Nephrotoxicity Associated with Novel Anticancer Agents (Aflibercept, Dasatinib, Nivolumab): Case Series and Nephrological Considerations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Reports
2.1. Case 1
2.2. Case 2
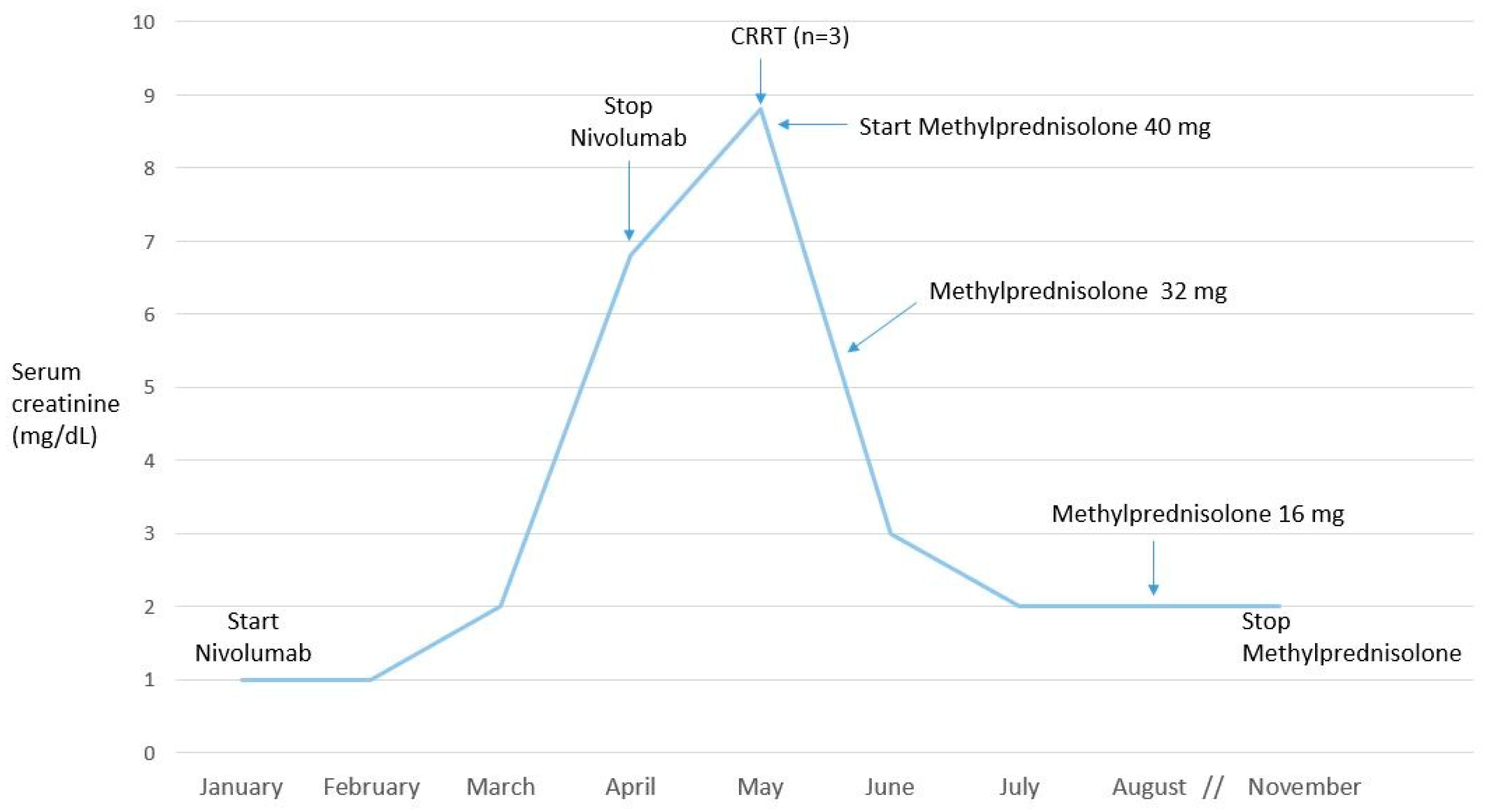
2.3. Case 3
3. Discussion
3.1. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling Pathway Inhibitors
3.1.1. Aflibercept
3.1.2. Dasatinib
3.2. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Nivolumab
4. Nephrological Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capasso, A.; Benigni, A.; Capitanio, U.; Danesh, F.R.; Di Marzo, V.; Gesualdo, L.; Grandaliano, G.; Jaimes, E.A.; Malyszko, J.; Perazella, M.A.; et al. International conference on onco-nephrology participants. Summary of the international conference on onco-nephrology: An emerging field in medicine. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, E.Z.; Perazella, M.A. Update on the nephrotoxicity of novel anticancer agents. Clin. Nephrol. 2018, 89, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sury, K.; Perazella, M.A. The nephrotoxicity of new immunotherapies. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Mirza, M.M.; Ganti, A.K.; Tendulkar, K. Renal toxicities of targeted therapy. Targ. Oncol. 2015, 10, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, C.C.; Maldonado, A.; Mallipattu, S.K. Therapeutic inhibition of VEGF signaling and associated nephrotoxicities. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larcher, F.; Robles, A.I.; Duran, H.; Murillas, R.; Quintanilla, M.; Cano, A.; Conti, C.J.; Jorcano, J.L. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in mouse skin carcinogenesis correlates with malignant progression state and activated H-ras expression levels. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 5391–5396. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Rikala, M.S.; Rys, J.; Lasota, J.; Wang, Z.F. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 as a marker for malignant vascular tumors and mesothelioma: An immunohistochemical study of 262 vascular endothelial and 1640 nonvascular tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, H.; Hamano, Y.; Charytan, D.; Cosgrove, D.; Kieran, M.; Sudhakar, A.; Kalluri, L. Neutralization of circulating vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF] by anti-VEGF antibodies and soluble VEGF receptor 1 (sFlt-1) induces proteinuria. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12605–12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, F.; Perazzella, M.A. Renal effects of anti-angiogenesis therapy: Update for the internist. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holash, J.; Davis, S.; Papadopoulos, N.; Croll, S.D.; Ho, L.; Russell, M.; Boland, P.; Leidich, R.; Hylton, D.; Burova, E.; et al. VEGF-Trap: A VEGF blocker with potent antitumor effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11393–11398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamnvik, O.