Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. BCC Risk Factors: Genetics and Phenotypes
3. BCC Risk Factors: Environment
4. BCC Histology, Immunohistochemical Profile and Differential Diagnosis
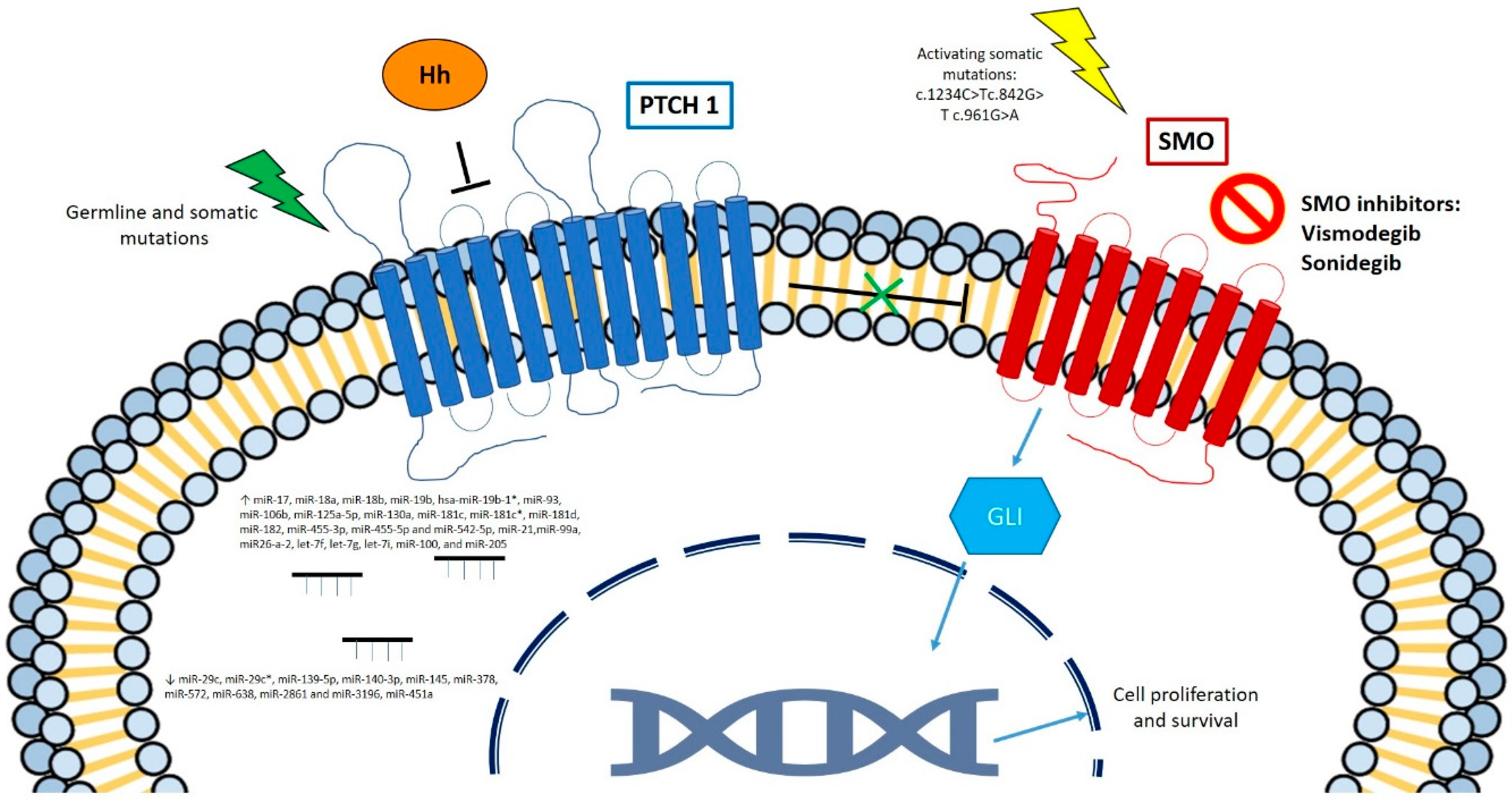
5. BCC Molecular Characteristics
6. BCC Therapeutical Management
7. Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCC | Basal cell carcinoma |
| NMSC | Non-melanoma skin cancer |
| LaBCC | Local advanced BCC |
| mBCC | Metastatic basal cell carcinoma |
| miRNA | microRNA |
References
- Rogers, H.W.; Weinstock, M.A.; Feldman, S.R.; Coldiron, B.M. Incidence Estimate of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer (Keratinocyte Carcinomas) in the US Population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin Cancer Facts. Available online: http://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/skin-cancer-facts (accessed on 17 May 2020).
