Parkin Coordinates Platelet Stress Response in Diabetes Mellitus: A Big Role in a Small Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Parkin Interacts with Various Key Platelet Proteins
2.2. Determining the Potential Roles of Platelet Parkin-Interacting Proteins through Literature Analysis
2.2.1. Parkin Plays an Important Role in Mitochondrial Protection through Mitophagy
Transitional Endoplasmic Reticulum ATPase (VCP/p97)
Lysosomal-Associated Membrane Protein 1 (LAMP1)
Mitochondrial Three Functional Protein A (TFPα, HADHA)
Prohibitin (PHB, Murine Only)
2.2.2. Parkin Regulates DM Platelets through Protein Interactions with Integrin Complex Proteins
14-3-3
Fermitin Family Homolog 3 (FERMT3: URP2/Kindlin-3)
Protein Disulfide-Isomerase (PDI, P4HB)
Integrin Linked Kinase
2.3. New Functions of Parkin and Parkin-Interacting Proteins in Platelets
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Human Platelet
4.2. Preparation of Mice Platelets
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Immunoprecipitation
4.5. Silver Staining and LC-Mass Analysis
4.6. Platelet Aggregation Test
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report from the american heart association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, J.L.; Angiolillo, D.J. Diabetes and antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndrome. Circulation 2011, 123, 798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leytin, V. Apoptosis in the anucleate platelet. Blood Rev. 2012, 26, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, S.; Tolley, N.D.; Dixon, D.A.; McIntyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Weyrich, A.S. Activated platelets mediate inflammatory signaling by regulated interleukin 1beta synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.; Stitham, J.; Gleim, S.; Di Febbo, C.; Porreca, E.; Fava, C.; Tacconelli, S.; Capone, M.; Evangelista, V.; Levantesi, G.; et al. Glucose and collagen regulate human platelet activity through aldose reductase induction of thromboxane. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4462–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Stitham, J.; Jin, Y.; Liu, R.; Lee, S.H.; Du, J.; Atteya, G.; Gleim, S.; Spollett, G.; Martin, K.; et al. Aldose reductase-mediated phosphorylation of p53 leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and damage in diabetic platelets. Circulation 2014, 129, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, K.D.; Carpinelli, M.R.; Fletcher, J.I.; Collinge, J.E.; Hilton, A.A.; Ellis, S.; Kelly, P.N.; Ekert, P.G.; Metcalf, D.; Roberts, A.W.; et al. Programmed anuclear cell death delimits platelet life span. Cell 2007, 128, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyrich, A.S.; Dixon, D.A.; Pabla, R.; Elstad, M.R.; McIntyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A. Signal-dependent translation of a regulatory protein, Bcl-3, in activated human platelets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5556–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Du, J.; Stitham, J.; Atteya, G.; Lee, S.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Jin, Y.; Leslie, K.L.; Spollett, G.; et al. Inducing mitophagy in diabetic platelets protects against severe oxidative stress. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouseph, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Banerjee, M.; Joshi, S.; MacDonald, L.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Xiang, B.; Zhang, G.; et al. Autophagy is induced upon platelet activation and is essential for hemostasis and thrombosis. Blood 2015, 126, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Chang, C.; Luo, D.; Su, H.; Yu, S.; Hua, W.; Chen, Z.; Hu, H.; Liu, W. Dissection of autophagy in human platelets. Autophagy 2014, 10, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Bermudez, M.; Lopez-Mejias, R.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Castaneda, S.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; Blanco, R.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, B.; Balsa, A.; Gonzalez-Alvaro, I.; Gomez-Vaquero, C.; et al. Association of the methionine sulfoxide reductase A rs10903323 gene polymorphism with cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 41, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenech, E.; Maestre, C.; Esteban-Martinez, L.; Partida, D.; Pascual, R.; Fernandez-Miranda, G.; Seco, E.; Campos-Olivas, R.; Perez, M.; Megias, D.; et al. AMPK and PFKFB3 mediate glycolysis and survival in response to mitophagy during mitotic arrest. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.; Du, J.; Jain, K.; Ding, M.; Kadado, A.J.; Atteya, G.; Jaji, Z.; Tyagi, T.; Kim, W.H.; et al. Mitochondrial MsrB2 serves as a switch and transducer for mitophagy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroud, T.; Uniacke, S.K.; Liu, L.; Pankratz, N.; Rudolph, A.; Halter, C.; Shults, C.; Marder, K.; Conneally, P.M.; Nichols, W.C. Heterozygosity for a mutation in the parkin gene leads to later onset Parkinson disease. Neurology 2003, 60, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunico, C.R.; Nakamura, T.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Adame, A.; Chan, S.F.; Newmeyer, T.F.; Masliah, E.; Nakanishi, N.; Lipton, S.A. S-Nitrosylation of parkin as a novel regulator of p53-mediated neuronal cell death in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Basso, V.; Ziviani, E. Post translational modification of Parkin. Biol. Direct. 2017, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Ao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Fa, H.G.; Wang, M.Y.; He, Y.Q.; Wang, J.X. Post-translational modification of Parkin and its research progress in cancer. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcan, T.M.; Fon, E.A. The three ‘P’s of mitophagy: PARKIN, PINK1, and post-translational modifications. Genes Dev. 2019, 29, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, K.; Komatsubara, A.T.; Nishimura, Y.; Sawada, T.; Kawafune, H.; Tsumoto, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kyotani, Y.; Tanaka, T.; et al. S-nitrosylation regulates mitochondrial quality control via activation of parkin. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truban, D.; Hou, X.; Caulfield, T.R.; Fiesel, F.C.; Springer, W. PINK1, Parkin, and Mitochondrial Quality Control: What can we Learn about Parkinson’s Disease Pathobiology? J. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 7, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, G.F.; Toth, R.; James, J.; Ganley, I.G. Loss of iron triggers PINK1/Parkin-independent mitophagy. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.; Weihl, C.C. The VCP/p97 system at a glance: Connecting cellular function to disease pathogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127 Pt 18, 3877–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.H. Golgi reassembly after mitosis: The AAA family meets the ubiquitin family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1744, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olzmann, J.A.; Richter, C.M.; Kopito, R.R. Spatial regulation of UBXD8 and p97/VCP controls ATGL-mediated lipid droplet turnover. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, D.; Vuk, M.; Kirchner, P.; Bug, M.; Schutz, S.; Hayer, A.; Bremer, S.; Lusk, C.; Baloh, R.H.; Lee, H.; et al. Endolysosomal sorting of ubiquitylated caveolin-1 is regulated by VCP and UBXD1 and impaired by VCP disease mutations. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bug, M.; Meyer, H. Expanding into new markets—VCP/p97 in endocytosis and autophagy. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 179, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, O.; Oral, O.; Kocaturk, N.M.; Akkoc, Y.; Eberhart, K.; Kosar, A.; Gozuacik, D. IBMPFD Disease-Causing Mutant VCP/p97 Proteins Are Targets of Autophagic-Lysosomal Degradation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sun, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, Y.J.; Fujioka, H.; Vyas, R.; Chakrapani, S.; Joshi, A.U.; Luo, Y.; Mochly-Rosen, D.; et al. VCP recruitment to mitochondria causes mitophagy impairment and neurodegeneration in models of Huntington’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Clark, C.; Geisbrecht, E.R. Drosophila clueless is involved in Parkin-dependent mitophagy by promoting VCP-mediated Marf degradation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1946–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiekerkoetter, U.; Sun, B.; Khuchua, Z.; Bennett, M.J.; Strauss, A.W. Molecular and phenotypic heterogeneity in mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency due to beta-subunit mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeyashiki, C.; Oshima, S.; Otsubo, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Nibe, Y.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Onizawa, M.; Nemoto, Y.; Nagaishi, T.; Okamoto, R.; et al. HADHA, the alpha subunit of the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, is involved in long-chain fatty acid-induced autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artal-Sanz, M.; Tavernarakis, N. Prohibitin and mitochondrial biology. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkwirth, C.; Langer, T. Prohibitin function within mitochondria: Essential roles for cell proliferation and cristae morphogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiria, A.S.; Butcher, L.D.; Feagins, L.A.; Souza, R.F.; Boland, C.R.; Theiss, A.L. Prohibitin 1 modulates mitochondrial stress-related autophagy in human colonic epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triplett, J.C.; Zhang, Z.; Sultana, R.; Cai, J.; Klein, J.B.; Bueler, H.; Butterfield, D.A. Quantitative expression proteomics and phosphoproteomics profile of brain from PINK1 knockout mice: Insights into mechanisms of familial Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2015, 133, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Chiang, W.C.; Sumpter, R., Jr.; Mishra, P.; Levine, B. Prohibitin 2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane mitophagy receptor. Cell 2017, 168, 224–238.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Gong, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Abou-Hamdan, H.; Tang, M.; Desaubry, L.; Song, Z. PHB2 (prohibitin 2) promotes PINK1-PRKN/Parkin-dependent mitophagy by the PARL-PGAM5-PINK1 axis. Autophagy 2020, 16, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Lee, W. Prohibitins are involved in protease-activated receptor 1-mediated platelet aggregation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.K.; Harris, S.J.; McNally, T.; Berndt, M.C. Binding of purified 14-3-3 zeta signaling protein to discrete amino acid sequences within the cytoplasmic domain of the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Bodnar, R.; Berndt, M.C.; Du, X. A critical role for 14-3-3zeta protein in regulating the VWF binding function of platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX and its therapeutic implications. Blood 2005, 106, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D. 14-3-3: Modulators of signaling proteins? Science 1994, 266, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKintosh, C.; Meek, S.E. Regulation of plant NR activity by reversible phosphorylation, 14-3-3 proteins and proteolysis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleppe, R.; Martinez, A.; Doskeland, S.O.; Haavik, J. The 14-3-3 proteins in regulation of cellular metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, S. Regulation of parkin and Parkinson’s disease. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso 2006, 51 (Suppl. 10), 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Chiba, T.; Sakata, E.; Kato, K.; Mizuno, Y.; Hattori, N.; Tanaka, K. 14-3-3eta is a novel regulator of parkin ubiquitin ligase. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Darbousset, R.; Cranmer, S.L.; Ramshaw, H.S.; Orive, S.L.; Sturgeon, S.; Yuan, Y.; Yao, Y.; Krycer, J.R.; Woodcock, J.; et al. 14-3-3zeta regulates the mitochondrial respiratory reserve linked to platelet phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant function. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Harris, S.J.; Tetaz, T.J.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Berndt, M.C. Association of a phospholipase A2 (14-3-3 protein) with the platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 18287–18290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mangin, P.; David, T.; Lavaud, V.; Cranmer, S.L.; Pikovski, I.; Jackson, S.P.; Berndt, M.C.; Cazenave, J.P.; Gachet, C.; Lanza, F. Identification of a novel 14-3-3zeta binding site within the cytoplasmic tail of platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha. Blood 2004, 104, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Huang, M.; Lai, J.; Mao, K.; Sun, P.; Cao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Schulte, M.L.; Jin, C.; et al. Kindlin supports platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation by interacting with paxillin. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 3764–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, J.J.; Gibbs, E.; Russell, M.; Goldman, D.; Minarcik, J.; Golden, J.A.; Feldman, E.L. Kindlin-2 is an essential component of intercalated discs and is required for vertebrate cardiac structure and function. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, J.J.; Vreede, A.P.; Kim, S.; Golden, J.; Feldman, E.L. Kindlin-2 is required for myocyte elongation and is essential for myogenesis. BMC Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanez, E.; Ussar, S.; Schifferer, M.; Bosl, M.; Zent, R.; Moser, M.; Fassler, R. Kindlin-2 controls bidirectional signaling of integrins. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabnis, H.; Kirpalani, A.; Horan, J.; McDowall, A.; Svensson, L.; Cooley, A.; Merck, T.; Jobe, S.; Hogg, N.; Briones, M. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-III in an African-American patient. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, P.; Canault, M.; Farnarier, C.; Nurden, A.; Grosdidier, C.; Barlogis, V.; Bongrand, P.; Pierres, A.; Chambost, H.; Alessi, M.C. A novel leukocyte adhesion deficiency III variant: Kindlin-3 deficiency results in integrin- and nonintegrin-related defects in different steps of leukocyte adhesion. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5273–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, V.L.; MacPherson, M.; Savinko, T.; Lek, H.S.; Prescott, A.; Fagerholm, S.C. The beta2 integrin-kindlin-3 interaction is essential for T-cell homing but dispensable for T-cell activation in vivo. Blood 2013, 122, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essex, D.W.; Wu, Y. Multiple protein disulfide isomerases support thrombosis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2018, 25, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essex, D.W.; Li, M. Protein disulphide isomerase mediates platelet aggregation and secretion. Br. J. Haematol. 1999, 104, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, N.; Sun, X.; Li, M.; Gazitt, Y.; Essex, D.W. Protein disulphide isomerase in platelet function. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 140, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.L.; Sage, T.; Stevens, J.M.; Jordan, P.A.; Jones, S.; Barrett, N.E.; St-Arnaud, R.; Frampton, J.; Dedhar, S.; Gibbins, J.M. A dual role for integrin-linked kinase in platelets: Regulating integrin function and alpha-granule secretion. Blood 2008, 112, 4523–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiarei, M.; Yazdi, S.A.; Gray, V.; Dedhar, S.; van Breemen, C. Integrin-linked kinase functions as a downstream signal of platelet-derived growth factor to regulate actin polymerization and vascular smooth muscle cell migration. BMC Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.I.; Tucker, K.L.; Sasikumar, P.; Sage, T.; Kaiser, W.J.; Moore, C.; Emerson, M.; Gibbins, J.M. Integrin-linked kinase regulates the rate of platelet activation and is essential for the formation of stable thrombi. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 12, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodehl, A.; Rezazadeh, S.; Williams, T.; Munsie, N.M.; Liedtke, D.; Oh, T.; Ferrier, R.; Shen, Y.; Jones, S.J.M.; Stiegler, A.L.; et al. Mutations in ILK, encoding integrin-linked kinase, are associated with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Transl. Res. 2020, 208, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Yao, D.; Shi, Y.; Kabakoff, J.; Wu, W.; Reicher, J.; Ma, Y.; Moosmann, B.; Masliah, E.; Lipton, S.A.; et al. Oxidation of the cysteine-rich regions of parkin perturbs its E3 ligase activity and contributes to protein aggregation. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Z.Q.; Steer, E.; Otero, P.A.; Bateman, N.W.; Cheng, M.H.; Scott, A.L.; Wu, C.; Bahar, I.; Shih, Y.T.; Hsueh, Y.P.; et al. PINK1 Interacts with VCP/p97 and Activates PKA to Promote NSFL1C/p47 Phosphorylation and Dendritic Arborization in Neurons. eNeuro 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.P.; Brandes, L.J.; Becker, A.B.; Simons, K.J.; LaBella, F.S.; Gerrard, J.M. Histamine is an intracellular messenger mediating platelet aggregation. Science 1989, 243, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravic, B.; Behrends, C.; Meyer, H. Regulation of lysosome integrity and lysophagy by the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2QL1. Autophagy 2020, 16, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
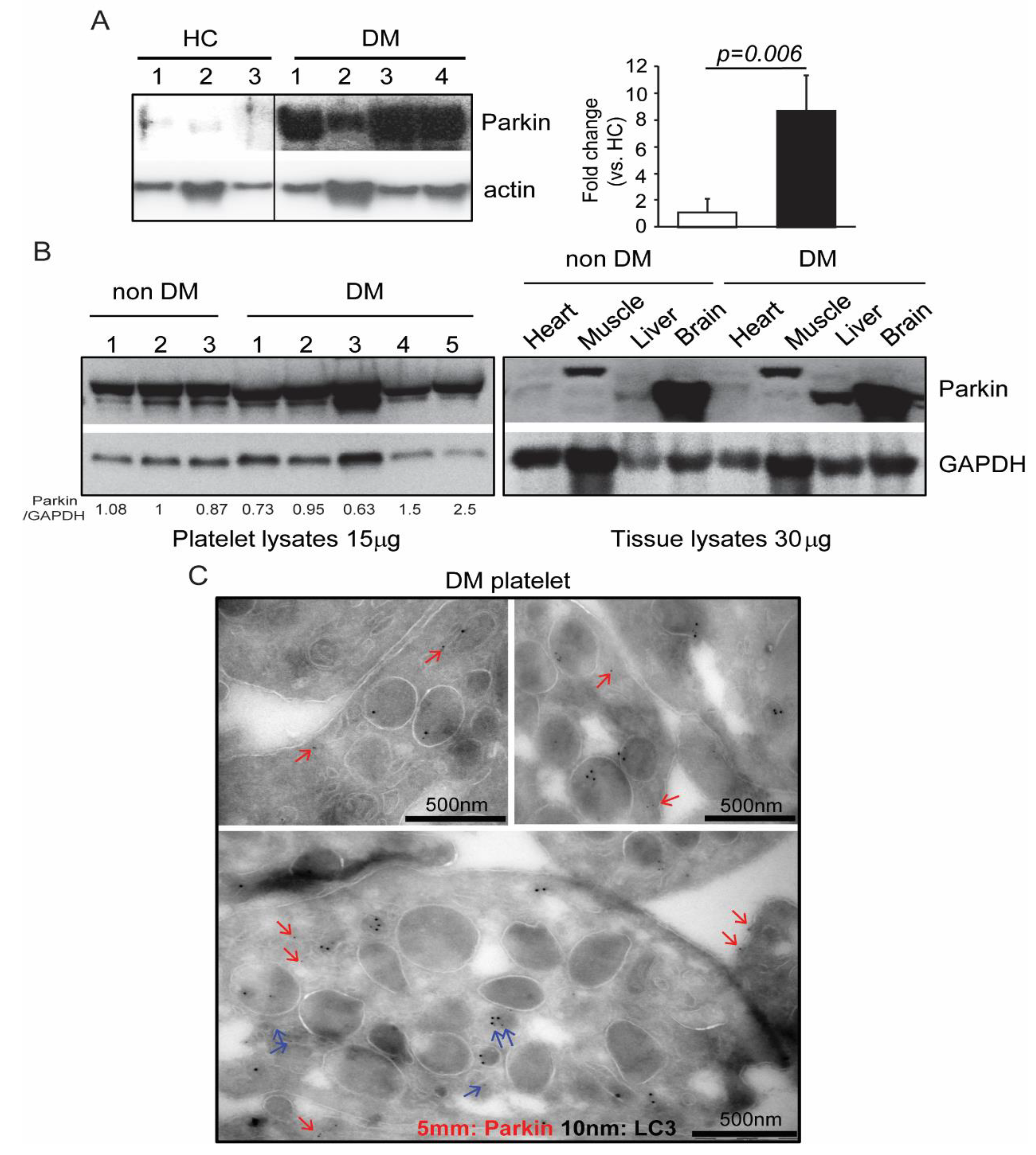


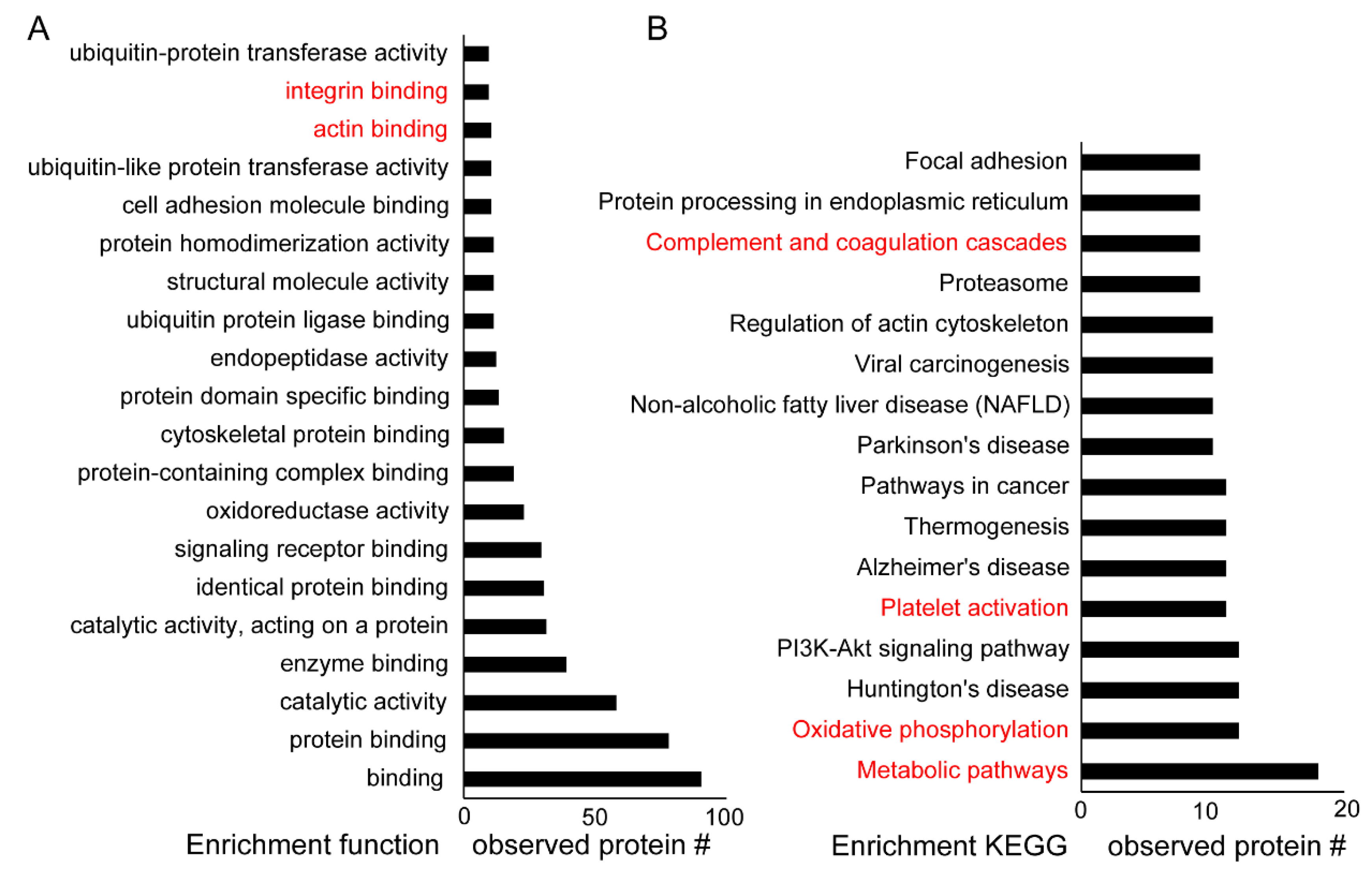


| Protein ID | Protein Name | MW (Da) | % Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIBG_HUMAN | Fibrinogen gamma chain OS = Homo sapiens GN = FGG PE = 1 SV = 3 | 51,479 | 78.8 |
| TERA_HUMAN | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase OS = Homo sapiens GN = VCP PE = 1 SV = 4 | 89,266 | 78.5 |
| FIBB_HUMAN | Fibrinogen beta chain OS = Homo sapiens GN = FGB PE = 1 SV = 2 | 55,892 | 75.4 |
| 1433Z_HUMAN | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta OS = Homo sapiens GN = YWHAZ PE = 1 SV = 1 | 27,728 | 74.7 |
| ARPC5_HUMAN | Actin-Related protein 2/3 complex subunit 5 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ARPC5 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 16,310 | 72.2 |
| 1433F_HUMAN | 14-3-3 protein eta OS = Homo sapiens GN=YWHAH PE = 1 SV = 4 | 28,201 | 69.1 |