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; Turchin, A.; McKay, R.R.; Goyal, L.; Davis, M.; Kaymakcalan, M.D.; Williams, J.S. Clinical risk factors for the development of hypertension in patients treated with inhibitors of the VEGF signaling pathway. Cancer 2015, 121, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Massard, C.; Spano, J.P.; Goldwasser, F.; Khayat, D.; Soria, J.C. VEGF signaling inhibition-induced proteinuria: Mechanisms significance and management. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 46, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, W.X.; Shen, Z.; Tang, L.N.; Yao, Y. Risk of hypertension in cancer patients treated with aflibercept: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Clin. Drug Investig. 2014, 34, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, J.D.; Meininger, C.J.; Ziche, M.; Granger, H.J. VEGF upregulates eNOS message, protein, and NO production in human endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, H1054–H1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, A.P.; Cowley, A.W. Role of nitric oxide in the control of renal function and salt sensitivity. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 1999, 1, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, E.S.; Khankin, E.V.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Humphreys, B.D. Hypertension induced by vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibition: Mechanisms and potential use as a biomarker. Semin. Nephrol. 2010, 30, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Pacheco, F.R.; Deudero, J.J.; Castellanos, M.C.; Castilla, M.A.; Alvarez-Arroyo, M.V.; Yague, S.; Caramelo, C. Mechanisms of endothelial response to oxidative aggression: Protective role of autologous VEGF and induction of VEGFR2 by H2O2. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1395–H1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanbayashi, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Tabuchi, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Ouchi, Y.; Otsuji, E.; Takayama, K.; Taguchi, T. Predictive factors for the development of proteinuria in cancer patients treated with bevacizumab, ramucirumab, and aflibercept: A single-institution retrospective analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamba, T.; Tam, B.Y.; Hashizume, H.; Haskell, A.; Sennino, B.; Mancuso, M.R.; Norberg, S.M.; O’Brien, S.M.; Davis, R.B.; Gowen, L.C.; et al. VEGF-dependent plasticity of fenestrated capillaries in the normal adult microvasculature. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H560–H576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izzedine, H.; Escudier, B.; Lhomme, C.; Pautier, P.; Rouvier, P.; Gueutin, V.; Baumelou, A.; Derosa, L.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Kidney diseases associated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) An 8-year observational study at a single center. Medicine 2014, 93, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzedine, H.; Mangier, M.; Ory, V.; Zhang, S.Y.; Sendeyo, K.; Bouachi, K.; Audard, V.; Pe’choux, C.; Soria, J.C.; Massard, C.; et al. Expression patterns of RelA and c-mip are associated with different glomerular diseases following anti-VEGF therapy. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izzedine, H.; Isnard-Bagnis, C.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Mercadal, L.; Tostivint, I.; Rixe, O.; Brocheriou, I.; Bourry, E.; Karie, S.; Saeb, S.; et al. Gemcitabine induced thrombotic microangiopathy: A systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 3038–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takase, O.; Marumo, T.; Imai, N.; Hirahashi, J.; Takayanagi, A.; Hishikawa, K.; Hayashi, M.; Shimizu, N.; Fujita, T.; Saruta, T. NF-kappaB-dependent increase in intrarenal angiotensin II induced by proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maitland, M.L.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Chen, H.X.; Durand, J.B.; Elliott, W.J.; Ivy, S.P.; Leier, C.V.; Lindenfeld, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Cardiovascular toxicities panel, convened by the angiogenesis task force of the national cancer institute investigational drug steering committee: Initial assessment, surveillance, and management of blood pressure in patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibitors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenon, N.N. Managing toxicities associated with antiangiogenic biologic agents in combination with chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2013, 17, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calizo, R.C.; Bhattacharya, S.; Coen van Hasselt, J.G. Disruption of podocyte cytoskeletal biomechanics by dasatinib leads to nephrotoxicity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demetri, G.D.; Russo, L.O.; Mac Pherson, I.R.; Wang, D.; Morgan, J.A.; Brunton, V.G.; Paliwal, P.; Agrawal, S.; Voi, M.; Evans, T.R.J. Phase I dose escalation and farmacokinetic study of dasatinib in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6232–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirano, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Korogi, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Miyanaka, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Tsuda, H. Dasatinib-induced nephrotic syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 726–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruebner, R.L.; Copelovitch, L.; Evageliou, N.F.; Denburg, M.R.; Belasco, J.B.; Kaplan, B.S. Nephrotic syndrome associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors for pediatric malignancy: Case series and review of the literature. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.T.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, Y.H.; Hah, J.O.; Lee, J.M. A case of dasatinib-induced nephrotic syndrome in a child with Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, C.; Abraham, S. Dasatinib induced chylothorax and nephrotic syndrome in a pediatric patient. In Pediatric Blood and Cancer, Proceedings of the American Society of Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 6–9 May 2015; Arceci, R.J., Newburger, P.E., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA; pp. 62, S71.
