LncRNAs in the Type I Interferon Antiviral Response
Abstract
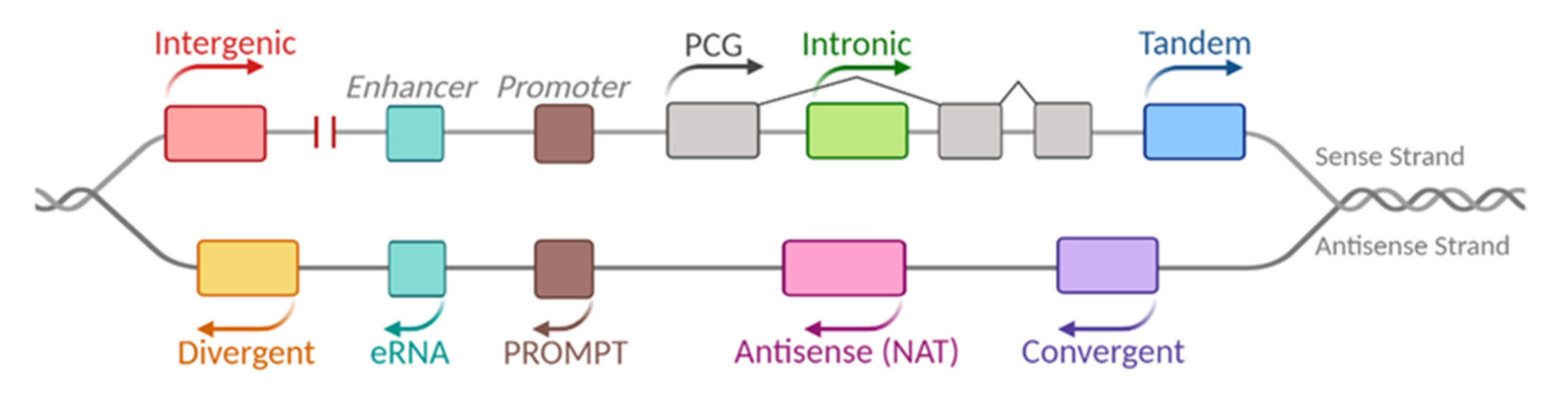
:1. LncRNAs
2. The Antiviral Interferon Response
2.1. IFN Synthesis
2.2. IFN Signaling
2.3. IFN Regulation
3. LncRNAs and the IFN Response
3.1. General Features of Viral-Induced lncRNAs Unrelated to the Antiviral Response
3.2. Virus-Induced lncRNAs Related to the Antiviral Response
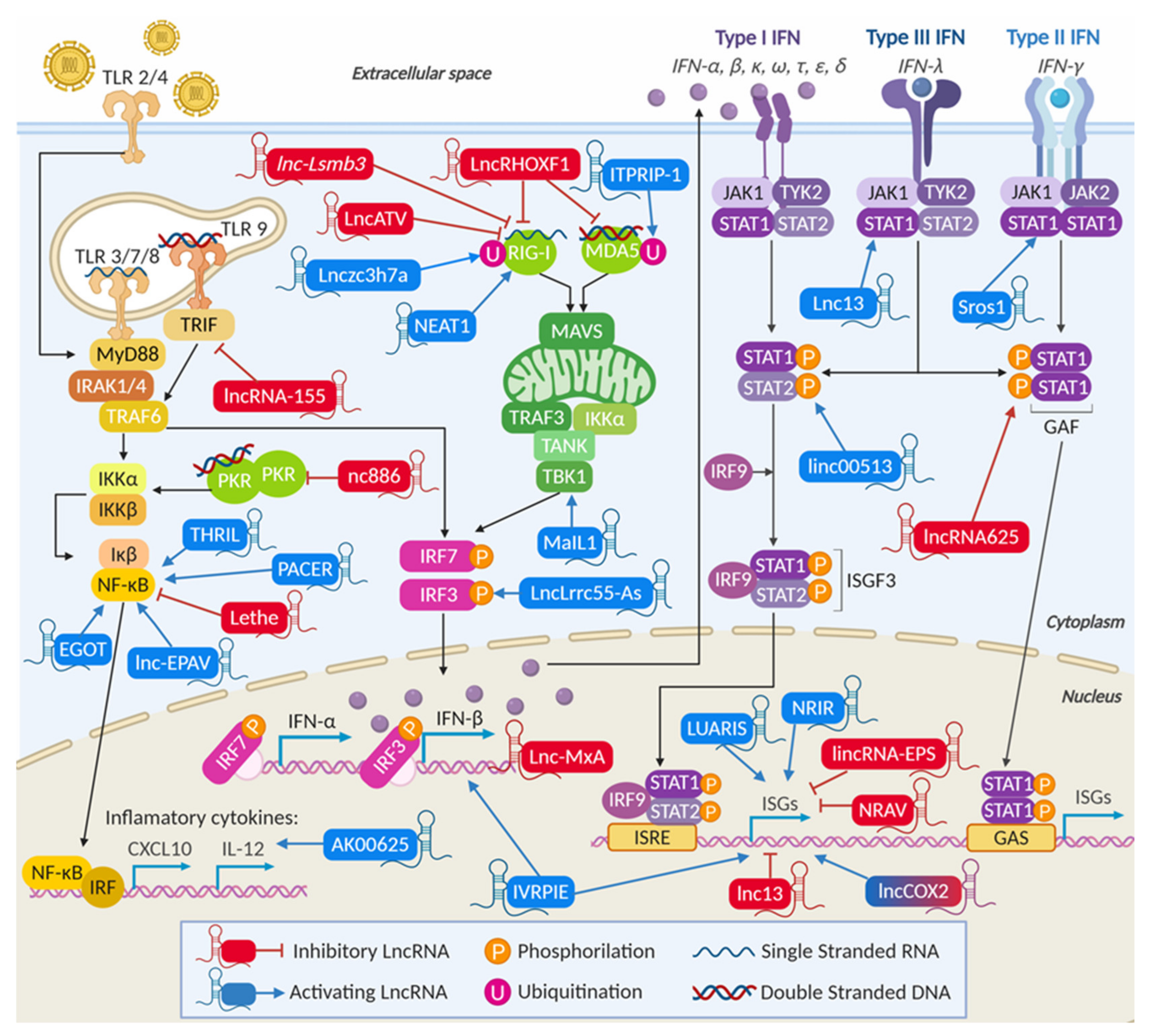
3.2.1. LncRNAs Are Involved in Viral Recognition and Modulate the Activity of Cellular Sensors
LncRNAs Can Regulate the Activity of Specific Nucleic Acid Sensors
LncRNAs Can Modulate the Levels of Nucleic-Acid Sensors
3.2.2. LncRNAs Modulate Transcription and Transcription Factors of the IFN Synthesis Pathway
LncRNAs Can Regulate Cellular Adaptors and Modulate IRF3 Phosphorylation
LncRNAs Modulate NF-κB Activity Affecting the Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines
LncRNAs Control IFN Transcription
3.2.3. LncRNAs Are Involved in IFN Signaling
3.2.4. LncRNAs Can Modulate the Transcription of Specific ISGs
3.2.5. LncRNAs Can Be General Regulators of the Transcription of Several ISGs and Inflammatory Genes
LncRNAs Can Negatively Regulate the Transcription of ISGs and Help Viral Replication
LncRNAs Can Positively Regulate the Transcription of ISGs and Prevent Viral Replication
Some lncRNAs Can Regulate ISGs by Targeting Specific Transcriptional Regulators
| LncRNA | Pathway | Stimuli | Study Design | Role | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITPRIP-1 | IFN-α | HCV | HLCZ01 (HCC) +/− IFN-α | AV | Binds, stabilizes, and activates MDA5, and improves direct binding of MDA5 to HCV genome | [122] |
| Lnczc3h7a | type I IFN | VSV, SeV | RAW264.7 (mouse Mφ) +/− VSV | AV | Forms a trimeric complex with TRIM25 and RIG-I that allows RIG-I signaling | [124] |
| LncATV | IFN-α,β,λ | HCV, ZIKV, NDV, SeV | HuH7 (HCC) +/− IFN-α2b and IFN-λ1 | PV | Binds RIG-I and prevents RIG-I signaling | [125] |
| Lnc-lsm3b | type I IFN | VSV | RAW264.7 (mouse Mφ) +/− VSV | PV | Competes with viral RNA for binding to RIG-I, stabilizing inactive RIG-I and preventing RIG-I activation | [126] |
| nc886 | eIF2-α, NF-κB | Adenovirus | CD4+ T cells +/− TCR activation | PV | Binds PKR and blocks PKR-mediated activation of eIF2-α and NF-κB pathways | [128,131] |
| lncRHOXF1 | IFN-β | SeV | Human trophoblasts +/− SeV | PV | Decreases the expression of RIG-I and MDA | [132] |
| NEAT1 | Type I IFN | HTNV, IAV, HSV | HUVECs +/− HTNV. Hela and A549 +/− p(I:C), IFN-α, IFN-β | AV | Relocates the transcriptional repressor SFPQ to paraspeckles, favoring the expression of RIG-I, DDX60, IFN-β, and IL-8 | [136,138] |
| LncRNA-155 | IFN-β | IAV, SeV, MDRV, HSV | C57BL/6J mice lungs or A549 +/− IAV | AV | Inhibits PTP1B expression, resulting in higher production of IFN-β and critical ISGs including Mx1, IFIT1, ISG15, OAS3 | [140] |
| lncLrrc55-AS | type I IFN | VSV, SeV HSV, LPS, p(I:C), IFN-α, IFN-β | WT and IFNα/β KO Mφ +/− VSV | AV | Supports PME-1-mediated inactivation of PP2A, enhancing IRF3 phosphorylation, activation, and IFN production | [144] |
| lnc-EPAV | NF-κB | p(I·C), SeV and VSV | Mouse BMDMs from C57BL/6 +/− p(I:C) | AV | Promotes expression of RELA by competitively binding to and displacing its transcriptional repressor SFPQ | [151] |
| NeST/IFNG-AS1/ TMEVPG1 | IFN-γ | TMEV | B10.S and SJL/J mice +/− TMEV | AV | Binds WDR5 to deposit activating epigenetic marks on the IFN-γ promoter of infection-resistant immune cells | [184] |
| Lnc-MxA | IFN-β | IAV, SeV, p(I:C) and IFN-β | A549 and HEK293T +/− IAV | PV | Forms an RNA-DNA triplex with the IFN-β promoter that prevents the binding of IRF3 and NF-κB | [185] |
| Morrbid | Type I IFN | LCMV, TCR + IFN-α or IFN-β | CD8+ T cells +/− LCMV | PV | Controls CD8 T cell expansion, survival, and effector function by regulating the expression of Bcl2l11 | [156,186] |
| Lnc13 | STAT1 | p(I:C) and CVB5 | Expression screen in EndoC-βH1 cells | AV | Interacts with PCBP2 to regulate the stability of the STAT1 mRNA, and the upregulation of CXCL10 and CCL5 | [157] |
| Lnc-ISG20 | type I IFN | IAV | A549 and HEK293T +/− IAV | AV | Binds miR-326 acting as a ceRNA and de-repressing the transcription of ISG20 | [155] |
| lncRNA-BST2/BISPR | IFN-α IFN-λ | IAV, VSV, HCV, IFN-α, and IFN-λ | HuH7 +/− IFN-α2 | AV | Activates the transcription of BST2 which prevents diffusion of viral particles after budding from infected cells | [163,164] |
| LncRNA-IFI6 | IFN-α | HCV, and HCV-JFH1 | Huh7.5.1 and PHH +/− IFN-α | PV | Negatively regulates IFI6 promoter by histone modification through a spatial structural domain | [167] |
| lncRNA-CMPK2/NRIR | IFN-α IFN-λ | HCV | PHH +/− IFN-α | PV | Negatively regulates the expression of several ISGs | [118] |
| TSPOAP1-AS1 | IFN-β, NF-κB | IAV and p(I:C) | A549 +/− AIV | PV | Negatively modulates IAV-induced Ifnb1 transcription, ISRE activation, and downstream ISG expression | [169] |
| NRAV | type I IFN | IAV, SeV, MVRD, HSV | A549 +/− AIV | PV | Regulates the transcription of multiple ISGs, including IFITM3 and MxA, by affecting their histone modifications | [170] |
| IVRPIE | IFN-β | IAV, SeV, VSV and p(I:C) | PBLs +/− IAV infection | AV | Regulates the transcription of IFN-β1 and ISGs, including IRF1, IFIT3, MxA, and ISG15, by epigenetic modification | [172] |
| lncCOX2 | NF-κB | LPS, p(I:C) and TMEV | BV2 (mouse microglia) +/− LPS | AV | Coactivator of NF-κB for the transcription of immune response genes through epigenetic remodeling by SWI/SNF | [174] |
| lncITM2C-1 | Type I IFN | HCV, p(I:C) | Huh-7.5 +/− miR-122 and/or HCV | PV | Stimulates the expression of neighboring gene GPR55, which in turn downregulates ISGs such as ISG15, Mx1, and IFITM1 | [177] |
| Loc107051710 | Type I IFN | IBDV | DF-1 (chicken fibroblasts) +/− IBDV | AV | Promotes the production of IFN-α and IFN-β by regulating IRF8, thereby promoting ISGs antiviral activity | [179] |
| LUARIS/lncRNA 32 | IFN-β | EMCV, HBV and HCV | HuS IRF3 KO cells +/− IFN-β | AV | Binds ATF2 to regulate the expression of chemokines such as IP-10 and CCL5 | [180] |
| AK006025 | NF-κB | HIV | Mouse astrocytes +/− HIV’s Nef protein | AV | Associates with NF-κB p65 and CBP/P300 to epigenetically regulate Nef-induced Cxcl9/10/11 cluster gene expression | [181] |
4. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ½-sbsRNA | Half-STAU1 Binding Site RNA |
| ADAR1 | Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA 1 |
| AIM2 | Absent in Melanoma 2 |
| APOBEC3 | Apolipoprotein B Editing Complex |
| ART | Antiretroviral Therapy |
| ASC | Apoptosis-Associated Speck-like Protein |
| ATF2 | Activating Transcription Factor 2 |
| Bcl2l11 | Bcl-2-like protein 11 |
| BISPR | BST2 Interferon-Stimulated Positive Regulator |
| BRD4 | Bromodomain-containing 4 |
| BST2 | Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Antigen 2 |
| CAPRIN1 | Cell Cycle-Associated Protein 1 |
| CBP | CREB-binding Protein |
| CCL5 | Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 5 |
| CDN | Cyclic Dinucleotide |
| ceRNA | Competing-endogenous RNA |
| cGAS | GMP-AMP Synthetase |
| ChIP | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation |
| CLR | C-type Lectin Receptors |
| CMPK2 | Cytidine/Uridine Monophosphate Kinase 2 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| CXCL | C-X-C Motif Chemokine |
| DAMP | Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern |
| DDX3 | DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp)-Box Helicase 3 |
| Deub | Deubiquitination |
| DHX9 | DexH-Box Helicase 9 |
| DHX33 | DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His)-Box Helicase 33 |
| DNA-PKcs | DNA-dependent Protein Kinase, Catalytic Subunit |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| EGOT | Eosinophil Granule Ontogeny Transcript |
| eIF2 | Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 |
| eRNA | Enhancer RNA |
| ERV | Endogenous Retroviruses |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 |
| FUS | Fused in Sarcoma |
| GAF | Gamma Activation Factor |
| GAS | Gamma Activation Sequence |
| GAS5 | Growth Arrest-Specific 5 |
| GBP | Guanylate Binding Protein |
| GOT2 | Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase 2 |
| GPR55 | G Protein-coupled Receptor 55 |
| H3K27me3 | Histone H3 trimethylation of Lysine 27 |
| H3K36me3 | Histone H3 trimethylation of Lysine 36 |
| H3K4me3 | Histone H3 trimethylation of Lysine 4 |
| HAT | Histone Acetyl Transferase |
| HBV | Hepatitis B Virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus |
| HDAC | Histone Deacetylases |
| HEAL | HIV-1 Enhanced lncRNA |
| HERVH | Human Endogenous Retrovirus Subfamily H |
| hESC | human Embryonic Stem Cell |
| HEXIM1 | Hexamethylene bis-acetamide-inducible Protein 1 |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| hnRNP | Heterogeneous Ribonucleoprotein Particle |
| hnRNPL | Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein L |
| HSP90a | Heat Shock Protein 90 Alpha |
| HSV | Herpes Simplex Virus |
| HTNV | Hantaan Virus |
| HULC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma Upregulated Long Non-Coding RNA |
| HuR | Human antigen R |
| IAV | Influenza A Virus |
| IBDV | Infectious Bursal Disease Virus |
| IFI6 | Interferon Alpha Inducible Protein 6 |
| IFIT1 | Interferon-Induced Protein with Tetratricopeptide Repeats 1 |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IFNAR | IFN Alpha Receptor |
| IFNG | Interferon Gamma |
| IFNGR | IFN Gamma Receptor |
| IFNLR | IFN Lambda Receptor |
| IKK | Iκβ Kinase |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL10Rβ | Interleukin 10 Receptor Subunit Beta |
| ILF3 | Interleukin Enhancer Binding Factor 3 |
| IPAN | Influenza virus PB1-associated Noncoding RNA |
| IRAK | Interleukin-1 Receptor-associated Kinase 1 |
| IRES | Internal Ribosome Entry Site |
| IRF | Interferon Regulatory Factor |
| ISG | Interferon-Stimulated Gene |
| ISGF3 | Interferon-Stimulated Gene Factor 3 |
| ISRE | IFN-stimulated Response Element |
| ITPRIP-1 | Inositol 1,4,5-Triphosphate Receptor Interacting Protein |
| IVRPIE | Inhibiting IAV Replication by Promoting IFN and ISG Expression |
| JAK1 | Janus-Activated Kinase 1 |
| lincRNA | Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs |
| lncCOX2 | Long non-Coding Cyclooxygenase 2b |
| Lnc-EPAV | Endogenous Retrovirus-Derived Long Non-Coding RNA |
| lncITM2C-1 | Long Non-coding RNA Integral Membrane Protein 2C |
| lncRHOXF1 | Long Non-Coding RNA Rhox Homeobox Family Member 1 |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| LTR | Long Terminal Repeat |
| LUARIS | lncRNA Upregulator of Antiviral Response Interferon Signaling |
| M5C | 5-Methylcytosine |
| M6A | N6-Methyladenosine |
| Mal | Myelin and Lymphocyte Protein |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MAVS | Mitochondrial Antiviral-Signaling Protein |
| MDA5 | Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Protein 5 |
| MDRV | Muscovy Duck Reovirus |
| MIR155HG | MicroRNA 155 Host Gene |
| miR-326 | MicroRNA 326 |
| miRNA | Micro RNA |
| MLL1 | WDR5-Mixed Lineage Leukemia Protein 1 |
| Morrbid | Myeloid RNA Repressor of BCL2L11-Induced Death |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| MST4 | Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase 26 |
| MxA | Mx Dynamin-Like GTPase1 |
| MyD88 | Myeloid Differentiation Factor 88 |
| ncRNA | Non-coding RNA |
| NDV | New Castle Disease Virus |
| NEAT1 | Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1 |
| NEST | Nettoie Salmonella pas Theiler’s |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa Beta |
| NKILA | NF-κB Interacting lncRNA |
| NLR | NOD-Like Receptors |
| NLRP3 | NACHT Domain-, Leucine-Rich Repeat-, and Pyrin-containing Protein 3 |
| NOD | Nucleotide Oligomerization domain |
| NONO | Non-POU Domain Containing Octamer Binding |
| NRAV | Negative Regulator of Antiviral Response |
| NRIR | Negative Regulator of Interferon Response |
| NRON | ncRNA Repressor of the Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells |
| NS3 | Nonstructural protein 3 |
| NuRD | Nucleosome Remodeling Deacetylase |
| OAS | 2′-5′-Oligoadenylate Synthetase |
| OCT-4 | Octamer-Binding Transcription Factor 4 |
| OPTN | Optineurin |
| P(I:C) | Polyinosinic: polycytidylic Acid |
| PAAN | PA-Associated noncoding RNA |
| PACER | P50-Associated COX-2 Extragenic RNA |
| PAMP | Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern |
| PCBP2 | Poly(rC) binding protein 2 |
| PCG | Protein-coding Gene |
| PEG-IFN-α | Pegylated IFN-α |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathway |
| PIAS1 | Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT1 |
| PIC | Preinitiation Complex |
| piRNA | (Piwi)-interacting RNA |
| PKR | Protein Kinase Regulated by RNA |
| PME-1 | Phosphatase Methylesterase 1 |
| PP2A | Protein Phosphatase 2A |
| PRC2 | Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 |
| PROMPT | Promoter Upstream Transcript |
| PRR | Pattern Recognition Receptors |
| PSF | (PTB (Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein)-associated Splicing Factor |
| PSPC1 | Paraspeckle Component 1 |
| PTP1B | Protein Effector Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase |
| RelA | v-rel Reticuloendotheliosis Viral Oncogene Homolog A |
| RIG-1 | Retinoic Acid-Inducible Gene 1 |
| RIP | RNA Immunoprecipitation |
| RISC | RNA-Induced Silencing Complex |
| RLR | RIG-Like Receptors |
| RNA pol II | RNA Polymerase II |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| rRNA | Ribosomal RNA |
| RSAD2 | Radical S-Adenosyl Methionine Domain Containing 2 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| SBE | Smad Binding Element |
| SETDB2 | SET Domain Bifurcated Histone Lysine Methyltransferase 2 |
| SeV | Sendai Virus |
| SFPQ | Splicing Factor Proline/Glutamine-Rich |
| SINEB2 | Short Interspersed Nuclear Element B2 |
| siRNA | Small Interfering RNA |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| smORF | Small Open Reading Frames |
| snoRNA | Small Nucleolar RNA |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms |
| snRNA | Small Nuclear Ribonucleic Acid |
| SOCS | Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling |
| STAT | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| STAU1 | Staufen Double-Stranded RNA Binding Protein 1 |
| STING | Stimulator of Interferon Genes |
| SUMO | Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier |
| SWI/SNF | Switch/Sucrose Non-Fermentable |
| TAD | Topologically associated Domains |
| (Tap)RNA | Topological Anchor Point RNA |
| TBK1 | TANK-Binding Kinase 1 |
| TBXL1 | T-Box Protein 1 |
References
