Electroacupuncture Modulates Spinal BDNF/Tr?B Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates the Sensitization of Dorsal Horn WDR Neurons in Spared Nerve Injury Rats
Abstract
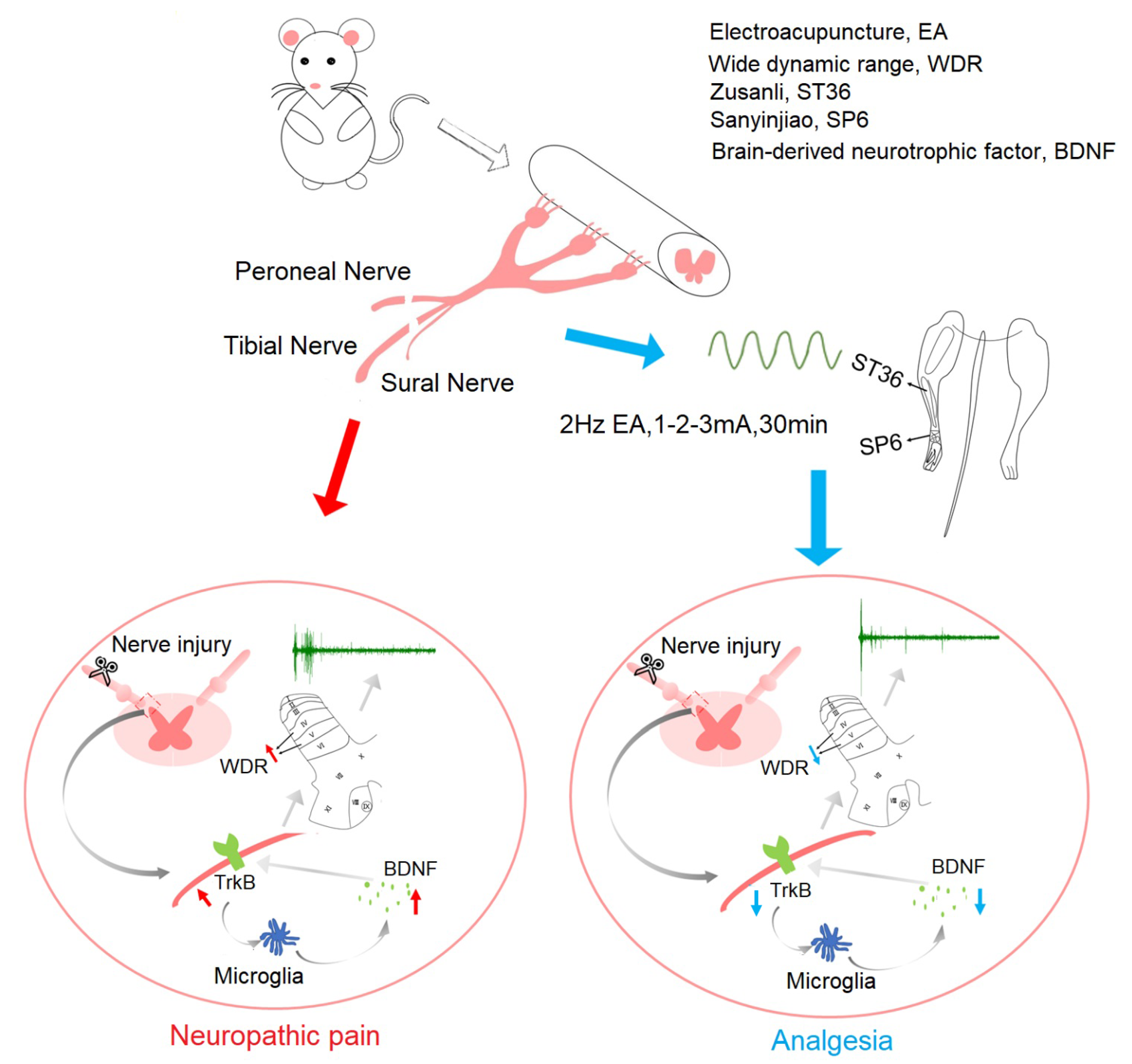
:1. Introduction
2. Results
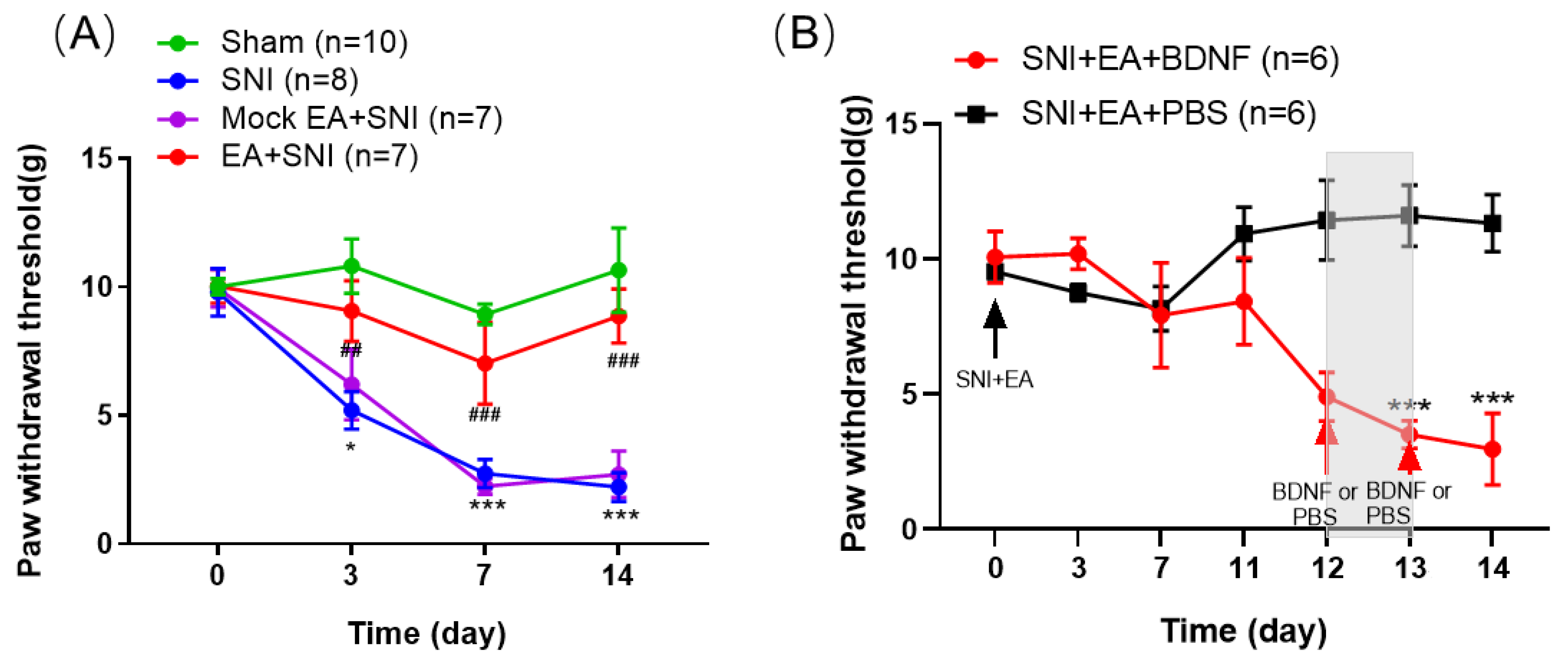
2.1. BDNF Reversed the Inhibitory Effect of 2 Hz EA on Mechanical Hypersensitivity in SNI Rats
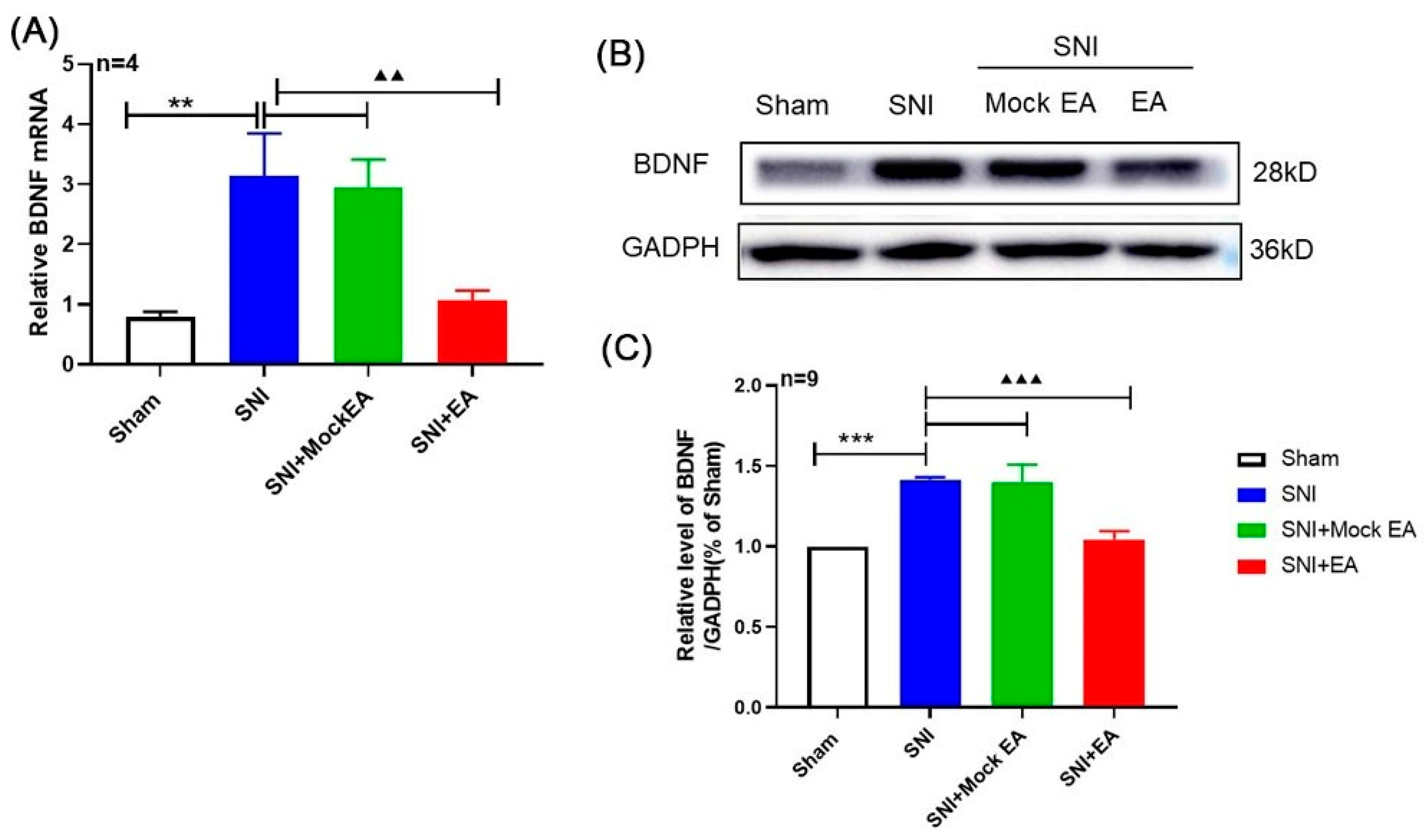
2.2. 2 Hz EA Induced the Down-Regulation of BDNF mRNA and Protein Levels in the Spinal Cord of SNI Rats
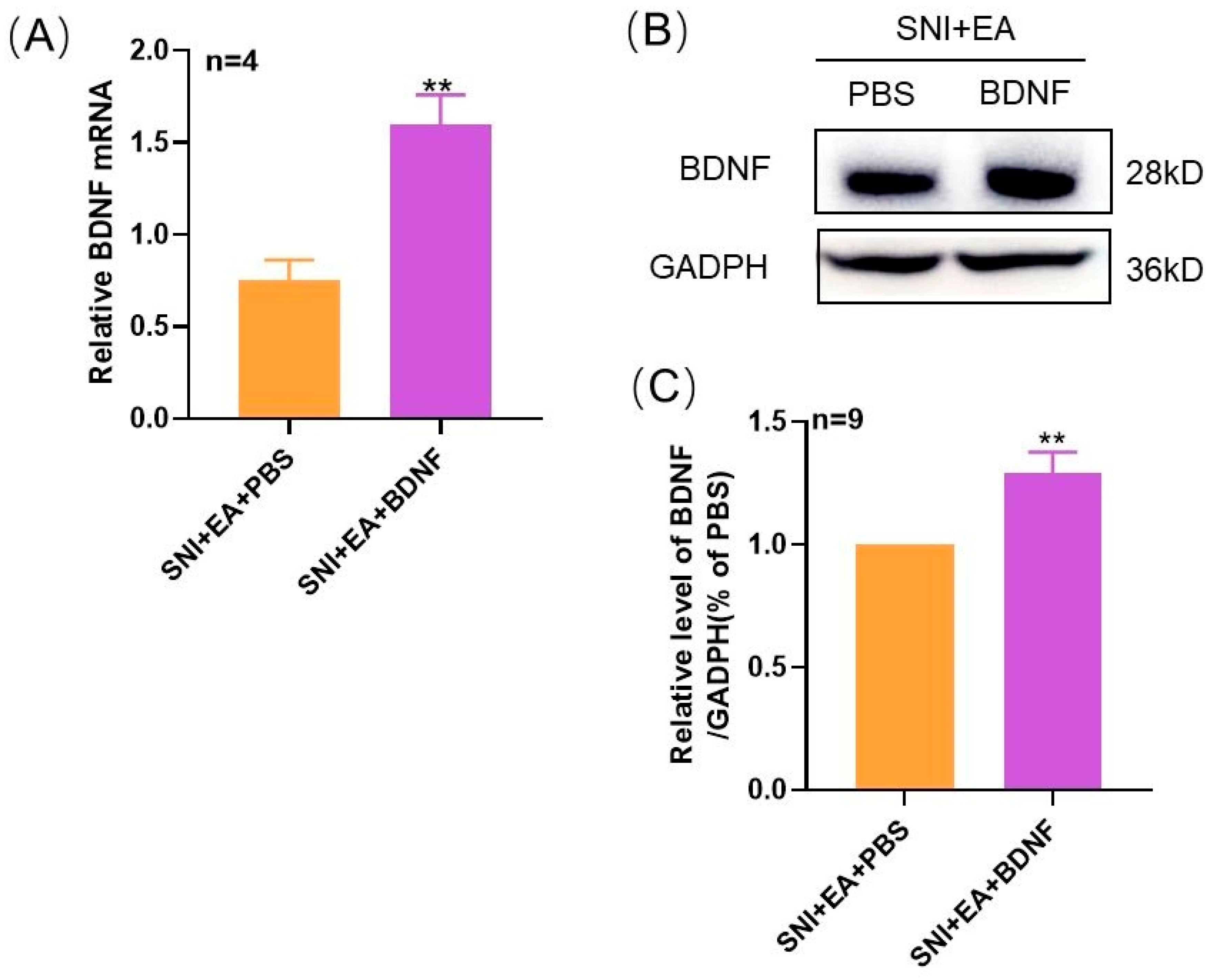
