Circulating Ouabain Modulates Expression of Claudins in Rat Intestine and Cerebral Blood Vessels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Low Ouabain Concentration Stimulates Epithelial Barrier Formation in IPEC-J2 Cells
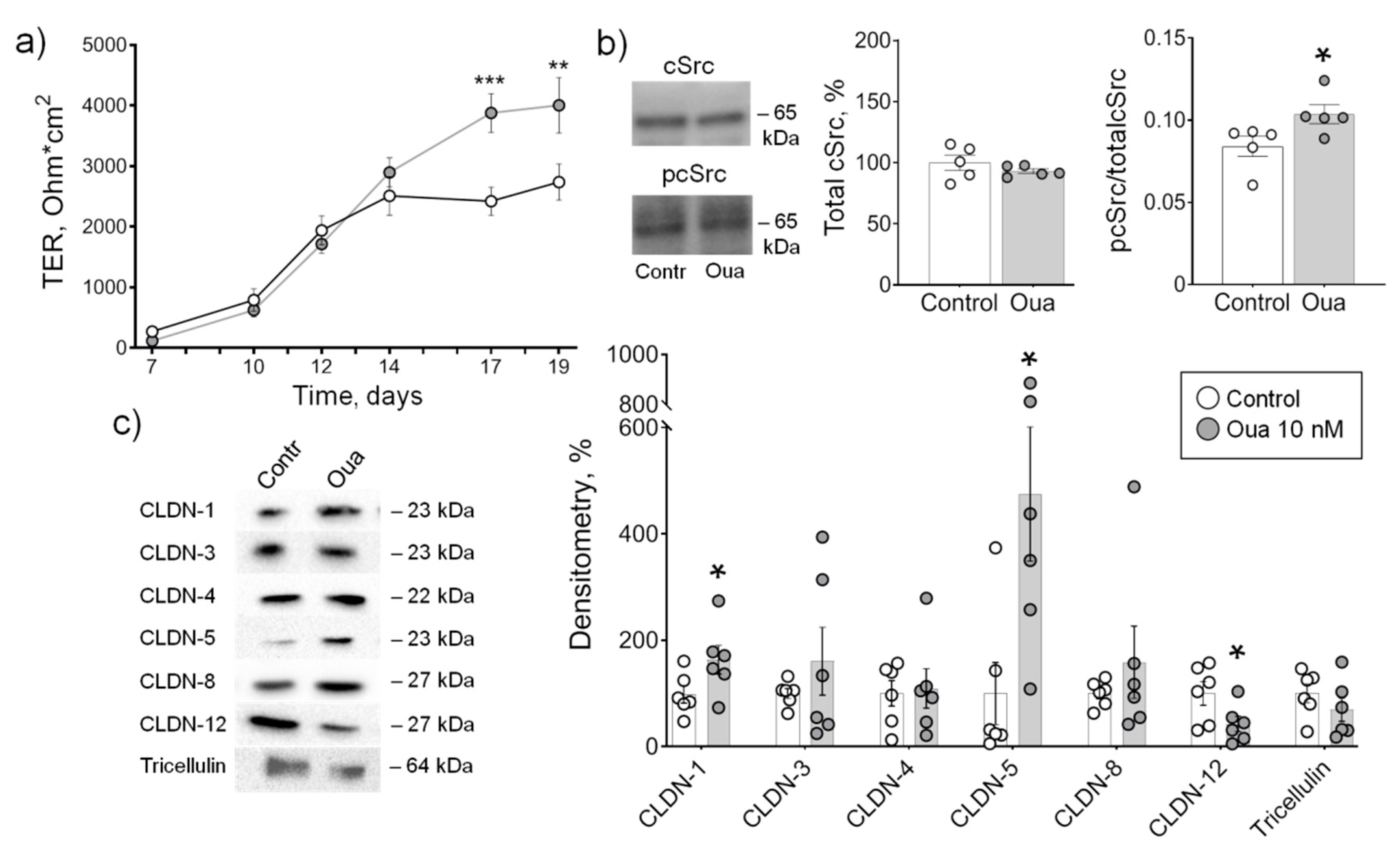
2.2. Chronic but Not Acute Ouabain Administration Modulates Intestine Epithelium Barrier Properties
2.3. Chronic Ouabain Administration Protects against Intestine Function Injury
2.4. Chronic Ouabain Administration Modulates Claudin Expression in Cerebral Blood Vessels
3. Discussion
- (1)
- Claudins of rat intestine and brain blood vessels as well as IPEC-J2 cells are subjected to regulation by chronic ouabain exposure.