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S.; et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, J.D.; Wei, Y.; Khavari, P.A. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unfried, J.P.; Serrano, G.; Suárez, B.; Sangro, P.; Ferretti, V.; Prior, C.; Boix, L.; Bruix, J.; Sangro, B.; Segura, V.; et al. Identification of Coding and Long Noncoding RNAs Differentially Expressed in Tumors and Preferentially Expressed in Healthy Tissues. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5167–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and Functions of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beckedorff, F.C.; Ayupe, A.C.; Verjovski-Almeida, S.; Tahira, A.C.; Reis, E.M.; Camargo, L. Global analysis of biogenesis, stability and sub-cellular localization of lncRNAs mapping to intragenic regions of the human genome. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 877–892. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, J.F.; Wu, Y.W.; Carmichael, G.G.; Chen, L.L. Long Noncoding RNAs with snoRNA Ends. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tycowski, K.T.; Di, S.M.; Borah, S.; Shi, M.; Steitz, J.A. Conservation of a triple-helix-forming RNA stability element in noncoding and genomic rnas of diverse viruses. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.A.; Valenstein, M.L.; Yario, T.A.; Tycowski, K.T.; Steitz, J.A. Formation of triple-helical structures by the 3′-end sequences of MALAT1 and MENβ noncoding RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19202–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilusz, J.E.; JnBaptiste, C.K.; Lu, L.Y.; Kuhn, C.D.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Sharp, P.A. A triple helix stabilizes the 3′ ends of long noncoding RNAs that lack poly(A) tails. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2392–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batista, P.J.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Bajic, V.B.; Zhang, Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscato, P.; Mattick, J.S.; Johnston, R.L.; Fox, A.H.; Dinger, M.E.; Inostroza-Ponta, M.; Fortini, E.; Clark, M.B.; Johnston, R.L.; Inostroza-Ponta, M.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA stability. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 885–898. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, N.; Ulitsky, I. Regulation of gene expression by cis-acting long non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Haines, J.E.; Perez, E.M.; Munson, G.; Chen, J.; Kane, M.; McDonel, P.E.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature 2016, 539, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faust, T.; Frankel, A.D.; D’Orso, I. Transcription control by long non-coding RNAs. Transcription 2012, 3, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kung, J.T.Y.; Lee, J.T. RNA in the Loop. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, F.; Orom, U.A.; Cesaroni, M.; Beringer, M.; Taatjes, D.J.; Blobel, G.A.; Shiekhattar, R. Activating RNAs associate with Mediator to enhance chromatin architecture and transcription. Nature 2013, 494, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigova, A.A.; Abraham, B.J.; Ji, X.; Molinie, B.; Hannett, N.M.; Guo, Y.E.; Jangi, M.; Giallourakis, C.C.; Sharp, P.A.; Young, R.A. Transcription factor trapping by RNA in gene regulatory elements. Science 2015, 350, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, R.Z.; Luo, D.X.; Mo, Y.Y. Emerging roles of lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Genes Dis. 2019, 6, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; et al. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemson, C.M.; Hutchinson, J.N.; Sara, S.A.; Ensminger, A.W.; Fox, A.H.; Chess, A.; Lawrence, J.B. An Architectural Role for a Nuclear Noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA Is Essential for the Structure of Paraspeckles. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.; Lou, Z.; Gupta, M. The long non-coding RNA GAS5 cooperates with the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E to regulate c-Myc translation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. LncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 39 UTRs via Alu eleme. Nature 2011, 470, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, H.; Kozhuharova, A.; Sharma, H.; Hirose, M.; Ohyama, T.; Fasolo, F.; Yamazaki, T.; Cotella, D.; Santoro, C.; Zucchelli, S.; et al. Identification of functional features of synthetic SINEUPs, antisense lncRNAs that specifically enhance protein translation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0183229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltran, M.; Puig, I.; Pena, C.; Garcia, J.M.; Alvarez, A.B.; Pena, R.; Bonilla, F.; de Herreros, A.G. A natural antisense transcript regulates Zeb2/Sip1 gene expression during Snail1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercer, T.R.; Mattick, J.S. Structure and function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zou, X.J.; Cao, C.H.; Zhang, T.; Lei, L.; Qi, X.L.; Liu, L.; Wu, D.H. Identification and functional characterization of long non-coding RNA MIR22HG as a tumor suppressor for hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3751–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Guo, X.; Xie, L.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Liu, L. The long intergenic noncoding RNA UFC1, a target of microRNA 34a, interacts with the mRNA stabilizing protein HuR to increase levels of ??-catenin in HCC cells. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauchotte, G.; Hergalant, S.; Vigouroux, C.; Casse, J.M.; Houlgatte, R.; Kaoma, T.; Helle, D.; Brochin, L.; Rech, F.; Peyre, M.; et al. Cytoplasmic overexpression of RNA-binding protein HuR is a marker of poor prognosis in meningioma, and HuR knockdown decreases meningioma cell growth and resistance to hypoxia. J. Pathol. 2017, 242, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.; Zhou, B.; Liu, L.; Yang, F.; Conran, C.; Ji, Y.; Hou, J.; Jiang, D. Molecular pattern of lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Dong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shen, F. Mechanisms and functions of long non-coding RNAs at multiple regulatory levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koirala, P.; Huang, J.; Ho, T.T.; Wu, F.; Ding, X.; Mo, Y.Y. LncRNA AK023948 is a positive regulator of AKT. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Yang, L. Long Noncoding RNA in Cancer: Wiring Signaling Circuitry. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Li, C.; Xing, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liang, K.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Hawke, D.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The LINK-A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1α signalling in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Xing, Z.; Ma, G.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Ye, Y.; Yao, J.; Liang, K.; et al. The LINK-A lncRNA interacts with PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 to hyperactivate AKT and confer resistance to AKT inhibitors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Kim, H.W.; Nam, J.W. The small peptide world in long noncoding RNAs. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeasmin, F.; Yada, T.; Akimitsu, N. Micropeptides encoded in transcripts previously identified as long noncoding RNAs: A new chapter in transcriptomics and proteomics. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Mo, Y.; Peng, M.; Tang, T.; Zhong, Y.; Deng, X.; Xiong, F.; Guo, C.