New Insights into Arrestin Recruitment to GPCRs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
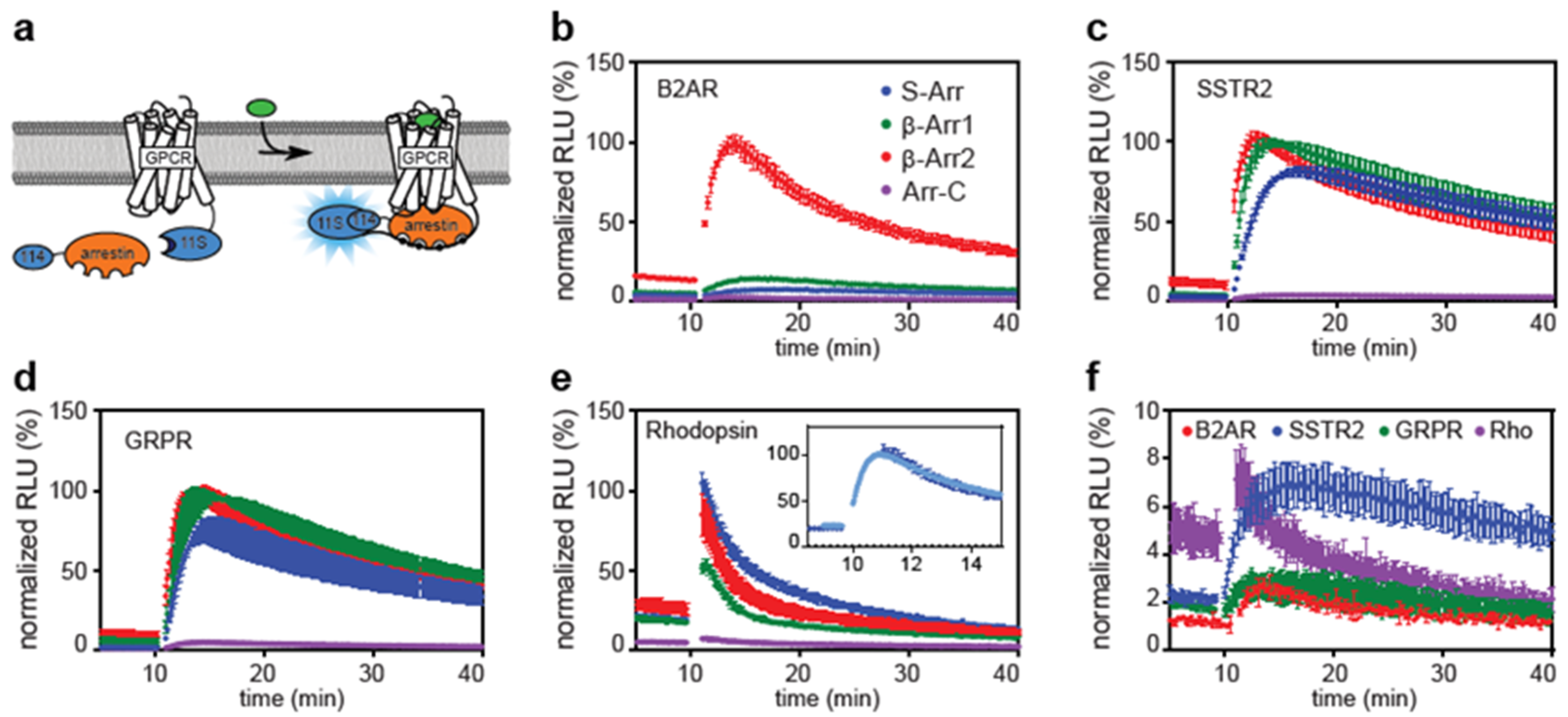
2.1. Direct and Indirect Recruitment of Arrestins to GPCRs
2.2. Comparison of Different Assay Types
2.3. The C-Tail of GPCRs Modulates Arrestin Selectivity
2.4. Influence of Expression Level on Arrestin Recruitment
2.5. Transduction of Cells with Baculoviruses
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Biology
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Split Luciferase Assay
4.4. BRET Assay
4.5. Data Analysis
4.6. Baculovirus Generation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data availability
References
- Peterson, Y.K.; Luttrell, L.M. The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 256–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Hanson, S.M.; Song, X.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Gurevich, E.V. The functional cycle of visual arrestins in photoreceptor cells. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oakley, R.H.; Laporte, S.A.; Holt, J.A.; Caron, M.G.; Barak, L.S. Differential affinities of visual arrestin, beta arrestin1, and beta arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17201–17210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shenoy, S.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. beta-Arrestin-mediated receptor trafficking and signal transduction. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moaven, H.; Koike, Y.; Jao, C.C.; Gurevich, V.V.; Langen, R.; Chen, J. Visual arrestin interaction with clathrin adaptor AP-2 regulates photoreceptor survival in the vertebrate retina. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9463–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichel, K.; Zastrow, M. Subcellular Organization of GPCR Signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWire, S.M.; Ahn, S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Shenoy, S.K. Beta-arrestins and cell signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 483–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.H.; MacGurn, J.A.; Chu, T.; Stefan, C.J.; Emr, S.D. Arrestin-related ubiquitin-ligase adaptors regulate endocytosis and protein turnover at the cell surface. Cell 2008, 135, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santini, F.; Penn, R.B.; Gagnon, A.W.; Benovic, J.L.; Keen, J.H. Selective recruitment of arrestin-3 to clathrin coated pits upon stimulation of G protein-coupled receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 13, 2463–2470. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Cvijic, M.E.; Krause, C.; Zhang, L.; Sum, C.S. Measurement of beta-Arrestin Recruitment for GPCR Targets. In Assay Guidance Manual; Sittampalam, G.S., Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Arkin, M., Auld, D., Austin, C.P., Baell, J., Bejcek, B., Caaveiro, J.M.M., Chung, T.D.Y., et al., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, B.J.; Wetter, J.; Bercher, M.R.; Kopp, L.; Fuerstenau-Sharp, M.; Vedvik, K.L.; Zielinski, T.; Doucette, C.; Whitney, P.J.; Revankar, C. A homogeneous fluorescent live-cell assay for measuring 7-transmembrane receptor activity and agonist functional selectivity through beta-arrestin recruitment. J. Biomol. Screen. 