P2X7 Receptors Amplify CNS Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
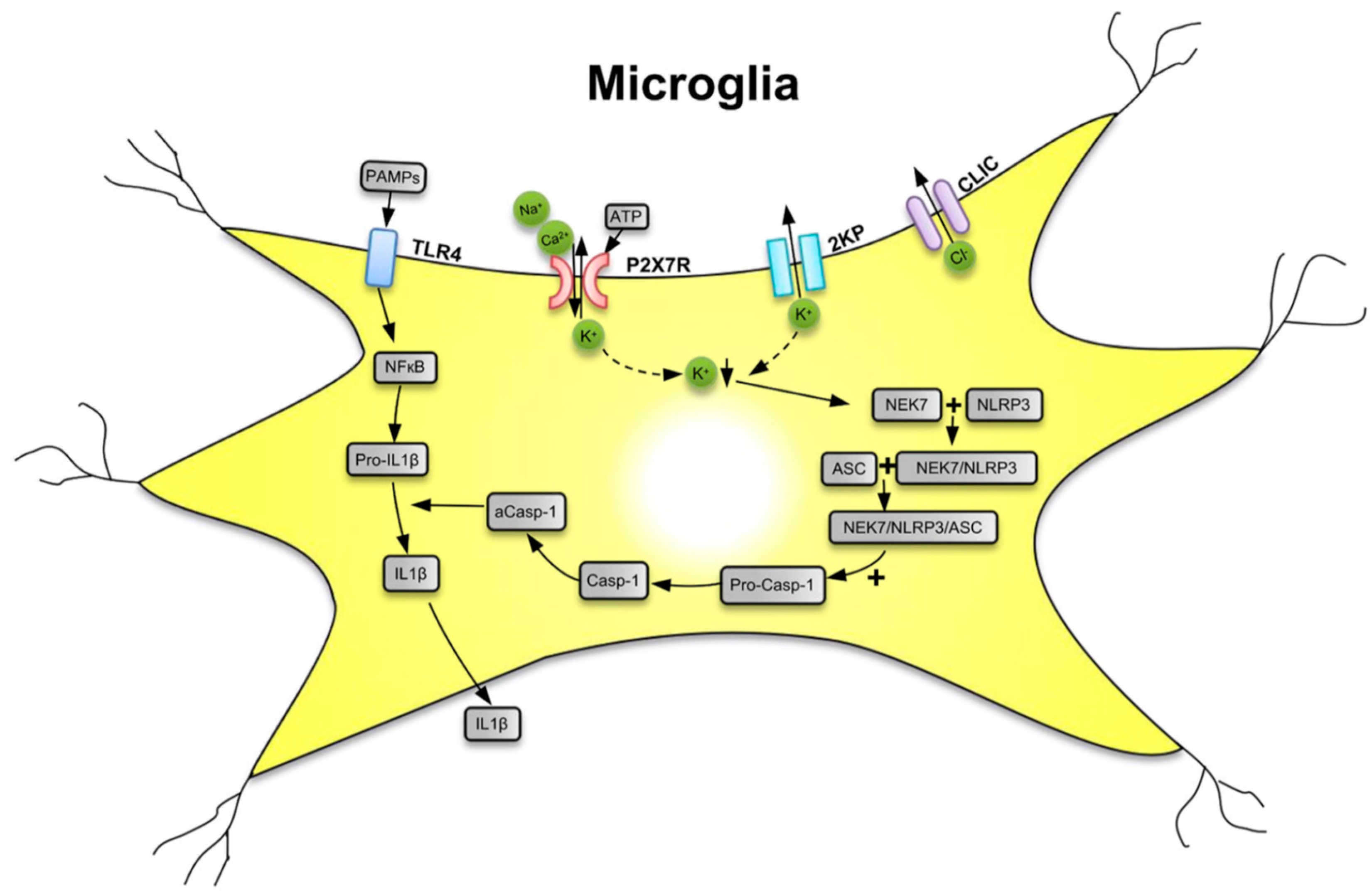
2. Purinergic P2X7 Receptors
3. Mechanical Damage to the CNS
4. Ischemic Damage to the CNS
5. Epilepsy
6. Chronic Pain
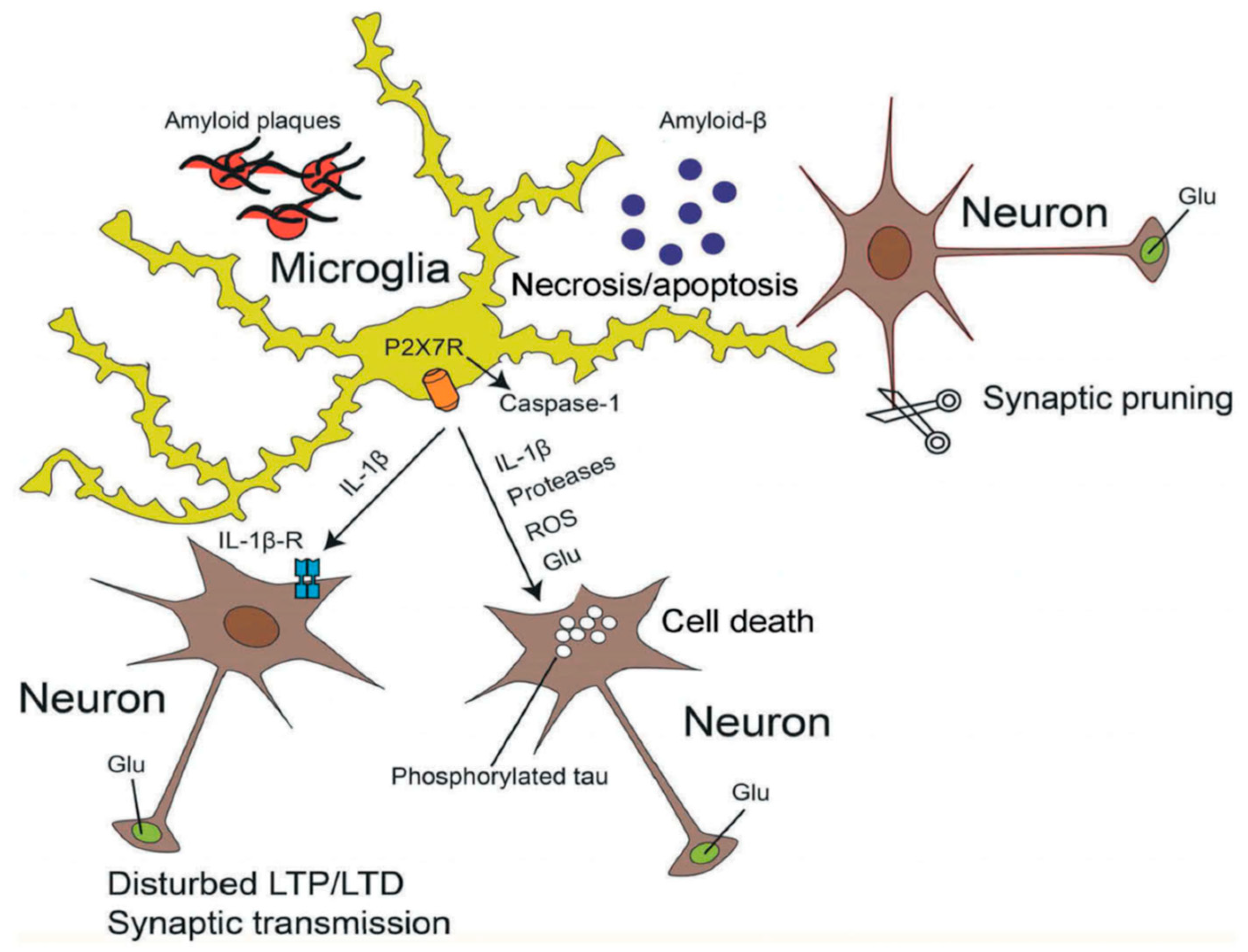
7. Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
8. Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
9. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
10. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
11. P2X7 Receptor Antagonists as Possible Pharmacological Tools to Treat Neurodegenerative Diseases
12. Transgenic P2X7 Mice as Experimental Tools for the Investigation of P2X7R Participation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
13. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BBB | blood brain barrier |
| BBG | Brilliant Blue G |
| Bz-ATP | Dibenzoyl-ATP |
| DAMPs | danger-associated molecular patterns |
| EGFP | enhanced green fluorescence protein |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| i.c.v. | intracerebroventricular |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IR | immunoreactivity |
| KO | knockout |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MCAO | medial cerebral artery occlusion |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NLRP3 | nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat pyrin domain containing 3 |
| NTPDases | ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolases |
| OGD | oxygen-glucose deficiency |
| oxATP | oxidized ATP |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecules |
| Panx-1 | pannexin-1 |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| R | receptor |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SE | status epilepticus |
| SOD-1 | superoxide dismutase 1 |
| Tg | transgenic |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling |
| α,β-meATP | α,β-methylene ATP |
References
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol. Rev. 1972, 24, 509–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnstock, G. Do some nerve cells release more than one transmitter? Neuroscience 1976, 1, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Knight, G.E. Cellular Distribution and Functions of P2 Receptor Subtypes in Different Systems. Adv. Virus Res. 2004, 240, 31–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Kennedy, C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1985, 16, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, R.A. Molecular Physiology of P2X Receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 1013–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbracchio, M.P.; Burnstock, G.; Boeynaems, J.-M.; Barnard, E.A.; Boyer, J.L.; Kennedy, C.; Knight, G.E.; Fumagalli, M.; Gachet, C.; Jacobson, K.A.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: Update on the P2Y G Protein-Coupled Nucleotide Receptors: From Molecular Mechanisms and Pathophysiology to Therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 281–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Linden, J.; Müller, C.E. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors—An update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Krügel, U.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Illes, P. Purinergic signalling: From normal behaviour to pathological brain function. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 95, 229–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic Signalling and Neurological Diseases: An Update. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surprenant, A.; Rassendren, F.; Kawashima, E.; North, R.A.; Buell, G.; Muragaki, Y.; Mundlos, S.; Upton, J.; Olsen, B.R. The Cytolytic P2Z Receptor for Extracellular ATP Identified as a P2X Receptor (P2X7). Science 1996, 272, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Cotransmission. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, G.E.; Egan, T.M.; Voigt, M.M. Hetero-oligomeric assembly of P2X receptor subunits. Specificities exist with regard to possible partners. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6653–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicke, A. Homotrimeric complexes are the dominant assembly state of native P2X7 subunits. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habermacher, C.; Dunning, K.; Chataigneau, T.; Grutter, T. Molecular structure and function of P2X receptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 104, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.E.; Yoshioka, C.; Mansoor, S.E. Full-Length P2X7 Structures Reveal How Palmitoylation Prevents Channel Desensitization. Cell 2019, 179, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheewatrakoolpong, B.; Gilchrest, H.; Anthes, J.C.; Greenfeder, S. Identification and characterization of splice variants of the human P2X7 ATP channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicke, A.; Kuan, Y.-H.; Masin, M.; Rettinger, J.; Marquez-Klaka, B.; Bender, O.; Górecki, D.C.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.D.; Soto, F. A Functional P2X7 Splice Variant with an Alternative Transmembrane Domain 1 Escapes Gene Inactivation in P2X7 Knock-out Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25813–25822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluyter, R. The P2X7 Receptor. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1051, 17–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Samways, D.S.K.; Wolf, K.J.; Bowles, E.A.; Richards, J.P.; Bruno, J.; Dutertre, S.; DiPaolo, R.J.; Egan, T.M. Quantifying Ca2+Current and Permeability in ATP-gated P2X7 Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 7930–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virginio, C.; MacKenzie, A.; Rassendren, F.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Pore dilation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Bao, X.R.; Labarca, C.; Lester, H.A. Neuronal P2X transmitter-gated cation channels change their ion selectivity in seconds. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. The Elusive P2X7 Macropore. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Junior, H.M.; Sarmento, V.F.; Coutinho-Silva, R. C terminus of the P2X7 receptor: Treasure hunting. Purinergic Signal. 2011, 7, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peverini, L.; Beudez, J.; Dunning, K.; Chataigneau, T.; Grutter, T. New Insights Into Permeation of Large Cations Through ATP-Gated P2X Receptors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Toombes, G.E.; Silberberg, S.D.; Swartz, K.J. Physical basis of apparent pore dilation of ATP-activated P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkat, M.; Peverini, L.; Cerdan, A.H.; Dunning, K.; Beudez, J.; Martz, A.; Calimet, N.; Specht, A.; Cecchini, M. On the permeation of large organic cations through the pore of ATP-gated P2X receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3786–E3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, A.; Michalski, K.; Mikhelzon, P.; Kawate, T. The P2X7 receptor forms a dye-permeable pore independent of its intracellular domain but dependent on membrane lipid composition. eLife 2017, 6, e31186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Dal Ben, D.; Sarti, A.C.; Giuliani, A.L.; Falzoni, S. The P2X7 Receptor in Infection and Inflammation. Immunity 2017, 47, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Jones, D.N.C. Emerging role of the P2X7-NLRP3-IL1β pathway in mood disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 98, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.M. ATP: A ubiquitous gliotransmitter integrating neuron-glial networks. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Verkhratsky, A.; Burnstock, G.; Franke, H. P2X receptors and their roles in astroglia in the central and peripheral nervous system. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek-Hajek, K.; Zhang, J.; Kopp, R.; Grosche, A.; Rissiek, B.; Saul, A.; Bruzzne, S.; Engel, T.; Jooss, T.; Krautloher, A.; et al. Re-evaluation of neuronal P2X7 expression using novel mouse models and a P2X7-specific nanobody. eLife 2018, 7, e36217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.N.J.; Gorecki, D.C. P2RX7 Purinoceptor as a Therapeutic Target-The Second Coming? Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Rubini, P.; Ulrich, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y. Regulation of Microglial Functions by Purinergic Mechanisms in the Healthy and Diseased CNS. Cells 2020, 9, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.; Amar, M.; Dalle, C.; Youssef, I.; Boucher, C.; Le Duigou, C.; Brückner, M.; Prigent, A.; Sazdovitch, V.; Halle, A.; et al. New role of P2X7 receptor in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustin, A.; Kirchmeyer, M.; Koncina, E.; Felten, P.; Losciuto, S.; Heurtaux, T.; Tardivel, A.; Heuschling, P.; Dostert, C. NLRP3 Inflammasome Is Expressed and Functional in Mouse Brain Microglia but Not in Astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illes, P.; Verkhratsky, A.; Tang, Y. Pathological ATPergic Signaling in Major Depression and Bipolar Disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, U.-K.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia: Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, P.; Attwell, D.; Madry, C. Ion Channels and Receptors as Determinants of Microglial Function. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kigerl, K.A.; Gensel, J.C.; Ankeny, D.P.; Alexander, J.K.; Donnelly, D.J.; Popovich, P.G. Identification of two distinct macrophage subsets with divergent effects causing either neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 13435–13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenmann, H.; Kirchhoff, F.; Verkhratsky, A. Microglia: New roles for the synaptic stripper. Neuron 2013, 77, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, C.; Napoli, G.; Pelegrín, P.; Volonté, C. M1 and M2 Functional Imprinting of Primary Microglia: Role of P2X7 Activation and miR-125b. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 2989548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.M.; Colonna, M. The identity and function of microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.-H.; Roger, S. Targeting the P2X7 receptor in microglial cells to prevent brain inflammation. Neural Regen Res. 2020, 15, 1245–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Chiozzi, P.; Falzoni, S.; Ferrari, D.; Sanz, J.M.; Venketaraman, V.; Baricordi, O.R. Cytolytic P2X purinoceptors. Cell Death Differ. 1998, 5, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, L.E.B.; de Andrade, M.P.; da Silva, C.G.; Coutinho-Silva, R. The P2X7 Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: Angel or Demon? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, R.; Krautloher, A.; Ramírez-Fernández, A.; Nicke, A. P2X7 Interactions and Signaling—Making Head or Tail of It. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Ceruti, S.; Colombo, A.; Fumagalli, M.; Ferrari, D.; Pizzirani, C.; Matteoli, M.; Di Virgilio, F.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Verderio, C. A role for P2X7 in microglial proliferation. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monif, M.; Reid, C.A.; Powell, K.L.; Smart, M.L.; Williams, D.A. The P2X7 receptor drives microglial activation and proliferation: A trophic role for P2X7R pore. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3781–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, E.; De Marchi, E.; Orioli, E.; Pegoraro, A.; Di Virgilio, F. Role of the P2X7 receptor in tumor-associated inflammation. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Khan, T.M.; Rubini, P. Neuronal P2X7 Receptors Revisited: Do They Really Exist? J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 7049–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Sebastián-Serrano, Á.; García, L.D.D.; Diaz-Hernandez, M. Neuronal P2X7 Receptor: Involvement in Neuronal Physiology and Pathology. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 7063–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.M.; Nedergaard, M. Emerging challenges of assigning P2X7 receptor function and immunoreactivity in neurons. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.A.; Young, M.T.; Sung, H.-Y.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Reanalysis of P2X7 receptor expression in rodent brain. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6307–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubini, P.; Pagel, G.; Mehri, S.; Marquardt, P.; Riedel, T.; Illes, P. Functional P2X7 receptors at cultured hippocampal astrocytes but not neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2014, 387, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficker, C.; Rozmer, K.; Kató, E.; Andó, R.D.; Schumann, L.; Krügel, U.; Franke, H.; Sperlágh, B.; Riedel, T.; Illes, P. Astrocyte-neuron interaction in the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord dorsal horn via P2X7 receptor-mediated release of glutamate and reactive oxygen species. Glia 2014, 62, 1671–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Deussing, J.M.; Tang, Y.; Illes, P. Astrocytic rather than neuronal P2X7 receptors modulate the function of the tri-synaptic network in the rodent hippocampus. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 151, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Burnstock, G.; Tang, Y. Astroglia-Derived ATP Modulates CNS Neuronal Circuits. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Arcuino, G.; Takano, T.; Lin, J.; Peng, W.G.; Wan, P.; Li, P.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Q.S.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. P2X7 receptor inhibition improves recovery after spinal cord injury. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Cotrina, M.L.; Han, X.; Yu, H.; Bekar, L.K.; Blum, L.; Takano, T.; Tian, G.-F.; Goldman, S.A.; Nedergaard, M. Systemic administration of an antagonist of the ATP-sensitive receptor P2X7 improves recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12489–12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcillo, A.; Frydel, B.; Bramlett, H.M.; Dietrich, W.D. A reassessment of P2X7 receptor inhibition as a neuroprotective strategy in rat models of contusion injury. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zimmermann, H.; Zebisch, M.; Sträter, N. Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 437–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegutkin, G.G. Enzymes involved in metabolism of extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides: Functional implications and measurement of activities. