Obesity and Cancer: 27-Hydroxycholesterol, the Missing Link
Abstract
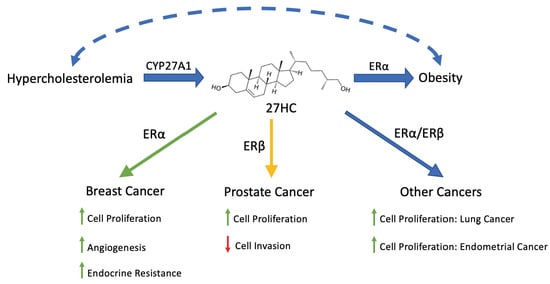
:1. Introduction
2. 27-Hydroxycholesterol, an Endogenous Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator
3. 27HC in Obesity
4. 27HC and Cancer
5. 27HC and Breast Cancer
6. 27HC and Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer
7. 27HC and Prostate Cancer
8. 27HC and Other Cancers
9. Enzymes and Drugs that Lower 27HC Levels
10. Conclusions and Future Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 27HC | 27-hydroxycholesterol |
| SERM | Selective estrogen receptor modulator |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| GPER | G protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| CYP27A1 | Sterol 27-hydroxylase |
| CYP7B1 | Oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase |
| E2 | 17β-Estradiol |
| LBD | Ligand binding domain |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
| HFHC | High fat/high cholesterol |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| TNBC | Triple negative breast cancer |
| LTED | Long time estrogen deprivation |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| LXR | Liver X receptor |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.T.; Newton, C.C.; Freedman, N.D.; Koshiol, J.; Alavanja, M.C.; Beane Freeman, L.E.; Buring, J.E.; Chan, A.T.; Chong, D.Q.; Datta, M.; et al. Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, Diabetes, and Risk of Liver Cancer for U.S. Adults. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6076–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Obesity and Diabetes: The Increased Risk of Cancer and Cancer-Related Mortality. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simone, V.; D’Avenia, M.; Argentiero, A.; Felici, C.; Rizzo, F.M.; De Pergola, G.; Silvestris, F. Obesity and Breast Cancer: Molecular Interconnections and Potential Clinical Applications. Oncologist 2016, 21, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and cancer risk: Emerging biological mechanisms and perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroo, B.J. Estrogen receptors and human disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couse, J.F.; Lindzey, J.; Grandien, K.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Korach, K.S. Tissue Distribution and Quantitative Analysis of Estrogen Receptor-α (ERα) and Estrogen Receptor-β (ERβ) Messenger Ribonucleic Acid in the Wild-Type and ERα-Knockout Mouse. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Pike, A.C.W.; Dauter, Z.; Hubbard, R.E.; Bonn, T.; Engström, O.; Öhman, L.; Greene, G.L.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Carlquist, M. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 1997, 389, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Barton, M. The G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPER in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DuSell, C.D.; Umetani, M.; Shaul, P.W.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; McDonnell, D.P. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Is an Endogenous Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DuSell, C.D.; Nelson, E.R.; Wang, X.; Abdo, J.; Mödder, U.I.; Umetani, M.; Gesty-Palmer, D.; Javitt, N.B.; Khosla, S.; McDonnell, D.P. The Endogenous Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator 27-Hydroxycholesterol Is a Negative Regulator of Bone Homeostasis. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3675–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umetani, M.; Domoto, H.; Gormley, A.K.