Direct Comparison of Therapeutic Effects on Diabetic Polyneuropathy between Transplantation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Administration of Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Secreted Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
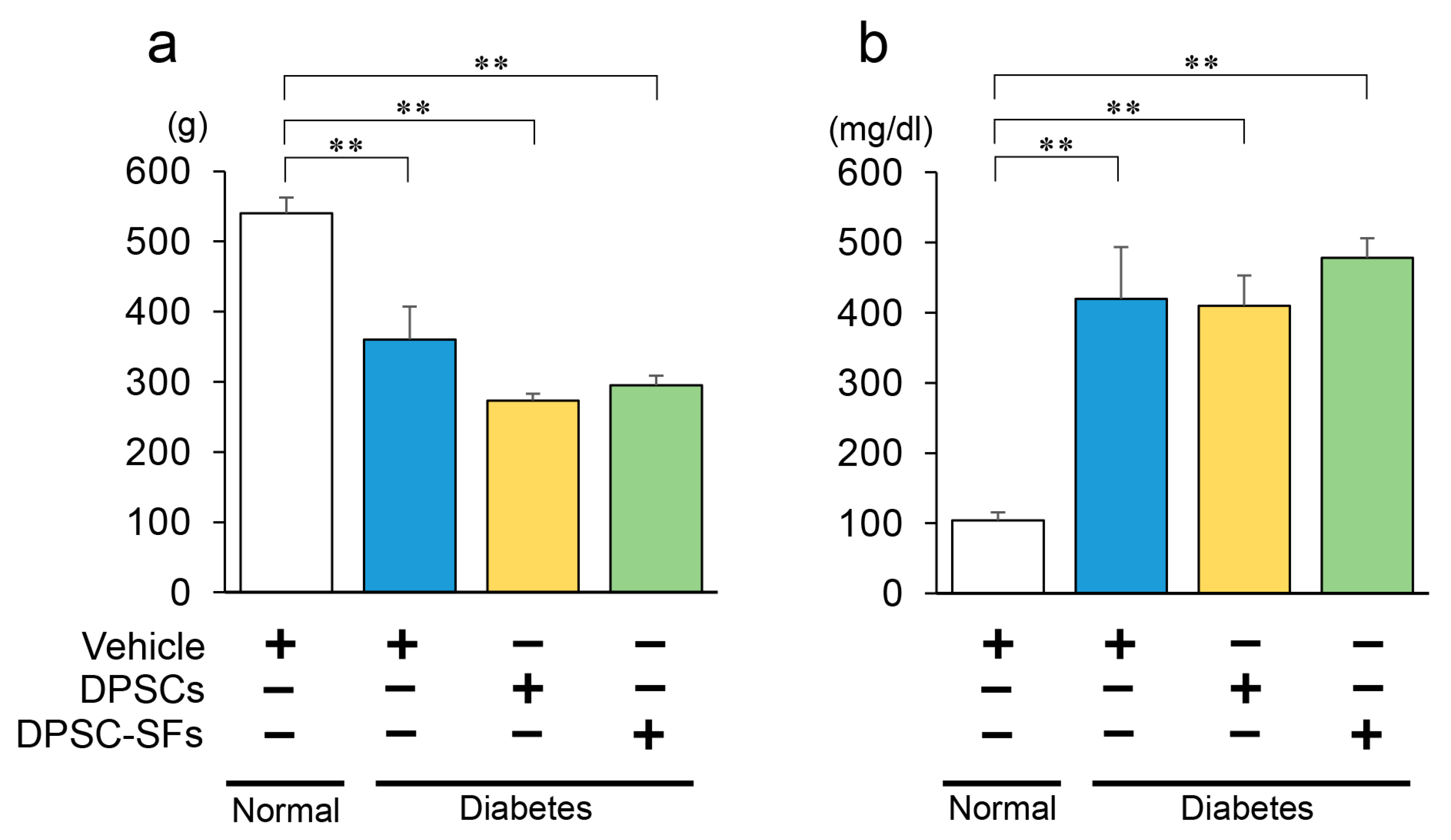
2.1. Blood Glucose Levels and Body Weights
2.2. Comparison between DPSC Transplantation and DPSC-SF Administration on Sciatic Motor Nerve Conduction Velocity (MNCV), Sciatic Sensory Nerve Conduction Velocity (SNCV), and Sciatic Nerve Blood Flow (SNBF)
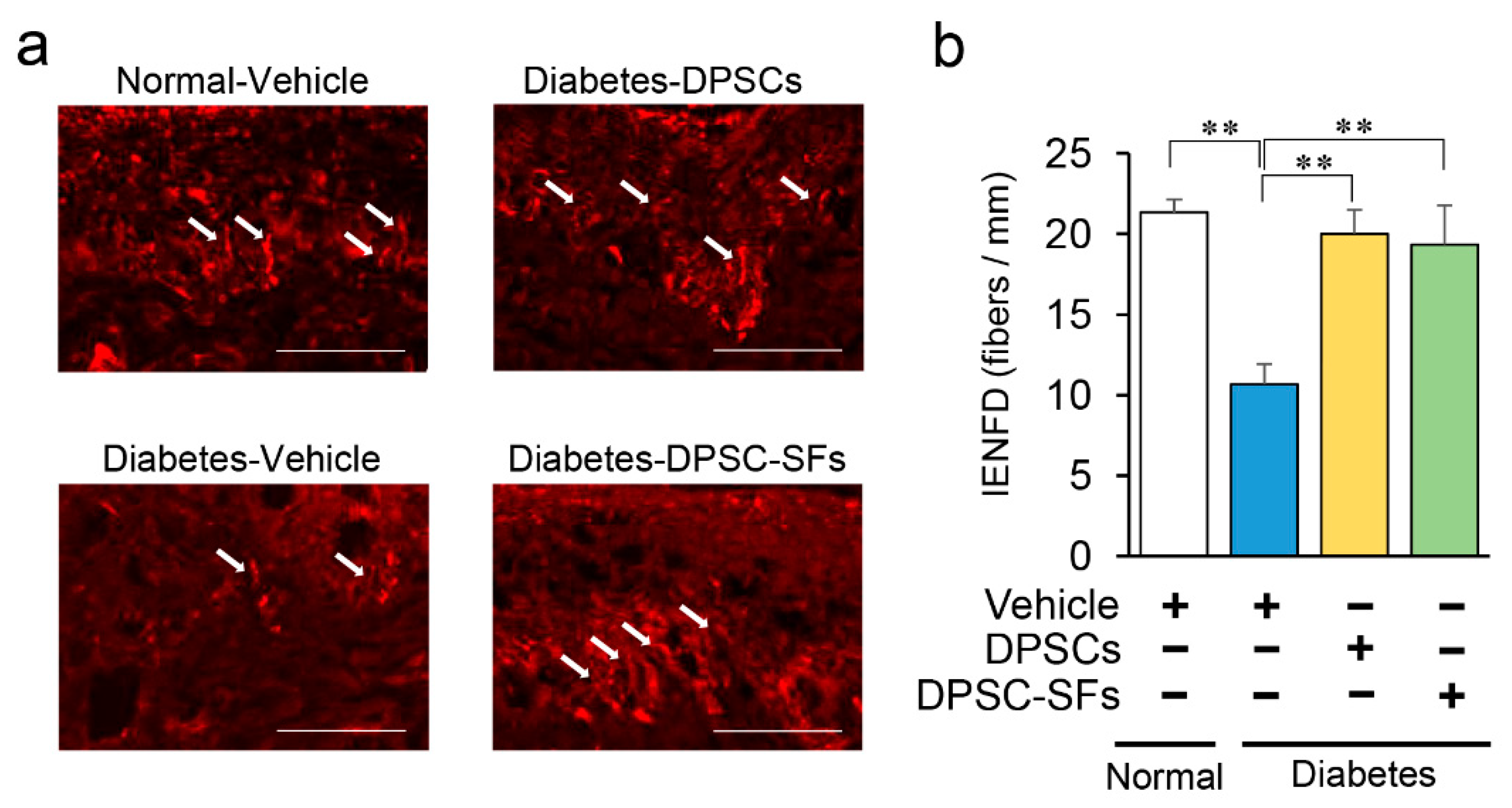
2.3. Effects of DPSC Transplantation and DPSC-SF Administration on Intraepidermal Nerve Fiber Density (IENFD)
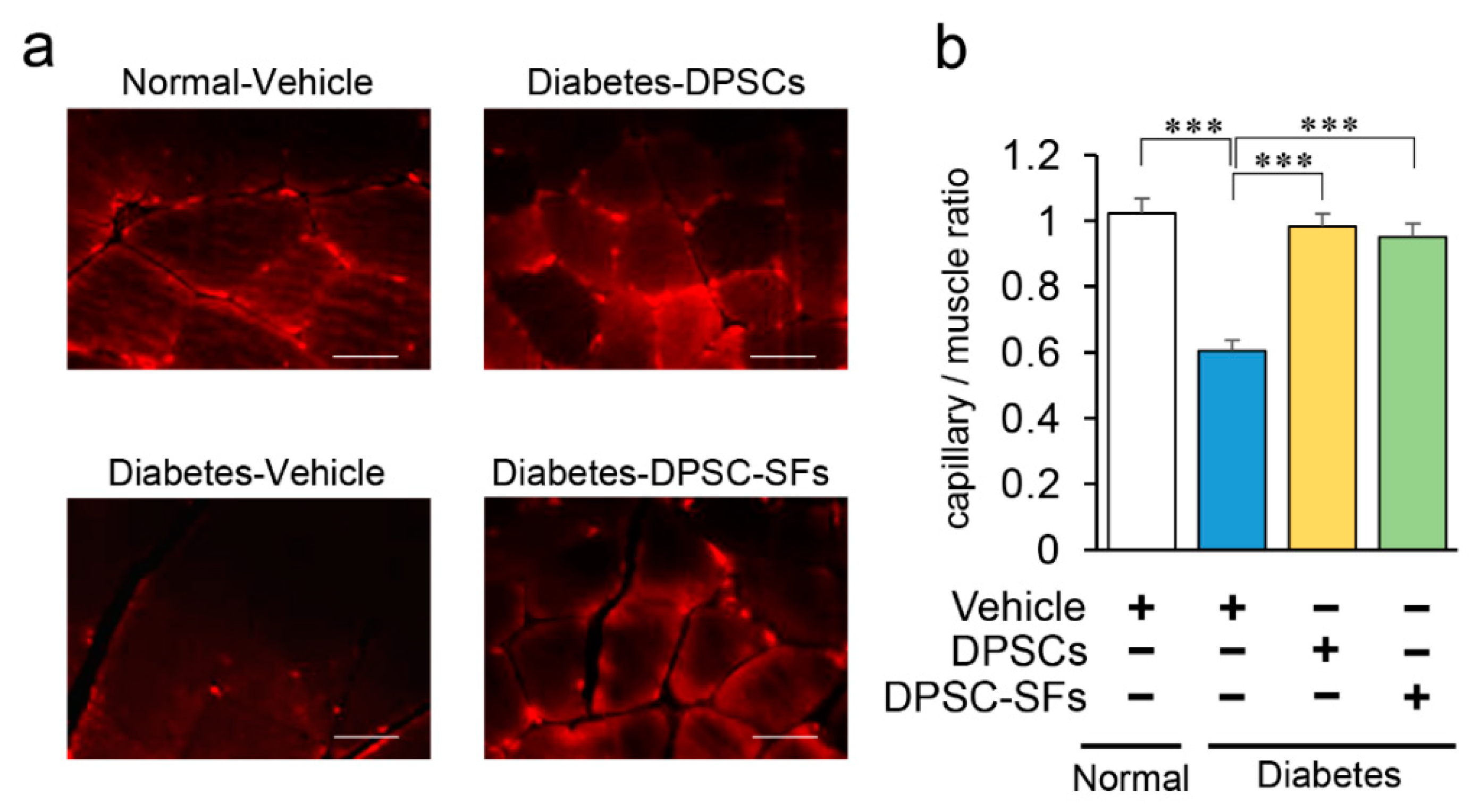
2.4. Effects of DPSC Transplantation and DPSC-SF Administration on the Hindlimb Skeletal Muscles
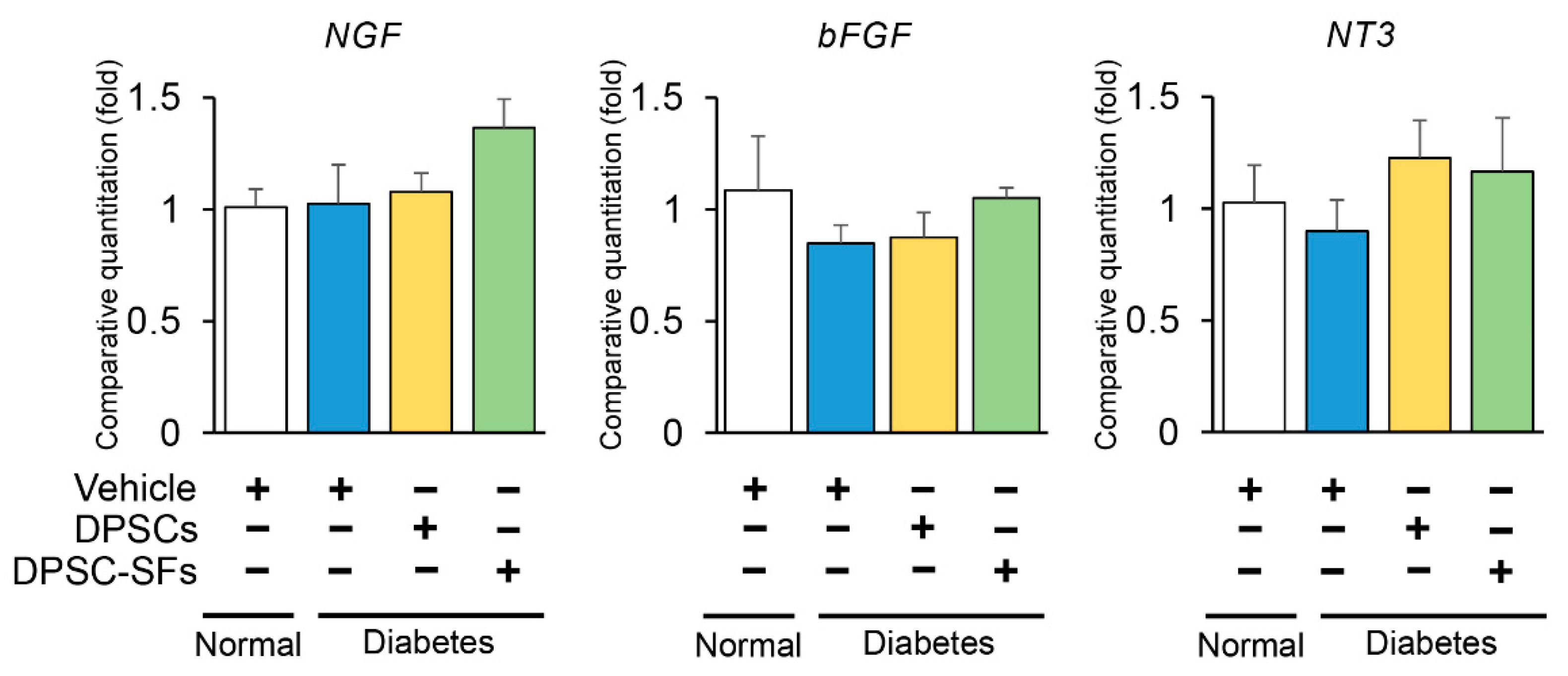
2.5. Effects of DPSC Transplantation and DPSC-SF Administration on mRNA Expressions of Neurotrophic Factors in the Hindlimb Skeletal Muscles
2.6. Characterization of Secreted Factors from Dental Pulp Stem Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Isolation and Culture of Rat DPSCs
4.3. Preparation of DPSC-SFs
4.4. Transplantation of DPSCs and Administration of DPSC-SFs
4.5. Sciatic Motor and Sensory Nerve Conduction Velocities
4.6. Sciatic Nerve Blood Flow
4.7. Intraepidremal Nerve Fiber Density
4.8. Histological Analysis and Immunohistological Staining
4.9. mRNA Expression Analyses
4.10. Analysis of Proteins in DPSC-SFs
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| DPSC | Dental pulp stem cell |
| DPSC-SF | Dental pulp stem cell-secreted factors |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ES | Embryonic stem |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| iPS | Induced pluripotent stem |
| M-CSF | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| MEM | Minimum essential medium |
| MNCV | Motor nerve conduction velocity |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| NT-3 | Neurotrophin-3 |