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljkovic, N.; Bjelobaba, I.; Subasic, S.; Lavrnja, I.; Pekovic, S.; Stojkov, D.; Vjestica, A.; Rakić, L.; Stojiljković, M. Up-regulation of ectonucleotidase activity after cortical stab injury in rats. Cell Biol. Int. 2006, 30, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, C.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Brilliant Blue G Inhibits Inflammasome Activation and Reduces Disruption of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Induced by Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 6359–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ji, R.; Zhu, J.; Sui, Q.-Q.; Knight, G.E.; Burnstock, G.; He, C.; Yuan, H.-B.; Xiang, Z.-H. Inhibition of P2X7 receptors improves outcomes after traumatic brain injury in rats. Purinergic Signal. 2017, 13, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlBalawi, F.; Lu, W.; Beckel, J.M.; Lim, J.C.; McCaughey, S.A.; Mitchell, C.H. The P2X7 Receptor Primes IL-1β and the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Astrocytes Exposed to Mechanical Strain. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal-Nicolás, F.M.; Galindo-Romero, C.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Barberà-Cremades, M.; Detorre-Minguela, C.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Pelegrín, P.; Agudo-Barriuso, M. Involvement of P2X7 receptor in neuronal degeneration triggered by traumatic injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, H.; Günther, A.; Grosche, J.; Schmidt, R.; Rossner, S.; Reinhardt, R.; Faber-Zuschratter, H.; Schneider, D.; Illes, P. P2X7 receptor expression after ischemia in the cerebral cortex of rats. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmer, A.; Günther, A.; Beck, A.; Krügel, U.; Kittner, H.; Schneider, D.; Illes, P.; Franke, H. Neuroprotective effects of the P2 receptor antagonist PPADS on focal cerebral ischaemia-induced injury in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 2824–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeloa, J.; Pérez-Samartín, A.; Gottlieb, M.; Matute, C. P2X7 receptor blockade prevents ATP excitotoxicity in neurons and reduces brain damage after ischemia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.; Yin, B.; Wang, J.; Peng, G.; Liang, H.; Xu, Z.; Du, Y.; Fang, M.; Xia, Q.; Luo, B. Inhibition of P2X7 receptor ameliorates transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating inflammatory responses in the rat hippocampus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, Q.; He, C.; Burnstock, G.; Yuan, H.-B.; Xiang, Z.-H. Block of P2X7 receptors could partly reverse the delayed neuronal death in area CA1 of the hippocampus after transient global cerebral ischemia. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.-Y.; Li, A.-P. P2X7 receptors in cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Bull. 2013, 29, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichsenring, A.; Riedel, T.; Qin, Y.; Rubini, P.; Illes, P. Anoxic depolarization of hippocampal astrocytes: Possible modulation by P2X7 receptors. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melani, A.; Amadio, S.; Gianfriddo, M.; Vannucchi, M.G.; Volonté, C.; Bernardi, G.; Pedata, F.; Sancesario, G. P2X7Receptor Modulation on Microglial Cells and Reduction of Brain Infarct Caused by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 26, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyo, U.; Miner, S.A.; Ahlers, K.E.; Wu, L.-J.; Dailey, M.E. P2X7 receptor activation regulates microglial cell death during oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neuropharmacology 2013, 73, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlágh, B.; Zsilla, G.; Baranyi, M.; Illes, P.; Vizi, E. Purinergic modulation of glutamate release under ischemic-like conditions in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirkner, K.; Köfalvi, A.; Fischer, W.; Günther, A.; Franke, H.; Gröger-Arndt, H.; Nörenberg, W.; Madarász, E.; Vizi, E.S.; Schneider, D.; et al. Supersensitivity of P2X7 receptors in cerebrocortical cell cultures after in vitro ischemia. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Koizumi, S. Astrocytes and ischemic tolerance. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 126, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Koizumi, S. Hypoxia-independent mechanisms of HIF-1α expression in astrocytes after ischemic preconditioning. Glia 2017, 65, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindra, C.S.; Jaggi, A.S.; Singh, N. Role of P2X7 purinoceptors in neuroprotective mechanism of ischemic postconditioning in mice. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 390, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros-Mejorado, A.; Gottlieb, M.; Cavaliere, F.; Magnus, T.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Scemes, E.; Pérez-Samartín, A.; Matute, C. Blockade of P2X7 receptors or pannexin-1 channels similarly attenuates postischemic damage. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 35, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.J.; Zhou, N.; MacVicar, B.A. Ischemia Opens Neuronal Gap Junction Hemichannels. Science 2006, 312, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Locovei, S.; Dahl, G. Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP. FEBS Lett. 2004, 572, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madry, C.; Haglerød, C.; Attwell, D. The role of pannexin hemichannels in the anoxic depolarization of hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain 2010, 133, 3755–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-E.; Kwak, S.-E.; Jo, S.-M.; Kang, T.-C. Blockade of P2X receptor prevents astroglial death in the dentate gyrus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Pacheco, A.; Mesuret, G.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Tanaka, K.; Mooney, C.; Conroy, R.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Henshall, D.C.; Engel, T. Increased neocortical expression of the P2X7 receptor after status epilepticus and anticonvulsant effect of P2X7 receptor antagonist A-438079. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Deng, X. Increased expression of the P2X7 receptor in temporal lobe epilepsy: Animal models and clinical evidence. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 5433–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Lang, B.; Aronica, E. Immunity and Inflammation in Epilepsy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 6, a022699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamer, E.; Fischer, W.; Engel, T. The ATP-Gated P2X7 Receptor As a Target for the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, N.; Sévigny, J.; Robson, S.C.; Enjyoji, K.; Guckelberger, O.; Hammer, K.; Di Virgilio, F.; Zimmermann, H. Assignment of ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1/cd39 expression to microglia and vasculature of the brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 4357–4366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lanser, A.J.; Rezende, R.M.; Rubino, S.; Lorello, P.J.; Donnelly, D.J.; Xu, H.; Lau, L.A.; Dulla, C.G.; Caldarone, B.J.; Robson, S.C.; et al. Disruption of the ATP/adenosine balance in CD39(−/−) mice is associated with handling-induced seizures. Immunology 2017, 152, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doná, F.; Ulrich, H.; Persike, D.S.; Conceição, I.M.; Blini, J.P.