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Cummins, C.L.; Javitt, N.B.; Korach, K.S.; Shaul, P.W.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. 27-Hydroxycholesterol is an endogenous SERM that inhibits the cardiovascular effects of estrogen. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D. Oxysterol biosynthetic enzymes. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2000, 1529, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuna, R.; Holleboom, A.G.; Motazacker, M.M.; Kuivenhoven, J.A.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Georgopoulos, S.; van Eck, M.; van Berkel, T.J.C.; von Eckardstein, A.; et al. Plasma levels of 27-hydroxycholesterol in humans and mice with monogenic disturbances of high density lipoprotein metabolism. Atherosclerosis 2011, 214, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirayama, T.; Mizokami, Y.; Honda, A.; Homma, Y.; Ikegami, T.; Saito, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Matsuzaki, Y. Serum concentration of 27-hydroxycholesterol predicts the effects of high-cholesterol diet on plasma LDL cholesterol level. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkard, I.; von Eckardstein, A.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P.; Rentsch, K.M. Lipoprotein distribution and biological variation of 24S- and 27-hydroxycholesterol in healthy volunteers. Atherosclerosis 2007, 194, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandak, W.M.; Ren, S.; Marques, D.; Hall, E.; Redford, K.; Mallonee, D.; Bohdan, P.; Heuman, D.; Gil, G.; Hylemon, P. Transport of Cholesterol into Mitochondria Is Rate-limiting for Bile Acid Synthesis via the Alternative Pathway in Primary Rat Hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48158–48164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
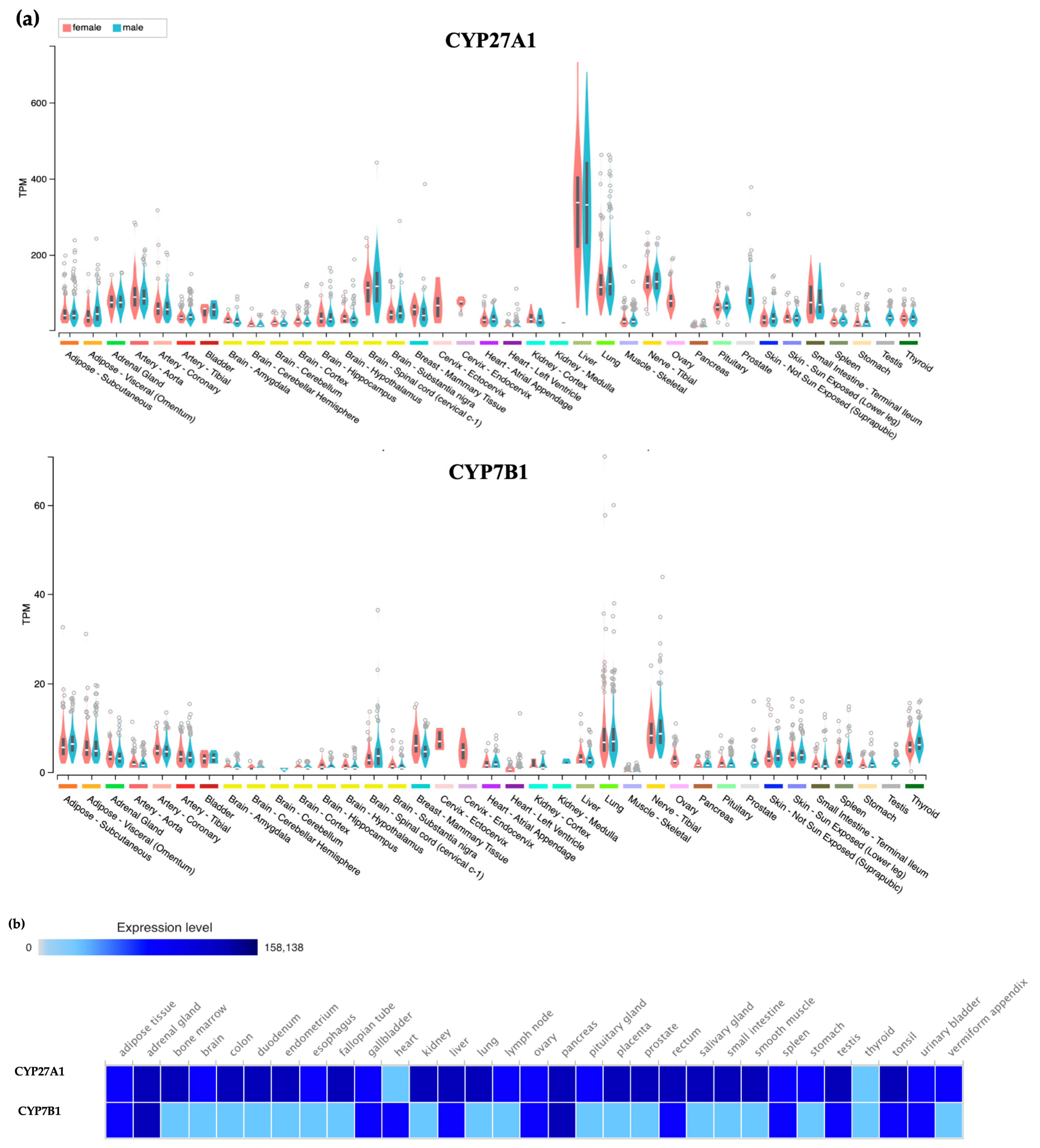
- Wang, D.; Eraslan, B.; Wieland, T.; Hallström, B.; Hopf, T.; Zolg, D.P.; Zecha, J.; Asplund, A.; Li, L.-H.; Meng, C.; et al. A deep proteome and transcriptome abundance atlas of 29 healthy human tissues. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2019, 15, e8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryszak, R.; Keays, M.; Tang, Y.A.; Fonseca, N.A.; Barrera, E.; Burdett, T.; Füllgrabe, A.; Fuentes, A.M.-P.; Jupp, S.; Koskinen, S.; et al. Expression Atlas update—an integrated database of gene and protein expression in humans, animals and plants. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2016, 44, D746–D752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Menke, J.G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; MacNaul, K.L.; Wright, S.D.; Sparrow, C.P.; Lund, E.G. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Is an Endogenous Ligand for Liver X Receptor in Cholesterol-loaded Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38378–38387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umetani, M.; Ghosh, P.; Ishikawa, T.; Umetani, J.; Ahmed, M.; Mineo, C.; Shaul, P.W. The Cholesterol Metabolite 27-Hydroxycholesterol Promotes Atherosclerosis via Proinflammatory Processes Mediated by Estrogen Receptor Alpha. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, E.R.; Wardell, S.E.; Jasper, J.S.; Park, S.; Suchindran, S.; Howe, M.K.; Carver, N.J.; Pillai, R.V.; Sullivan, P.M.; Sondhi, V.; et al. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Links Hypercholesterolemia and Breast Cancer Pathophysiology. Science 2013, 342, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marwarha, G.; Ghribi, O. Does the oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol underlie Alzheimer’s disease–Parkinson’s disease overlap? Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 68, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marwarha, G.; Raza, S.; Hammer, K.; Ghribi, O. 27-hydroxycholesterol: A novel player in molecular carcinogenesis of breast and prostate cancer. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2017, 207, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramitsu, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Lee, W.-R.; Khan, T.; Crumbley, C.; Khwaja, N.; Zamanian, F.; Asghari, A.; Sen, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Estrogen Receptor Beta-Mediated Modulation of Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation by 27-Hydroxycholesterol. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Hiramitsu, S.; Lee, W.-R.; Umetani, J.; Bui, L.; Korach, K.S.; Umetani, M. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Promotes Adiposity and Mimics Adipogenic Diet-Induced Inflammatory Signaling. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of All-Cause Mortality With Overweight and Obesity Using Standard Body Mass Index Categories: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2013, 309, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hales, C.; Carroll, M.; Fryar, C.; Ogden, C. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity among Adults: United States, 2017–2018 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db360.htm (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- Ahima, R.S.; Flier, J.S. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siiteri, P.K. Adipose tissue as a source of hormones. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1987, 45, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, H.T.; Kim, Y.J. The role of estrogen in adipose tissue metabolism: Insights into glucose homeostasis regulation [Review]. Endocr. J. 2014, 61, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooke, P.S.; Naaz, A. Role of Estrogens in Adipocyte Development and Function. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2004, 229, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, E.; Bhattacharya, I.; Brailoiu, E.; Damjanović, M.; Brailoiu, G.C.; Gao, X.; Mueller-Guerre, L.; Marjon, N.A.; Gut, A.; Minotti, R.; et al. Regulatory Role of G Protein–Coupled Estrogen Receptor for Vascular Function and Obesity. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, G.; Prossnitz, E.R. GPER/GPR30 Knockout Mice: Effects of GPER on Metabolism. In Estrogen Receptors; Eyster, K.M., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4939-3126-2. [Google Scholar]
- Heine, P.A.; Taylor, J.A.; Iwamoto, G.A.; Lubahn, D.B.; Cooke, P.S. Increased adipose tissue in male and female estrogen receptor-alpha knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12729–12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohlsson, C.; Hellberg, N.; Parini, P.; Vidal, O.; Bohlooly, M.; Rudling, M.; Lindberg, M.K.; Warner, M.; Angelin, B.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Obesity and Disturbed Lipoprotein Profile in Estrogen Receptor-α-Deficient Male Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 278, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaz, A.; Zakroczymski, M.; Heine, P.; Taylor, J.; Saunders, P.; Lubahn, D.; Cooke, P.S. Effect of Ovariectomy on Adipose Tissue of Mice in the Absence of Estrogen Receptor Alpha (ERα): A Potential Role for Estrogen Receptor Beta (ERβ). Horm. Metab. Res. 2002, 34, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zou, P.; Zheng, L.; Linarelli, L.E.; Amarell, S.; Passaro, A.