HIV Associated Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Factors Contributing to the Development of Stroke in HIV Infected Subjects
2.1. Coagulopathies
2.2. Opportunistic Infections
2.3. HIV Associated Vasculopathy
2.4. Cardioembolism
2.5. Atherosclerosis
2.6. Antiretroviral Therapy
2.7. Traditional Risk Factors
3. Experimental Studies on HIV-Associated Ischemic Stroke
4. Approaches to Improve Ischemic Stroke Outcomes in HIV Infected Subjects
4.1. ART With a High CNS Penetration Efficacy (CPE)Score
4.2. Tat Fusion Protein
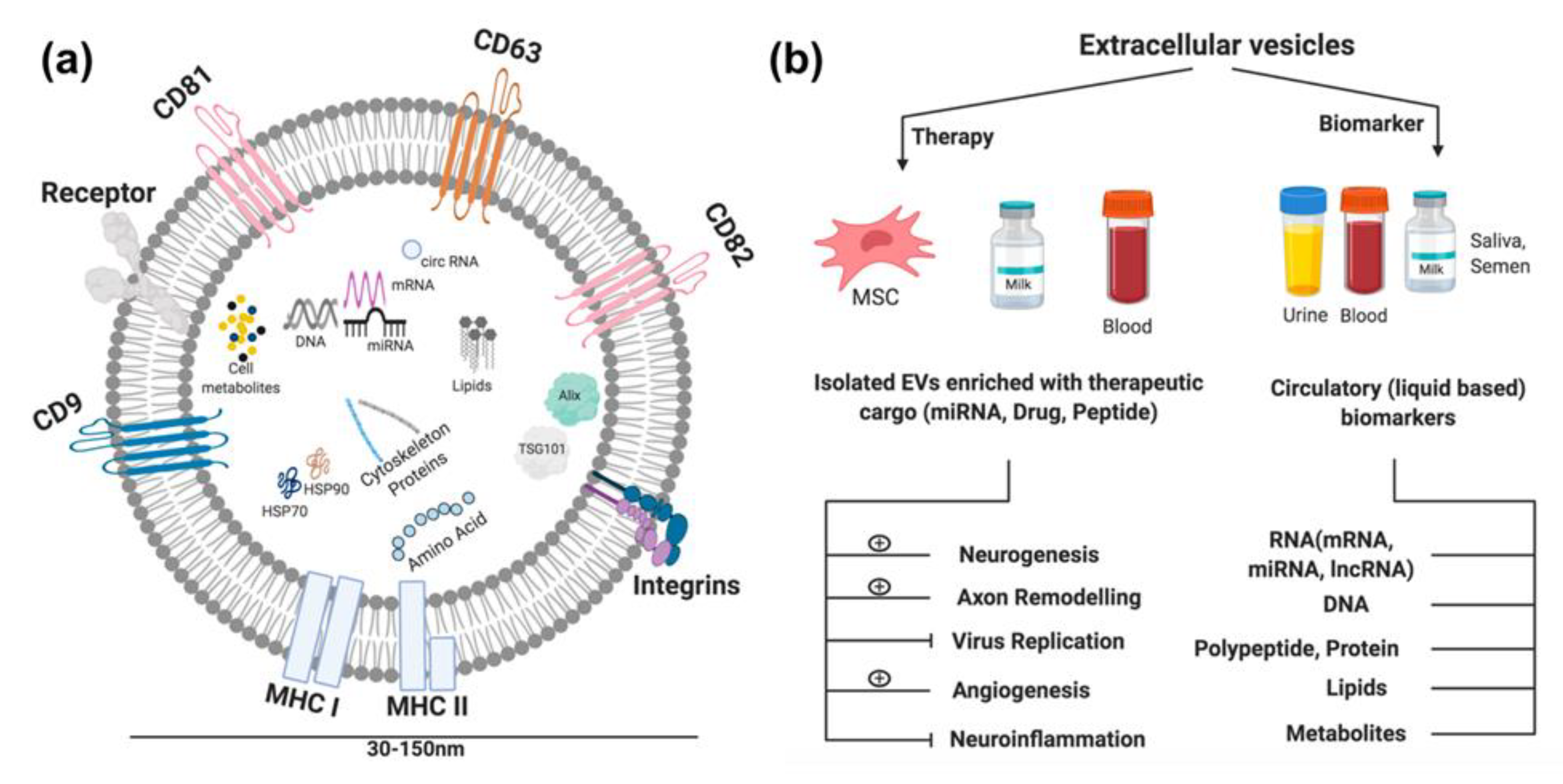
4.3. Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers
4.3.1. EVs: Ischemic Stroke Diagnosis
4.3.2. EVs: Ischemic Stroke Therapy
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIDS | Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome |
| ART | Antiretroviral therapy |
| BBB | Blood-brain barrier |
| CAMS | Cell adhesion molecules |
| CCCR-5 | C:C chemokine receptor type 5 |
| CCL2 | Chemokine ligand 2 |
| cIMT | Carotid intima-media thickness |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DAD | Data Collection on Adverse Events of Anti:HIV Drugs |
| ER stress | Endoplasmic reticulum stress |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| Gp120 | Glycoprotein-120 |
| hCMEC | human cerebral microvascular cells |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| miRNA | Micro RNA |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| Nef | Negative regulatory factor |
| NF:κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| NNRTI | Reverse transcriptase inhibitor |
| PLWH | People living with HIV |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatograohy |
| Tat | Trans-Activator of Transcription |
| TB | Tubercle bacillus |
| TIA | Transient ischemic attack |
| TIMs | Tissue inhibitors of MMPs |
| VWF | von Willebrand factor |
| ZO-1 | Zonula occludens-1 |
References
- Cohen, M.S.; Chen, Y.Q.; McCauley, M.; Gamble, T.; Hosseinipour, M.C.; Kumarasamy, N.; Hakim, J.G.; Kumwenda, J.; Grinsztejn, B.; Pilotto, J.H.S.; et al. Prevention of HIV-1 infection with early antiretroviral therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, M.S.; Chen, Y.Q.; McCauley, M.; Gamble, T.; Hosseinipour, M.C.; Kumarasamy, N.; Hakim, J.G.; Kumwenda, J.; Grinsztejn, B.; Pilotto, J.H.S.; et al. Antiretroviral Therapy for the Prevention of HIV-1 Transmission. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, J.; Cinque, P.; Gisslen, M.; Reiss, P.; Portegies, P. HIV-1 infection and cognitive impairment in the cART era: A review. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2011, 25, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranick, S.M.; Nath, A. Neurologic complications of HIV-1 infection and its treatment in the era of antiretroviral therapy. Contin. Minneap. Minn 2012, 18, 1319–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration Causes of death in HIV-1-infected patients treated with antiretroviral therapy, 1996-2006: Collaborative analysis of 13 HIV cohort studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2010, 50, 1387–1396. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, J.; Albuquerque, A.L.A.; Falzon, L. HIV infection as vascular risk: A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. PloS One 2017, 12, e0176686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovbiagele, B.; Nath, A. Increasing incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with HIV infection. Neurology 2011, 76, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, F. HIV Infection, Vascular Disease, and Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2014, 34, 035–046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, L.; Méroth, F.; Tournebize, M.; Leda, A.R.; Sun, E.; Toborek, M. Targeting the HIV-infected brain to improve ischemic stroke outcome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, L.A.; Bryer, A.; Emsley, H.C.; Khoo, S.; Solomon, T.; Connor, M.D. HIV infection and stroke: Current perspectives and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogorodskaya, M.; Chow, F.C.; Triant, V.A. Stroke in HIV. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Barnes, A.E.; Guest, J.L.; Shah, A.; Shao, I.Y.; Marconi, V. HIV Infection and Incidence of Cardiovascular Diseases: An Analysis of a Large Healthcare Database. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orviz, E.; Suárez-Robles, M.; Jerez-Fernández, P.; Fernández-Revaldería, M. HIV screening and its possible involvement in patients with stroke. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, I.; Kim, A.S.; Chow, F.C. Prevention of stroke in people living with HIV. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, D.B.; Post, W.S.; Deal, J.A.; Hodis, H.N.; Jacobson, L.P.; Mack, W.J.; Anastos, K.; Gange, S.J.; Landay, A.L.; Lazar, J.M.; et al. HIV Infection Is Associated With Progression of Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2015, 61, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruse, B.; Cysique, L.A.; Markus, R.; Brew, B.J. Cerebrovascular disease in HIV-infected individuals in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. J. Neurovirol. 2012, 18, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-F.; Chen, M.; Jen, I.; Lan, Y.-C.; Chuang, P.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.; Chen, Y.