| DYL1_HUMAN | Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic OS = Homo sapiens GN = DYNLL1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 10,359 | 64 |
| 1433B_HUMAN | 14-3-3 protein beta/alpha OS = Homo sapiens GN = YWHAB PE = 1 SV = 3 | 28,065 | 63 |
| GSTO1_HUMAN | Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 OS=Homo sapiens GN = GSTO1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 27,548 | 61.4 |
| TPM4_HUMAN | Tropomyosin alpha-4 chain OS=Homo sapiens GN = TPM4 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 28,504 | 60.1 |
| 1433E_HUMAN | 14-3-3 protein epsilon OS = Homo sapiens GN = YWHAE PE = 1 SV = 1 | 29,155 | 59.2 |
| TSP1_HUMAN | Thrombospondin-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = THBS1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 129,300 | 58.1 |
| FIBA_HUMAN | Fibrinogen alpha chain OS = Homo sapiens GN = FGA PE = 1 SV = 2 | 94,914 | 56.9 |
| URP2_HUMAN | Fermitin family homolog 3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = FERMT3 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 75,905 | 55.8 |
| PRDX6_HUMAN | Peroxiredoxin-6 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PRDX6 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 25,019 | 54 |
| CAP1_HUMAN | Adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 OS=Homo sapiens GN = CAP1 PE = 1 SV = 5 | 51,869 | 53.5 |
| S10A8_HUMAN | Protein S100-A8 OS = Homo sapiens GN = S100A8 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 10,828 | 52.7 |
| 1433T_HUMAN | 14-3-3 protein theta OS = Homo sapiens GN = YWHAQ PE = 1 SV = 1 | 27,747 | 51.4 |
| F13A_HUMAN | Coagulation factor XIII A chain OS = Homo sapiens GN = F13A1 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 83,215 | 51.2 |
| PDIA5_HUMAN | Protein disulfide-isomerase A5 OS=Homo sapiens GN = PDIA5 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 59,556 | 50.5 |
| PHB_HUMAN | Prohibitin OS = Homo sapiens GN = PHB PE = 1 SV = 1 | 29,786 | 50.4 |
| ILK_HUMAN | Integrin-linked protein kinase OS = Homo sapiens GN =I LK PE = 1 SV = 2 | 51,386 | 49.1 |
| MMRN1_HUMAN | Multimerin-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = MMRN1 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 138,023 | 48.4 |
| COF1_HUMAN | Cofilin-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = CFL1 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 18,491 | 47 |
| 1433G_HUMAN | 14-3-3 protein gamma OS = Homo sapiens GN = YWHAG PE = 1 SV = 2 | 28,285 | 47 |
| LTOR1_HUMAN | Ragulator complex protein LAMTOR1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = LAMTOR1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 17,734 | 45.3 |
| UB2V1_HUMAN | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 variant 1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBE2V1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 16,484 | 44.2 |
| CALR_HUMAN | Calreticulin OS = Homo sapiens GN = CALR PE = 1 SV = 1 | 48,112 | 43.9 |
| PLF4_HUMAN | Platelet factor 4 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PF4 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 10,838 | 43.6 |
| PDIA6_HUMAN | Protein disulfide-isomerase A6 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PDIA6 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 48,091 | 42 |
| ATP5I_HUMAN | ATP synthase subunit e, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = ATP5I PE = 1 SV = 2 | 7928 | 40.6 |
| EMIL1_HUMAN | EMILIN-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = EMILIN1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 106,601 | 40.4 |
| NDUA2_HUMAN | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = NDUFA2 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 10,915 | 40.4 |
| Protein ID | Protein Name | MW (Da) | % Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDE5A_HUMAN | cGMP-specific 3′,5′-cyclic phosphodiesterase OS = Homo sapiens GN = PDE5A PE = 1 SV = 2 | 99,921 | 38.7 |
| CXCL7_HUMAN | Platelet basic protein OS = Homo sapiens GN = PPBP PE = 1 SV = 3 | 13,885 | 38.3 |
| ATP5L_HUMAN | ATP synthase subunit g, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = ATP5L PE = 1 SV = 3 | 11,421 | 37.9 |
| S10A9_HUMAN | Protein S100-A9 OS = Homo sapiens GN = S100A9 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 13,234 | 37.7 |
| NDUA4_HUMAN | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit NDUFA4 OS = Homo sapiens GN = NDUFA4 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 9,364 | 37 |
| CALM_HUMAN | Calmodulin OS = Homo sapiens GN = CALM1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 16,827 | 36.9 |