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Z. Tamoxifen reduces fat mass by boosting reactive oxygen species. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, B.; Gomez, N.A.; de Avila, J.M.; Zhu, M.-J.; Du, M. Even a low dose of tamoxifen profoundly induces adipose tissue browning in female mice. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirouchi, B.; Kashima, K.; Horiuchi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Tong, L.-T.; Sato, M. 27-Hydroxycholesterol suppresses lipid accumulation by down-regulating lipogenic and adipogenic gene expression in 3T3-L1 cells. Cytotechnology 2017, 69, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Daly, E.; Campioli, E.; Wabitsch, M.; Papadopoulos, V. De Novo Synthesis of Steroids and Oxysterols in Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vucenik, I.; Stains, J.P. Obesity and cancer risk: Evidence, mechanisms, and recommendations: Obesity and cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1271, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, Obesity, and Mortality from Cancer in a Prospectively Studied Cohort of U.S. Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kyrgiou, M.; Kalliala, I.; Markozannes, G.; Gunter, M.J.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Gabra, H.; Martin-Hirsch, P.; Tsilidis, K.K. Adiposity and cancer at major anatomical sites: Umbrella review of the literature. BMJ 2017, j477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuzu, O.F.; Noory, M.A.; Robertson, G.P. The Role of Cholesterol in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llaverias, G.; Danilo, C.; Mercier, I.; Daumer, K.; Capozza, F.; Williams, T.M.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P.; Frank, P.G. Role of Cholesterol in the Development and Progression of Breast Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simigdala, N.; Gao, Q.; Pancholi, S.; Roberg-Larsen, H.; Zvelebil, M.; Ribas, R.; Folkerd, E.; Thompson, A.; Bhamra, A.; Dowsett, M.; et al. Cholesterol biosynthesis pathway as a novel mechanism of resistance to estrogen deprivation in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelton, K.; Freeman, M.R.; Solomon, K.R. Cholesterol and prostate cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafique, K.; McLoone, P.; Qureshi, K.; Leung, H.; Hart, C.; Morrison, D.S. Cholesterol and the risk of grade-specific prostate cancer incidence: Evidence from two large prospective cohort studies with up to 37 years’ follow up. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, S.F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Bojesen, S.E. Statin Use and Reduced Cancer-Related Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravnskov, U.; Rosch, P.J.; McCully, K.S. Statins Do Not Protect Against Cancer: Quite the Opposite. JCO 2015, 33, 810–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerre, L.M.; LeLorier, J. Do statins cause cancer? A meta-analysis of large randomized clinical trials. Am. J. Med. 2001, 110, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, T.B.; Hulley, S.B. Carcinogenicity of lipid-lowering drugs. JAMA 1996, 275, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravnskov, U.; McCully, K.S.; Rosch, P.J. The statin-low cholesterol-cancer conundrum. QJM 2012, 105, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, M.; Kita, T.; Mabuchi, H.