- (2)
- Claudin-1 is specifically up-regulated by ouabain in contrast to other claudins that demonstrated a variety of tissue-specific changes.
- (3)
- Chronic ouabain differently affects claudin expression in rat jejunum and colon.
- (4)
- During LPS- or HS-induced injury, the jejunum is predominantly targeting by circulating ouabain and ouabain pre-treatment prevents the functional impairment in this tissue; the colon is relatively resistant to these injuries alone and in a combination with ouabain pre-treatment.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Transepithelial Electrical Resistance Recording
4.3. Epithelium Permeability Measurements
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. cSrc-kinase Phosphorylation Measurement
4.6. Western Blot Assays
4.7. Materials
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADPKD | autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease |
| CLDN | claudin |
| CTS | cardiotonic steroids |
| HS | hindlimb suspension |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MDCK | Madin–Darby canine kidney |
| OUA | ouabain |
| TER | transepithelial resistance |
| TJ | tight junction |
References
- Blanco, G.; Mercer, R.W. Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: Heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, F633–F655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijatovic, T.; Van Quaquebeke, E.; Delest, B.; Debeir, O.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. Cardiotonic steroids on the road to anti-cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophysica Acta 2007, 1776, 32–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matchkov, V.V.; Krivoi, I.I. Specialized functional diversity and interactions of the Na,K-ATPase. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirkmajer, S.; Chibalin, A.V. Na,K-ATPase regulation in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E1–E31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, M.V.; Hilbers, F.; Poulsen, H. The Structure and Function of the Na,K-ATPase Isoforms in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doris, P.A.; Bagrov, A.Y. Endogenous sodium pump inhibitors and blood pressure regulation: An update on recent progress. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1998, 218, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; Shapiro, J.I.; Fedorova, O.V. Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: Physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingrel, J.B. The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na,K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Askari, A. Na+/K+-ATPase as a signal transducer. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Xie, Z. Protein Interaction and Na/K-ATPase-Mediated Signal Transduction. Molecules 2017, 22, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, J.; Blanco, G. On the Many Actions of Ouabain: Pro-Cystogenic Effects in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Molecules 2017, 22, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlyn, J.M.; Blaustein, M.P.; Bova, S.; DuCharme, D.W.; Harris, D.W.; Mandel, F.; Mathews, W.R.; Ludens, J.H. Identification and characterization of a ouabain-like compound from human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6259–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; Fedorova, O.V.; Dmitrieva, R.I.; Howald, W.N.; Hunter, A.P.; Kuznetsova, E.A.; Shpen, V.M. Characterization of a urinary bufodienolide Na+,K+-ATPase inhibitor in patients after acute myocardial infarction. Hypertension 1998, 31, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtstein, D.; Rosen, H. Endogenous digitalis-like Na,K-ATPase inhibitors, and brain function. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoner, W.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides and their mechanisms of action. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2007, 7, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, M.P.; Hamlyn, J.M. Ouabain, endogenous ouabain and ouabain-like factors: The Na+ pump/ouabain receptor, its linkage to NCX, and its myriad functions. Cell Calcium. 