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Fernandes, M.J.D.S. Alteration of purinergic P2X4 and P2X7 receptor expression in rats with temporal-lobe epilepsy induced by pilocarpine. Epilepsy Res. 2009, 83, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beamer, E.; Conte, G.; Engel, T. ATP release during seizures—A critical evaluation of the evidence. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 151, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, A.J.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Arribas-Blázquez, M.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Olivos-Oré, L.A.; Artalejo, A.R.; Alves, M.; Letavic, M.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Conroy, R.; et al. Transient P2X7 Receptor Antagonism Produces Lasting Reductions in Spontaneous Seizures and Gliosis in Experimental Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5920–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deussing, J.M.; Arzt, E. P2X7 Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Depression? Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmann, L.; Levavasseur, F.; Avignone, E.; Peyroutou, R.; Hirbec, H.; Audinat, E.; Rassendren, F. Involvement of P2X4 receptors in hippocampal microglial activation after status epilepticus. Glia 2013, 61, 1306–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Franke, H.; Krügel, U.; Muller, H.; Dinkel, K.; Lord, B.; Letavic, M.A.; Henshall, D.C.; Engel, T. Critical Evaluation of P2X7 Receptor Antagonists in Selected Seizure Models. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-E.; Kang, T.-C. The P2X7 receptor-pannexin-1 complex decreases muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated seizure susceptibility in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieoczym, D.; Socała, K.; Wlaź, P. Evaluation of the Anticonvulsant Effect of Brilliant Blue G, a Selective P2X7 Receptor Antagonist, in the iv PTZ-, Maximal Electroshock-, and 6 Hz-Induced Seizure Tests in Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3114–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; Engel, T.; Quinlan, S.; Reschke, C.R.; Conroy, R.; Bhattacharya, A.; Boylan, G.; Henshall, D.C. Effects of P2X7 receptor antagonists on hypoxia-induced neonatal seizures in mice. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesuret, G.; Engel, T.; Hessel, E.V.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Jimenez-Pacheco, A.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Henshall, D.C. P2X7 Receptor Inhibition Interrupts the Progression of Seizures in Immature Rats and Reduces Hippocampal Damage. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.-F.; Azmi, H.; Takano, T.; Xu, Q.; Peng, W.; Lin, J.; Oberheim, N.; Lou, N.; Wang, X.; Zielke, H.R.; et al. An astrocytic basis of epilepsy. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, L.-P.; Ase, A.R.; Seguela, P. P2X receptor channels in chronic pain pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozmer, K.; Gao, P.; Araújo, M.G.; Khan, M.T.; Liu, J.; Rong, W.; Tang, Y.; Franke, H.; Krügel, U.; Fernandes, M.J.D.S.; et al. Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus Increases the Sensitivity of P2X7 and P2Y1 Receptors to Nucleotides at Neural Progenitor Cells of the Juvenile Rodent Hippocampus. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 27, bhw178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Illes, P. Regulation of adult neural progenitor cell functions by purinergic signaling. Glia 2016, 65, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Liu, J.; Nerlich, J.; Tang, Y.; Franke, H.; Illes, P. Regulation of P2X7 receptor function of neural progenitor cells in the hippocampal subgranular zone by neuronal activity in the dentate gyrus. Neuropharmacology 2018, 140, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlágh, B.; Illes, P. P2X7 receptor: An emerging target in central nervous system diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, M.F. The neural–glial purinergic receptor ensemble in chronic pain states. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Inoue, K. Pain and purinergic signaling. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Neff, R.A.; Wickenden, A.D. The physiology, pharmacology and future of P2X7 as an analgesic drug target: Hype or promise? Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Shigemoto-Mogami, Y.; Koizumi, S.; Mizokoshi, A.; Kohsaka, S.; Salter, M.W.; Inoue, K. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 2003, 424, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coull, J.A.M.; Beggs, S.; Boudreau, M.; Boivin, D.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K.; Gravel, C.; Salter, M.W.; De Koninck, Y. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 2005, 438, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Antonio, G.; Quattrini, A.; Cin, E.D.; Fulgenzi, A.; Ferrero, M.E. Relief of inflammatory pain in rats by local use of the selective P2X7 ATP receptor inhibitor, oxidized ATP. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 3378–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chessell, I.P.; Hatcher, J.P.; Bountra, C.; Michel, A.D.; Hughes, J.P.; Green, P.; Egerton, J.; Murfin, M.; Richardson, J.; Peck, W.L.; et al. Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 2005, 114, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Takahashi, E.; Miyagawa, Y.; Yamanaka, H.; Noguchi, K. Induction of the P2X7 receptor in spinal microglia in a neuropathic pain model. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 504, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.K.; Staniland, A.A.; Marchand, F.; Kaan, T.K.Y.; McMahon, S.B.; Malcangio, M. P2X7-dependent release of interleukin-1beta and nociception in the spinal cord following lipopolysaccharide. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perregaux, D.G.; Gabel, C.A. Post-translational processing of murine IL-1: Evidence that ATP-induced release of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta occurs via a similar mechanism. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar]
- Honore, P.; Donnelly-Roberts, D.; Namovic, M.; Zhong, C.; Wade, C.; Chandran, P.; Zhu, C.; Carroll, W.; Perez-Medrano, A.; Iwakura, Y.; et al. The antihyperalgesic activity of a selective P2X7 receptor antagonist, A-839977, is lost in IL-1αβ knockout mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 204, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Pravettoni, E.; Colombo, A.; Schenk, U.; Möller, T.; Matteoli, M.; Verderio, C. Astrocyte-derived ATP induces vesicle shedding and IL-1βrelease from microglia. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7268–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, I.; Furlan, R.; Matteoli, M.; Verderio, C. Classical and unconventional pathways of vesicular release in microglia. Glia 2013, 61, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Yang, M.; Yang, R.; Burnstock, G.; Xiang, Z.-H.; Yuan, H.-B. Microvesicles shed from microglia activated by the P2X7-p38 pathway are involved in neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Purinergic Signal. 2016, 13, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, G.; Suekawa, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, K.; Inubushi, T.; Murasaki, K.; Hirose, N.; Hiyama, S.; Uchida, T.; Tanne, K. P2X7receptor in the trigeminal sensory nuclear complex contributes to tactile allodynia/hyperalgesia following trigeminal nerve injury. Eur. J. Pain 2012, 17, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, F.M.; Gao, R.; Tian, Y.; Henstenburg, B.A.; Barrett, J.E.; Hu, H. Neuronal P2X7 receptor-induced reactive oxygen species production contributes to nociceptive behavior in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.