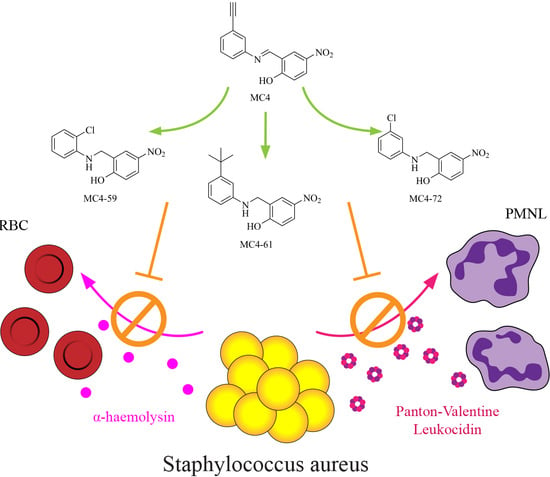
Nusbiarylins Inhibit Transcription and Target Virulence Factors in Bacterial Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Interaction between Bacterial Transcription Factors NusB-NusE as a Drug Target
1.2. Toxins as Virulence Factors in S. aureus
1.3. Global Regulatory Picture of agr and Associated Pathways in S. aureus
1.4. Aim
2. Results
2.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
2.2. Time–Kill Kinetics and Central Metabolism
2.3. Exotoxin Release
2.4. Rabbit Erythrocyte Haemolysis
2.5. Real-Time qPCR of Virulence-Associated Gene Expression
2.5.1. Effects on rRNA Complex and Implications on the Housekeeping Genes
2.5.2. Quantitative PCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Determining Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs)
4.2. Time–Kill Kinetics
4.3. ATP Production Assay
4.4. S. aureus Toxin Release
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Rabbit RBC Lysis
4.7. Real-Time qPCR
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MSSA | Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus |
| HA-MRSA | Hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| CA-MRSA | Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| PVL | Panton–Valentine Leukocidin |
| Nus | N-utilisation substances |
| RNAP | RNA polymerase |
| rRNA | Ribosomal RNA |
| PPI | Protein-protein interaction |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| CLSI | Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute |
| ATCC® | American Type Culture Collection |
| MHB | Mueller-Hinton broth |
| CA-MHB | Cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth |
| TSB | Tryptic soy broth |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| DEPC | Diethyl pyrocarbonate |
| RBC | Red blood cell |
| ODXXX | Optical density at XXX nm wavelength |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| cDNA | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
References
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, W.A.; Malachowa, N.; DeLeo, F.R. Vancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- Zhanel, G.G.; Walkty, A.J.; Karlowsky, J.A. Fidaxomicin: A novel agent for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artsimovitch, I.; Knauer, S.H. Ancient Transcription Factors in the News. mBio 2019, 10, e01547-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belogurov, G.A.; Artsimovitch, I. Regulation of Transcript Elongation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Bubunenko, M.; Weber, G.; Court, D.L.; Gottesman, M.E.; Urlaub, H.; Wahl, M.C. Structural and Functional Analysis of the E. coli NusB-S10 Transcription Antitermination Complex. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Said, N.; Loll, B.; Wahl, M.C. Structural basis for the function of SuhB as a transcription factor in ribosomal RNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 6488–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudenhoeffer, B.R.; Schneider, H.; Schweimer, K.; Knauer, S.H. SuhB is an integral part of the ribosomal antitermination complex and interacts with NusA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 6504–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greive, S.J.; Lins, A.F.; von Hippel, P.H. Assembly of an RNA-protein complex. Binding of NusB and NusE (S10) proteins to boxA RNA nucleates the formation of the antitermination complex involved in controlling rRNA transcription in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36397–36408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodwell, J.R.; Greenblatt, J. Recognition of boxA antiterminator RNA by the E. coli antitermination factors NusB and ribosomal protein S10. Cell 1993, 72, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Chan, S.T.; Lin, L.; Shek, T.L.; Tsang, T.F.; Zhang, Y.; Ip, M.; Chan, P.K.; Blanchard, N.; Hanquet, G.; et al. Nusbiarylins, a new class of antimicrobial agents: Rational design of bacterial transcription inhibitors targeting the interaction between the NusB and NusE proteins. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Chan, S.T.; Lin, L.; Shek, T.L.; Tsang, T.F.; Barua, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ip, M.; Chan, P.K.; Blanchard, N.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of antimicrobial diarylimine and –amine compounds targeting the interaction between the bacterial NusB and NusE proteins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 178, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Luo, M.J.; Yeung, A.C.M.; Lewis, P.J.; Chan, P.K.S.; Ip, M.; Ma, C. First-In-Class Inhibitor of Ribosomal RNA Synthesis with Antimicrobial Activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 5049–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenul, C.; Horswill, A.R. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.L.; Novick, R.P.; Kreiswirth, B.; Kornblum, J.; Schlievert, P. Cloning, characterization, and sequencing of an accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 4365–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsen, K.; Koller, K.P.; Hacker, J. Analysis of expression of the alpha-toxin gene (hla) of Staphylococcus aureus by using a chromosomally encoded hla::lacZ gene fusion. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3606–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas-ali, B.; Coleman, G. The characteristics of extracellular protein secretion by Staphylococcus aureus (Wood 46) and their relationship to the regulation of alpha-toxin formation. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1977, 99, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNiven, A.C.; Arbuthnott, J.P. Cell-Associated Alpha-Toxin From Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Med. Microbiol. 1972, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. Staphylococcus aureus α-Toxin: Nearly a Century of Intrigue. Toxins 2013, 5, 1140–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubeck Wardenburg, J.; Bae, T.; Otto, M.; DeLeo, F.R.; Schneewind, O. Poring over pores: α-hemolysin and Panton-Valentine leukocidin in Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1405–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B. Review on Panton Valentine leukocidin toxin carriage among Staphylococcus aureus. J. Nepal Health Res. Counc. 2013, 11, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shallcross, L.J.; Fragaszy, E.; Johnson, A.M.; Hayward, A.C. The role of the Panton-Valentine leucocidin toxin in staphylococcal disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.; Ganner, M.; McGuane, S.; Pitt, T.L.; Cookson, B.D.; Kearns, A.M. Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Carrying Panton-Valentine Leucocidin Genes in England and Wales: Frequency, Characterization, and Association with Clinical Disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2384–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Jin, D.; Kim, H.B.; Stratton, C.W.; Wu, B.; Tang, Y.-W.; Sun, X. Update on Antimicrobial Resistance in Clostridium difficile: Resistance Mechanisms and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recsei, P.; Kreiswirth, B.; O’Reilly, M.; Schlievert, P.; Gruss, A.; Novick, R.P. Regulation of exoprotein gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by agar. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1986, 202, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, R.P.; Ross, H.F.; Projan, S.J.; Kornblum, J.; Kreiswirth, B.; Moghazeh, S. Synthesis of staphylococcal virulence factors is controlled by a regulatory RNA molecule. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3967–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, R.P. Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1429–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Li, S.R.; Jiang, B.; Hu, X.M.; Li, S. Therapeutic Targeting of the Staphylococcus aureus Accessory Gene Regulator (agr) System. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronner, S.; Monteil, H.; Prévost, G. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus: Complexity and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, K.L.; Krishna, A.; Wigneshweraraj, S.; Edwards, A.M. What role does the quorum-sensing accessory gene regulator system play during Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia? Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, D.; Andrey, D.O.; Monod, A.; Kelley, W.L.; Zhang, G.; Cheung, A.L. Coordinated Regulation by AgrA, SarA, and SarR To Control agr Expression in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6020–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.L.; Bayer, M.G.; Heinrichs, J.H. sar Genetic determinants necessary for transcription of RNAII and RNAIII in the agr locus of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 3963–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.L.; Nishina, K.A.; Trotonda, M.P.; Tamber, S. The SarA protein family of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bien, J.; Sokolova, O.; Bozko, P. Characterization of Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus aureus: Novel Function of Known Virulence Factors That Are Implicated in Activation of Airway Epithelial Proinflammatory Response. J. Pathog. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quave, C.L.; Horswill, A.R. Flipping the switch: Tools for detecting small molecule inhibitors of staphylococcal virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novick, R.P.; Geisinger, E. Quorum Sensing in Staphylococci. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, (M100Ed29), 29th ed.; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Balemans, W.; Vranckx, L.; Lounis, N.; Pop, O.; Guillemont, J.; Vergauwen, K.; Mol, S.; Gilissen, R.; Motte, M.; Lançois, D.; et al. Novel Antibiotics Targeting Respiratory ATP Synthesis in Gram-Positive Pathogenic Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4131–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobritz, M.A.; Belenky, P.; Porter, C.B.M.; Gutierrez, A.; Yang, J.H.; Schwarz, E.G.; Dwyer, D.J.; Khalil, A.S.; Collins, J.J. Antibiotic efficacy is linked to bacterial cellular respiration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8173–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Bening, S.C.; Collins, J.J. Antibiotic efficacy—Context matters. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 39, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, O.; Boisset, S.; Badiou, C.; Bes, M.; Benito, Y.; Reverdy, M.-E.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J.; Lina, G. Effect of Antibiotics on Staphylococcus aureus Producing Panton-Valentine Leukocidin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.L.; Ma, Y.; Salmi, D.B.; McIndoo, E.; Wallace, R.J.; Bryant, A.E. Impact of Antibiotics on Expression of Virulence-Associated Exotoxin Genes in Methicillin-Sensitive and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangamani, S.; Mohammad, H.; Abushahba, M.F.N.; Sobreira, T.J.P.; Hedrick, V.E.; Paul, L.N.; Seleem, M.N. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of auranofin against multi-drug resistant bacterial pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Rocha, M.A.; Chintalacharuvu, K.R.; Beenhouwer, D.O. Detection and quantification of Panton–Valentine leukocidin in Staphylococcus aureus cultures by ELISA and Western blotting: Diethylpyrocarbonate inhibits binding of protein A to IgG. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 356, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Baniulyte, G.; Singh, N.; Benoit, C.; Johnson, R.; Ferguson, R.; Paramo, M.; Stringer, A.M.; Scott, A.; Lapierre, P.; Wade, J.T. Identification of regulatory targets for the bacterial Nus factor complex. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, Y. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Staphylococcus aureus. In Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Protocols: Cutting-Edge Technologies and Advancements; Ji, Y., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 95–102. ISBN 978-1-4939-9849-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, D.J.P.; Santos, C.S.; Pacheco, L.G.C. Bacterial reference genes for gene expression studies by RT-qPCR: Survey and analysis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 108, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudkin, J.K.; Laabei, M.; Edwards, A.M.; Joo, H.-S.; Otto, M.; Lennon, K.L.; O’Gara, J.P.; Waterfield, N.R.; Massey, R.C. Oxacillin Alters the Toxin Expression Profile of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureti, L.; Matic, I.; Gutierrez, A. Bacterial Responses and Genome Instability Induced by Subinhibitory Concentrations of Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2013, 2, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katahira, E.J.; Davidson, S.M.; Stevens, D.L.; Bolz, D.D. Subinhibitory concentrations of tedizolid potently inhibit extracellular toxin production by methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Spiegelman, G.B.; Yim, G. The world of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yang, X.; Lewis, P.J. Bacterial transcription as a target for antibacterial drug development. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, (M07Ed11), 11th ed.; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fávero Bonesso, M.; Faccioli-Martins, P.Y.; Alencar Marques, S.; Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha, M.L. Molecular analysis of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from skin and soft tissue infections, Botucatu Medical School, Brazil. In Microbes in Applied Research; World Scientific: Singapore, 2012; pp. 556–560. ISBN 978-981-4405-03-4. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, G.J.; Krishnadasan, A.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Fosheim, G.E.; McDougal, L.K.; Carey, R.B.; Talan, D.A. Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus Infections among Patients in the Emergency Department. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Community-associated MRSA: What makes them special? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2013, 303, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monday, S.R.; Bohach, G.A. Use of Multiplex PCR To Detect Classical and Newly Described Pyrogenic Toxin Genes in Staphylococcal Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3411–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaibani, P.; Mariconti, M.; Bua, G.; Bonora, S.; Sassera, D.; Landini, M.P.; Mulatto, P.; Novati, S.; Bandi, C.; Sambri, V. Development of a Broad-Range 23S rDNA Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection and Quantification of Pathogenic Bacteria in Human Whole Blood and Plasma Specimens. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.; Anderson, K.L.; Murphy, E.; Projan, S.J.; Mounts, W.; Hurlburt, B.; Smeltzer, M.; Overbeek, R.; Disz, T.; Dunman, P.M. Characterizing the Effect of the Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Factor Regulator, SarA, on Log-Phase mRNA Half-Lives. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidl, K.; Chen, L.; Bayer, A.S.; Hady, W.A.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Xiong, Y.Q. Relationship of agr Expression and Function with Virulence and Vancomycin Treatment Outcomes in Experimental Endocarditis Due to Meth54icillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5631–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleaume, H.; Jabbouri, S. Comparison of two standardisation methods in real-time quantitative RT-PCR to follow Staphylococcus aureus genes expression during in vitro growth. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 59, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambanthamoorthy, K.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Elasri, M.O. Identification and characterization of msa (SA1233), a gene involved in expression of SarA and several virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compd. | 25923 | 29213 | USA300 | ST22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC4 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 4 |
| MC4-59 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MC4-61 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| MC4-72 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| Van | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Oxa | 1 | 1 | >64 | >64 |
| Rif | 0.0079 | 0.0079 | 0.0079 | 0.0039 |
| Primer | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 16S_rRNA_F1 | GTAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATCC | [57] |
| 16S_rRNA_R1 | CGCACATCAGCGTCAG | [57] |
| PAN23S-F | TCGCTCAACGGATAAAAG | [58] |
| PAN23S-R | GATGAACCGACATCGAGGTGC | [58] |
| gyrA-F | CTGAGCGTAATGGTAATGTTGTATG | [59] |
| gyrA-R | TGCATCTTCTTTTACTTTAGCAACC | [59] |
| gyrB.MB-F2 | CGCAGGCGATTTTACCATTA | [60] |
| gyrB.MB-R2 | GCTTTCGCTAGATCAAAGTCG | [60] |
| gmk-1 | TCGTTTTATCAGGACCATCTGGAGTAGGTA | [61] |
| gmk-2 | CATCTTTAATTAAAGCTTCAAACGCATCCC | [61] |
| RNAII-11 | TATGAATAAATGCGCTGATGATATACCACG | [61] |
| RNAII-12 | TTTTAAAGTTGATAGACCTAAACCACGACC | [61] |
| RNA3.MB-F | GCCATCCCAACTTAATAACCA | [60] |
| RNA3.MB-R | TGTTGTTTACGATAGCTTACATGC | [60] |
| agrA (F) | TGATAATCCTTATGAGGTGCTT | [59] |
| agrA (R) | CACTGTGACTCGTAACGAAAA | [59] |
| hla (F) * | GGGGACCATATGATAGAGATT | [59] |
| hla (R) * | TGTAGCGAAGTCTGGTGAAA | [59] |
| hla-3 forward ** | TGGCCTTCAGCATTTAAGGT | [48] |
| hla-3 reverse ** | CAATCAAACCGCCAATTTTT | [48] |
| lukS forward | TGAGGTGGCCTTTCCAATAC | [48] |
| lukS reverse | CCTCCTGTTGATGGACCACT | [48] |
| spa-F | CAGATAACAAATTAGCTGATAAAAACAT | [59] |
| spa-R | CTAAGGCTAATGATAATCCACCAAATAC | [59] |
| sarA_F4 | TCTTGTTAATGCACAACAACGTAA | [62] |
| sarA_R4 | TGTTTGCTTCAGTGATTCGTTT | [62] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, A.J.; Qiu, Y.; Harper, R.; Lin, L.; Ma, C.; Yang, X. Nusbiarylins Inhibit Transcription and Target Virulence Factors in Bacterial Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165772
Chu AJ, Qiu Y, Harper R, Lin L, Ma C, Yang X. Nusbiarylins Inhibit Transcription and Target Virulence Factors in Bacterial Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(16):5772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165772
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Adrian Jun, Yangyi Qiu, Rachel Harper, Lin Lin, Cong Ma, and Xiao Yang. 2020. "Nusbiarylins Inhibit Transcription and Target Virulence Factors in Bacterial Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 16: 5772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165772
APA StyleChu, A. J., Qiu, Y., Harper, R., Lin, L., Ma, C., & Yang, X. (2020). Nusbiarylins Inhibit Transcription and Target Virulence Factors in Bacterial Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(16), 5772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165772