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Nakaya, N.; Oikawa, S.; Saito, Y.; Sasaki, J.; Shimamoto, K.; Itakura, H.; et al. Large Scale Cohort Study of the Relationship Between Serum Cholesterol Concentration and Coronary Events With Low-Dose Simvastatin Therapy in Japanese Patients With Hypercholesterolemia. Circ. J. 2002, 66, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jerusalem, G.; Collignon, J.; Schroeder, H.; Lousberg, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: Treatment challenges and solutions. BCTT 2016, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerr, J.; Anderson, C.; Lippman, S.M. Physical activity, sedentary behaviour, diet, and cancer: An update and emerging new evidence. The Lancet Oncology 2017, 18, e457–e471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Roberts, D.L.; Dive, C. Obesity and cancer: Pathophysiological and biological mechanisms. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 114, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Estevez, L.; Moreno-Bueno, G. Updating the role of obesity and cholesterol in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Nelson, E.R. 27-Hydroxycholesterol, an endogenous selective estrogen receptor modulator. Maturitas 2017, 104, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.R.; Uppal, H.; Chandran, S.; Bainey, K.R.; Potluri, R. Algorithm for Comorbidities, Associations, Length of Stay and Mortality (ACALM) Research Unit Patients with a diagnosis of hyperlipidaemia have a reduced risk of developing breast cancer and lower mortality rates: A large retrospective longitudinal cohort study from the UK ACALM registry. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.d.M.; Yang, H.-C.; Nguyen, P.-A.; Poly, T.N.; Huang, C.-W.; Kekade, S.; Khalfan, A.M.; Debnath, T.; Li, Y.-C.J.; Abdul, S.S. Exploring association between statin use and breast cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 296, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-J.; Tu, C.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhu, J.; Qian, K.-Q.; Li, W.-J.; Wu, L. Statin use and breast cancer survival and risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.F.; McGuire, V. Evidence of Association Between Plasma High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Risk Factors for Breast Cancer. JNCI: J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilo, C.; Frank, P.G. Cholesterol and breast cancer development. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ishikawa, T.; Sirianni, R.; Tang, H.; McDonald, J.G.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Thompson, B.; Girard, L.; Mineo, C.; Brekken, R.A.; et al. 27-Hydroxycholesterol Promotes Cell-Autonomous, ER-Positive Breast Cancer Growth. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
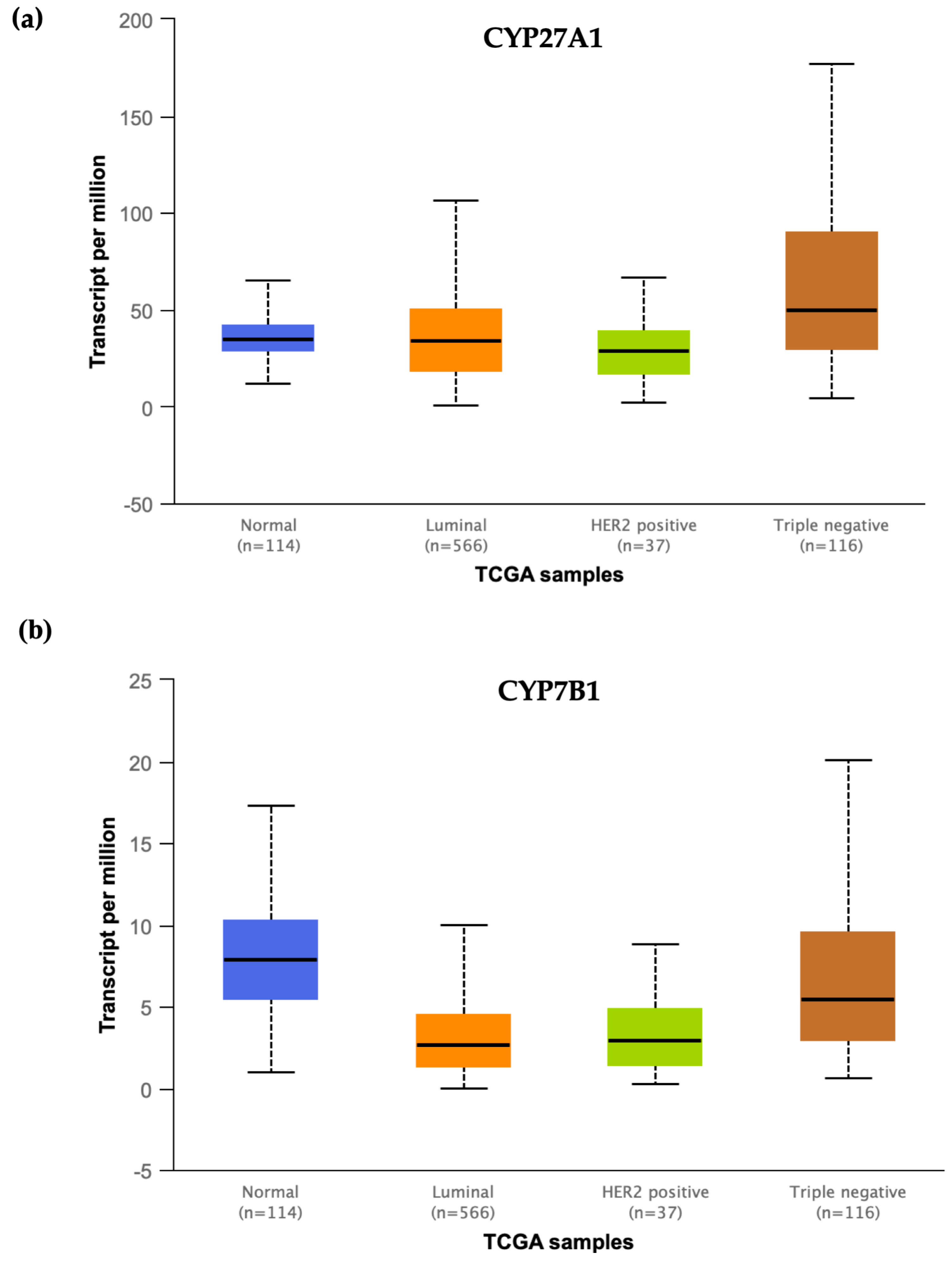
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Shen, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. The ROS-mediated activation of STAT-3/VEGF signaling is involved in the 27-hydroxycholesterol-induced angiogenesis in human breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 264, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, A.E.; Yu, Y.-R.A.; He, S.; Wardell, S.E.; Chang, C.-Y.; Kwon, S.; Pillai, R.V.; McDowell, H.B.; Thompson, J.W.; Dubois, L.G.; et al. The cholesterol metabolite 27 hydroxycholesterol facilitates breast cancer metastasis through its actions on immune cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbung, S.; Chang, C.; Bendahl, P.