- Ochiai, S.; Sato, Y.; Minakawa, A.; Fukuda, A.; Fujimoto, S. Dasatinib-induced nephrotic syndrome in a patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia: A case report BMC. Nephrology 2019, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, E.; Lyndon, W.; Chumley, P.; Jaimes, E.A.; Fatima, H. Dasatinib-induced nephrotic-range proteinuria. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, M.L.; Carmosino, I.; Stefanizzi, C.; Campanelli, M.; De Angelis, F.; Cesini, L.; Latagliata, R.; Alimena, G. Nephrotic proteinuria developed under dasatinib treatment in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature. Ann. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 3, 1106. [Google Scholar]
- Koinuma, K.; Sakairi, T.; Watanabe, Y.; IIzuka, A.; Watanabe, M.; Hamatani, H.; Nakasatomi, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Ikeuchi., H.; Kaneko, Y.; et al. A Case of long-term dasatinib-induced proteinuria and glomerular injury. CEN Case Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.D.; Wanchoo, R.; Sakhiya, V.; Ross, D.W.; Fishbane, S. Adverse renal effects of novel molecular oncologic targeted therapies: A narrative review. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller-Hansma, A.H.G.; van der Lugt, J.; Zwaan, C.M. Nephrotic syndrome under treatment with dasatinib: Be aware of a possible adverse drug reaction. Neth. J. Med. 2017, 75, 428–431. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Kujawski, M.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Herrmann, A.; Loera, S.; Yen, Y.; Lee, F.; Yu, H.; Wen, W.; et al. Antitumor activity of targeting SRC kinases in endothelial and myeloid cell compartments of the tumor microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Advani, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor and the kidney: Something of the marvellous. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Higuchi, O.; Ohashi, K.; Nagata, K.; Wada, A.; Kangawa, K.; Nishida, E.; Mizuno, K. Cofilin phosphorylation by LIM-kinase 1 and its role in Rac-mediated actin reorganization. Nature 1998, 393, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenberg, C.V.; Azeloglu, E.U.; Stothers, M.; Deerinck, T.J.; Chen, Y.; He, J.C.; Ellisman, M.H.; Hone, J.C.; Iyengar, R.; Loew, L.M. Fragility of foot process morphology in kidney podocytes arises from chaotic spatial propagation of cytoskeletal instability. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embry, A.E.; Liu, Z.; Henderson, J.M.; Byfield, F.J.; Liu, L.; Yoon, J.; Wu, Z.; Cruz, K.; Moradi, S.; Gillombardo, C.B.; et al. Similar biophysical abnormalities in glomeruli and podocytes from two distinct models. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perazella, M.A.; Shirali, A.C. Immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity: What do we know and what should we do? Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anari, F.; Ramamurthy, C.; Zibelman, M. Impact of tumor microenvironment composition on therapeutic responses and clinical outcomes in cancer. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cui, J. Present and future of cancer immunotherapy: A tumor microenvironmental perspective. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4105–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwai, Y.; Hamanishi, J.; Chamoto, K.; Honjo, T. Cancer immunotherapies targeting the PD-1 signaling pathway. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luke, J.J.; Ott, P.A. PD-1 pathway inhibitors: The next generation of immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3479–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pico de Coaña, Y.; Choudhury, A.; Kiessling, R. Checkpoint blockade for cancer therapy: Revitalizing a suppressed immune system. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Duffy, C.R.; Allison, J.P. Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.F.; Chen, Y.; Song, S.Y.; Wang, T.J.; Ji, W.J.; Li, S.W.; Liu, N.; Yan, C.X. Immune-related adverse events associated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment for malignancies: A meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Marrone, K.A.; Troxell, M.L.; Ralto, K.M.; Hoenig, M.P.; Brahmer, J.R.; Le, D.T.; Lipson, E.J.; Glezerman, I.G.; Wolchok, J.; et al. Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2016, 83, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haslam, A.; Prasad, V. Estimation of the percentage of US patients with cancer who are eligible for and respond to checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy drugs. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e192535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bavi, P.; Kiehl, R.; Adeyi, O.; Mete, O.; Avila-Casado, C.; Sharifzad, H.; Joshua, A.; Butany, J.; Roehrl, M.H. Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) following CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in advanced melanoma: A comprehensive rapid autopsy study. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–18 March 2016; pp. 3, A4. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab is previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirali, A.C.; Perazella, M.A.; Gettinger, S. Association of acute interstitial nephritis with programmed cell death 1 inhibitor therapy in lung cancer patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliere, J.; Meyer, N.; Mazieres, J.; Ollier, S.; Boulinguez, S.; Delas, A.; Ribes, D.; Faguer, S. Acute interstitial nephritis related to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, N.; Borges, T.J.; Yamashita, M.; Riella, L.V. Severe acute interstitial nephritis after combination immune-checkpoint inhibitor therapy for metastatic melanoma. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escandon, J.; Peacock, S.; Trabolsi, A.; Thomas, D.B.; Layka, A.; Lutzky, J. Interstitial nephritis in melanoma patients secondary to PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koda, R.; Watanabe, H.; Tsuchida, M.; Iino, N.; Suzuki, K.; Hasegawa, G.; Imai, N.; Narita, I. Immune checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab)-associated kidney injury and the importance of recognizing concomitant medications known to cause acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: A case report. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, R.; Cheema, A.; Khan, T.; Amirpour, A.; Paul, A.; Chaughtai, S.; Patel, S.; Patel, T.; Bramson, J.; Gupta, V.; et al. Adverse effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors (programmed death-1 inhibitors and cytotoxic T-limphocyte- associated protein-4 inhibitors): Result of retrospective study. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2019, 11, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamlouk, O.; Selamet, U.; Machado, S.; Abdelrahim, M.; Glass, W.S.; Tchakarov, A.; Gaber, L.; Lahoti, A.; Workeneh, B.; Chen, S.; et al. Nephrotoxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors beyond tubulointerstitial nephritis: Single center experience. J. Immuno. Ther. Cancer 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Shimonishi, A.; Matsuura, H.; Ozeki, T.; Nishimura, J.; Kayatani, H.; Minami, D.; Shinno, Y.; Sato, K.; et al. Rapidly progressive acute kidney injury associated with nivolumab treatment. Case Rep. Oncol. 