-M.; Sun, H.-P.; Xu, X.; Ling, B.-Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Cao, H.; Xu, L. Spinal P2X7R contributes to streptozotocin-induced mechanical allodynia in mice. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tao, J.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, C. Effects of LncRNA BC168687 siRNA on Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by P2X7 Receptor on SGCs in DRG of Rats. BioMed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, L.Y. Neuronal somatic ATP release triggers neuron-satellite glial cell communication in dorsal root ganglia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9864–9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, G.; Gu, Y.; Huang, L.Y. Activation of P2X7 receptors in glial satellite cells reduces pain through downregulation of P2X3 receptors in nociceptive neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16773–16778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, B.; Lu, N.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-Q. Involvement of spinal glia in tetanically sciatic stimulation-induced bilateral mechanical allodynia in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandkühler, J. Understanding LTP in pain pathways. Mol. Pain 2007, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-Q. Involvement of microglial P2X7 receptors and downstream signaling pathways in long-term potentiation of spinal nociceptive responses. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, M.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-Q. Involvement of Spinal Microglial P2X7 Receptor in Generation of Tolerance to Morphine Analgesia in Rats. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8042–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc-Pessah, H.; Weilinger, N.L.; Fan, C.Y.; Burma, N.E.; Thompson, R.J.; Trang, T. Site-Specific Regulation of P2X7 Receptor Function in Microglia Gates Morphine Analgesic Tolerance. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 10154–10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Cao, H.; Chu, Y.X.; Cheng, L.Z.; Liang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q. Role of P2X7 receptor-mediated IL-18/IL-18R signaling in morphine tolerance: Multiple glial-neuronal dialogues in the rat spinal cord. J. Pain 2012, 13, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, P.M.; Strand, K.A.; Galer, E.L.; Urban, D.J.; Wang, X.; Baratta, M.V.; Fabisiak, T.J.; Anderson, N.D.; Cheng, K.; Greene, L.I.; et al. Morphine paradoxically prolongs neuropathic pain in rats by amplifying spinal NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3441–E3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, P.M.; Strand, K.; Galer, E.L.; Rice, K.C.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Protraction of neuropathic pain by morphine is mediated by spinal damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in male rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 72, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, R.E.; Trang, T.; Dorfman, R.; Smith, S.B.; Beggs, S.; Ritchie, J.; Austin, J.-S.; Zaykin, D.V.; Meulen, H.V.; Costigan, M.; et al. Genetically determined P2X7 receptor pore formation regulates variability in chronic pain sensitivity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursu, D.; Ebert, P.J.; Langron, E.; Ruble, C.L.; Munsie, L.; Zou, W.; Fijal, B.; Qian, Y.-W.; McNearney, T.A.; Mogg, A.J.; et al. Gain and loss of function of P2X7 receptors: Mechanisms, pharmacology and relevance to diabetic neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, J.; Bodea, L.-G.; Goedert, M. Rodent models for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingo, T.S.; Lah, J.J.; Levey, A.I.; Cutler, D.J. Autosomal Recessive Causes Likely in Early-Onset Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacace, R.; Sleegers, K.; Van Broeckenhoven, C. Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.; Smailagic, N.; Brayne, C. Aβ and the dementia syndrome: Simple versus complex perspectives. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e13025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Rubini, P.; Huang, L.; Tang, Y. The P2X7 receptor: A new therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Stott, J.; Visser, S.A.G.; Bendtsen, C. Interplay between α-, β-, and γ-Secretases Determines Biphasic Amyloid-β Protein Level in the Presence of a γ-Secretase Inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 288, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillé, I.; Allinquant, B.; Dupont, E.; Bouillot, C.; Langer, A.; Müller, U.; Prochiantz, A. Soluble form of amyloid precursor protein regulates proliferation of progenitors in the adult subventricular zone. Development 2004, 131, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Beati, H.; Nilsson, J.; Wodarz, A. The Drosophila Microtubule-Associated Protein Mars Stabilizes Mitotic Spindles by Crosslinking Microtubules through Its N-Terminal Region. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; López-González, I.; Carmona, M.; Arregui, L.; Dalfó, E.; Torrejón-Escribano, B.; Diehl, R.; Kovacs, G.G. Glial and Neuronal Tau Pathology in Tauopathies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 73, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease as a target for therapy. Bratisl. Med. J. 2018, 119, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Wolfe, M.S. Presenilin: Running with Scissors in the Membrane. Cell 2007, 131, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, C.; Mayeux, R. Alzheimer disease: Epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeer, P.L.; McGeer, E.G. Local Neuroinflammation and the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurovirol. 2002, 8, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, B.; Landreth, G.E. Inflammation, microglia, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lue, L.-F.; Kuo, Y.-M.; Beach, T.; Walker, D.G. Microglia Activation and Anti-inflammatory Regulation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.K.; McLarnon, J.G. Block of purinergic P2X(7) receptor is neuroprotective in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 2008, 19, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, J.M.; Chiozzi, P.; Ferrari, D.; Colaianna, M.; Idzko, M.; Falzoni, S.; Fellin, R.; Trabace, L.; Di Virgilio, F. Activation of microglia by amyloid {beta} requires P2X7 receptor expression. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4378–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLarnon, J.G.; Ryu, J.K.; Walker, D.G.; Choi, H.B. Upregulated expression of purinergic P2X(7) receptor in Alzheimer disease and amyloid-beta peptide-treated microglia and in peptide-injected rat hippocampus. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianca, V.D.; Dusi, S.; Bianchini, E.; Prà, I.D.; Rossi, F. beta-amyloid activates the O-2 forming NADPH oxidase in microglia, monocytes, and neutrophils. A possible inflammatory mechanism of neuronal damage in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15493–15499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Liu, Y.; Cooper, C.; Liu, B.; Wilson, B.; Hong, J.