-M.A. Association of HIV and Opportunistic Infections With Incident Stroke: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2017, 74, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, B. Toward Understanding the When and Why of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Stroke. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 509–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, F.C.; Wilson, M.R.; Wu, K.; Ellis, R.J.; Bosch, R.J.; Linas, B.P. Stroke incidence is highest in women and non-Hispanic blacks living with HIV in the AIDS Clinical Trials Group Longitudinal Linked Randomized Trials cohort. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2018, 32, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bearden, D.R.; Omech, B.; Rulaganyang, I.; Sesay, S.O.; Kolson, D.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Mullen, M.T. Stroke and HIV in Botswana: A prospective study of risk factors and outcomes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 413, 116806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gaetano Donati, K.; Rabagliati, R.; Iacoviello, L.; Cauda, R. HIV infection, HAART, and endothelial adhesion molecules: Current perspectives. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, K.; Steinsapir, K.D.; Iverson, D.J.; Glasgow, B.J.; Layfield, L.J.; Brown, W.J.; Cancilla, P.A.; Verity, M.A.; Vinters, H.V. Neuropathologic findings in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clin. Neuropathol. 1986, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singer, E.J.; Valdes-Sueiras, M.; Commins, D.L.; Yong, W.; Carlson, M. HIV stroke risk: Evidence and implications. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2013, 4, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Janssen, R.S.; Karon, J.M.; Weissman, J.P.; Akbar, M.S.; Safdar, K.; Frankel, M.R. Human immunodeficiency virus infection and stroke in young patients. Arch. Neurol. 1997, 54, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, K.H.; Guerra, W.F.; Tomiyasu, U.; Verity, M.A.; Vinters, H.V. The neuropathology of AIDS. UCLA experience and review. Am. J. Pathol. 1986, 124, 537–558. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, A.N. AIDS and cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 1996, 27, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusawa, H.; Hirano, A.; Llena, J.F.; Shintaku, M. Cerebrovascular lesions in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 1988, 76, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.W.; Pinto, A.N.; Hebel, J.R.; Buchholz, D.W.; Earley, C.J.; Johnson, C.J.; Macko, R.F.; Price, T.R.; Sloan, M.A.; Stern, B.J.; et al. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and the risk of stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engstrom, J.W.; Lowenstein, D.H.; Bredesen, D.E. Cerebral infarctions and transient neurologic deficits associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Berger, J.R.; Nath, A.; Rayens, M. Cerebrovascular disease in young, HIV-infected, black Africans in the KwaZulu Natal Province of South Africa. J. Neurovirol. 2000, 6, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, J.L.; Leyden, W.A.; Chao, C.R.; Chow, F.C.; Horberg, M.A.; Hurley, L.B.; Klein, D.B.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Towner, W.J.; Silverberg, M.J. HIV infection and incidence of ischemic stroke. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2014, 28, 1911–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, F.C.; Regan, S.; Feske, S.; Meigs, J.B.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Triant, V.A. Comparison of ischemic stroke incidence in HIV-infected and non-HIV-infected patients in a US health care system. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2012, 60, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, L.D.; Engsig, F.N.; Christensen, H.; Gerstoft, J.; Kronborg, G.; Pedersen, C.; Obel, N. Risk of cerebrovascular events in persons with and without HIV: A Danish nationwide population-based cohort study. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2011, 25, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subsai, K.; Kanoksri, S.; Siwaporn, C.; Helen, L.; Kanokporn, O.; Wantana, P. Neurological complications in AIDS patients receiving HAART: A 2-year retrospective study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, F.C.; Boscardin, W.J.; Mills, C.; Ko, N.; Carroll, C.; Price, R.W.; Deeks, S.; Sorond, F.A.; Hsue, P.Y. Cerebral vasoreactivity is impaired in treated, virally suppressed HIV-infected individuals. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2016, 30, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, F.C.; Regan, S.; Zanni, M.V.; Looby, S.E.; Bushnell, C.D.; Meigs, J.B.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Feske, S.K.; Triant, V.A. Elevated ischemic stroke risk among women living with HIV infection. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2018, 32, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-L.; Muo, C.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Chen, P.-C. Incidence of stroke in patients with HIV infection: A population-based study in Taiwan. PloS One 2019, 14, e0217147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monreal, E.; Gullón, P.; Pérez-Torre, P.; Escobar-Villalba, A.; Acebron, F.; Quereda Rodríguez-Navarro, C.; Sánchez-Ruano, L.; Fernández-Félix, B.M.; Muriel, A.; Pérez-Elías, M.J.; et al. Increased HIV infection in patients with stroke in Spain. A 16-year population-based study. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-B.; Yang, H.; Manaenko, A.; Lu, J.; Mei, Q.; Hu, Q. Potential of Exosomes for the Treatment of Stroke. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Laso-García, F.; Frutos, M.C.G.; Diekhorst, L.; Martínez-Arroyo, A.; Alonso-López, E.; García-Bermejo, M.L.; Rodríguez-Serrano, M.; Arrúe-Gonzalo, M.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; et al. Low dose of extracellular vesicles identified that promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.-B.; Liu, J.-L.; Wang, W.; Luo, X.-M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.-P.; Cao, X.-L.; Long, X.-H.; Chen, J.-G.; Qin, C. Plasma Exosomal miRNA-122-5p and miR-300-3p as Potential Markers for Transient Ischaemic Attack in Rats. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henrich, T.J.; Deeks, S.G.; Pillai, S.K. Measuring the Size of the Latent Human Immunodeficiency Virus Reservoir: The Present and Future of Evaluating Eradication Strategies. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S134–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kandathil, A.J.; Sugawara, S.; Balagopal, A. Are T cells the only HIV-1 reservoir? Retrovirology 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, J.; Menshawy, K.; Gonzalez, M.; Goldman, J.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Marshall, R.; Morgello, S. Brain large artery inflammation associated with HIV and large artery remodeling. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2016, 30, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishnu, P.; Aboulafia, D.M. Haematological manifestations of human immune deficiency virus infection. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 171, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, G.; Koch, S.; Romano, J.G.; Forteza, A.M.; Rabinstein, A.A. Mechanisms of ischemic stroke in HIV-infected patients. Neurology 2007, 68, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, C.P.; Wideman, C.S.; Spira, T.J.; Haff, E.C.; Hixon, G.J.; Evatt, B.L. Protein S deficiency in men with long-term human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood 1993, 81, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, B.; Passam, F.; Ioannou, Y.; Krilis, S.A. How we diagnose the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2009, 113, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugaard, A.K.; Lund, T.T.; Birch, C.; Rönsholt, F.; Trøseid, M.; Ullum, H.; Gerstoft, J.; Johansson, P.I.; Nielsen, S.D.; Ostrowski, S.R. Discrepant coagulation profile in HIV infection: Elevated D-dimer but impaired platelet aggregation and clot initiation. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2013, 27, 2749–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, D.; Harries, A.; Getahun, H. Tuberculosis and HIV interaction in sub-Saharan Africa: Impact on patients and programmes; implications for policies. Trop. Med. Int. Health TM IH 2005, 10, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammie, G.A.; Hewlett, R.H.; Schoeman, J.F.; Donald, P.R. Tuberculous cerebrovascular disease: A review. J. Infect. 2009, 59, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.; Ortiz, G. HIV/AIDS Patients with HIV Vasculopathy and VZV Vasculitis. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2011, 21, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahine, L.M.; Khoriaty, R.N.; Tomford, W.J.; Hussain, M.S. The Changing Face of Neurosyphilis. Int. J. Stroke 2011, 6, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.M.; Fountain, J.A.; Green, S.B.; Bloom, S.A.; Palmore, M.P. Human immunodeficiency virus—associated cytomegalovirus infection with multiple small vessel cerebral infarcts in the setting of early immune reconstitution. J. Neurovirol. 2010, 16, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieburtz, K.D.; Eskin, T.A.; Ketonen, L.; Tuite, M.J. Opportunistic Cerebral Vasculopathy and Stroke in Patients With the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 1993, 50, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.K.; Sinha, M.K. Tuberculous meningitis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, B.F.; Gomes, H.R.; Lucato, L.T.; Puglia, P.; Nitrini, R.; Castro, L.H.M. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated vasculopathy with CNS compartmentalization of HIV-1. J. Neurovirol. 2015, 21, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilla, R.; Nabavi, D.G.; Schulte-Altedorneburg, G.; Kemény, V.; Reichelt, D.; Evers, S.; Schiemann, U.; Husstedt, I.W. Cerebral vasculopathy in HIV infection revealed by transcranial Doppler: A pilot study. Stroke 1999, 30, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ake, J.A.; Erickson, J.C.; Lowry, K.J. Cerebral aneurysmal arteriopathy associated with HIV infection in an adult. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2006, 43, e46–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossorotoff, M.; Touzé, E.; Godon-Hardy, S.; Serre, I.; Mateus, C.; Mas, J.-L.; Zuber, M. Cerebral vasculopathy with aneurysm formation in HIV-infected young adults. Neurology 2006, 66, 1121–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.M.; Steverson, A.B.; Pawlowski, A.E.; Schneider, D.; Achenbach, C.J.