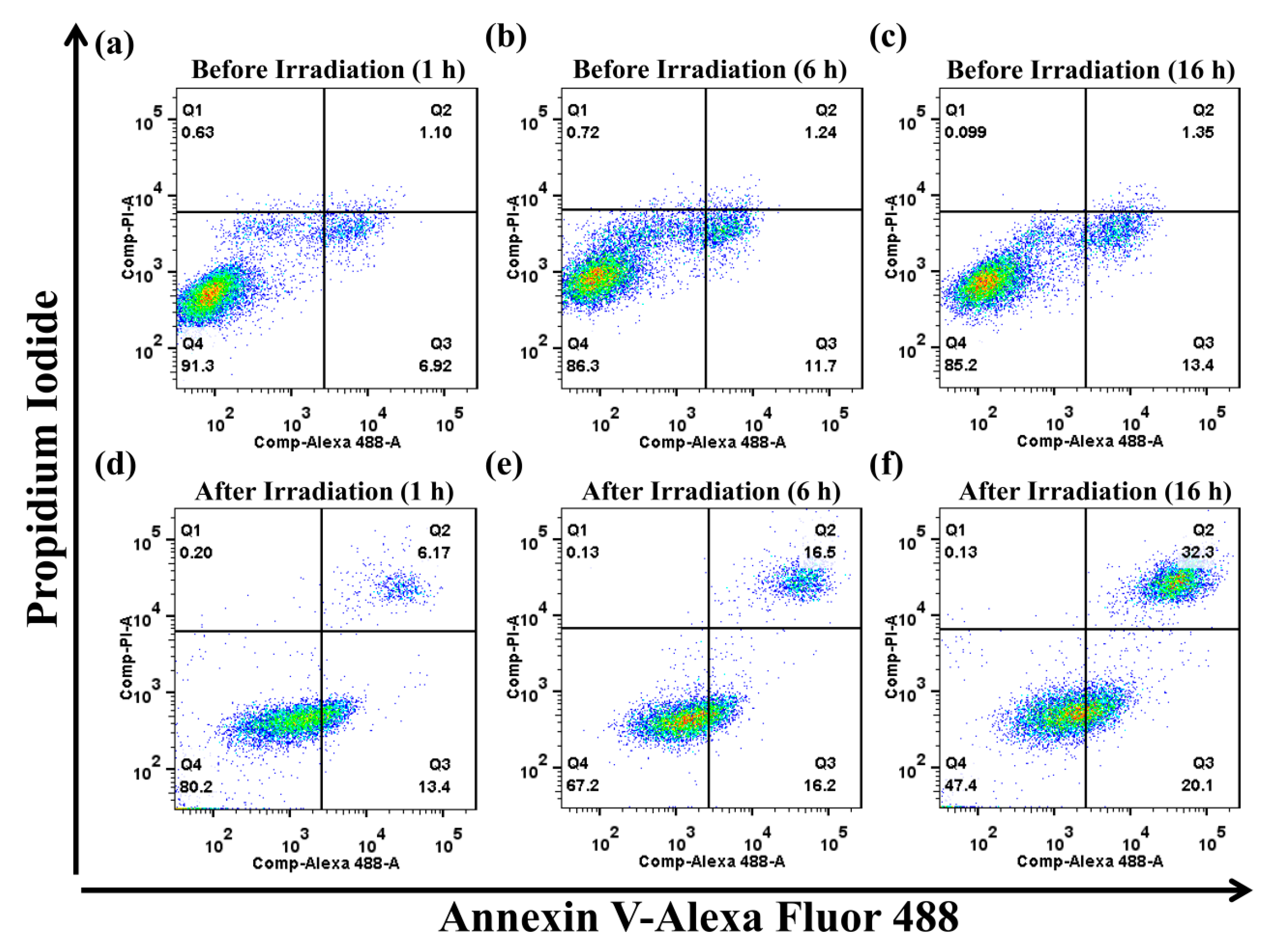
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miragoli, M.; Ceriotti, P.; Iafisco, M.; Vacchiano, M.; Salvarani, N.; Alogna, A.; Carullo, P.; Ramirez-Rodríguez, G.B.; Patrício, T.; Esposti, L.D.; et al. Inhalation of peptide-loaded nanoparticles improves heart failure. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibori, H.; Eliyahu, S.; Krivitsky, A.; Ben-Shushan, D.; Epshtein, Y.; Tiram, G.; Blau, R.; Ofek, P.; Lee, J.S.; Ruppin, E.; et al. Amphiphilic nanocarrier-induced modulation of PLK1 and MiR-34a leads to improved therapeutic response in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, I.; Harnoy, A.J.; Tirosh, E.; Buzhor, M.; Segal, M.; Frid, L.; Shaharabani, R.; Avinery, R.; Beck, R.; Amir, R.J. Encapsulation and covalent binding of molecular payload in enzymatically activated micellar nanocarriers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskas, L.M.; McLeod, V.M.; Porter, C.J.H.; Boyd, B.J. Association of chemotherapeutic drugs with dendrimer nanocarriers: An assessment of the merits of covalent conjugation compared to noncovalent encapsulation. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2012, 9, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liechty, W.B.; Kryscio, D.R.; Slaughter, B.V.; Peppas, N.A. Polymers for drug delivery systems. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2010, 1, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaan, K.; Kumar, S.; Poonia, N.; Lather, V.; Pandita, D. Dendrimers in drug delivery and targeting: Drug-dendrimer interactions and toxicity issues. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2014, 6, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Inorganic nanomaterials for bioimaging, targeted drug delivery and therapeutics. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14071–14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Ruiz-Molina, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent advances in porous nanoparticles for drug delivery in antitumoral applications: Inorganic nanoparticles and nanoscale metal-organic frameworks. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraee, H.; Eatemadi, A.; Abbasi, E.; Aval, S.F.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Application of gold nanoparticles in biomedical and drug delivery. Artif. Cell. Nanomed. B. 2016, 44, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.C.; Chan, D.P.Y.; Shoichet, M.S. Polymeric micelle stability. Nano Today 2012, 7, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tian, H. Stimuli-responsive supramolecular polymers in aqueous solution. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1971–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Duval, K.; Fan, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, Z. Dimeric drug polymeric micelles with acid-active tumor targeting and FRET-traceable drug release. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, S.; Ge, L.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Translatable high drug loading drug delivery systems based on biocompatible polymer nanocarriers. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1732–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulfam, M.; Matini, T.; Monteiro, P.F.; Riva, R.; Collins, H.; Spriggs, K.; Howdle, S.M.; Jérôme, C.; Alexander, C. Bioreducible cross-linked core polymer micelles enhance in vitro activity of methotrexate in breast cancer cells. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Su, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhu, B.; Pang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Tu, C.; Yan, D.; Zhu, X. Supramolecular copolymer micelles based on the complementary multiple hydrogen bonds of nucleobases for drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, W.; Mao, Z.; Gao, C.; Huang, F. A pillararene-based ternary drug-delivery system with photocontrolled anticancer drug release. Small 2015, 11, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Yin, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.-F.; Zhang, X. Supramolecular polymer chemistry: From structural control to functional assembly. Prog.Polym. Sci. 2020, 100, 101167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.A.; Huck, W.T.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M.; et al. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.C.; Wang, J.H.; Chuang, W.T.; Liao, Z.S.; Huang, J.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Fan, W.L.; Lee, D.J. Dynamic supramolecular self-assembly: Hydrogen bonding-induced contraction and extension of functional polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3294–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.L.; Yu, A.C.; Agmon, G.; Appel, E.A. Supramolecular polymeric biomaterials. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.K.; Zimmerman, S.C. Hydrogen bonding modules for use in supramolecular polymers. Isr. J. Chem. 2013, 53, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, R.; O’Reilly, R.K. Nucleobase containing synthetic polymers: Advancing biomimicry via controlled synthesis and self-assembly. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 7665–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y.; Shen, J. Functional supramolecular polymers for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 498–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Lee, D.J.; Chen, J.K. Self-assembled supramolecular polymers with tailorable properties that enhance cell attachment and proliferation. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Tang, C. Supramolecular nucleobase-functionalized polymers: Synthesis and potential biological applications. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2020, 8, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganta, S.; Devalapally, H.; Shahiwala, A.; Amiji, M. A review of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Yuan, J.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y. Redox-responsive polymers for drug delivery: From molecular design to applications. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Chang, F.C.; Kao, W.Y.; Hwang, S.M.; Liao, L.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Liang, M.C.; Chen, J.K.; Lee, D.J. Highly efficient drug delivery systems based on functional supramolecular polymers: In vitro evaluation. Acta Biomater. 2016, 33, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Zhang, R. Remote light-responsive nanocarriers for controlled drug delivery: Advances and perspectives. Small 2019, 15, 1903060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deirram, N.; Zhang, C.; Kermaniyan, S.S.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Such, G.K. pH-Responsive polymer nanoparticles for drug delivery. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1800917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-H.; Luo, G.-F.; Lei, Q.; Jia, H.-Z.; Hong, S.; Wang, Q.