| S10A4_HUMAN | Protein S100-A4 OS = Homo sapiens GN = S100A4 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 11,721 | 36.6 |
| MIC60_HUMAN | MICOS complex subunit MIC60 OS = Homo sapiens GN = IMMT PE = 1 SV = 1 | 83,626 | 35.6 |
| FINC_HUMAN | Fibronectin OS = Homo sapiens GN = FN1 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 262,460 | 34.5 |
| NEXN_HUMAN | Nexilin OS = Homo sapiens GN = NEXN PE = 1 SV = 1 | 80,609 | 34.5 |
| ITB3_HUMAN | Integrin beta-3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ITGB3 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 87,000 | 33.6 |
| PSA7_HUMAN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-7 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSMA7 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 27,870 | 33.1 |
| SAMP_HUMAN | Serum amyloid P-component OS = Homo sapiens GN = APCS PE = 1 SV = 2 | 25,371 | 32.7 |
| SKAP2_HUMAN | Src kinase-associated phosphoprotein 2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = SKAP2 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 41,191 | 32.3 |
| NUBP2_HUMAN | Cytosolic Fe-S cluster assembly factor NUBP2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = NUBP2 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 28,807 | 31.4 |
| SSBP_HUMAN | Single-Stranded DNA-binding protein, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = SSBP1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 17,249 | 31.1 |
| GPIX_HUMAN | Platelet glycoprotein IX OS = Homo sapiens GN = GP9 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 19,034 | 30.5 |
| A4_HUMAN | Amyloid beta A4 protein OS = Homo sapiens GN = APP PE = 1 SV = 3 | 86,888 | 30 |
| PSME2_HUMAN | Proteasome activator complex subunit 2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSME2 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 27,384 | 29.3 |
| CXCL7_HUMAN | Platelet basic protein OS = Homo sapiens GN = PPBP PE = 1 SV = 3 | 13,885 | 27.3 |
| KAD2_HUMAN | Adenylate kinase 2, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN = AK2 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 26,461 | 27.2 |
| UB2L3_HUMAN | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 L3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBE2L3 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 17,850 | 26.6 |
| KPYM_HUMAN | Pyruvate kinase PKM OS = Homo sapiens GN = PKM PE = 1 SV = 4 | 57,900 | 26.2 |
| DHB4_HUMAN | Peroxisomal multifunctional enzyme type 2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = HSD17B4 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 79,636 | 25.7 |
| NDUA7_HUMAN | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 7 OS =Homo sapiens GN = NDUFA7 PE =1 SV=3 | 12,544 | 25.7 |
| PSA3_HUMAN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSMA3 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 28,415 | 24.7 |
| PRDX1_HUMAN | Peroxiredoxin-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PRDX1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 22,096 | 23.6 |
| PLMN_HUMAN | Plasminogen OS = Homo sapiens GN = PLG PE = 1 SV = 2 | 90,510 | 23.5 |
| UBP5_HUMAN | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 5 OS = Homo sapiens GN = USP5 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 95,725 | 23.3 |
| HECD3_HUMAN | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HECTD3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = HECTD3 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 97,051 | 22.8 |
| CAN1_HUMAN | Calpain-1 catalytic subunit OS = Homo sapiens GN = CAPN1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 81,838 | 22.5 |
| RGS18_HUMAN | Regulator of G-protein signaling 18 OS = Homo sapiens GN = RGS18 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 27,565 | 22.1 |
| PSME1_HUMAN | Proteasome activator complex subunit 1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSME1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 28,705 | 22.1 |
| PDIA1_HUMAN | Protein disulfide-isomerase OS = Homo sapiens GN = P4HB PE = 1 SV = 3 | 57,081 | 22 |
| GPX1_HUMAN | Glutathione peroxidase 1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = GPX1 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 22,075 | 21.7 |
| PDIA3_HUMAN | Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PDIA3 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 56,747 | 21 |
| VWF_HUMAN | von Willebrand factor OS = Homo sapiens GN = VWF PE = 1 SV = 4 | 309,058 | 20.1 |
| Protein ID | Protein Name | MW (Da) | % Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAC1_HUMAN | Ras-Related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = RAC1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 21,436 | 19.8 |