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Feinstein, M.J. Atrial arrhythmia prevalence and characteristics for human immunodeficiency virus-infected persons and matched uninfected controls. PloS One 2018, 13, e0194754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pugliese, A.; Isnardi, D.; Saini, A.; Scarabelli, T.; Raddino, R.; Torre, D. Impact of highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV-positive patients with cardiac involvement. J. Infect. 2000, 40, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, G.; Fisher, S.D.; Lipshultz, S.E. Pathogenesis of HIV-associated cardiovascular complications. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2001, 1, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magula, N.P.; Mayosi, B.M. Cardiac involvement in HIV-infected people living in Africa: A review. Cardiovasc. J. South Afr. Off. J. South. Afr. Card. Soc. South Afr. Soc. Card. Pract. 2003, 14, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ntsekhe, M.; Mayosi, B.M. Cardiac manifestations of HIV infection: An African perspective. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 6, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.W.; Stephan, C.; Harmjanz, A.; Staszewski, S.; Buehler, A.; Bickel, M.; von Kegler, S.; Ruhkamp, D.; Steinmetz, H.; Sitzer, M. Both long-term HIV infection and highly active antiretroviral therapy are independent risk factors for early carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaberg, E.C.; Benning, L.; Sharrett, A.R.; Lazar, J.M.; Hodis, H.N.; Mack, W.J.; Siedner, M.J.; Phair, J.P.; Kingsley, L.A.; Kaplan, R.C. Association between human immunodeficiency virus infection and stiffness of the common carotid artery. Stroke 2010, 41, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliviero, U.; Bonadies, G.; Apuzzi, V.; Foggia, M.; Bosso, G.; Nappa, S.; Valvano, A.; Leonardi, E.; Borgia, G.; Castello, G.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus per se exerts atherogenic effects. Atherosclerosis 2009, 204, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Baker, J.V.; Calmy, A.; Duprez, D.; La Rosa, A.; Kuller, L.H.; Pett, S.L.; Ristola, M.; Ross, M.J.; et al. Markers of inflammation, coagulation, and renal function are elevated in adults with HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Leducq Transatlantic Network on Atherothrombosis Inflammation in atherosclerosis: From pathophysiology to practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, D.; Henry, J.; Kelley, J.; Thorpe, R.; Smith, J.K.; Krishnaswamy, G. The effects of HIV infection on endothelial function. Endothel. J. Endothel. Cell Res. 2000, 7, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniar, A.; Ellis, C.; Asmuth, D.; Pollard, R.; Rutledge, J. HIV infection and atherosclerosis: Evaluating the drivers of inflammation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2013, 20, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eugenin, E.A.; Morgello, S.; Klotman, M.E.; Mosoian, A.; Lento, P.A.; Berman, J.W.; Schecter, A.D. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infects Human Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells in Vivo and in Vitro: Implications for the Pathogenesis of HIV-Mediated Vascular Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schved, J.-F.; Gris, J.-C.; Arnaud, A.; Martinez, P.; Sanchez, N.; Wautier, J.-L.; Sarlat, C. Von Willebrand factor antigen, tissue-type plasminogen activator antigen, and risk of death in human immunodeficiency virus 1-related clinical disease: Independent prognostic relevance of tissue-type plasminogen activator. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1992, 120, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, E.R.; Sutliff, R.L. The Roles of HIV-1 Proteins and Antiretroviral Drug Therapy in HIV-1-Associated Endothelial Dysfunction. J. Investig. Med. 2008, 56, 752–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, S.D.; Miller, T.L.; Lipshultz, S.E. Impact of HIV and highly active antiretroviral therapy on leukocyte adhesion molecules, arterial inflammation, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2006, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonaguro, L.; Barillari, G.; Chang, H.K.; Bohan, C.A.; Kao, V.; Morgan, R.; Gallo, R.C.; Ensoli, B. Effects of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein on the expression of inflammatory cytokines. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7159–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scala, G.; Ruocco, M.R.; Ambrosino, C.; Mallardo, M.; Giordano, V.; Baldassarre, F.; Dragonetti, E.; Quinto, I.; Venuta, S. The expression of the interleukin 6 gene is induced by the human immunodeficiency virus 1 TAT protein. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rieckmann, P.; Poli, G.; Fox, C.H.; Kehrl, J.H.; Fauci, A.S. Recombinant gp120 specifically enhances tumor necrosis factor-alpha production and Ig secretion in B lymphocytes from HIV-infected individuals but not from seronegative donors. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 2922–2927. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Liu, Q.-H.; Tomkowicz, B.; Yi, Y.; Freedman, B.D.; Collman, R.G. Macrophage activation through CCR5- and CXCR4-mediated gp120-elicited signaling pathways. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swingler, S.; Mann, A.; Jacqué, J.; Brichacek, B.; Sasseville, V.G.; Williams, K.; Lackner, A.A.; Janoff, E.N.; Wang, R.; Fisher, D.; et al. HIV-1 Nef mediates lymphocyte chemotaxis and activation by infected macrophages. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsue, P.Y.; Hunt, P.W.; Schnell, A.; Kalapus, S.C.; Hoh, R.; Ganz, P.; Martin, J.N.; Deeks, S.G. Role of Viral Replication, Antiretroviral Therapy, and Immunodeficiency in HIV- Associated Atherosclerosis. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2009, 23, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arminio, A.; Sabin, C.A.; Phillips, A.N.; Reiss, P.; Weber, R.; Kirk, O.; El-Sadr, W.; De Wit, S.; Mateu, S.; Petoumenos, K.; et al. Cardio- and cerebrovascular events in HIV-infected persons. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2004, 18, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, F.C.; Bacchetti, P.; Kim, A.S.; Price, R.W.; Hsue, P.Y. Effect of CD4+ cell count and viral suppression on risk of ischemic stroke in HIV infection. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2014, 28, 2573–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabin, C.; Ryom, L.; Wit, S.D.; Mocroft, A.; Phillips, A.; Worm, S.; Weber, R.; Monforte, A.D.; Reiss, P.; Kamara, D.; et al. Associations between immune depression and cardiovascular events in HIV infection. Aids 2013, 27, 2735–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, H.C.A.; Tyrrell, P.J. Inflammation and Infection in Clinical Stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002, 22, 1399–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solages, A.; Vita, J.A.; Thornton, D.J.; Murray, J.; Heeren, T.; Craven, D.E.; Horsburgh, C.R. Endothelial function in HIV-infected persons. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2006, 42, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.C.; Rizk, N.; O’Riordan, M.A.; Dogra, V.; El-Bejjani, D.; Storer, N.; Harrill, D.; Tungsiripat, M.; Adell, J.; McComsey, G.A. Relationship between inflammatory markers, endothelial activation markers, and carotid intima-media thickness in HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2009, 49, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryom, L.; Lundgren, J.D.; El-Sadr, W.; Reiss, P.; Kirk, O.; Law, M.; Phillips, A.; Weber, R.; Fontas, E.; d’ Arminio Monforte, A.; et al. Cardiovascular disease and use of contemporary protease inhibitors: The D:A:D international prospective multicohort study. Lancet HIV 2018, 5, e291–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, J.H.; Ribaudo, H.J.; Hodis, H.N.; Brown, T.T.; Tran, T.T.T.; Yan, M.; Brodell, E.L.; Kelesidis, T.; McComsey, G.A.; Dube, M.P.; et al. A prospective, randomized clinical trial of antiretroviral therapies on carotid wall thickness: AIDS Clinical Trial Group Study A5260s. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2015, 29, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bavinger, C.; Bendavid, E.; Niehaus, K.; Olshen, R.A.; Olkin, I.; Sundaram, V.; Wein, N.; Holodniy, M.; Hou, N.; Owens, D.K.; et al. Risk of Cardiovascular Disease from Antiretroviral Therapy for HIV: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, L.; Velichkovska, M.; Toborek, M. Cerebral Vascular Toxicity of Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sico, J.J.; Chang, C.-C.H.; So-Armah, K.; Justice, A.C.; Hylek, E.; Skanderson, M.; McGinnis, K.; Kuller, L.H.; Kraemer, K.L.; Rimland, D.; et al. HIV status and the risk of ischemic stroke among men. Neurology 2015, 84, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Triant, V.A.; Lee, H.; Hadigan, C.; Grinspoon, S.K. Increased acute myocardial infarction rates and cardiovascular risk factors among patients with human immunodeficiency virus disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, L.A.; Corbett, E.L.; Connor, M.D.; Mzinganjira, H.; Kampondeni, S.; Choko, A.; Hopkins, M.; Emsley, H.C.A.; Bryer, A.; Faragher, B.; et al. HIV, antiretroviral treatment, hypertension, and stroke in Malawian adults: A case-control study. Neurology 2016, 86, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mochan, A.; Modi, M.; Modi, G. Protein S deficiency in HIV associated ischaemic stroke: An epiphenomenon of HIV infection. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1455–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allie, S.; Stanley, A.; Bryer, A.; Meiring, M.; Combrinck, M.I. High levels of von Willebrand factor and low levels of its cleaving protease, ADAMTS13, are associated with stroke in young HIV-infected patients. Int. J. Stroke Off. J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2015, 10, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, R.K.; Franklin, D.R.; Ellis, R.J.; McCutchan, J.A.; Letendre, S.L.; Leblanc, S.; Corkran, S.H.; Duarte, N.A.; Clifford, D.B.; Woods, S.P.; et al. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders before and during the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: Differences in rates, nature, and predictors. J. Neurovirol. 2011, 17, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, L.A.; Allain, T.J.; Mzinganjira, H.; Connor, M.D.; Smith, C.; Lucas, S.; Joekes, E.; Kampondeni, S.; Chetcuti, K.; Turnbull, I.; et al. The Role of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Vasculopathy in the Etiology of Stroke. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, I.; Quereda, C.; Moreno, A.; Pérez-Elías, M.-J.; Dronda, F.; Casado, J.