2009, 14, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jones, A.; Olson, K.R.; Peng, K.; Wehrman, T.; Park, A.; Mallari, R.; Nebalasca, D.; Young, S.W.; Xiao, S.H. A homogeneous enzyme fragment complementation-based beta-arrestin translocation assay for high-throughput screening of G-protein-coupled receptors. J. Biomol. Screen. 2008, 13, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, R.N.; DeBiasio, R.; Hudson, C.C.; Ramer, E.R.; Cowan, C.L.; Oakley, R.H. Quantitative cell-based high-content screening for vasopressin receptor agonists using transfluor technology. J. Biomol. Screen. 2005, 10, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angers, S.; Salahpour, A.; Joly, E.; Hilairet, S.; Chelsky, D.; Dennis, M.; Bouvier, M. Detection of beta 2-adrenergic receptor dimerization in living cells using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3684–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, L.; Parent, S.; Caron, M.; Legault, M.; Joly, E.; Angers, S.; Bouvier, M.; Brown, M.; Houle, B.; Menard, L. The BRET2/arrestin assay in stable recombinant cells: A platform to screen for compounds that interact with G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRS). J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2002, 22, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, Y.; LeGouill, C.; Kumar, S.; Cao, Y.; Teixeira, L.B.; Lukasheva, V.; Giubilaro, J.; Simoes, S.C.; Longpre, J.M.; Devost, D.; et al. Functional selectivity profiling of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor using pathway-wide BRET signaling sensors. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charest, P.G.; Terrillon, S.; Bouvier, M. Monitoring agonist-promoted conformational changes of beta-arrestin in living cells by intramolecular BRET. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.H.; Appleton, K.M.; Strungs, E.G.; Kwon, J.Y.; Morinelli, T.A.; Peterson, Y.K.; Laporte, S.A.; Luttrell, L.M. The conformational signature of beta-arrestin2 predicts its trafficking and signalling functions. Nature 2016, 531, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuber, S.; Zabel, U.; Lorenz, K.; Nuber, A.; Milligan, G.; Tobin, A.B.; Lohse, M.J.; Hoffmann, C. beta-Arrestin biosensors reveal a rapid, receptor-dependent activation/deactivation cycle. Nature 2016, 531, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichel, K.; Jullie, D.; Barsi-Rhyne, B.; Latorraca, N.R.; Masureel, M.; Sibarita, J.B.; Dror, R.O.; von Zastrow, M. Catalytic activation of beta-arrestin by GPCRs. Nature 2018, 557, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, Y.; Le Gouill, C.; Lukashova, V.; Kobayashi, H.; Hogue, M.; Khoury, E.; Song, M.; Bouvier, M.; Laporte, S.A. Monitoring G protein-coupled receptor and beta-arrestin trafficking in live cells using enhanced bystander BRET. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Branchini, B.R.; Southworth, T.L.; Fontaine, D.M.; Kohrt, D.; Florentine, C.M.; Grossel, M.J. A Firefly Luciferase Dual Color Bioluminescence Reporter Assay Using Two Substrates To Simultaneously Monitor Two Gene Expression Events. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodroofe, C.C.; Meisenheimer, P.L.; Klaubert, D.H.; Kovic, Y.; Rosenberg, J.C.; Behney, C.E.; Southworth, T.L.; Branchini, B.R. Novel heterocyclic analogues of firefly luciferin. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9807–9813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoef, L.G.; Mattioli, M.; Ricci, F.; Li, Y.C.; Wade, M. Multiplex detection of protein-protein interactions using a next generation luciferase reporter. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Y.J.; Gong, B.Q.; Li, J.F. Split Nano luciferase complementation for probing protein-protein interactions in plant cells. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriz, A.; Schmid, K.; Baumgartner, N.; Ziegler, U.; Berger, I.; Ballmer-Hofer, K.; Berger, P. A plasmid-based multigene expression system for mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansouri, M.; Bellon-Echeverria, I.; Rizk, A.; Ehsaei, Z.; Cianciolo Cosentino, C.; Silva, C.S.; Xie, Y.; Boyce, F.M.; Davis, M.W.; Neuhauss, S.C.; et al. Highly efficient baculovirus-mediated multigene delivery in primary cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansouri, M.; Berger, P. Baculovirus for gene delivery to mammalian cells: Past, present and future. Plasmid 2018, 98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.S.; Schwinn, M.K.; Hall, M.P.; Zimmerman, K.; Otto, P.; Lubben, T.H.; Butler, B.L.; Binkowski, B.F.; Machleidt, T.; Kirkland, T.A.; et al. NanoLuc Complementation Reporter Optimized for Accurate Measurement of Protein Interactions in Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littmann, T.; Gottle, M.; Reinartz, M.T.; Kalble, S.; Wainer, I.W.; Ozawa, T.; Seifert, R. Recruitment of beta-arrestin 1 and 2 to the beta2-adrenoceptor: Analysis of 65 ligands. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 355, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, X.; Gimenez, L.E.; Gurevich, V.V.; Spiller, B.W. Crystal structure of arrestin-3 reveals the basis of the difference in receptor binding between two non-visual subtypes. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 406, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Namkung, Y.; Laporte, S.A. Methods to Monitor the Trafficking of beta-Arrestin/G Protein-Coupled Receptor Complexes Using Enhanced Bystander BRET. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1957, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, D.A.; Violin, J.D.; Newton, A.C.; Tsien, R.Y. Partitioning of lipid-modified monomeric GFPs into membrane microdomains of live cells. Science 2002, 296, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baillie, G.S.; Adams, D.R.; Bhari, N.; Houslay, T.M.; Vadrevu, S.; Meng, D.; Li, X.; Dunlop, A.; Milligan, G.; Bolger, G.B.; et al. Mapping binding sites for the PDE4D5 cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase to the N- and C-domains of beta-arrestin using spot-immobilized peptide arrays. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.S.; Wilhelm, F.; Rizk, A.; Mutt, E.; Deupi, X.; Peterhans, C.; Muhle, J.; Berger, P.; Schertler, G.F.X.; Standfuss, J.; et al. Arrestin-1 engineering facilitates complex stabilization with native rhodopsin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, M.T.; Didenko, T.; Stevens, R.C.; Wuthrich, K. beta2-Adrenergic Receptor Conformational Response to Fusion Protein in the Third Intracellular Loop. Structure 2016, 24, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Ishchenko, A.; Barty, A.; White, T.A.; Yefanov, O.; Han, G.W.; et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser. Nature 