| KAP0_HUMAN | cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit OS = Homo sapiens GN = PRKAR1A PE = 1 SV = 1 | 42,955 | 19.4 |
| PSA4_HUMAN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-4 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSMA4 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 29,465 | 19.2 |
| FA5_HUMAN | Coagulation factor V OS = Homo sapiens GN = F5 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 251,546 | 17.9 |
| NDUAC_HUMAN | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone)1 alpha subcomplex subunit 12 OS =Homo sapiensGN = NDUFA12 PE =1 SV=1 | 17,104 | 17.9 |
| VATG1_HUMAN | V-type proton ATPase subunit G 1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ATP6V1G1 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 13,749 | 16.9 |
| S10A6_HUMAN | Protein S100-A6 OS = Homo sapiens GN = S100A6 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 10,173 | 16.7 |
| EMRE_HUMAN | Essential MCU regulator, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = SMDT1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 11,434 | 15.9 |
| ACO13_HUMAN | Acyl-Coenzyme A thioesterase 13 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ACOT13 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 14,951 | 15.7 |
| UBL4A_HUMAN | Ubiquitin-Like protein 4A OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBL4A PE = 1 SV = 1 | 17,766 | 15.3 |
| IMB1_HUMAN | Importin subunit beta-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = KPNB1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 97,108 | 15.1 |
| STAT3_HUMAN | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = STAT3 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 88,011 | 13.6 |
| ATP8_HUMAN | ATP synthase protein 8 OS = Homo sapiens GN = MT-ATP8 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 7986 | 13.2 |
| RBX1_HUMAN | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = RBX1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 12,266 | 13 |
| THIO_HUMAN | Thioredoxin OS = Homo sapiens GN = TXN PE = 1 SV = 3 | 11,730 | 12.4 |
| TGFB1_HUMAN | Transforming growth factor beta-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = TGFB1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 44,313 | 12.1 |
| ROCK2_HUMAN | Rho-Associated protein kinase 2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ROCK2 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 16,0799 | 12 |
| S10A9_HUMAN | Protein S100-A9 OS = Homo sapiens GN = S100A9 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 13,234 | 11.4 |
| QCR9_HUMAN | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 9 OS = Homo sapiens GN = UQCR10 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 7304 | 11.1 |
| PSB7_HUMAN | Proteasome subunit beta type-7 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSMB7 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 29,946 | 10.8 |
| TGFI1_HUMAN | Transforming growth factor beta-1-induced transcript 1 protein OS = Homo sapiens GN = TGFB1I1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 49,782 | 10.6 |
| GLRX1_HUMAN | Glutaredoxin-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = GLRX PE = 1 SV = 2 | 11,768 | 10.4 |
| ANT3_HUMAN | Antithrombin-III OS = Homo sapiens GN = SERPINC1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 52,569 | 10.1 |
| UB2L6_HUMAN | Ubiquitin/ISG15-Conjugating enzyme E2 L6 OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBE2L6 PE = 1 SV = 4 | 17,757 | 9.8 |
| UFM1_HUMAN | Ubiquitin-Fold modifier 1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = UFM1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 9112 | 9.4 |
| MGST3_HUMAN | Microsomal glutathione S-transferase 3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = MGST3 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 16,506 | 9.2 |
| ECHA_HUMAN | Trifunctional enzyme subunit alpha, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = HADHA PE = 1 SV = 2 | 82,947 | 9 |
| ECHB_HUMAN | Trifunctional enzyme subunit beta, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = HADHB PE = 1 SV = 3 | 51,262 | 8.9 |
| PSA5_HUMAN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSMA5 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 26,394 | 8.7 |
| PSA2_HUMAN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PSMA2 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 25,882 | 8.1 |
| DNJA2_HUMAN | DnaJ homolog subfamily A member 2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = DNAJA2 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 45,717 | 8 |