2.3. Intrathecal Administration of Exogenous BDNF Reversed the 2 Hz EA-Induced Down-Regulation of BDNF mRNA and Protein Levels in the Spinal Cord of SNI Rats
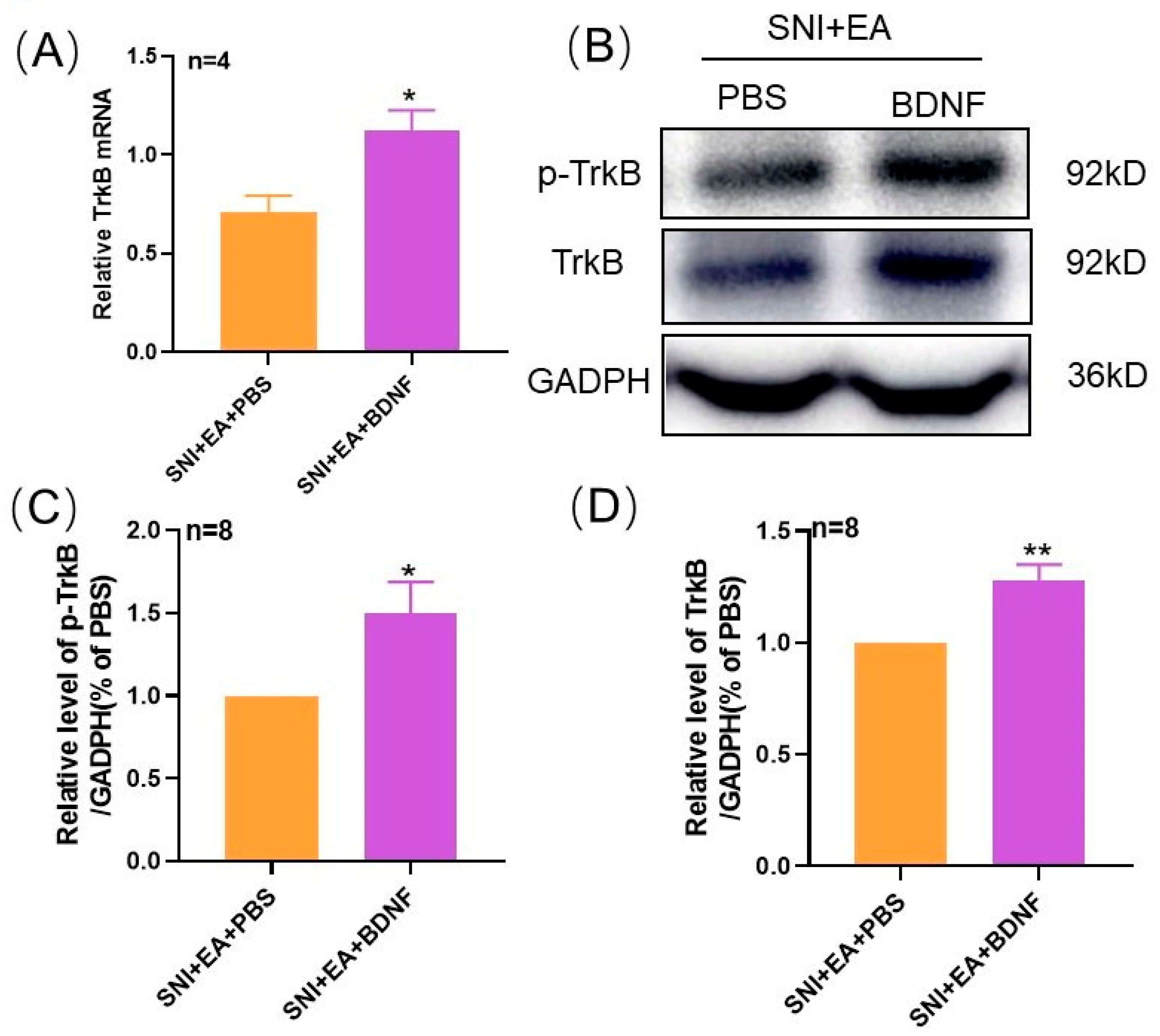
2.4. 2 Hz EA Induced the Reduction of TrκB mRNA and Protein Levels in Spinal Cord of SNI Rats
2.5. Intrathecal Injection of Exogenous BDNF Reversed the 2 Hz EA-Induced Down-Regulation of TrκB mRNA and Protein Levels in the Spinal Cord of SNI Rats
2.6. 2 Hz EA Decreased the C-Fiber-Evoked Discharges of Dorsal Horn WDR Neurons in SNI Rats
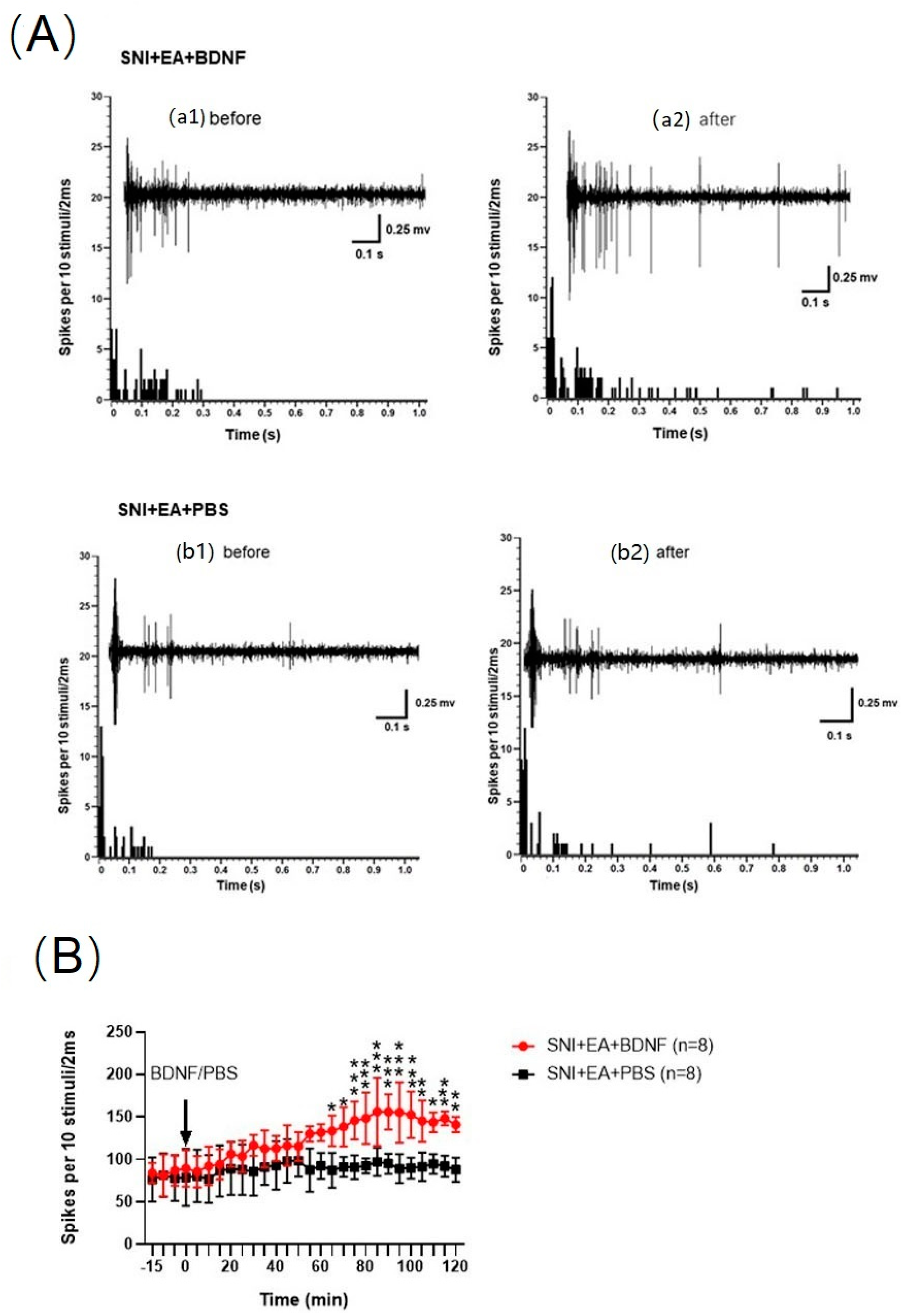
2.7. Intrathecal Injection of BDNF Reversed the 2 Hz EA-Induced Reduction of C-Fiber-Evoked Discharges of Dorsal Horn WDR Neurons in SNI Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