2020, 13, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Kibbelaar, Z.A.; Glezerman, I.G.; Abudayyeh, A.; Mamlouk, O.; Motwani, S.S.; Murakami, N.; Herrmann, S.M.; Manohar, S.; Shirali, A.C.; et al. Clinical features and outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated AKI: A multicenter study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Schiff, M.; Salvatore, S.; Shoustari, A.; Glezerman, I. Membranous nephropathy related to the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab. In Proceedings of the American Society of Nephrology Kidney Week, Chicago, IL, USA, 15–20 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daanen, R.A.; Maas, R.J.H.; Koornstra, R.H.T.; Steenbergen, E.J.; van Herpen, C.M.L.; Willemsen, A.E.C.A.B. Nivolumab-associated nephrotic syndrome in a patient with renal cell carcinoma: A case report. J. Immunother. 2017, 40, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, M.; Yarlagadda, S. Nivolumab induced renal failure with collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). In Proceedings of the American Society of Nephrology Kidney Week, Chicago, IL, USA, 15–20 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Crutz-Whitley, J.; Giehl, N.; Jen, K.; Young, B.l. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis associated with nivolumab therapy. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2020, 2020, 2638283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Zeng, X.; Bilusic, M. Nivolumab-associated acute glomerulonephritis; a case report and literature review. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kishi, S.; Minato, M.; Saigo, A.; Murakami, N.; Tamaki, M.; Matsuura, M.; Murakami, T.; Nagai, K.; Abe, H.; Nishioka, Y.; et al. IgA nephropathy after nivolumab therapy for postoperative recurrence of squamous cell carcinoma. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francisco, L.M.; Sage, P.T.; Sharpe, A.H. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 236, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoop, R.; Wahl, P.; Le Hir, M.; Heemann, U.; Wang, M.; Wüthrich, R.P. Suppressed T-cell activation by IFNgamma-induced expression of PD-L1 on renal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2713–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuchroo, V.K.; Ohashi, P.S.; Sartor, R.B.; Vinuesa, C.G. Dysregulation of immune homeostasis in autoimmune diseases. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perazella, M.A. Kidney biopsy should be performed to document the cause of immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated acute kidney injury: Commentary. Kidney360 2020, 1, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutgarts, V.; Glezerman, I.G. Kidney biopsy should be performed to document the cause of immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated acute kidney injury: CON. Kidney360 2020, 1, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eijgelsheim, M.; Sprangers, B. Kidney biopsy should be performed to document the cause of immune checkpoint inhibitor–associated acute kidney injury: PRO. Kidney360 2020, 1, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moledina, D.G.; Wilson, F.P.; Pober, J.S.; Perazella, M.A.; Singh, N.; Luciano, R.L.; Obeid, W.; Lin, H.; Kuperman, M.; Moeckel, G.W.; et al. Urine TNF-a and IL-9 for clinical diagnosis of acute interstitial nephritis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e127456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yekeduz, E.; Dursun, B.; Aydin, G.C.; Yazgan, S.C.; Öztürk, H.H.; Azap, A.; Utkan, G.; Ürün, Y. Clinical course of COVID-19 infection in elderly patient with melanoma on nivolumab. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 19, 1078155220924084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmai, L.; Porta, C.; Perazella, M.