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Emerging role of tumor-related functional peptides encoded by lncRNA and circRNA. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnero, E.; Fortes, P. HCV infection, IFN response and the coding and non-coding host cell genome. Virus Res. 2016, 212, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriocanal, M.; Fortes, P. Long Non-coding RNAs in hepatitis C virus-infected cells. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moelling, K.; Broecker, F. Viruses and Evolution–Viruses First? A Personal Perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pestka, S.; Langer, J.A.; Zoon, K.C.; Samuel, C.E. Interferons and their Actions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 727–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, A.; Lindenmann, J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1957, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pestka, S.; Krause, C.D.; Walter, M.R. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 202, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type i interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-Stimulated Genes: A Complex Web of Host Defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, S.B. Viral inhibition of the IFN-induced JAK/STAT signalling pathway: Development of live attenuated vaccines by mutation of viral-encoded IFN-antagonists. Vaccines 2016, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haller, O.; Kochs, G.; Weber, F. The interferon response circuit: Induction and suppression by pathogenic viruses. Virology 2006, 344, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrat, F.J.; Crow, M.K.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Interferon target-gene expression and epigenomic signatures in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Bowie, A.G. Sensing and Signaling in Antiviral Innate Immunity. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R328–R333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X. Self-regulation and cross-regulation of pattern-recognition receptor signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Innate signaling in the inflammatory immune disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wen, M.; Cao, X. Nuclear hnRNPA2B1 initiates and amplifies the innate immune response to DNA viruses. Science 2019, 365, eaav0758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.J.; Mansur, D.S.; Peters, N.E.; Ren, H.; Smith, G.L. DNA-PK is a DNA sensor for IRF-3-dependent innate immunity. Elife 2012, 1, e00047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen Recognition and Innate Immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heaton, S.M.; Borg, N.A.; Dixit, V.M. Ubiquitin in the activation and attenuation of innate antiviral immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Antiviral Signaling Through Pattern Recognition Receptors. J. Biochem. 2006, 141, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yi, M.; Qin, S.; Song, Y.; Chu, Q.; Wu, K. Activating cGAS-STING pathway for the optimal effect of cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Magupalli, V.G.; Ruan, J.; Yin, Q.; Atianand, M.K.; Vos, M.R.; Schröder, G.F.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Wu, H.; Egelman, E.H. Unified Polymerization Mechanism for the Assembly of ASC-Dependent Inflammasomes. Cell 2014, 156, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, H.; Miao, E.A.; Ting, J.P.-Y. Mechanisms of NOD-like Receptor-Associated Inflammasome Activation. Immunity 2013, 39, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, S.A.; Salditt-Georgieff, M.; Darnell, J.E. Tyrosine-phosphorylated Stat1 and Stat2 plus a 48-kDa protein all contact DNA in forming interferon-stimulated-gene factor 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3829–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murira, A.; Lamarre, A. Type-I Interferon Responses: From Friend to Foe in the Battle against Chronic Viral Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Regulation of type I interferon signaling in immunity and inflammation: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Young, H.A. Interferons: Success in anti-viral immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargreaves, D.C.; Horng, T.; Medzhitov, R. Control of Inducible Gene Expression by Signal-Dependent Transcriptional Elongation. Cell 2009, 138, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichlmair, A.; Lassnig, C.; Eberle, C.A.; Górna, M.W.; Baumann, C.L.; Burkard, T.R.; Búrckstúmmer, T.; Stefanovic, A.; Krieger, S.; Bennett, K.L.; et al. IFIT1 is an antiviral protein that recognizes 5′-triphosphate RNA. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, J.; Hulpiau, P.; Saelens, X. Mx Proteins: Antiviral Gatekeepers That Restrain the Uninvited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adomavicius, T.; Guaita, M.; Zhou, Y.; Jennings, M.D.; Latif, Z.; Roseman, A.M.; Pavitt, G.D. The structural basis of translational control by eIF2 phosphorylation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perng, Y.C.; Lenschow, D.J. ISG15 in antiviral immunity and beyond. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qian, C.; Cao, X. Post-Translational Modification Control of Innate Immunity. Immunity 2016, 45, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.Y.U.; Kang, J.S.; Hwang, Y.S.A.; Kim, Y.J. Oligoadenylate synthase-like (OASL) proteins: Dual functions and associations with diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pidugu, V.K.; Pidugu, H.B.; Wu, M.M.; Liu, C.J.; Lee, T.C. Emerging Functions of Human IFIT Proteins in Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arimoto, K.I.; Miyauchi, S.; Stoner, S.A.; Fan, J.B.; Zhang, D.E. Negative regulation of type I IFN signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choubey, D.; Moudgil, K.D. Interferons in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Regulation and Roles. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, X. Epigenetic regulation of the innate immune response to infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, M.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Chen, M.; et al. The kinase MST4 limits inflammatory responses through direct phosphorylation of the adaptor TRAF6. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, A.; Smith, R.; Doyle, S.L.; Gray, P.; Fenner, J.E.; Crack, P.J.; Nicholson, S.E.; Hilton, D.J.; O’Neill, L.A.J.; Hertzog, P.J. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 negatively regulates Toll-like receptor signaling by mediating Mal degradation. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Fu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, H. SUMOylation of RIG-I positively regulates the type I interferon signaling. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, G.; Tang, H. MDA5 is SUMOylated by PIAS2β in the upregulation of Type I interferon signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tempé, D.; Vives, E.; Brockly, F.; Brooks, H.; De Rossi, S.; Piechaczyk, M.; Bossis, G. SUMOylation of the inducible (c-Fos:c-Jun)/AP-1 transcription complex occurs on target promoters to limit transcriptional activation. Oncogene 2014, 33, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, Y.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Mao, A.-P.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.-J.; Cheng, J.-K.; Shu, H.