-L.; Muriel, A.; Masjuán, J.; Alonso-de-Leciñana, M.; Moreno, S. Cerebrovascular ischemic events in HIV-1-infected patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy: Incidence and risk factors. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Basel Switz. 2009, 27, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulignier, A.; Savatovsky, J.; Assoumou, L.; Lescure, F.-X.; Lamirel, C.; Godin, O.; Valin, N.; Tubiana, R.; Canestri, A.; Roux, P.; et al. Silent Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease Is Twice as Prevalent in Middle-Aged Individuals With Well-Controlled, Combination Antiretroviral Therapy–Treated Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Than in HIV-Uninfected Individuals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, L.; Dygert, L.; Toborek, M. Antiretroviral Treatment with Efavirenz Disrupts the Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity and Increases Stroke Severity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, A.M.; Heverling, H.; Pham, P.A.; Stolbach, A. A review of the toxicity of HIV medications. J. Med. Toxicol. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, A.-R.; Kim, J.Y.; Hyun, H.-W.; Kim, J.-E. Endothelial NOS activation induces the blood–brain barrier disruption via ER stress following status epilepticus. Brain Res. 2015, 1622, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The Blood–Brain Barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullahi, W.; Tripathi, D.; Ronaldson, P.T. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: Targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 315, C343–C356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Shepherd, N.; Lan, J.; Li, W.; Rane, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Yu, Q. MMPs/TIMPs imbalances in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid are associated with the pathogenesis of HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gras, G.; Kaul, M. Molecular mechanisms of neuroinvasion by monocytes-macrophages in HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atluri, V.S.R.; Hidalgo, M.; Samikkannu, T.; Kurapati, K.R.V.; Jayant, R.D.; Sagar, V.; Nair, M.P.N. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus on blood-brain barrier integrity and function: An update. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopalco, L. CCR5: From Natural Resistance to a New Anti-HIV Strategy. Viruses 2010, 2, 574–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joy, M.T.; Assayag, E.B.; Shabashov-Stone, D.; Liraz-Zaltsman, S.; Mazzitelli, J.; Arenas, M.; Abduljawad, N.; Kliper, E.; Korczyn, A.D.; Thareja, N.S.; et al. CCR5 Is a Therapeutic Target for Recovery after Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injury. Cell 2019, 176, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AbdelRazek, M.A.; Gutierrez, J.; Mampre, D.; Cervantes-Arslanian, A.; Ormseth, C.; Haussen, D.; Thakur, K.T.; Lyons, J.L.; Smith, B.R.; O’Connor, O.; et al. Intravenous Thrombolysis for Stroke and Presumed Stroke in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Adults: A Retrospective, Multicenter US Study. Stroke 2018, 49, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, M. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and stroke: Targets for intervention. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 10, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worm, S.W.; Sabin, C.; Weber, R.; Reiss, P.; El-Sadr, W.; Dabis, F.; De Wit, S.; Law, M.; Monforte, A.D.; Friis-Møller, N.; et al. Risk of myocardial infarction in patients with HIV infection exposed to specific individual antiretroviral drugs from the 3 major drug classes: The data collection on adverse events of anti-HIV drugs (D:A:D) study. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currier, J.S.; Lundgren, J.D.; Carr, A.; Klein, D.; Sabin, C.A.; Sax, P.E.; Schouten, J.T.; Smieja, M. Working Group 2 Epidemiological evidence for cardiovascular disease in HIV-infected patients and relationship to highly active antiretroviral therapy. Circulation 2008, 118, e29–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, A.D.; Pabo, C.O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell 1988, 55, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, E.; Kilic, U.; Hermann, D.M. TAT fusion proteins against ischemic stroke: Current status and future perspectives. Front. Biosci. J. Virtual Libr. 2006, 11, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akers, J.C.; Gonda, D.; Kim, R.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): Exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lane, R.E.; Korbie, D.; Hill, M.M.; Trau, M. Extracellular vesicles as circulating cancer biomarkers: Opportunities and challenges. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Kodidela, S.; Gerth, K.; Hatami, E.; Verma, N.; Kumar, S. Extracellular Vesicles in Smoking-Mediated HIV Pathogenesis and their Potential Role in Biomarker Discovery and Therapeutic Interventions. Cells 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyaki, S.; Lotz, M.K. Extracellular vesicles in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, A.; Subra, C.; Jenabian, M.-A.; Tremblay Labrecque, P.-F.; Tremblay, C.; Laffont, B.; Provost, P.; Routy, J.-P.; Gilbert, C. Elevated Abundance, Size, and MicroRNA Content of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles in Viremic HIV-1+ Patients: Correlations With Known Markers of Disease Progression. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1999 2015, 70, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skalnikova, H.K.; Bohuslavova, B.; Turnovcova, K.; Juhasova, J.; Juhas, S.; Rodinova, M.; Vodicka, P. Isolation and Characterization of Small Extracellular Vesicles from Porcine Blood Plasma, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Seminal Plasma. Proteomes 2019, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eyileten, C.; Wicik, Z.; De Rosa, S.; Mirowska-Guzel, D.; Soplinska, A.; Indolfi, C.; Jastrzebska-Kurkowska, I.; Czlonkowska, A.; Postula, M. MicroRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Ischemic Stroke-A Comprehensive Review and Bioinformatic Analysis. Cells 2018, 7, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.; Qu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.-Y. Increased Circulating Exosomal miRNA-223 Is Associated with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Q.; Ji, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y. Increased Brain-Specific MiR-9 and MiR-124 in the Serum Exosomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. PloS One 2016, 11, e0163645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, M.; Lam, T.K.; Hebert, E.; Divi, R.L. Extracellular vesicles: Potential applications in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and epidemiology. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2015, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Verrilli, M.A.; Court, F.A. Exosomes: Mediators of communication in eukaryotes. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickhout, A.; Koenen, R.R. Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease; Chances and Risks. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen-Heravi, F. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles by Ultracentrifugation. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2017, 1660, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Heiskanen, M.; Navarro-Ferrandis, V.; Das Gupta, S.; Lipponen, A.; Puhakka, N.; Rilla, K.; Koistinen, A.; Pitkänen, A. Precipitation-based extracellular vesicle isolation from rat plasma co-precipitate vesicle-free microRNAs. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1555410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreimer, S.; Ivanov, A.R. Rapid Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles from Blood Plasma with Size-Exclusion Chromatography Followed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomic Profiling. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2017, 1660, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Adda, C.G.; Liem, M.; Ang, C.-S.; Mechler, A.; Simpson, R.J.; Hulett, M.D.; Mathivanan, S. Comparative proteomics evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics 2013, 13, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, S.; Israel, S.; Nagy, C.; Turecki, G. The emerging role of exosomes in mental disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xin, H.; Katakowski, M.; Wang, F.; Qian, J.-Y.; Liu, X.S.; Ali, M.M.; Buller, B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 Cluster in Exosomes Enhance Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats. Stroke 2017, 48, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster-Matanzo, A.; Gessler, F.; Leonardi, T.; Iraci, N.; Pluchino, S. Acellular approaches for regenerative medicine: On the verge of clinical trials with extracellular membrane vesicles? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Exosomes in stroke pathogenesis and therapy. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, H.-X.; He, C.-P.; Fan, S.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Qi, C.; Huang, N.-P.; Xiao, Z.-D.; Lu, Z.-H.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 150, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, M.N.; Roller, R.J.; Okeoma, C.M. Human semen contains exosomes with potent anti-HIV-1 activity. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madison, M.N.; Jones, P.H.; Okeoma, C.M. Exosomes in human semen restrict HIV-1 transmission by vaginal cells and block intravaginal replication of LP-BM5 murine AIDS virus complex. Virology 2015, 482, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Näslund, T.I.; Paquin-Proulx, D.; Paredes, P.T.; Vallhov, H.; Sandberg, J.K.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomes from breast milk inhibit HIV-1 infection of dendritic cells and subsequent viral transfer to CD4+ T cells. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2014, 28, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, A.; Iordanskiy, S.; Das, R.; Van Duyne, R.; Santos, S.; Jaworski, E.; Guendel, I.; Sampey, G.; Dalby, E.; Iglesias-Ussel, M.; et al. Exosomes derived from HIV-1-infected cells contain trans-activation response element RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20014–20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kadiu, I.; Narayanasamy, P.; Dash, P.K.; Zhang, W.; Gendelman, H.E. Biochemical and biologic characterization of exosomes and microvesicles as facilitators of HIV-1 infection in macrophages. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2012, 189, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, H.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.-E.; Cheung, W.