| PECAM | Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule |
| SD | Sprague–Dawley |
| SNBF | Sciatic nerve blood flow |
| SNCV | Sensory nerve conduction velocity |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nathan, D.M.; Genuth, S.; Lachin, J.; Cleary, P.; Crofford, O.; Davis, M.; Rand, L.; Siebert, C. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo, Y.; Kishikawa, H.; Araki, E.; Miyata, T.; Isami, S.; Motoyoshi, S.; Kojima, Y.; Furuyoshi, N.; Shichiri, M. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: A randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1995, 28, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail-Beigi, F.; Craven, T.; Banerji, M.A.; Basile, J.; Calles, J.; Cohen, R.M.; Cuddihy, R.; Cushman, W.C.; Genuth, S.; Grimm, R.H.; et al. Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: An analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gæde, P.; Vedel, P.; Parving, H.-H.; Pedersen, O. Intensified multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: The Steno type 2 randomised study. Lancet 1999, 353, 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Naruse, K.; Kamiya, H.; Kozakae, M.; Kondo, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Ota, K.; Tosaki, T.; Matsuki, T.; et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves diabetic polyneuropathy in rats. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3099–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Himeno, T.; Kamiya, H.; Naruse, K.; Cheng, Z.; Ito, S.; Kondo, M.; Okawa, T.; Fujiya, A.; Kato, J.; Suzuki, H. Mesenchymal stem cell-like cells derived from mouse induced pluripotent stem cells ameliorate diabetic polyneuropathy in mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 259187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monfrini, M.; Donzelli, E.; Rodriguez-Menendez, V.; Ballarini, E.; Carozzi, V.A.; Chiorazzi, A.; Meregalli, C.; Canta, A.; Oggioni, N.; Crippa, L.; et al. Therapeutic potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 288, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okawa, T.; Kamiya, H.; Himeno, T.; Kato, J.; Seino, Y.; Fujiya, A.; Kondo, M.; Tsunekawa, S.; Naruse, K.