| SODC_HUMAN | Superoxide dismutase (Cu–Zn) OS = Homo sapiens GN = SOD1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 15,926 | 7.8 |
| UB2D2_HUMAN | Ubiquitin-Conjugating enzyme E2 D2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBE2D2 PE = 1 SV = 1indistinguishable | 16,724 | 7.5 |
| UBE2N_HUMAN | Ubiquitin-Conjugating enzyme E2 N OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBE2N PE = 1 SV = 1indistinguishable | 17,127 | 7.2 |
| GSTM3_HUMAN | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 3 OS = Homo sapiens GN = GSTM3 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 26,542 | 7.1 |
| CH10_HUMAN | 10 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = HSPE1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 10,925 | 6.9 |
| UBE2O_HUMAN | (E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBE2O PE = 1 SV = 3 | 141,205 | 6.9 |
| NDUS5_HUMAN | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) iron–sulfur protein 5 OS = Homo sapiens GN = NDUFS5 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 12,509 | 6.6 |
| TIM16_HUMAN | Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit TIM16 OS = Homo sapiens GN = PAM16 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 13,816 | 6.4 |
| COX5B_HUMAN | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5B, mitochondrial OS=Homo sapiens GN=COX5B PE=1 SV=2 | 13,687 | 6.2 |
| CD36_HUMAN | Platelet glycoprotein 4 OS = Homo sapiens GN = CD36 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 53,019 | 5.3 |
| COX41_HUMAN | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 1, mitochondrial OS = Homo sapiens GN = COX4I1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 19,564 | 4.7 |
| AN32B_HUMAN | Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member B OS = Homo sapiens GN = ANP32B PE = 1 SV = 1 | 28,770 | 4.4 |
| TXND9_HUMAN | Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 9 OS = Homo sapiens GN = TXNDC9 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 26,517 | 4 |
| ITB1_HUMAN | Integrin beta-1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ITGB1 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 88,357 | 3.9 |
| ROCK1_HUMAN | Rho-Associated protein kinase 1 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ROCK1 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 158,076 | 3.8 |
| GRCR2_HUMAN | Glutaredoxin domain-containing cysteine-rich protein 2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = GRXCR2 PE = 3 SV = 1 | 28,266 | 3.6 |
| CATA_HUMAN | Catalase OS = Homo sapiens GN = CAT PE = 1 SV = 3 | 59,719 | 3.6 |
| VPS35_HUMAN | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 35 OS = Homo sapiens GN = VPS35 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 91,649 | 3.6 |
| ITA2B_HUMAN | Integrin alpha-IIb OS = Homo sapiens GN = ITGA2B PE = 1 SV = 3 | 113,306 | 2.9 |
| ANGL5_HUMAN | Angiopoietin-rrelated protein 5 OS = Homo sapiens GN = ANGPTL5 PE = 2 SV = 3 | 44,115 | 2.6 |
| FA10_HUMAN | Coagulation factor X OS = Homo sapiens GN = F10 PE = 1 SV = 2 | 54,697 | 1.4 |
| UBP8_HUMAN | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 8 OS = Homo sapiens GN = USP8 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 127,444 | 1 |
| UBR4_HUMAN | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR4 OS = Homo sapiens GN = UBR4 PE = 1 SV = 1 | 573,476 | 0.9 |
| HD_HUMAN | Huntingtin OS = Homo sapiens GN = HTT PE = 1 SV = 2 | 347,383 | 0.7 |
| MYCB2_HUMAN | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MYCBP2 OS = Homo sapiens GN = MYCBP2 PE = 1 SV = 3 | 509,759 | 0.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.H.; Du, J.; Hwa, J.; Kim, W.-H. Parkin Coordinates Platelet Stress Response in Diabetes Mellitus: A Big Role in a Small Cell. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165869
Lee SH, Du J, Hwa J, Kim W-H. Parkin Coordinates Platelet Stress Response in Diabetes Mellitus: A Big Role in a Small Cell. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(16):5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165869
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung Hee, Jing Du, John Hwa, and Won-Ho Kim. 2020. "Parkin Coordinates Platelet Stress Response in Diabetes Mellitus: A Big Role in a Small Cell" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 16: 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165869
APA StyleLee, S. H., Du, J., Hwa, J., & Kim, W.-H. (2020). Parkin Coordinates Platelet Stress Response in Diabetes Mellitus: A Big Role in a Small Cell. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(16), 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165869