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Rosner, M.H.; Kenar, J.; Floris, M.; Pani, A.; Teuma, C.; Szczylik, C.; et al. Opening an onconephrology clinic: Recommendations and basic requirements. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izzedine, H.; Perazella, M.A. Anticancer drug-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanna, R.M.; Barsoum, M.; Arman, F.; Selamet, U.; Hasnain, H.; Kurtz, I. Nephrotoxicity induced by intravitreal vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors: Emerging evidence. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus-Gonzalez, N.; Robinson, E.; Moslehi, J.; Humphreys, B.D. Management of antiangiogenic therapy-induced hypertension. Hypertension 2012, 60, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sprangers, B.; Abudayyeh, A.; Latcha, S.; Perazella, M.A.; Jhaveri, K.D. How to determine kidney function in cancer patients? Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 132, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowitz, T.; Williams, E.H.; Marshall, A.; Ainsworth, N.; Thomas, P.B.; Sammut, S.J.; Shepherd, S.; White, J.; Mark, P.B.; Lynch, A.G.; et al. New model for estimating glomerular filtration rate in patients with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tool to Estimate Glomerular Filtration. Available online: http://tavarelab.cruk.cam.ac.UK/JanowitzWulliamsGFR (accessed on 2 June 2020).
- Okamoto, S.; Ureshino, H.; Kawaguchi, A.; Miyazono, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Kimura, S. Assessment of estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia following discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirolli, V.; Pieroni, L.; Di Liberato, L.; Urbani, A.; Bonomini, M. Urinary peptidomic biomarkers in kidney diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

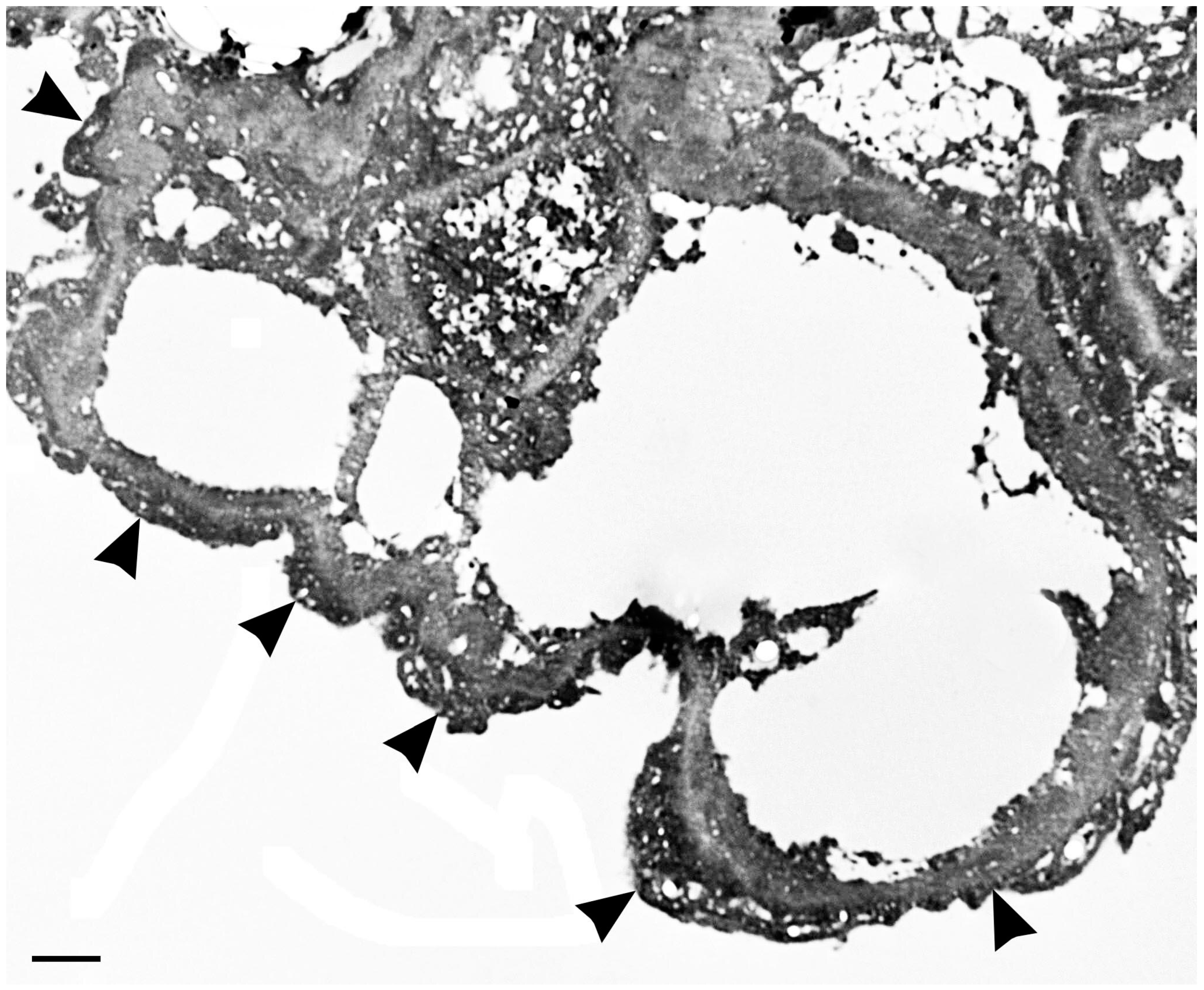

| Embryonic stage and development |
| • Endothelial cell differentiation, migration, and maturation during nephron formation (metanephric stage); |
| • Induction of fenestrations, transcellular gaps, caveolae, and inter-endothelial gaps. |
| Adult stage, developed kidney |
| • Vascular permeability/regulation of glomerular permeability; |
| • Regulation of slit diaphragm by upregulation of podocin and its interaction with CD2AP; |
| • Protection of renal tubular cells; |
| • Maintenance of basement membrane composition; |
| • Calcium homeostasis and podocyte survival; |
| • Mediation of endothelium dependent vasodilation; |
| • Remodeling of interstitial matrix. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piscitani, L.; Sirolli, V.; Di Liberato, L.; Morroni, M.; Bonomini, M. Nephrotoxicity Associated with Novel Anticancer Agents (Aflibercept, Dasatinib, Nivolumab): Case Series and Nephrological Considerations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144878
Piscitani L, Sirolli V, Di Liberato L, Morroni M, Bonomini M. Nephrotoxicity Associated with Novel Anticancer Agents (Aflibercept, Dasatinib, Nivolumab): Case Series and Nephrological Considerations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144878
Chicago/Turabian StylePiscitani, Luca, Vittorio Sirolli, Lorenzo Di Liberato, Manrico Morroni, and Mario Bonomini. 2020. "Nephrotoxicity Associated with Novel Anticancer Agents (Aflibercept, Dasatinib, Nivolumab): Case Series and Nephrological Considerations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144878
APA StylePiscitani, L., Sirolli, V., Di Liberato, L., Morroni, M., & Bonomini, M. (2020). Nephrotoxicity Associated with Novel Anticancer Agents (Aflibercept, Dasatinib, Nivolumab): Case Series and Nephrological Considerations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144878