2015, 523, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, A.K.; Westfield, G.H.; Xiao, K.; Reis, R.I.; Huang, L.Y.; Tripathi-Shukla, P.; Qian, J.; Li, S.; Blanc, A.; Oleskie, A.N.; et al. Visualization of arrestin recruitment by a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature 2014, 512, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepek, M.; Beyriere, F.; Hofmann, K.P.; Elgeti, M.; Kazmin, R.; Rose, A.; Bartl, F.J.; von Stetten, D.; Heck, M.; Sommer, M.E.; et al. Crystal structure of a common GPCR-binding interface for G protein and arrestin. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, A.R.B.; Plouffe, B.; Cahill, T.J., III; Shukla, A.K.; Tarrasch, J.T.; Dosey, A.M.; Kahsai, A.W.; Strachan, R.T.; Pani, B.; Mahoney, J.P.; et al. GPCR-G Protein-beta-Arrestin Super-Complex Mediates Sustained G Protein Signaling. Cell 2016, 166, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, D.; Damberger, F.F.; Samarasimhareddy, M.; Feldmueller, M.; Vuckovic, Z.; Flock, T.; Bauer, B.; Mutt, E.; Zosel, F.; Allain, F.H.T.; et al. Distinct G protein-coupled receptor phosphorylation motifs modulate arrestin affinity and activation and global conformation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorraca, N.R.; Wang, J.K.; Bauer, B.; Townshend, R.J.L.; Hollingsworth, S.A.; Olivieri, J.E.; Xu, H.E.; Sommer, M.E.; Dror, R.O. Molecular mechanism of GPCR-mediated arrestin activation. Nature 2018, 557, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yu, X.; Liu, C.; Qu, C.X.; Gong, Z.; Liu, H.D.; Li, F.H.; Wang, H.M.; He, D.F.; Yi, F.; et al. Phospho-selective mechanisms of arrestin conformations and functions revealed by unnatural amino acid incorporation and (19)F-NMR. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Lin, A.; Liu, C.; Xiao, P.; Yu, X.; Sun, J.P. Phosphorylation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors: From the Barcode Hypothesis to the Flute Model. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 92, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y. Determination of binding stoichiometry by the continuous variation method: The Job plot. Methods Enzymol. 1982, 87, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spillmann, M.; Thurner, L.; Romantini, N.; Zimmermann, M.; Meger, B.; Behe, M.; Waldhoer, M.; Schertler, G.F.X.; Berger, P. New Insights into Arrestin Recruitment to GPCRs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144949
Spillmann M, Thurner L, Romantini N, Zimmermann M, Meger B, Behe M, Waldhoer M, Schertler GFX, Berger P. New Insights into Arrestin Recruitment to GPCRs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144949
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpillmann, Martin, Larissa Thurner, Nina Romantini, Mirjam Zimmermann, Benoit Meger, Martin Behe, Maria Waldhoer, Gebhard F. X. Schertler, and Philipp Berger. 2020. "New Insights into Arrestin Recruitment to GPCRs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144949
APA StyleSpillmann, M., Thurner, L., Romantini, N., Zimmermann, M., Meger, B., Behe, M., Waldhoer, M., Schertler, G. F. X., & Berger, P. (2020). New Insights into Arrestin Recruitment to GPCRs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144949