-S. Microglia enhance β-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity in cortical and mesencephalic neurons by producing reactive oxygen species. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathenani, L.K.; Tertyshnikova, S.; Greco, C.R.; Roberts, S.B.; Robertson, B.; Posmantur, R. P2X7 mediates superoxide production in primary microglia and is up-regulated in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 13309–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, S.U.; Lee, Y.B. ATP released from β-amyloid-stimulated microglia induces reactive oxygen species production in an autocrine fashion. Exp. Mol. Med. 2007, 39, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.G.; Won, S.M.; Gwag, B.J.; Lee, Y.B. Microglial P2X7 receptor expression is accompanied by neuronal damage in the cerebral cortex of the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Frailes, C.; Di Lauro, C.; Bianchi, C.; De Diego-García, L.; Sebastián-Serrano, Á.; Boscá, L.; Díaz-Hernández, M. Amyloid Peptide Induced Neuroinflammation Increases the P2X7 Receptor Expression in Microglial Cells, Impacting on Its Functionality. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, J.M.; Falzoni, S.; Rizzo, R.; Cipollone, F.; Zuliani, G.; Di Virgilio, F. Possible protective role of the 489C>T P2X7R polymorphism in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 60, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delarasse, C.; Auger, R.; Gonnord, P.; Fontaine, B.; Kanellopoulos, J.M. The Purinergic Receptor P2X7 Triggers α-Secretase-dependent Processing of the Amyloid Precursor Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 286, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Otegui, M.; Gómez-Villafuertes, R.; Diaz-Hernandez, J.I.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Gualix, J. Opposite effects of P2X7 and P2Y2nucleotide receptors on α-secretase-dependent APP processing in Neuro-2a cells. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Hernandez, J.I.; Gomez-Villafuertes, R.; León-Otegui, M.; Hontecillas-Prieto, L.; del Puerto, A.; Trejo, J.L.; Lucas, J.J.; Garrido, J.J.; Gualix, J.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; et al. In vivo P2X7 inhibition reduces amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease through GSK3β and secretases. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Jiang, L.; Xu, S.; Zheng, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Chang, L.; Wang, Q. Brilliant Blue G improves cognition in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease and inhibits amyloid-β-induced loss of filopodia and dendrite spines in hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 2014, 279, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jin, M.; Koeglsperger, T.; Shepardson, N.E.; Shankar, G.M.; Selkoe, D.J. Soluble Aβ oligomers inhibit long-term potentiation through a mechanism involving excessive activation of extrasynaptic NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6627–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacor, P.N.; Buniel, M.C.; Furlow, P.W.; Clemente, A.S.; Velasco, P.T.; Wood, M.; Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. Aβ oligomer-induced aberrations in synapse composition, shape, and density provide a molecular basis for loss of connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lin, R.; Chang, L.; Xu, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Anwyl, R.; Wang, Q. Enhancement of long-term depression by soluble amyloid β protein in rat hippocampus is mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptor and involves activation of p38MAPK, STEP and caspase-3. Neuroscience 2013, 253, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facci, L.; Barbierato, M.; Zusso, M.; Skaper, S.D.; Giusti, P. Serum amyloid A primes microglia for ATP-dependent interleukin-1β release. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, L.; Ren, H.; Qian, M.; Du, B. Presenilin 2 deficiency facilitates Aβ-induced neuroinflammation and injury by upregulating P2X7 expression. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.-K.; Chao, Y.X.; West, A.; Chan, L.-L.; Poewe, W.; Jankovic, J. Parkinson disease and the immune system—Associations, mechanisms and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, Z.A.; Giasson, B.I. The emerging role of α-synuclein truncation in aggregation and disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betarbet, R.; Sherer, T.B.; Greenamyre, J.T. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Bioessays 2002, 24, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufekci, K.U.; Genc, S.; Genc, K. The Endotoxin-Induced Neuroinflammation Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Dis. 2011, 2011, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeer, P.L.; Itagaki, S.; Boyes, B.E.; McGeer, E.G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 1988, 38, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, M.; Harada, M.; Riederer, P.; Narabayashi, H.; Fujita, K.; Nagatsu, T. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) increases both in the brain and in the cerebrospinal fluid from parkinsonian patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 165, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum-Degen, D.; Müller, T.; Kuhn, W.; Gerlach, M.; Przuntek, H.; Riederer, P. Interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s and de novo Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 202, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatouk, L.; Yi, C.; Sauvage, M.-A.C.-D.; Compagnion, A.-C.; Hunot, S.; Ezan, P.; Hirsch, E.C.; Koulakoff, A.; Pfrieger, F.; Tronche, F.; et al. Glucocorticoid receptor in astrocytes regulates midbrain dopamine neurodegeneration through connexin hemichannel activity. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 26, 580–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, M.R.D.; Menezes, A.P.F.; Nunes, A.C.L.; Pliássova, A.; Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M.; Cunha, R.A.; Canas, P.M.; De Andrade, G.M. The P2X7 receptor antagonist Brilliant Blue G attenuates contralateral rotations in a rat model of Parkinsonism through a combined control of synaptotoxicity, neurotoxicity and gliosis. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrazoli, E.G.; de Souza, H.D.; Nascimento, I.C.; Oliveira-Giacomelli, A.; Schwindt, T.T.; Britto, L.R.; Ulrich, H. Brilliant Blue G, But Not Fenofibrate, Treatment Reverts Hemiparkinsonian Behavior and Restores Dopamine Levels in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabbé, M.; Van Der Perren, A.; Bollaerts, I.; Kounelis, S.; Baekelandt, V.; Bormans, G.; Casteels, C.; Moons, L.; Van Laere, K. Increased P2X7 Receptor Binding Is Associated With Neuroinflammation in Acute but Not Chronic Rodent Models for Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Giacomelli, Á.; Albino, C.M.; De Souza, H.D.N.; Corrêa-Velloso, J.; Santos, A.P.D.J.; Baranova, J.; Ulrich, H. P2Y6 and P2X7 Receptor Antagonism Exerts Neuroprotective/ Neuroregenerative Effects in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mishra, A.; Krishnamurthy, S. Purinergic Antagonism Prevents Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Behavioral Deficits Associated with Dopaminergic Toxicity Induced by 6-OHDA in Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3414–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, D.