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Secondary Release of Exosomes From Astrocytes Contributes to the Increase in Neural Plasticity and Improvement of Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats Treated With Exosomes Harvested From MicroRNA 133b-Overexpressing Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Laso-García, F.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.D.C.; Rodríguez-Frutos, B.; Pascual-Guerra, J.; Fuentes, B.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, M. White Matter Repair After Extracellular Vesicles Administration in an Experimental Animal Model of Subcortical Stroke. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Risk Factors | Causes | Effect on Stroke | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coagulopathies | Thrombocytopenia purpura Protein S & C deficiency Elevated von willebrand factor (VWF) increment in antiphospholipid antibody titres, increase in D-dimer level, microbial translocation, altered platelet morphology | Platelet activation Inflammation Endothelial activation Venous thrombosis. | [45,46,47,48,49] |
| Opportunistic infections | Mycobacterium tuberculosis, neurosyphilis, Candida albicans, cytomegalovirus, varicella-zoster | Neurovascular inflammation leading to endarteritis and a prothrombotic state vasculitis and endarteritis elevated meningovascular complications | [50,51,52,53,54,55,56] |
| HIV-associated vasculopathy | Intracranial or extracranial cerebral abnormality of the blood vessels (etacia and aneurism) arterial inflammation in the adventitial intima | Vascular inflammation atheroschlerosis reduced cerebral blood flow and cerebrovascular reserve capacity | [44,57,58,59,60] |
| Cardioembolism | Opportunistic infections including bacterial endocarditis valvular disorders cardiac chamber abnormalities dilated cardiomyopathy, ischemic heart diseases | Atrial fibrillation | [61,62,63,64,65] |
| Atherosclerosis | Increased carotid intimal thickness (cIMT), vascular inflammation, abnormalities in vascular compliance, activation of immune cells Elevated release of pro-inflammatory mediators by viral proteins Increased oxidative stress, chemo attractants (eg: CCL2), cell adhesion molecule (CAM) elevated endothelial specific coagulatoty molecules | Immune activation, vascular inflammation, endothelial activation, development of atherosclerotic plaques | [23,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82] |
| Antiretroviral therapy | Endothelial toxicity, low grade systemic inflammation, dyslipidemia and vascular dysfunction, enhancement of large-vessel atherosclerosis | Vascular dysfunction, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular diseases | [10,11,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] |
| Traditional risk factors | Hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, coronary artery disease (CAD) and atrial fibrillation | Hypertension, diabetes can lead to chronic inflammation myocardial remodeling, and atrial fibrillation likelihood of large-vessel atherosclerosis | [6,61,93,94,95] |
| Sources of EVs/Exosomes | Study Mode | Effector Molecule/Component | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles | In vivo | miRNA-17–92 | Increase neural plasticity and functional recovery after stroke | [136] |
| Human semen exosome | In vitro and In vivo | mRNA | Inhibit intravaginal transmission and proliferation of HIV complex. | [140,141] |
| Human milk exosomes | In vitro | Mucin 1 | Inhibit the vertical transmission of HIV to monocyte-derived dendritic cells | [142] |
| Cell culture supernatants of HIV-1-infected cells and HIV-1- patient serum derived exosomes | In vitro | trans-activation response element (TAR) miRNA | Promote HIV infection | [143] |
| Cell culture exosomes and Microvesicles | In vitro | immune response factors, adhesion and viral proteins | Facilitate HIV-1 infection | [144] |
| Cell culture exosomes | In vivo | miR-133b | Improve neural plasticity and functional recovery after stroke | [145] |
| Rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells exosomes | In vivo | Proteins | Improve functional recovery, axonal sprouting and white matter repair fiber tract integrity | [146] |
| Rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles. | In vivo | MiRNA-17–92 | Increase neural plasticity and functional recovery after stroke | [136] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismael, S.; Moshahid Khan, M.; Kumar, P.; Kodidela, S.; Mirzahosseini, G.; Kumar, S.; Ishrat, T. HIV Associated Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155306
Ismael S, Moshahid Khan M, Kumar P, Kodidela S, Mirzahosseini G, Kumar S, Ishrat T. HIV Associated Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(15):5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155306
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmael, Saifudeen, Mohammad Moshahid Khan, Prashant Kumar, Sunitha Kodidela, Golnoush Mirzahosseini, Santhosh Kumar, and Tauheed Ishrat. 2020. "HIV Associated Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke and Future Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 15: 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155306
APA StyleIsmael, S., Moshahid Khan, M., Kumar, P., Kodidela, S., Mirzahosseini, G., Kumar, S., & Ishrat, T. (2020). HIV Associated Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155306