-O.; Dubois, L.; Thompson, J.W.; McDonnell, D.P.; Borgquist, S. Impact of 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) and 27-hydroxycholesterol in breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.-L.; Le Cornet, C.; Sookthai, D.; Johnson, T.S.; Kaaks, R.; Fortner, R.T. Circulating 27-Hydroxycholesterol and Breast Cancer Risk: Results From the EPIC-Heidelberg Cohort. JNCI: J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, C.E.; Ma, J.; Gaudet, M.M.; Newman, L.A.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toy, W.; Shen, Y.; Won, H.; Green, B.; Sakr, R.A.; Will, M.; Li, Z.; Gala, K.; Fanning, S.; King, T.A.; et al. ESR1 ligand-binding domain mutations in hormone-resistant breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiavon, G.; Hrebien, S.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Cutts, R.J.; Pearson, A.; Tarazona, N.; Fenwick, K.; Kozarewa, I.; Lopez-Knowles, E.; Ribas, R.; et al. Analysis of ESR1 mutation in circulating tumor DNA demonstrates evolution during therapy for metastatic breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 313ra182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.T.M.; Barozzi, I.; Faronato, M.; Lombardo, Y.; Steel, J.H.; Patel, N.; Darbre, P.; Castellano, L.; Győrffy, B.; Woodley, L.; et al. Differential epigenetic reprogramming in response to specific endocrine therapies promotes cholesterol biosynthesis and cellular invasion. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalenc, F.; Iuliano, L.; Filleron, T.; Zerbinati, C.; Voisin, M.; Arellano, C.; Chatelut, E.; Marquet, P.; Samadi, M.; Roché, H.; et al. Circulating oxysterol metabolites as potential new surrogate markers in patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: Results of the OXYTAM study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 169, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaqih, M.A.; Nelson, E.R.; Liu, W.; Safi, R.; Jasper, J.S.; Macias, E.; Geradts, J.; Thompson, J.W.; Dubois, L.G.; Freeman, M.R.; et al. CYP27A1 Loss Dysregulates Cholesterol Homeostasis in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magura, L.; Blanchard, R.; Hope, B.; Beal, J.R.; Schwartz, G.G.; Sahmoun, A.E. Hypercholesterolemia and prostate cancer: A hospital-based case–control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2008, 19, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gann, P.H. Risk factors for prostate cancer. Rev. Urol. 2002, 4 Suppl 5, S3–S10. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, K.; Hayashi, T.; Matsushita, M.; Uemura, M.; Nonomura, N. Obesity, Inflammation, and Prostate Cancer. JCM 2019, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allott, E.H.; Masko, E.M.; Freedland, S.J. Obesity and Prostate Cancer: Weighing the Evidence. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hager, M.H.; Solomon, K.R.; Freeman, M.R. The role of cholesterol in prostate cancer. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2006, 9, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.R.; Solomon, K.R. Cholesterol and prostate cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 91, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Algotar, A.M.; Behnejad, R.; Stratton, M.S.; Stratton, S.P. Chronic Use of NSAIDs and/or Statins Does Not Affect PSA or PSA Velocity in Men at High Risk for Prostate Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2196–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kantor, E.D.; Lipworth, L.; Fowke, J.H.