-B. SENP2 negatively regulates cellular antiviral response by deSUMOylating IRF3 and conditioning it for ubiquitination and degradation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 3, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, D.; Kuo, A.J.; Chang, Y.; Schaefer, U.; Kitson, C.; Cheung, P.; Espejo, A.; Zee, B.M.; Liu, C.L.; Tangsombatvisit, S.; et al. Lysine methylation of the NF-κB subunit RelA by SETD6 couples activity of the histone methyltransferase GLP at chromatin to tonic repression of NF-κB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, K.; Shen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, N.; et al. Methyltransferase Dnmt3a upregulates HDAC9 to deacetylate the kinase TBK1 for activation of antiviral innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, M.; Anwar, M.A.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S. Advances in Antiviral Therapies Targeting Toll-like Receptors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coit, P.; Jeffries, M.; Altorok, N.; Dozmorov, M.G.; Koelsch, K.A.; Wren, J.D.; Merrill, J.T.; McCune, W.J.; Sawalha, A.H. Genome-wide DNA methylation study suggests epigenetic accessibility and transcriptional poising of interferon-regulated genes in naïve CD4+ T cells from lupus patients. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 43, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadler, A.J.; Suliman, B.A.; Yu, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, D.; Irving, A.T.; Sarvestani, S.T.; Banerjee, A.; Mansell, A.S.; Liu, J.P.; et al. The acetyltransferase HAT1 moderates the NF-κB response by regulating the transcription factor PLZF. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.C.; Schaefer, U.; Mecklenbrauker, I.; Stienen, A.; Dewell, S.; Chen, M.S.; Rioja, I.; Parravicini, V.; Prinjha, R.K.; Chandwani, R.; et al. Histone H3 lysine 9 di-methylation as an epigenetic signature of the interferon response. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroetz, D.N.; Allen, R.M.; Schaller, M.A.; Cavallaro, C.; Ito, T.; Kunkel, S.L. Type I Interferon Induced Epigenetic Regulation of Macrophages Suppresses Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Acute Respiratory Viral Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Tian, B.; Sun, H.; Garofalo, R.P.; Brasier, A.R. Epigenetic silencing of IRF1 dysregulates type III interferon responses to respiratory virus infection in epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, P.; Morris, K.V. Long noncoding RNAs in viral infections. Virus Res. 2016, 212, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valadkhan, S.; Plasek, L.M. Long Non-Coding RNA-Mediated Regulation of the Interferon Response: A New Perspective on a Familiar Theme. Pathog. Immun. 2018, 3, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnero, E.; Barriocanal, M.; Prior, C.; Pablo Unfried, J.; Segura, V.; Guruceaga, E.; Enguita, M.; Smerdou, C.; Gastaminza, P.; Fortes, P. Long noncoding RNA EGOT negatively affects the antiviral response and favors HCV replication. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unfried, J.P.; Fortes, P. LncRNAs in HCV infection and HCV-related liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winterling, C.; Koch, M.; Koeppel, M.; Garcia-Alcalde, F.; Karlas, A.; Meyer, T.F. Evidence for a crucial role of a host non-coding RNA in influenza A virus replication. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, D.C.; Morris, K.V.; Saayman, S.M. The emerging role of long non-coding RNAs in HIV infection. Virus Res. 2016, 212, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- More, S.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, K.; Huang, C.; Pushparaj, S.; Liang, Y.; Sathiaseelan, R.; Yang, X.; Liu, L. Long non-coding RNA PSMB8-AS1 regulates influenza virus replication. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, P.J.; Macfarlan, T.S.; Lorincz, M.C. Long Terminal Repeats: From Parasitic Elements to Building Blocks of the Transcriptional Regulatory Repertoire. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Sachs, F.; Ramsay, L.; Jacques, P.-É.; Göke, J.; Bourque, G.; Ng, H.-H. The retrovirus HERVH is a long noncoding RNA required for human embryonic stem cell identity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Ma, X.; Geng, G.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, F.; Liu, C.; Yin, Y.; et al. Long noncoding RNA NRON contributes to HIV-1 latency by specifically inducing tat protein degradation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, D.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Guo, F.; Liang, C.; et al. Host Long Noncoding RNA lncRNA-PAAN Regulates the Replication of Influenza A Virus. Viruses 2018, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Yi, D.; Ding, J.; Zhao, F.; Hu, S.; Zhou, J.; Deng, T.; et al. Influenza Virus Exploits an Interferon-Independent lncRNA to Preserve Viral RNA Synthesis through Stabilizing Viral RNA Polymerase PB1. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3295–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, T.-C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Tiwari, S.K.; Qin, Y.; Yau, E.; Sanchez, A.; Singh, G.; Chang, K.; Kaul, M.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA HEAL Regulates HIV-1 Replication through Epigenetic Regulation of the HIV-1 Promoter. MBio 2019, 10, e02016–e02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Li, F.; Xiao, J.; Qin, S.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis identifies host long noncoding RNA MAMDC2-AS1 as a co-factor for HSV-1 nuclear transport. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1586–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, G.; Tripathi, S.K.; Das, S. lncRNA HULC facilitates efficient loading of HCV-core protein onto lipid droplets and subsequent virus-particle release. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X. An interferon-independent lncRNA promotes viral replication by modulating cellular metabolism. Science 2017, 358, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, X.; Xu, C.; Zhao, P.; Qi, Z. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 inhibited hepatitis C virus replication by binding viral NS3 protein. Virology 2016, 492, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drayman, N.; Patel, P.; Vistain, L. HSV-1 single-cell analysis reveals the activation of anti-viral and developmental programs in distinct sub-populations. Elife 2019, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero, E.; Barriocanal, M.; Segura, V.; Guruceaga, E.; Prior, C.; Barner, K.; Grimm, D.; Fortes, P. Type I Interferon Regulates the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambara, H.; Niazi, F.; Kostadinova, L.; Moonka, D.K.; Siegel, C.T.; Post, A.B.; Carnero, E.; Barriocanal, M.; Fortes, P.; Anthony, D.D.; et al. Negative regulation of the interferon response by an interferon-induced long non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 10668–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joslyn, R.C.; Forero, A.; Green, R.; Parker, S.E.; Savan, R. Long Noncoding RNA Signatures Induced by Toll-Like Receptor 7 and Type i Interferon Signaling in Activated Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisse, M.; Ly, H. Comparative structure and function analysis of the RIG-I-like receptors: RIG-I and MDA5. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanpouille-Box, C.