-R.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. MMP-2 responsive polymeric micelles for cancer-targeted intracellular drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z. Strategies to improve micelle stability for drug delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4985–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.; Wu, S.; Meng, F.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Huang, Y. Core-crosslinked amphiphilic biodegradable copolymer based on the complementary multiple hydrogen bonds of nucleobases: Synthesis, self-assembly and in vitro drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24832–24840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.L.; Kwon, G.S. Relative aggregation state and hemolytic activity of amphotericin B encapsulated by poly(ethylene oxide)-block–poly (N-hexyl-l-aspartamide)-acyl conjugate micelles: effects of acyl chain length. J. Control. Release 2003, 87, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, H.M.; Lavasanifar, A. Polymeric micelles for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2006, 3, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, B.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Lee, A.W.; Chen, J.K.; Lai, J.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Cheng, C.C. Dual stimuli-responsive nucleobase-functionalized polymeric systems as efficient tools for manipulating micellar self-assembly behavior. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, B.T.; Huang, S.Y.; Lee, A.W.; Muhabie, A.; Lai, J.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Cheng, C.C. Highly stable photosensitive supramolecular micelles for tunable, efficient controlled drug release. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Johnston, P.; Saito, K. Photo-reversible dimerisation reactions and their applications in polymeric systems. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lv, Q.; Gao, X.; Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Yu, S.; He, C.; Chen, X. pH-Responsive poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(L-lactide) supramolecular micelles based on host–guest interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8404–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Huang, J.J.; Chen, J.K.; Lee, A.W.; Lai, J.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Cheng, C.C. Self-assembled pH-responsive polymeric micelles for highly efficient, noncytotoxic delivery of doxorubicin chemotherapy to inhibit macrophage activation: In vitro investigation. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alemayehu, Y.A.; Fan, W.-L.; Ilhami, F.B.; Chiu, C.-W.; Lee, D.-J.; Cheng, C.-C. Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677
Alemayehu YA, Fan W-L, Ilhami FB, Chiu C-W, Lee D-J, Cheng C-C. Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(13):4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlemayehu, Yihalem Abebe, Wen-Lu Fan, Fasih Bintang Ilhami, Chih-Wei Chiu, Duu-Jong Lee, and Chih-Chia Cheng. 2020. "Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 13: 4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677
APA StyleAlemayehu, Y. A., Fan, W.-L., Ilhami, F. B., Chiu, C.-W., Lee, D.-J., & Cheng, C.-C. (2020). Photosensitive Supramolecular Micelle-Mediated Cellular Uptake of Anticancer Drugs Enhances the Efficiency of Chemotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(13), 4677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134677