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Mucci, L.A.; Signorello, L.B. Statin use and risk of prostate cancer: Results from the Southern Community Cohort Study: Statin Use and Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2015, 75, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, S.; Meyer, M.; Schommer, J.; Hammer, K.D.P.; Guo, B.; Ghribi, O. 27-Hydroxycholesterol stimulates cell proliferation and resistance to docetaxel-induced apoptosis in prostate epithelial cells. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Meyer, M.; Goodyear, C.; Hammer, K.D.P.; Guo, B.; Ghribi, O. The cholesterol metabolite 27-hydroxycholesterol stimulates cell proliferation via ERβ in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olsson, M.; Gustafsson, O.; Skogastierna, C.; Tolf, A.; Rietz, B.D.; Morfin, R.; Rane, A.; Ekström, L. Regulation and expression of human CYP7B1 in prostate: Overexpression of CYP7B1 during progression of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Prostate 2007, 67, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.A.; Collins, F.; Cousins, F.L.; Esnal Zufiaurre, A.; Saunders, P.T.K. The impact of 27-hydroxycholesterol on endometrial cancer proliferation. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warns, J.; Marwarha, G.; Freking, N.; Ghribi, O. 27-hydroxycholesterol decreases cell proliferation in colon cancer cell lines. Biochimie 2018, 153, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, M.; Xing, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. The oncogenic roles of 27-hydroxycholesterol in glioblastoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umetani, M. Re-adopting classical nuclear receptors by cholesterol metabolites. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 157, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javitt, N.B.; Lee, Y.C.; Shimizu, C.; Fuda, H.; Strott, C.A. Cholesterol and Hydroxycholesterol Sulfotransferases: Identification, Distinction from Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfotransferase, and Differential Tissue Expression. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falany, C.N.; Rohn-Glowacki, K.J. SULT2B1: Unique properties and characteristics of a hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase family. Drug Metab. Rev. 2013, 45, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Guo, F.; Yang, M.; Xu, D.; Zhuang, Z.; Niu, B.; Bai, Q.; Li, X. Hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase 2B1 affects gastric epithelial function and carcinogenesis induced by a carcinogenic agent. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repa, J.J.; Lund, E.G.; Horton, J.D.; Leitersdorf, E.; Russell, D.W.; Dietschy, J.M.; Turley, S.D. Disruption of the Sterol 27-Hydroxylase Gene in Mice Results in Hepatomegaly and Hypertriglyceridemia: Reversal by Cholic Acid Feeding. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39685–39692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asghari, A.; Umetani, M. Obesity and Cancer: 27-Hydroxycholesterol, the Missing Link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144822
Asghari A, Umetani M. Obesity and Cancer: 27-Hydroxycholesterol, the Missing Link. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144822
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsghari, Arvand, and Michihisa Umetani. 2020. "Obesity and Cancer: 27-Hydroxycholesterol, the Missing Link" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144822
APA StyleAsghari, A., & Umetani, M. (2020). Obesity and Cancer: 27-Hydroxycholesterol, the Missing Link. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144822