-J.; Kim, J.; Jung, S.-Y.; Song, R.; Noh, J.-H.; Park, Y.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kong, Y.-Y.; Chung, J.-M.; et al. Extracellular ATP Mediates Necrotic Cell Swelling in SN4741 Dopaminergic Neurons through P2X7Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 37350–37358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Hoekstra, J.; Heng, X.; Kang, W.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J. P2X7 receptor is critical in α-synuclein–mediated microglial NADPH oxidase activation. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2304–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkaniec, A.; Gassowska, M.; Czapski, G.A.; Cieslik, M.; Sulkowski, G.; Adamczyk, A. P2X7 receptor-pannexin 1 interaction mediates extracellular α-synuclein-induced ATP release in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Purinergic Signal. 2017, 13, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.D.S.; Acuña, L.; Hamadat, S.; Rocca, J.; González-Lizárraga, F.; Chehín, R.; Sepulveda-Diaz, J.; Del Bel, E.A.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Michel, P.P. Microglial glutamate release evoked by α-synuclein aggregates is prevented by dopamine. Glia 2018, 66, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Xie, X.; Luo, X.G.; Shang, H.; He, Z.Y. Inhibiting purinergic P2X7 receptors with the antagonist brilliant blue G is neuroprotective in an intranigral lipopolysaccharide animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, B. The lipopolysaccharide Parkinson’s disease animal model: Mechanistic studies and drug discovery. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 22, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendrou, C.A.; Fugger, L.; Friese, M.A. Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domercq, M.; Matute, C. Targeting P2X4 and P2X7 receptors in multiple sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 47, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domercq, M.; Zabala, A.; Matute, C. Purinergic receptors in multiple sclerosis pathogenesis. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 151, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahad, D.H.; Trapp, B.D.; Lassmann, H. Pathological mechanisms in progressive multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, A.; Vazquez-Villoldo, N.; Rissiek, B.; Gejo, J.; Martín, A.; Palomino, A.; Perez-Samartín, A.; Pulagam, K.R.; Lukowiak, M.; Capetillo-Zarate, E.; et al. P2X4 receptor controls microglia activation and favors remyelination in autoimmune encephalitis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Sarti, A.C. Microglia P2X4 receptors as pharmacological targets for demyelinating diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiangou, Y.; Facer, P.; Durrenberger, P.F.; Chessell, I.P.; Naylor, A.; Bountra, C.; Banati, R.R.; Anand, P. COX-2, CB2 and P2X7-immunoreactivities are increased in activated microglial cells/macrophages of multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. BMC Neurol. 2006, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadio, S.; Parisi, C.; Piras, E.; Fabbrizio, P.; Apolloni, S.; Montilli, C.; Luchetti, S.; Ruggieri, S.; Gasperini, C.; Laghi-Pasini, F.; et al. Modulation of P2X7 Receptor during Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygorowicz, T.; Dabrowska-Bouta, B.; Strużyńska, L. Administration of an antagonist of P2X7 receptor to EAE rats prevents a decrease of expression of claudin-5 in cerebral capillaries. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.J.; Polak, P.E.; Simonini, V.; Lin, S.X.; Richardson, J.C.; Bongarzone, E.R.; Feinstein, D.L. P2x7 deficiency suppresses development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygorowicz, T.; Wełniak-Kamińska, M.; Strużyńska, L. Early P2X7R-related astrogliosis in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 74, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, S.E.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, E.; Ventura, J.C.; Perez-Samartin, A.; Tarassishin, L.; Negoro, H.; Patel, N.K.; Suadicani, S.O.; Lee, S.C.; Matute, C.; et al. Contribution of pannexin1 to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute, C. P2X7 Receptors in Oligodendrocytes: A Novel Target for Neuroprotection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 38, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute, C.; Torre, I.; Pérez-Cerdá, F.; Pérez-Samartín, A.; Alberdi, E.; Etxebarria, E.; Arranz, A.M.; Ravid, R.; Rodríguez-Antigüedad, A.; Sánchez-Gómez, M.V.; et al. P2X7 Receptor Blockade Prevents ATP Excitotoxicity in Oligodendrocytes and Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9525–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Brosnan, C.F. Exacerbation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in P2X7R−/− mice: Evidence for loss of apoptotic activity in lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3115–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonda, M.; Amoruso, A.; Grasso, R.; Di Francescantonio, V.; Avolio, C. Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Affect Monocyte-Derived Microvesicle Production. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.J.; Field, J.; Dutertre, S.; Ou, A.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Lechner-Scott, J.; Scott, R.; Lea, R.A.; Taylor, B.V.; Stankovich, J.; et al. A rare P2X7 variant Arg307Gln with absent pore formation function protects against neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5644–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.M.; Boulter, N.R.; Fuller, S.J.; Zakrzewski, A.M.; Lees, M.P.; Saunders, B.M.; Wiley, J.S.; Smith, N.C. The Role of the P2X7 Receptor in Infectious Diseases. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyanguren-Desez, O.; Rodríguez-Antigüedad, A.; Villoslada, P.; Domercq, M.; Alberdi, E.; Matute, C. Gain-of-function of P2X7 receptor gene variants in multiple sclerosis. Cell Calcium 2011, 50, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volonté, C.; Apolloni, S.; Carri, M.T.; D’Ambrosi, N. ALS: Focus on purinergic signalling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 132, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, M.; Brown, R.H. Genetics of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 8, a024125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, M.; Roszek, K.; Wujak, M. Purinergic implication in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—From pathological mechanisms to therapeutic perspectives. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, D.; Dongol, A.; Cuthbertson, P.; Guy, T.V.; Geraghty, N.J.; Sophocleous, R.A.; Sin, L.; Turner, B.J.; Watson, D.; Yerbury, J.J.; et al. The P2X7 receptor antagonist JNJ-47965567 administered thrice weekly from disease onset does not alter progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in SOD1G93A mice. Purinergic Signal. 