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Transplantation of neural crest-like cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells improves diabetic polyneuropathy in mice. Cell Transplant. 2013, 22, 1767–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hata, M.; Omi, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Tosaki, T.; Miyabe, M.; Kojima, N.; Kubo, K.; Ozawa, S.; Maeda, H.; et al. Transplantation of cultured dental pulp stem cells into the skeletal muscles ameliorated diabetic polyneuropathy: Therapeutic plausibility of freshly isolated and cryopreserved dental pulp stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Himeno, T.; Kamiya, H.; Naruse, K.; Cheng, Z.; Ito, S.; Shibata, T.; Kondo, M.; Kato, J.; Okawa, T.; Fujiya, A. Angioblast Derived from ES Cells Construct Blood Vessels and Ameliorate Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Mice. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 257230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omi, M.; Hata, M.; Nakamura, N.; Miyabe, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kamiya, H.; Nakamura, J.; Ozawa, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Takebe, J.; et al. Transplantation of dental pulp stem cells suppressed inflammation in sciatic nerves by promoting macrophage polarization towards anti-inflammation phenotypes and ameliorated diabetic polyneuropathy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omi, M.; Hata, M.; Nakamura, N.; Miyabe, M.; Ozawa, S.; Nukada, H.; Tsukamoto, M.; Sango, K.; Himeno, T.; Kamiya, H.; et al. Transplantation of dental pulp stem cells improves long-term diabetic polyneuropathy together with improvement of nerve morphometrical evaluation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, W.; Guo, Y.; Tao, L.; Lau, W.B.; Gan, L.; Yan, Z.; Guo, R.; Gao, E.; Wong, G.W.; Koch, W.L.; et