- Verkouteren, J.A.C.; Ramdas, K.H.R.; Wakkee, M.; Nijsten, T. Epidemiology of basal cell carcinoma: Scholarly review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, L.J. Incidence of Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinomas in a Population Younger Than 40 Years. JAMA 2005, 294, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schierbeck, J.; Vestergaard, T.; Bygum, A. Skin Cancer Associated Genodermatoses: A Literature Review. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaju, P.D.; Ransohoff, K.J.; Tang, J.Y.; Sarin, K.Y. Familial skin cancer syndromes. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, M.C.; Lee, E.; Hibler, B.P.; Giordano, C.N.; Barker, C.A.; Mori, S.; Cordova, M.; Nehal, K.S.; Rossi, A.M. Basal cell carcinoma: Contemporary approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, D.; Bermejo, J.L.; Rudnai, P.; Gurzau, E.; Koppova, K.; Hemminki, K.; Kumar, R. MC1R variants associated susceptibility to basal cell carcinoma of skin: Interaction with host factors and XRCC3 polymorphism. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 122, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.M.; Cartmel, B.; Molinaro, A.M.; Gordon, P.B.; Leffell, D.J.; Bale, A.E.; Mayne, S.T. Host Phenotype Characteristics and MC1R in Relation to Early-Onset Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Sulem, P.; Stacey, S.N.; Goldstein, A.M.; Rafnar, T.; Sigurgeirsson, B.; Benediktsdottir, K.R.; Thorisdottir, K.; Ragnarsson, R.; Sveinsdottir, S.G.; et al. ASIP and TYR pigmentation variants associate with cutaneous melanoma and basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Lear, J.T.; Ramsay, H.; Smith, A.G.; Bowers, B.; Hutchinson, P.E.; Jones, P.W.; Fryer, A.A.; Strange, R.C. Presentation with multiple cutaneous basal cell carcinomas: Association of glutathione S-transferase and cytochrome P450 genotypes with clinical phenotype. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1999, 8, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- De Zwaan, S.E.; Haass, N.K. Genetics of basal cell carcinoma: Basal cell carcinoma genetics. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2009, 51, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, X.; Parmentier, L.; King, B.; Bezrukov, F.; Kaya, G.; Zoete, V.; Seplyarskiy, V.B.; Sharpe, H.J.; McKee, T.; Letourneau, A.; et al. Genomic analysis identifies new drivers and progression pathways in skin basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, S.S.; Rayhan, D.J.; Hazany, S.; Kolodney, M.S. Mutational Landscape of Basal Cell Carcinomas by Whole-Exome Sequencing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Athar, M.; Tang, X.; Lee, J.L.; Kopelovich, L.; Kim, A.L. Hedgehog signalling in skin development and cancer. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifenberger, J.; Wolter, M.; Knobbe, C.B.; Köhler, B.; Schönicke, A.; Scharwächter, C.; Kumar, K.; Blaschke, B.; Ruzicka, T.; Reifenberger, G. Somatic mutations in the PTCH, SMOH, SUFUH and TP53 genes in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Maturo, M.; Di Nardo, L.; Ciciarelli, V.; Gutiérrez García-Rodrigo, C.; Fargnoli, M. Understanding the Molecular Genetics of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnidar, H.; Eberl, M.; Klingler, S.; Mangelberger, D.; Kasper, M.; Hauser-Kronberger, C.; Regl, G.; Kroismayr, R.; Moriggl, R.; Sibilia, M.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Synergizes with Hedgehog/GLI in Oncogenic Transformation via Activation of the MEK/ERK/JUN Pathway. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riobo, N.A.; Lu, K.; Ai, X.; Haines, G.M.; Emerson, C.P. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Akt are essential for Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4505–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naldi, L.; DiLandro, A.; D’Avanzo, B.; Parazzini, F. Host-related and environmental risk factors for cutaneous basal cell carcinoma: Evidence from an Italian case-control study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 42, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, M.R.; Shive, M.L.; Chren, M.-M.; Han, J.; Qureshi, A.A.; Linos, E. Indoor tanning and non-melanoma skin cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2012, 345, e5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern, R.S. The risk of squamous cell and basal cell cancer associated with psoralen and ultraviolet A therapy: A 30-year prospective study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, I.; Crombie, I.K.; Dawe, R.S.; Ibbotson, S.H.; Ferguson, J. The photocarcinogenic risk of narrowband UVB (TL-01) phototherapy: Early follow-up data. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.N.; Zens, M.S.; Perry, A.E.; Spencer, S.K.; Duell, E.J.; Karagas, M.R. Photosensitizing Agents and the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: A Population-Based Case–Control Study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1950–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watt, T.C.; Inskip, P.D.; Stratton, K.; Smith, S.A.; Kry, S.F.; Sigurdson, A.J.; Stovall, M.; Leisenring, W.; Robison, L.L.; Mertens, A.C. Radiation-Related Risk of Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Report From the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dika, E.; Patrizi, A.; Veronesi, G.; Manuelpillai, N.; Lambertini, M. Malignant cutaneous tumors of the scalp: Always remember to examine the head. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchelli, L.; Baraldi, C.; Misciali, C.; Dika, E.; Ravaioli, G.M.; Fanti, P.A. Neoplastic Leg Ulcers. Dermatopathology 2018, 5, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dika, E.; Patrizi, A.; Fanti, P.A.; Alessandrini, A.; Sorci, R.; Piraccini, B.M.; Vaccari, S.; Misciali, C.; Maibach, H.I. Two synchronous periungual BCC treated with Mohs surgery. Nail polish related? Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misciali, C.; Dika, E.; Fanti, P.A.; Vaccari, S.; Baraldi, C.; Sgubbi, P.; Patrizi, A. Frequency of Malignant Neoplasms in 257 Chronic Leg Ulcers. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.E.; Goldman, R.H. Arsenic and skin cancer in the USA: The current evidence regarding arsenic-contaminated drinking water. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, e585–e591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowson, A.N. Basal cell carcinoma: Biology, morphology and clinical implications. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, S127–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, J.; Epstein, E.H., Jr.; Kossard, S. Basal cell carcinoma. In World Health Organization Classification of Skin Tumours; Elder, D.E., Massi, D., Scolyer, R.A., Willemze, R., Eds.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2018; pp. 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchmann, T.T.; Prieto, V.G.; Smoller, B.R. CD34 staining pattern distinguishes basal cell carcinoma from trichoepithelioma. Arch. Dermatol. 1994, 130, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellheyer, K.; Nelson, P.; Kutzner, H.; Patel, R.M. The immunohistochemical differential diagnosis of microcystic adnexal carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morpheaform basal cell carcinoma using BerEP4 and stem cell markers: BerEP4 and stem cell markers in adnexal neoplasms. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2013, 40, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellheyer, K.; Krahl, D. PHLDA1 (TDAG51) is a follicular stem cell marker and differentiates between morphoeic basal cell carcinoma and desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: PHLDA1 in BCC and trichoepithelioma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessi, E.; Venegoni, L.; Fanoni, D.; Berti, E. Cytokeratin Profile in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2008, 30, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellheyer, K.; Nelson, P.; Kutzner, H. Fibroepithelioma of Pinkus is a true basal cell carcinoma developing in association with a newly identified tumour-specific type of epidermal hyperplasia: Fibroepithelioma of Pinkus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Garbe, C.; Kaufmann, R.; Bastholt, L.; Seguin, N.B.; Bataille, V.; Del Marmol, V.; Dummer, R.; Harwood, C.A.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma: European consensus–based interdisciplinary guidelines. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 118, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dika, E.; Fanti, P.A.; Venturi, M.; Baraldi, C.; Patrizi, A. Non-melanoma skin cancer: To Mohs or not to Mohs? G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 150, 630–632. [Google Scholar]
- Dika, E.; Veronesi, G.; Patrizi, A.; De Salvo, S.; Misciali, C.; Baraldi, C.; Mussi, M.; Fabbri, E.; Tartari, F.; Lambertini, M. It’s time for Mohs: Micrographic surgery for the treatment of high-risk basal cell carcinomas of the head and neck regions. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, e13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, L.; Sangüeza, O. Cutaneous Adnexal Neoplasms; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanoszek, L.M.; Wang, G.Y.; Harms, P.W. Histologic Mimics of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riefolo, M.; Porcellini, E.; Dika, E.; Broseghini, E.; Ferracin, M. Interplay between small and long non-coding RNAs in cutaneous melanoma: A complex jigsaw puzzle with missing pieces. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 74–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, M.; Sand, D.; Altmeyer, P.; Bechara, F.G. MicroRNA in non-melanoma skin cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2012, 11, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sand, M.; Skrygan, M.; Georgas, D.; Arenz, C.; Gambichler, T.; Sand, D.; Altmeyer, P.; Bechara, F.G. Expression levels of the microRNA maturing microprocessor complex component DGCR8 and the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) components argonaute-1, argonaute-2, PACT, TARBP1, and TARBP2 in epithelial skin cancer: THE MICRORNA PATHWAY IN EPITHELIAL SKIN CANCER. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sand, M.; Hessam, S.; Amur, S.; Skrygan, M.; Bromba, M.; Stockfleth, E.; Gambichler, T.; Bechara, F.G. Expression of oncogenic miR-17-92 and tumor suppressive miR-143-145 clusters in basal cell carcinoma and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 86, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heffelfinger, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Engberg, A.; Leffell, D.J.; Hanlon, A.M.; Gordon, P.B.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, H.; Snyder, M.P.; Bale, A.E. Correlation of Global MicroRNA Expression With Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtype. G3 2012, 2, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonkoly, E.; Lovén, J.; Xu, N.; Meisgen, F.; Wei, T.; Brodin, P.; Jaks, V.P.; Kasper, M.; Shimokawa, T.; Harada, M.; et al. MicroRNA-203 functions as a tumor suppressor in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sand, M.; Skrygan, M.; Sand, D.; Georgas, D.; Hahn, S.A.; Gambichler, T.; Altmeyer, P.; Bechara, F.G. Expression of microRNAs in basal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, M.; Bechara, F.G.; Gambichler, T.; Sand, D.; Friedländer, M.R.; Bromba, M.; Schnabel, R.; Hessam, S. Next-generation sequencing of the basal cell carcinoma miRNome and a description of novel microRNA candidates under neoadjuvant vismodegib therapy: An integrative molecular and surgical case study. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, M.; Bromba, A.; Sand, D.; Gambichler, T.; Hessam, S.; Becker, J.C.; Stockfleth, E.; Meyer, T.; Bechara, F.G. Dicer Sequencing, Whole Genome Methylation Profiling, mRNA and smallRNA Sequencing Analysis in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jiang, P. MicroRNA-451a acts as tumor suppressor in cutaneous basal cell carcinoma. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, S.; Ayaz, L.; Gorur, A.; Yildirim Yaroglu, H.; Akbayir, S.; Dogruer Unal, N.; Bulut, B.; Tursen, U.; Tamer, L. microRNA profiling for early detection of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 41, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Ma, L.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, G.; Li, J. Expression of miR-34a in basal cell carcinoma patients and its relationship with prognosis. J. BUON 2019, 24, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peris, K.; Licitra, L.; Ascierto, P.A.; Corvò, R.; Simonacci, M.; Picciotto, F.; Gualdi, G.; Pellacani, G.; Santoro, A. Identifying locally advanced basal cell carcinoma eligible for treatment with vismodegib: An expert panel consensus. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelson, M.; Liu, K.; Jiang, X.; He, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Palmby, T.; Dong, Z.; Russell, A.M.; Miksinski, S.; et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approval: Vismodegib for Recurrent, Locally Advanced, or Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2289–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekulic, A.; Migden, M.R.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Garbe, C.; Gesierich, A.; Lao, C.D.; Miller, C.; Mortier, L.; Murrell, D.F.; Hamid, O.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of vismodegib in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma: Final update of the pivotal ERIVANCE BCC study. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekulic, A.; Migden, M.R.; Oro, A.E.; Dirix, L.; Lewis, K.D.; Hainsworth, J.D.; Solomon, J.A.; Yoo, S.; Arron, S.T.; Friedlander, P.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Vismodegib in Advanced Basal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basset-Séguin, N.; Hauschild, A.; Kunstfeld, R.; Grob, J.; Dréno, B.; Mortier, L.; Ascierto, P.A.; Licitra, L.; Dutriaux, C.; Thomas, L.; et al. Vismodegib in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma: Primary analysis of STEVIE, an international, open-label trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 86, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Chang, J.; Li, S.; Henry, A.S.; Wood, D.J.; Chang, A.L.S. Increased Risk of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Vismodegib Therapy for Basal Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khamaysi, Z.; Bochner, R.; Indelman, M.; Magal, L.; Avitan-Hersh, E.; Sarig, O.; Sprecher, E.; Bergman, R. Segmental basal cell naevus syndrome caused by an activating mutation in smoothened. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, D.; Demko, S.; Shord, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, H.; He, K.; Putman, A.; Helms, W.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Sonidegib for Locally Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Migden, M.R.; Guminski, A.; Gutzmer, R.; Dirix, L.; Lewis, K.D.; Combemale, P.; Herd, R.M.; Kudchadkar, R.; Trefzer, U.; Gogov, S.; et al. Treatment with two different doses of sonidegib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma (BOLT): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Aria, A.B.; Silapunt, S.; Lee, H.-H.; Migden, M.R. Treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma with sonidegib: Perspective from the 30-month update of the BOLT trial. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.P.; Setser, A.; Anadkat, M.J.; Cotliar, J.; Olsen, E.A.; Garden, B.C.; Lacouture, M.E. Grading dermatologic adverse events of cancer treatments: The Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 4.0. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odom, D.; Mladsi, D.; Purser, M.; Kaye, J.A.; Palaka, E.; Charter, A.; Jensen, J.A.; Sellami, D. A Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison of Sonidegib and Vismodegib in Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Skin Cancer 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atwood, S.X.; Chang, A.L.S.; Oro, A.E. Hedgehog pathway inhibition and the race against tumor evolution. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, A.L.S.; Oro, A.E. Initial Assessment of Tumor Regrowth After Vismodegib in Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuonen, F.; Huskey, N.E.; Shankar, G.; Jaju, P.; Whitson, R.J.; Rieger, K.E.; Atwood, S.X.; Sarin, K.Y.; Oro, A.E. Loss of Primary Cilia Drives Switching from Hedgehog to Ras/MAPK Pathway in Resistant Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, H.J.; Pau, G.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Modrusan, Z.; Januario, T.; Tsui, V.; Durham, A.B.; Dlugosz, A.A.; Haverty, P.M. Genomic Analysis of Smoothened Inhibitor Resistance in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| miRNA (Published Name) | miRNA (Current Name) | Expression in BCC | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-203 | miR-203a-3p | Downregulated | [49] |
| miR-17 | miR-17-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-18a | miR-18a-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-18b | miR-18b-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-19b | miR-19b-3p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-19b-1* | miR-19b-1-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-93 | miR-93-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-106b | miR-106b-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-125a-5p | miR-125a-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-130a | miR-130a-3p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-181c | miR-181c-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-181c* | miR-181c-3p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-181d | miR-181d-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-182 | miR-182-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-455-3p | miR-455-3p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-455-5p | miR-455-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-542-5p | miR-542-5p | Upregulated | [50] |
| miR-29c | miR-29c-3p | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-29c * | miR-29c-5p | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-139-5p | miR-139-5p | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-140-3p | miR-140-3p | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-145 | miR-145-5p | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-378 | miR-378a-5p | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-572 | miR-572 | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-638 | miR-638 | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-2861 | miR-2861 | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-3196 | miR-3196 | Downregulated | [50] |
| miR-21 | miR-21-5p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-99a | miR-99a-5p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-26a-2 | miR-26a-2-3p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-let-7f | let-7f-5p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-let-7g | let-7g-5p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-let-7i | let-7i-5p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-100 | miR-100-5p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-205 | miR-205-5p | Upregulated in sclerosing BBC | [52] |
| miR-451a | miR-451a | Downregulated | [53] |
| miR-34a | miR-34a-5p | Downregulated (serum) | [54] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dika, E.; Scarfì, F.; Ferracin, M.; Broseghini, E.; Marcelli, E.; Bortolani, B.; Campione, E.; Riefolo, M.; Ricci, C.; Lambertini, M. Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155572
Dika E, Scarfì F, Ferracin M, Broseghini E, Marcelli E, Bortolani B, Campione E, Riefolo M, Ricci C, Lambertini M. Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(15):5572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155572
Chicago/Turabian StyleDika, Emi, Federica Scarfì, Manuela Ferracin, Elisabetta Broseghini, Emanuela Marcelli, Barbara Bortolani, Elena Campione, Mattia Riefolo, Costantino Ricci, and Martina Lambertini. 2020. "Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 15: 5572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155572
APA StyleDika, E., Scarfì, F., Ferracin, M., Broseghini, E., Marcelli, E., Bortolani, B., Campione, E., Riefolo, M., Ricci, C., & Lambertini, M. (2020). Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(15), 5572. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155572