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Galluzzi, L. Pharmacological modulation of nucleic acid sensors—Therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, S.; Tian, R.; Huang, X.; Deng, R.; Xue, B.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, M.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA ITPRIP-1 Positively Regulates the Innate Immune Response through Promotion of Oligomerization and Activation of MDA5. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, H.; Dittmann, M.; Peisley, A.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Gilmore, R.H.; Schmidt, T.; Schmid-Burgk, J.L.; Hornung, V.; Rice, C.M.; Hur, S. ATP-Dependent effector-like functions of RIG-I-like receptors. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Jiang, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X. The long noncoding RNA Lnczc3h7a promotes a TRIM25-mediated RIG-I antiviral innate immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Cheng, M.; Chi, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, W. A Human Long Non-coding RNA LncATV Promotes Virus Replication Through Restricting RIG-I-Mediated Innate Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhu, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; et al. Self-Recognition of an Inducible Host lncRNA by RIG-I Feedback Restricts Innate Immune Response. Cell 2018, 173, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkeaw, N.; Jeon, S.H.; Lee, K.; Johnson, B.H.; Tanasanvimon, S.; Javle, M.; Pairojkul, C.; Chamgramol, Y.; Wongfieng, W.; Gong, B.; et al. Cell death/proliferation roles for nc886, a non-coding RNA, in the protein kinase R pathway in cholangiocarcinoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3722–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkeaw, N.; Lee, Y.S.; Im, W.R.; Jang, J.J.; Song, M.J.; Yang, B.; Park, J.L.; Kim, S.Y.; Ku, Y.; Kim, Y.; et al. Mechanism mediated by a noncoding RNA, nc886, in the cytotoxicity of a DNA-reactive compound. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8289–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, S.H.; Lee, K.; Lee, K.S.; Kunkeaw, N.; Johnson, B.H.; Holthauzen, L.M.F.; Gong, B.; Leelayuwat, C.; Lee, Y.S. Characterization of the direct physical interaction of nc886, a cellular non-coding RNA, and PKR. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calderon, B.M.; Conn, G.L. Human noncoding RNA 886 (nc886) adopts two structurally distinct conformers that are functionally opposing regulators of PKR. RNA 2017, 23, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golec, E.; Lind, L.; Qayyum, M.; Blom, A.M.; King, B.C. The Noncoding RNA nc886 Regulates PKR Signaling and Cytokine Production in Human Cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penkala, I.; Wang, J.; Syrett, C.M.; Goetzl, L.; López, C.B.; Anguera, M.C. lncRHOXF1, a Long Noncoding RNA from the X Chromosome That Suppresses Viral Response Genes during Development of the Early Human Placenta. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Hu, P.W.; Couturier, J.; Lewis, D.E.; Rice, A.P. HIV-1 replication in CD4+ T cells exploits the down-regulation of antiviral NEAT1 long non-coding RNAs following T cell activation. Virology 2018, 522, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H.; et al. Granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells contribute to IFN-I signaling activation of B cells and disease progression through the lncRNA NEAT1-BAFF axis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Xie, W.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y. NEAT1 modulates herpes simplex virus-1 replication by regulating viral gene transcription. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Han, P.; Ye, W.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, Z.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Exerts Antihantaviral Effects by Acting as Positive Feedback for RIG-I Signaling. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshiumi, H.; Miyashita, M.; Okamoto, M.; Morioka, Y.; Okabe, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. DDX60 Is Involved in RIG-I-Dependent and Independent Antiviral Responses, and Its Function Is Attenuated by Virus-Induced EGFR Activation. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Imamachi, N.; Akizuki, G.; Kumakura, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K.; Kato, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Sato, H.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1-Dependent SFPQ Relocation from Promoter Region to Paraspeckle Mediates IL8 Expression upon Immune Stimuli. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morchikh, M.; Cribier, A.; Raffel, R.; Amraoui, S.; Cau, J.; Severac, D.; Dubois, E.; Schwartz, O.; Bennasser, Y.; Benkirane, M. HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarouf, M.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Rai, K.R.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chen, J.L. Identification of lncRNA-155 encoded by MIR155HG as a novel regulator of innate immunity against influenza A virus infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; An, H.; Hou, J.; Han, C.; Wang, P.; Yu, Y.; Cao, X. Phosphatase PTP1B negatively regulates MyD88- and TRIF-dependent proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon production in TLR-triggered macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3545–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, C.J.; Zheng, H.; Bhattacharya, S.; Lewis, J.R.; Reiter, A.M.; Henthorn, P.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Baker, D.P.; Ukkiramapandian, R.; Bence, K.K.; et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B is a key regulator of IFNAR1 endocytosis and a target for antiviral therapies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19226–19231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aznaourova, M.; Janga, H.; Sefried, S.; Kaufmann, A.; Dorna, J.; Volkers, S.M.; Georg, P.; Lechner, M.; Hoppe, J.; Dökel, S.; et al. Noncoding RNA MaIL1 is an integral component of the TLR4–TRIF pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9042–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Wen, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Z.; Cao, X. Interferon-inducible cytoplasmic lncLrrc55-AS promotes antiviral innate responses by strengthening IRF3 phosphorylation. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Awasthee, N.; Rai, V.; Chava, S.; Gunda, V.; Challagundla, K.B. Long non-coding RNAs and nuclear factor-κB crosstalk in cancer and other human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chao, T.C.; Chang, K.Y.; Lin, N.; Patil, V.S.; Shimizu, C.; Head, S.R.; Burns, J.C.; Rana, T.M. The long noncoding RNA THRIL regulates TNFα expression through its interaction with hnRNPL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atianand, M.K.; Hu, W.; Satpathy, A.T.; Shen, Y.; Ricci, E.P.; Alvarez-Dominguez, J.R.; Bhatta, A.; Schattgen, S.A.; McGowan, J.D.; Blin, J.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA lincRNA-EPS Acts as a Transcriptional Brake to Restrain Inflammation. Cell 2016, 165, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krawczyk, M.; Emerson, B.M. P50-associated COX-2 Extragenic RNA (pacer) activates human COX-2 gene expression by occluding repressive NF-κB p50 complexes. Elife 2014, 2014, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q.; Gong, C.; Yao, Y.; Lv, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, H.; Su, F.; Li, D.; et al. A Cytoplasmic NF-κB Interacting Long Noncoding RNA Blocks IκB Phosphorylation and Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapicavoli, N.A.