2020, 16, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosi, N.; Finocchi, P.; Apolloni, S.; Cozzolino, M.; Ferri, A.; Padovano, V.; Pietrini, G.; Carri, M.T.; Volonté, C. The Proinflammatory Action of Microglial P2 Receptors Is Enhanced in SOD1 Models for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4648–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolloni, S.; Parisi, C.; Pesaresi, M.G.; Rossi, S.; Carrı, M.T.; Cozzolino, M.; Volonté, C.; D’Ambrosi, N. The NADPH Oxidase Pathway Is Dysregulated by the P2X7 Receptor in the SOD1-G93A Microglia Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5187–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandelman, M.; Peluffo, H.; Beckman, J.S.; Cassina, P.; Barbeito, L. Extracellular ATP and the P2X7 receptor in astrocyte-mediated motor neuron death: Implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deora, V.; Lee, J.D.; Albornoz, E.A.; McAlary, L.; Jagaraj, C.J.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Atkin, J.D.; Cooper, M.A.; Schroder, K.; Yerbury, J.J.; et al. The microglial NLRP3 inflammasome is activated by amyotrophic lateral sclerosis proteins. Glia 2019, 68, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolloni, S.; Amadio, S.; Montilli, C.; Volonté, C.; D’Ambrosi, N. Ablation of P2X7 receptor exacerbates gliosis and motoneuron death in the SOD1-G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 4102–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolloni, S.; Amadio, S.; Parisi, C.; Matteucci, A.; Potenza, R.L.; Armida, M.; Popoli, P.; D’Ambrosi, N.; Volonté, C. Spinal cord pathology is ameliorated by P2X7 antagonism in a SOD1-mutant mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Dis. Model. Mech. 2014, 7, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, R.; Sluyter, V.; Watson, D.; Sluyter, R.; Yerbury, J.J. P2X7 antagonism using Brilliant Blue G reduces body weight loss and prolongs survival in female SOD1G93A amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. PeerJ 2017, 5, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluyter, R.; Bartlett, R.; Ly, D.; Yerbury, J.J. P2X7 receptor antagonism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, M.F.; Khakh, B.S. ATP-gated P2X cation-channels. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A. Recent Advances in CNS P2X7 Physiology and Pharmacology: Focus on Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Biber, K. The microglial ATP-gated ion channel P2X7 as a CNS drug target. Glia 2016, 64, 1772–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, J.C.; Bhattacharya, A.; Letavic, M.A.; Savall, B.M. The evolution of P2X7 antagonists with a focus on CNS indications. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3838–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-C. P2X7 receptor antagonists: A patent review (2010–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2016, 27, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keystone, E.C.; Wang, M.M.; Layton, M.; Hollis, S.; McInnes, I. Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of the P2X7 purinergic receptor antagonist AZD9056 on the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with active disease despite treatment with methotrexate or sulphasalazine. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, T.; Bloom, B.J.; Wei, N.; Ishaq, S.; Park, W.; Wang, X.; Gupta, P.; Mebus, C.A.; Shiozawa, S.; Kawasaki, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of CE-224,535, an Antagonist of P2X7Receptor, in Treatment of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Inadequately Controlled by Methotrexate. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eser, A.; Colombel, J.F.; Rutgeerts, P.; Vermeire, S.; Vogelsang, H.; Braddock, M.; Persson, T.; Reinisch, W. Safety and Efficacy of an Oral Inhibitor of the Purinergic Receptor P2X7 in Adult Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease: A Randomized Placebo-controlled, Double-blind, Phase IIa Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.-H.; MacKenzie, A.B.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Brilliant Blue G Selectively Blocks ATP-Gated Rat P2X7Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Bean, B.P. Inhibition of neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels by brilliant blue G. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Wang, Q.; Ao, H.; Shoblock, J.R.; Lord, B.; Aluisio, L.; Fraser, I.; Nepomuceno, D.; Neff, R.A.; Welty, N.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of a novel centrally permeable P2X7 receptor antagonist: JNJ-47965567. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 624–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letavic, M.A.; Lord, B.; Bischoff, F.; Hawryluk, N.A.; Pieters, S.; Rech, J.C.; Sales, Z.; Velter, A.I.; Ao, H.; Bonaventure, P.; et al. Synthesis and Pharmacological Characterization of Two Novel, Brain Penetrating P2X7 Antagonists. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, D.; Celen, S.; Gijsbers, R.; Haute, C.V.D.; Postnov, A.; Koole, M.; Vandeputte, C.; Andrés, J.-I.; De Angelis, M.; Langlois, X.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of a P2X7 receptor selective radiotracer: PET studies in a rat model with local overexpression of the human P2X7 receptor and in non-human primates. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, B.; Ameriks, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Fourgeaud, L.; Vliegen, M.; Verluyten, W.; Haspeslagh, P.; Carruthers, N.I.; Lovenberg, T.W.; Bonaventure, P.; et al. A novel radioligand for the ATP-gated ion channel P2X7: [3H] JNJ-54232334. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 765, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, M.; Schmidt, M.E.; Hijzen, A.; Ravenstijn, P.; Vandermeulen, C.; Van Weehaeghe, D.; Serdons, K.; Celen, S.; Bormans, G.; Ceusters, M.; et al. 18F-JNJ-64413739, a Novel PET Ligand for the P2X7 Ion Channel: Radiation Dosimetry, Kinetic Modeling, Test-Retest Variability, and Occupancy of the P2X7 Antagonist JNJ-54175446. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 60, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; Smith, J.; Nicke, A.; Engel, T. Regulation of P2X7 receptor expression and function in the brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 151, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masin, M.; Young, C.; Lim, K.; Barnes, S.J.; Xu, X.J.; Marschall, V.; Brutkowski, W.; Mooney, E.R.; Górecki, D.C.; Murrell-Lagnado, R. Expression, assembly and function of novel C-terminal truncated variants of the mouse P2X7 receptor: Re-evaluation of P2X7 knockouts. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solle, M.; Labasi, J.; Perregaux, D.G.; Stam, E.; Petrushova, N.; Koller, B.H.; Griffiths, R.J.; Gabel, C.A. Altered Cytokine Production in Mice Lacking P2X7Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 276, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.W.; Walser, S.M.; Aprile-Garcia, F.; Dedic, N.; Chen, A.; Holsboer, F.; Arzt, E.; Wurst, W.; Deussing, J.M. Genetically dissecting P2rx7 expression within the central nervous system using conditional humanized mice. Purinergic Signal. 2016, 13, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Illes, P. P2X7 Receptors Amplify CNS Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21175996
Illes P. P2X7 Receptors Amplify CNS Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21175996
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlles, Peter. 2020. "P2X7 Receptors Amplify CNS Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21175996
APA StyleIlles, P. (2020). P2X7 Receptors Amplify CNS Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 5996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21175996