al. C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein-9 Regulates the Fate of Implanted Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mobilizes Their Protective Effects Against Ischemic Heart Injury via Multiple Novel Signaling Pathways. Circulation 2017, 136, 2162–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-de Frutos, M.C.; Laso-García, F.; Diekhorst, L.; Otero-Ortega, L.; Fuentes, B.; Jolkkonen, J.; Detante, O.; Moisan, A.; Martínez-Arroyo, A.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; et al. Intravenous delivery of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves brain repair in hyperglycemic stroke rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toma, C.; Pittenger, M.F.; Cahill, K.S.; Byrne, B.J.; Kessler, P.D. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart. Circulation 2002, 105, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Kong, M.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; et al. A Large-Scale Investigation of Hypoxia-Preconditioned Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Myocardial Repair in Nonhuman Primates: Paracrine Activity Without Remuscularization. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, E.; Nakamura, N.; Miyabe, M.; Ito, M.; Kanada, S.; Hata, M.; Saiki, T.; Sango, K.; Kamiya, H.; Nakamura, J.; et al. Conditioned media from dental pulp stem cells improved diabetic polyneuropathy through anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and angiogenic actions: Cell-free regenerative medicine for diabetic polyneuropathy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 20, 13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabeeb, D.; Najafi, M.; Hasanzadeh, G.; Hadian, M.R.; Musa, A.E.; Shirazi, A. Electrophysiological measurements of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, N.; Akanuma, Y.; Kawamori, R.; Matsuoka, K.; Oka, Y.; Shichiri, M.; Toyota, T.; Nakashima, M.; Yoshimura, I.; Sakamoto, N.; et al. Long-term clinical effects of epalrestat, an aldose reductase inhibitor, on diabetic peripheral neuropathy: The 3-year, multicenter, comparative Aldose Reductase Inhibitor-Diabetes Complications Trial. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Velde, J.; Koster, A.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Mess, W.H.; Hilkman, D.; Reulen, J.P.H.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Henry, R.M.A.; Schram, M.T.; van der Kallen, C.J.H.; et al. Cardiometabolic risk factors as determinants of peripheral nerve function: The Maastricht Study. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruse, K.; Hamada, Y.; Nakashima, E.; Kato, K.; Mizubayashi, R.; Kamiya, H.; Yuzawa, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Murohara, T.; Matsubara, T.; et al. Therapeutic neovascularization using cord blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells for diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brini, A.T.; Amodeo, G.; Ferreira, L.M.; Milani, A.; Niada, S.; Moschetti, G.; Franchi, S.; Borsani, E.; Rodella, L.F.; Panerai, A.E.; et al. Therapeutic effect of human adipose-derived stem cells and their secretome in experimental diabetic pain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garbuzova-Davis, S.; Haller, E.; Lin, R.; Borlongan, C.V. Intravenously Transplanted Human Bone Marrow Endothelial Progenitor Cells Engraft Within Brain Capillaries, Preserve Mitochondrial Morphology, and Display Pinocytotic Activity Toward Blood-Brain Barrier Repair in Ischemic Stroke Rats. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, Y.; Fujimoto, A.; Ito, A.; Yoshimi, R.; Ueda, M. Cluster analysis and gene expression profiles: A cDNA microarray system-based comparison between human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) and human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) for tissue engineering cell therapy. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3766–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Hong, I.S. Double-edged sword of mesenchymal stem cells: Cancer-promoting versus therapeutic potential. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1939–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanada, S.; Makino, E.; Nakamura, N.; Miyabe, M.; Ito, M.; Hata, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Sawada, N.; Kondo, S.; Saiki, T.; et al. Direct Comparison of Therapeutic Effects on Diabetic Polyneuropathy between Transplantation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Administration of Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Secreted Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176064
Kanada S, Makino E, Nakamura N, Miyabe M, Ito M, Hata M, Yamauchi T, Sawada N, Kondo S, Saiki T, et al. Direct Comparison of Therapeutic Effects on Diabetic Polyneuropathy between Transplantation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Administration of Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Secreted Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176064
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanada, Saki, Eriko Makino, Nobuhisa Nakamura, Megumi Miyabe, Mizuho Ito, Masaki Hata, Taisuke Yamauchi, Noritaka Sawada, Shun Kondo, Tomokazu Saiki, and et al. 2020. "Direct Comparison of Therapeutic Effects on Diabetic Polyneuropathy between Transplantation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Administration of Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Secreted Factors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176064
APA StyleKanada, S., Makino, E., Nakamura, N., Miyabe, M., Ito, M., Hata, M., Yamauchi, T., Sawada, N., Kondo, S., Saiki, T., Minato, T., Miyazawa, K., Goto, S., Matsubara, T., & Naruse, K. (2020). Direct Comparison of Therapeutic Effects on Diabetic Polyneuropathy between Transplantation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Administration of Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Secreted Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176064