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Mikhail, M.; Laberge, R.M.; Chang, H.Y. A mammalian pseudogene lncRNA at the interface of inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Elife 2013, 2, e00762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Qi, F.; Wu, F.; Nie, H.; Song, Y.; Shao, L.; Han, J.; Wu, Z.; Saiyin, H.; Wei, G.; et al. Endogenous Retrovirus-Derived Long Noncoding RNA Enhances Innate Immune Responses via Derepressing RELA Expression. MBio 2019, 10, e00937–e001019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petermann, F.; Pękowska, A.; Johnson, C.A.; Jankovic, D.; Shih, H.Y.; Jiang, K.; Hudson, W.H.; Brooks, S.R.; Sun, H.W.; Villarino, A.V.; et al. The Magnitude of IFN-γ Responses Is Fine-Tuned by DNA Architecture and the Non-coding Transcript of Ifng-as1. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 1229–1242.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, J.A.; Wapinski, O.L.; Yang, Y.W.; Bureau, J.F.; Gopinath, S.; Monack, D.M.; Chang, H.Y.; Brahic, M.; Kirkegaard, K. The NeST Long ncRNA Controls Microbial Susceptibility and Epigenetic Activation of the Interferon-γ Locus. Cell 2013, 152, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collier, S.P.; Collins, P.L.; Williams, C.L.; Boothby, M.R.; Aune, T.M. Cutting Edge: Influence of Tmevpg1, a Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA, on the Expression of Ifng by Th1 Cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2084–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chai, W.; Li, J.; Shangguan, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Qi, D.; Tong, X.; Liu, W.; Ye, X. Lnc-ISG20 Inhibits Influenza A Virus Replication by Enhancing ISG20 Expression. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotzin, J.J.; Iseka, F.; Wright, J.; Basavappa, M.G.; Clark, M.L.; Ali, M.A.; Abdel-Hakeem, M.S.; Robertson, T.F.; Mowel, W.K.; Joannas, L.; et al. The long noncoding RNA Morrbid regulates CD8 T cells in response to viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11916–11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Moro, I.; Olazagoitia-Garmendia, A.; Colli, M.L.; Cobo-Vuilleumier, N.; Postler, T.S.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Ghosh, S.; Gauthier, B.R.; Eizirik, D.L.; et al. The T1D-associated lncRNA Lnc13 modulates human pancreatic β cell inflammation by allele-specific stabilization of STAT1 mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9022–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Huang, B.; Cao, X. Inducible degradation of lncRNA Sros1 promotes IFN-γ-mediated activation of innate immune responses by stabilizing Stat1 mRNA. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo-Wei, H.; Chun-Quan, L.; Lian-Di, L.; Ji-Wei, J.; Lin, L.; Ji-Yu, D.; Jin-Cheng, G.; En-Min, L.; Li-Yan, X. LncRNA625 inhibits STAT1-mediated transactivation potential in esophageal cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 117, 105626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Ye, Z.; Xue, Z.; Wu, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Yao, C.; Cui, C.; Xu, N.; Ma, J.; Hou, G.; et al. Identification of Renal Long Non-coding RNA RP11-2B6.2 as a Positive Regulator of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway in Lupus Nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Cui, C.; Liao, Z.; Xia, S.; Zhang, P.; Qin, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, S.; Fu, Q.; Yin, Z.; et al. Identification of LncRNA Linc00513 Containing Lupus-Associated Genetic Variants as a Novel Regulator of Interferon Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kambara, H.; Gunawardane, L.; Zebrowski, E.; Kostadinova, L.; Jobava, R.; Krokowski, D.; Hatzoglou, M.; Anthony, D.D.; Valadkhan, S. Regulation of Interferon-Stimulated Gene BST2 by a lncRNA Transcribed from a Shared Bidirectional Promoter. Front. Immunol. 2015, 5, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barriocanal, M.; Carnero, E.; Segura, V.; Fortes, P. Long non-coding RNA BST2/BISPR is induced by IFN and regulates the expression of the antiviral factor Tetherin. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, D.; Joshi, P.; Panda, S.K. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) egress: Role of BST2 (Tetherin) and interferon induced long non- coding RNA (lncRNA) BISPR. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Che, Y.; Mao, S.; Lei, Y.; Zang, R.; Zheng, S.; Liu, C.; et al. Interferon-inducible lncRNA IRF1-AS represses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by promoting interferon response. Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Duan, X.; Holmes, J.A.; Li, W.; Lee, S.H.; Tu, Z.; Zhu, C.; Salloum, S.; Lidofsky, A.; Schaefer, E.A.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Regulates Hepatitis C Virus Infection Through Interferon Alpha–Inducible Protein 6. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanucchi, S.; Fok, E.T.; Dalla, E.; Shibayama, Y.; Börner, K.; Chang, E.Y.; Stoychev, S.; Imakaev, M.; Grimm, D.; Wang, K.C.; et al. Immune genes are primed for robust transcription by proximal long noncoding RNAs located in nuclear compartments. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Feng, W.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.; Duan, M. Long noncoding RNA TSPOAP1 antisense RNA 1 negatively modulates type I IFN signaling to facilitate influenza A virus replication. J. Med. Virol. 2019. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Chi, X.; Qi, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, G.F.; et al. NRAV, a long noncoding RNA, modulates antiviral responses through suppression of interferon-stimulated gene transcription. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Tan, Y.; Luo, H. MALAT1 is involved in type I IFNs-mediated systemic lupus erythematosus by up-regulating OAS2, OAS3, and OASL. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Xia, M.; Wang, K.; Lai, C.; Fan, H.; Gu, H.; Yang, P.; Wang, X. A Long Non-coding RNA IVRPIE Promotes Host Antiviral Immune Responses Through Regulating Interferon β1 and ISG Expression. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Atianand, M.K.; Ricci, E.P.; Gandhi, P.; Hall, L.L.; Byron, M.; Monks, B.; Henry-Bezy, M.; Lawrence, J.B.; et al. A long noncoding RNA mediates both activation and repression of immune response genes. Science 2013, 341, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.; Gong, A.Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Su, C.J.; Shibata, A.; Strauss-Soukup, J.K.; Drescher, K.M.; et al. LincRNA-Cox2 Promotes Late Inflammatory Gene Transcription in Macrophages through Modulating SWI/SNF-Mediated Chromatin Remodeling. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; et al. lincRNA-Cox2 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy mediated neuroinflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balenga, N.A.B.; Aflaki, E.; Kargl, J.; Platzer, W.; Schröder, R.; Blättermann, S.; Kostenis, E.; Brown, A.J.; Heinemann, A.; Waldhoer, M. GPR55 regulates cannabinoid 2 receptor-mediated responses in human neutrophils. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1452–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, P.; Wilhelm, J.; Gerresheim, G.; Shalamova, L.; Niepmann, M. Lnc-ITM2C-1 and GPR55 Are Proviral Host Factors for Hepatitis C Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hambleton, S.; Salem, S.; Bustamante, J.; Bigley, V.; Boisson-Dupuis, S.; Azevedo, J.; Fortin, A.; Haniffa, M.; Ceron-Gutierrez, L.; Bacon, C.M.; et al. IRF8 Mutations and Human Dendritic-Cell Immunodeficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhao, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, W.; et al. Determination of antiviral action of long non-coding RNA loc107051710 during infectious bursal disease virus infection due to enhancement of interferon production. Virulence 2020, 11, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishitsuji, H.; Ujino, S.; Yoshio, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Mizokami, M.; Kanto, T.; Shimotohno, K. Long noncoding RNA #32 contributes to antiviral responses by controlling interferon-stimulated gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10388–10393. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, X.; Zuo, D.; Xue, M.; Gao, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Niu, L.; Cao, Q.; Li, X.; et al. HIV-1 Nef-induced lncRNA AK006025 regulates CXCL9/10/11 cluster gene expression in astrocytes through interaction with CBP/P300. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barriocanal, M.; Prior, C.; Suarez, B.; Unfried, J.P.; Nerea, R.; Sandra, H.-S.; Bruno, S.; Victor, S.; Puri, F. LncRNA EGOT responds to stress signals to regulate cell inflammation and growth. Submitt. Manuscr. 2020. (Unpublished Work). [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Fernandez-Jimenez, N.; Kratchmarov, R.; Luo, X.; Bhagat, G.; Green, P.H.R.; Schneider, R.; Kiledjian, M.; Bilbao, J.R.; Ghosh, S. A long noncoding RNA associated with susceptibility to celiac disease. Science 2016, 352, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigneau, S.; Rohrlich, P.S.; Brahic, M.; Bureau, J.F. Tmevpg1, a Candidate Gene for the Control of Theiler’s Virus Persistence, Could Be Implicated in the Regulation of Gamma Interferon. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5632–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Guo, G.; Lu, M.; Chai, W.; Li, Y.; Tong, X.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Liu, W.; Qi, D.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA Lnc-MxA Inhibits Beta Interferon Transcription by Forming RNA-DNA Triplexes at Its Promoter. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00786–e00819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotzin, J.J.; Spencer, S.P.; McCright, S.J.; Kumar, D.B.U.; Collet, M.A.; Mowel, W.K.; Elliott, E.N.; Uyar, A.; Makiya, M.A.; Dunagin, M.C.; et al. The long non-coding RNA Morrbid regulates Bim and short-lived myeloid cell lifespan. Nature 2016, 537, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: The impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singanayagam, A.; Glanville, N.; Girkin, J.L.; Ching, Y.M.; Marcellini, A.; Porter, J.D.; Toussaint, M.; Walton, R.P.; Finney, L.J.; Aniscenko, J.; et al. Corticosteroid suppression of antiviral immunity increases bacterial loads and mucus production in COPD exacerbations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.J.; Porritt, R.A.; Hertzog, P.J.; Bardin, P.G.; Tate, M.D. Glucocorticosteroids enhance replication of respiratory viruses: Effect of adjuvant interferon. Sci. Rep. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwa, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Mori, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Yasui, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Karayama, M.; Hozumi, H.; Furuhashi, K.; Enomoto, N.; et al. IL-17A Attenuates IFN-λ Expression by Inducing Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling Expression in Airway Epithelium. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, H. Factors associated with the response to interferon-based antiviral therapies for chronic hepatitis C. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, E.B.; Brooks, D.G. Decoding the complexity of type I interferon to treat persistent viral infections. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felgenhauer, U.; Schoen, A.; Gad, H.H.; Hartmann, R.; Schaubmar, A.R.; Failing, K.; Drosten, C.; Weber, F. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by type I and type III interferons. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 013788, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Kirsch, M.A. The Type i Interferonopathies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodero, M.P.; Crow, Y.J. Type I interferon-mediated monogenic autoinflammation: The type i interferonopathies, a conceptual overview. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2527–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, M.; Lyons, S.M.; Zdioruk, M.; von Spreckelsen, N.; Ferrer-Luna, R.; Ito, H.; Alayo, Q.A.; Kharel, P.; Giantini Larsen, A.; Fan, W.Y.; et al. Tumor Interferon Signaling Is Regulated by a lncRNA INCR1 Transcribed from the PD-L1 Locus. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1207–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LncRNA | Stimuli | Study Design | Role | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRON | HIV | CD4 + T cells screen | AV | Links Tat to the ubiquitin/proteasome components CUL4B and PSMD11, thus facilitating Tat degradation | [109] |
| PAAN | IAV | HEK293T +/− IAV | PV | Promotes the assembly of viral RNA polymerase, warranting efficient viral RNA synthesis | [110] |
| IPAN | IAV | HEK293T +/− IAV | PV | Stabilizes viral RNA polymerase PB1, enabling efficient viral RNA synthesis | [111] |
| HEAL | HIV | MDMs +/− Mφ-tropic HIV-1 | PV | Forms a complex with FUS, which facilitates HIV replication by recruiting p300 to the HIV promoter | [112] |
| MAMDC2-AS1 | HSV-1 | HDFn +/− HSV-1 | PV | Interacts with Hsp90α to facilitate the nuclear transport of VP16, the core factor initiating the expression of HSV-1 IE genes. | [113,116] |
| HULC | HCV | Huh7.5 +/− HCV | PV | Manipulates the lipid pool to favor loading of HCV-core protein onto lipid droplets and subsequent virus-particle release | [114] |
| GAS5 | HCV | Huh7 +/− HCV | AV | Inhibits viral replication by decoying HCV NS3 protein | [110] |
| ACOD | SeV, VSV, HSV-1, VACV | WT and Ifnar−/− Mφ +/− VSV | PV | Facilitates viral replication by binding to GOT2, increasing the catalytic activity of the enzyme and activating cellular metabolism | [115] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suarez, B.; Prats-Mari, L.; Unfried, J.P.; Fortes, P. LncRNAs in the Type I Interferon Antiviral Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176447
Suarez B, Prats-Mari L, Unfried JP, Fortes P. LncRNAs in the Type I Interferon Antiviral Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176447
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuarez, Beatriz, Laura Prats-Mari, Juan P. Unfried, and Puri Fortes. 2020. "LncRNAs in the Type I Interferon Antiviral Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176447
APA StyleSuarez, B., Prats-Mari, L., Unfried, J. P., & Fortes, P. (2020). LncRNAs in the Type I Interferon Antiviral Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176447