2020, 86, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtstein, D.; Ilani, A.; Rosen, H.; Horesh, N.; Singh, S.V.; Buzaglo, N.; Hodes, A. Na+,K+-ATPase Signaling and Bipolar Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, N.; Müller-Ehmsen, J.; Krämer, U.; Hambarchian, N.; Zobel, C.; Schwinger, R.H.; Neu, H.; Kirch, U.; Grünbaum, E.G.; Schoner, W. Ouabain-like compound changes rapidly on physical exercise in humans and dogs: Effects of β-blockade and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition. Hypertension 2005, 45, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereijido, M.; Larre, I.; Paez, O.; Shoshani, L.; Ponce, A. Na+/K+-ATPase Drives Most Asymmetric Transports and Modulates the Phenotype of Epithelial Cells. In Ion Channels and Transporters of Epithelia in Health and Disease; Hamilton, K.L., Devor, D.C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 351–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larre, I.; Lazaro, A.; Contreras, R.G.; Balda, M.S.; Matter, K.; Flores-Maldonado, C.; Ponce, A.; Flores-Benitez, D.; Rincon-Heredia, R.; Padilla-Benavides, T.; et al. Ouabain modulates epithelial cell tight junction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11387–11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietze, R.; Shihan, M.; Stammler, A.; Konrad, L.; Scheiner-Bobis, G. Cardiotonic steroid ouabain stimulates expression of blood–testis barrier proteins claudin-1 and -11 and formation of tight junctions in Sertoli cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 405, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, J.; McDermott, J.; Sanchez, G.; Sharma, M.; Barbosa, L.; Reif, G.A.; Wallace, D.P.; Blanco, G. Ouabain promotes partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) changes in human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 2017, 355, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasheh, S.; Fromm, M.; Günzel, D. Claudins of Intestine and Nephron—A Correlation of Molecular Tight Junction Structure and Barrier Function. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2011, 201, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Kong, W. Endothelial Tight Junctions and Their Regulatory Signaling Pathways in Vascular Homeostasis and Disease. Cell Signal. 2020, 66, 109485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, A.G.; Amasheh, S. Tight junction physiology of pleural mesothelium. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günzel, D.; Fromm, M. Claudins and other tight junction proteins. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1819–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, A.G.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Amasheh, S. Claudin clusters as determinants of epithelial barrier function. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, A.G.; Veshnyakova, A.; Fromm, M.; Amasheh, M.; Amasheh, S. Segmental expression of claudin proteins correlates with tight junction barrier properties in rat intestine. J. Comp. Physiol. B. 2010, 180, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Hata, M.; Gotoh, S.; Seo, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J. Cell. Biol. 2003, 161, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewski, S.S.; Richter, J.F.; Krug, S.M.; Jebautzke, B.; Lee, I.-F.M.; Rieger, J.; Sachtleben, M.; Bondzio, A.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M.; et al. Improved Cell Line IPEC-J2, Characterized as a Model for Porcine Jejunal Epithelium. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, A.A.; Cornelius, V.; Amasheh, S.; Krivoi, I.I.; Markov, A.G. Low Ouabain Concentrations Stimulate Epithelial Barrier Formation in IPEC-J2 Cells. J. Evol. Biochem. Phys. 2019, 55, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravtsova, V.V.; Bouzinova, E.V.; Matchkov, V.V.; Krivoi, I.I. Skeletal Muscle Na,K-ATPase as a Target for Circulating Ouabain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, A.; Larre, I.; Castillo, A.; García-Villegas, R.; Romero, A.; Flores-Maldonado, C.; Martinez-Rendón, J.; Contreras, R.G.; Cereijido, M. Ouabain increases gap junctional communication in epithelial cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nighot, M.; Al-Sadi, R.; Guo, S.; Rawat, M.; Nighot, P.; Watterson, M.D.; Ma, T.Y. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Increase in Intestinal Epithelial Tight Permeability Is Mediated by Toll-Like Receptor 4/Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response 88 (MyD88) Activation of Myosin Light Chain Kinase Expression. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 2698–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, M.; Bo, L.; Deng, X. Ouabain protects mice against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 4455–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Li, P.; Jin, R.; Wang, K.; Xu, X.; Hao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Intestinal microbiota contributes to colonic epithelial changes in simulated microgravity mouse model. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3695–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belay, T.; Aviles, H.; Vance, M.; Fountain, K.; Sonnenfeld, G. Effects of the hindlimb-unloading model of spaceflight conditions on resistance of mice to infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, K.; Xu, C.; Shao, D.; Huang, Q.; Shi, J.; Yang, H. Responses of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Functions of Rats to Simulated Weightlessness. Front Physiol. 2018, 9, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinemann, A.; Galm, I.; Chip, S.; Nitsch, C.; Maly, I.P. Claudin-1, -2 and -3 Are Selectively Expressed in the Epithelia of the Choroid Plexus of the Mouse from Early Development and into Adulthood While Claudin-5 is Restricted to Endothelial Cells. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Hu, W.; Yang, Z.; Li, T.; Jiang, S.; Ma, Z.; Chen, F.; Yang, Y. Focusing on claudin-5: A promising candidate in the regulation of BBB to treat ischemic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 161, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günzel, D. Claudins: Vital partners in transcellular and paracellular transport coupling. Pflugers Arch. 2017, 469, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, A.G.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Amasheh, S. The epithelial barrier and beyond: Claudins as amplifiers of physiological organ functions. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthouser, K.A.; Mandal, A.; Merchant, M.L.; Schelling, J.R.; Delamere, N.A.; Valdes, R.R., Jr.; Tyagi, S.C.; Lederer, E.D.; Khundmiri, S.J. Ouabain stimulates Na-K-ATPase through a sodium/hydrogen exchanger-1 (NHE-1)-dependent mechanism in human kidney proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2010, 299, F77–F90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketchem, C.J.; Conner, C.D.; Murray, R.D.; DuPlessis, M.; Lederer, E.D.; Wilkey, D.; Merchant, M.; Khundmiri, S.J. Low dose ouabain stimulates Na-K ATPase α1 subunit association with angiotensin II type 1 receptor in renal proximal tubule cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2624–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tverskoi, A.M.; Sidorenko, S.V.; Klimanova, E.A.; Akimova, O.A.; Smolyaninova, L.V.; Lopina, O.D.; Orlov, S.N. Effects of ouabain on proliferation of human endothelial cells correlate with Na+,K+-ATPase activity and intracellular ratio of Na+ and K+. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2016, 81, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimanova, E.A.; Tverskoi, A.M.; Koltsova, S.V.; Sidorenko, S.V.; Lopina, O.D.; Tremblay, J.; Hamet, P.; Kapilevich, L.V.; Orlov, S.N. Time- and dose-dependent actions of cardiotonic steroids on transcriptome and intracellular content of Na+ and K+: A comparative analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, S.N.; Klimanova, E.A.; Tverskoi, A.M.; Vladychenskaya, E.A.; Smolyaninova, L.V.; Lopina, O.D. Na+i,K+i-Dependent and -Independent Signaling Triggered by Cardiotonic Steroids: Facts and Artifacts. Molecules 2017, 22, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, A.G.; Kruglova, N.M.; Fomina, Y.A.; Fromm, M.; Amasheh, S. Altered Expression of Tight Junction Proteins in Mammary Epithelium After Discontinued Suckling in Mice. Pflugers Arch. 2012, 463, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, A.G.; Falchuk, E.L.; Kruglova, N.M.; Rybalchenko, O.V.; Fromm, M.; Amasheh, S. Comparative analysis of theophylline and cholera toxin in rat colon reveals an induction of sealing tight junction proteins. Pflugers Arch. 2014, 466, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.; O’Neill, C.A.; Padfield, P.J. Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin increases permeability of Caco-2 cell monolayers by displacing specific claudins from cholesterol rich domains associated with tight junctions. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, I.J.P.; Kinoshita, P.F.; de Oliveira Braga, I.; Parreira, G.M.; Mignaco, J.A.; Scavone, C.; Barbosa, L.A.; de Lima Santos, H. Ouabain attenuates the oxidative stress induced by lipopolysaccharides in the cerebellum of rats. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2156–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilchinskaya, N.A.; Krivoi, I.I.; Shenkman, B.S. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase as a Key Trigger for the Disuse-Induced Skeletal Muscle Remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mießler, K.S.; Markov, A.G.; Amasheh, S. Hydrostatic pressure incubation affects barrier properties of mammary epithelial cell monolayers, in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, S.; Yu, A.S.L. Regulation of Epithelial Cell Functions by the Osmolality and Hydrostatic Pressure Gradients: A Possible Role of the Tight Junction as a Sensor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.K.; Gangwar, R.; Manda, B.; Meena, A.S.; Yadav, N.; Szabo, E.; Balogh, A.; Lee, S.C.; Tigyi, G.; Rao, R. Rapid disruption of intestinal epithelial tight junction and barrier dysfunction by ionizing radiation in mouse colon in vivo: Protection by N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G705–G715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, A.G.; Vishnevskaya, O.N.; Okorokova, L.S.; Fedorova, A.A.; Kruglova, N.M.; Rybalchenko, O.V.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Amasheh, S. Cholera toxin perturbs the paracellular barrier in the small intestinal epithelium of rats by affecting claudin-2 and tricellulin. Pflugers Arch. 2019, 471, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.; Lax, E.; Gispan-Herman, I.; Ovadia, H.; Rosen, H.; Yadid, G.; Lichtstein, D. Neutralization of endogenous digitalis-like compounds alters catecholamines metabolism in the brain and elicits anti-depressive behavior. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 22, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, W.C.; Martin, L.J. Low-dose ouabain protects against excitotoxic apoptosis and up-regulates nuclear BCL-2 in vivo. Neuroscience 2006, 137, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oselkin, M.; Tian, D.; Bergold, P.J. Low-dose cardiotonic steroids increase sodium-potassium ATPase activity that protects hippocampal slice cultures from experimental ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 473, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibarov, D.A.; Bolshakov, A.E.; Abushik, P.A.; Krivoi, I.I.; Antonov, S.M. Na+,K+-ATPase functionally interacts with the plasma membrane Na+,Ca2+ exchanger to prevent Ca2+ overload and neuronal apoptosis in excitotoxic stress. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvela-Levitt, M.; Ami, H.C.; Rosen, H.; Shohami, E.; Lichtstein, D. Ouabain improves functional recovery following traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana, A.M.; Kinoshita, P.F.; Leite, J.A.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Scavone, C. Cardiotonic Steroids as Modulators of Neuroinflammation. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, WA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–246. [Google Scholar]
- Morey-Holton, E.; Globus, R.K.; Kaplansky, A.; Durnova, G. The hindlimb unloading rat model: Literature overview, technique update and comparison with space flight data. Adv. Space Biol. Med. 2005, 10, 7–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radloff, J.; Cornelius, V.; Markov, A.G.; Amasheh, S. Caprate Modulates Intestinal Barrier Function in Porcine Peyer’s Patch Follicle-Associated Epithelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenda, N.; Urbanova, K.; Weiser, N.; Kusche-Vihrog, K.; Günzel, D.; Schillers, H. Paracellular transport through healthy, cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cell lines-do we have a proper model? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markov, A.G.; Fedorova, A.A.; Kravtsova, V.V.; Bikmurzina, A.E.; Okorokova, L.S.; Matchkov, V.V.; Cornelius, V.; Amasheh, S.; Krivoi, I.I. Circulating Ouabain Modulates Expression of Claudins in Rat Intestine and Cerebral Blood Vessels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145067
Markov AG, Fedorova AA, Kravtsova VV, Bikmurzina AE, Okorokova LS, Matchkov VV, Cornelius V, Amasheh S, Krivoi II. Circulating Ouabain Modulates Expression of Claudins in Rat Intestine and Cerebral Blood Vessels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145067
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkov, Alexander G., Arina A. Fedorova, Violetta V. Kravtsova, Anastasia E. Bikmurzina, Larisa S. Okorokova, Vladimir V. Matchkov, Valeria Cornelius, Salah Amasheh, and Igor I. Krivoi. 2020. "Circulating Ouabain Modulates Expression of Claudins in Rat Intestine and Cerebral Blood Vessels" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145067
APA StyleMarkov, A. G., Fedorova, A. A., Kravtsova, V. V., Bikmurzina, A. E., Okorokova, L. S., Matchkov, V. V., Cornelius, V., Amasheh, S., & Krivoi, I. I. (2020). Circulating Ouabain Modulates Expression of Claudins in Rat Intestine and Cerebral Blood Vessels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145067