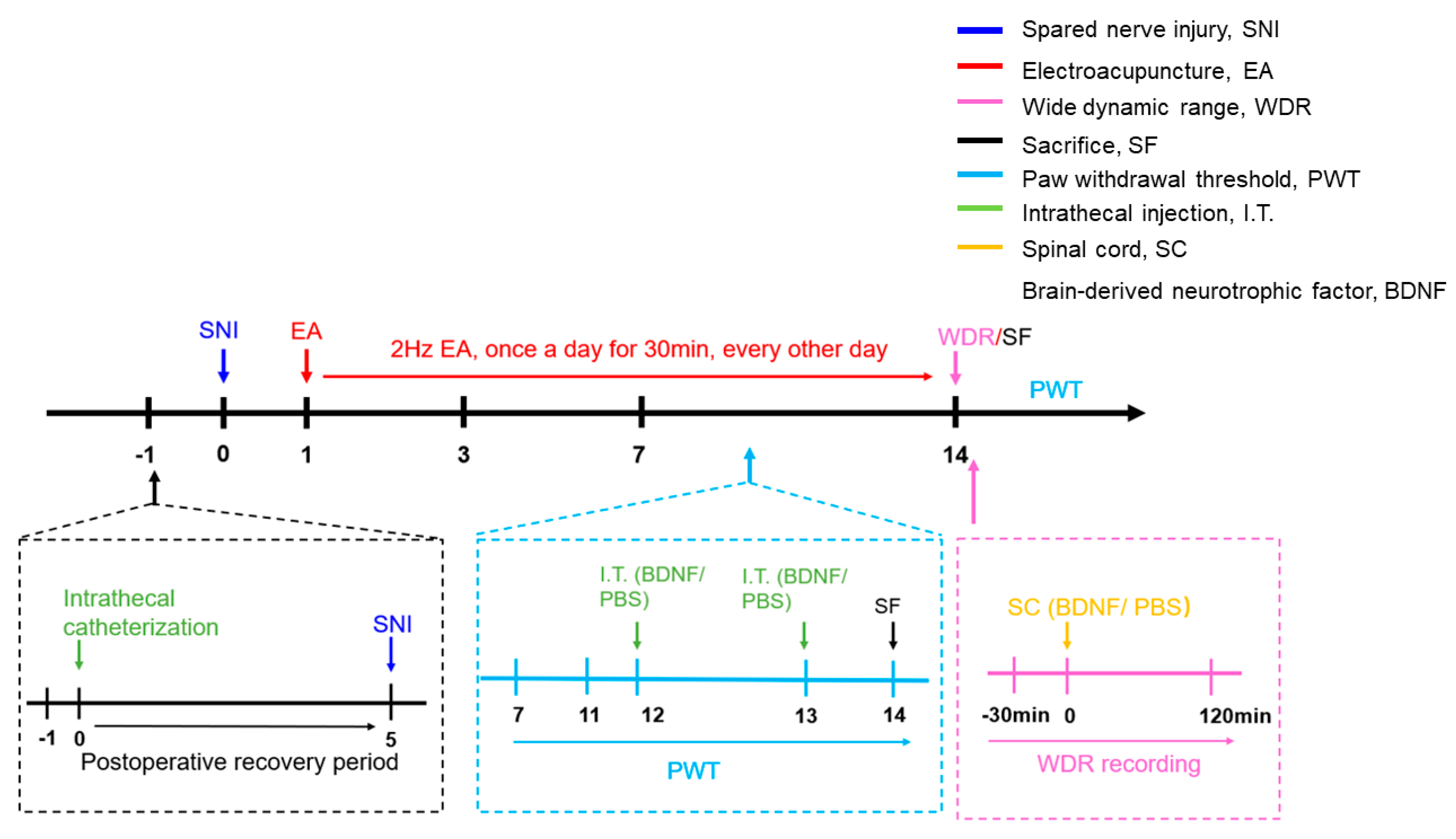
4.2. Experimental Protocols
4.3. A Rat Model of Spared Nerve Injury (SNI)
4.4. Intrathecal Administration
4.5. Assessment of Mechanical Hypersensitivity
4.6. Electroacupuncture Stimulation
4.7. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Extracellular Electrophysiological Recording
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orza, F.; Boswell, M.V.; Rosenberg, S.K. Neuropathic pain: Review of mechanisms anpharmacologic management. NeuroRehabilitation 2000, 14, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.F.; Brooks, K.G. Systematic review of topical amitriptyline for the treatment of neuropathic pain. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, A.M.; Lucero, M.A.; Le, T.; Robinson, R.L.; Dworkin, R.H.; Chappell, A.S. Epidemiology, public health burden, and treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: A review. Pain Med. 2007, 8, S50–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Lv, Y.; Ren, F. PI3K/Akt Pathway is Required for Spinal Central Sensitization in Neuropathic Pain. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.E.; Lu, V.B.; Stebbing, M.J.; Balasubramanyan, S.; Smith, P.A. Is BDNF sufficient for information transfer between microglia and dorsal horn neurons during the onset of central sensitization? Mol. Pain. 2010, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hildebrand, M.E.; Xu, J.; Dedek, A.; Li, Y.; Sengar, A.S.; Beggs, S.; Lombroso, P.J.; Salter, M.W. Potentiation of Synaptic GluN2B NMDAR Currents by Fyn Kinase Is Gated through BDNF-Mediated Disinhibition in Spinal Pain Processing. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terada, Y.; Morita-Takemura, S.; Isonishi, A.; Tanaka, T.; Okuda, H.; Tatsumi, K.; Shinjo, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Wanaka, A. NGF and BDNF expression in mouse DRG after spared nerve injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 686, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M. Contribution of BDNF/TrκB signalling in the rACC to the development of pain-related aversion via activation of ERK in rats with spared nerve injury. Brain Res. 2017, 1671, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Cai, J.; Li, S.; Liu, X.D.; Wan, Y.; Xing, G.G. BDNF contributes to the development of neuropathic pain by induction of spinal long-term potentiation via SHP2 associated GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors activation in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 73, 428–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Hou, W.; Liu, R.; Gao, Y.; Kong, X.; Yang, L.; Shi, Z.; Li, W.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, S.; et al. PAR2-mediated upregulation of BDNF contributes to central sensitization in bone cancer pain. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malcangio, M. Spinal mechanisms of neuropathic pain: Is there a P2X4-BDNF controversy? Neurobiol. Pain 2017, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, X.Q.; Xue, Q.S.; Yan, L.; Huang, J.L.; Zhang, S.; Shao, H.J.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.Y.; Yu, B.W. The BDNF/TrκB signaling pathway is involved in heat hyperalgesia mediated by Cdk5 in rats. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e85536. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, S.J.; Liao, F.F.; Dang, W.H.; Ding, X.; Liu, X.D.; Cai, J.; Han, J.S.; Wan, Y.; Xing, G.G. Contribution of the spinal cord BDNF to the development of neuropathic pain by activation of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 222, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leysen, L.; Adriaenssens, N.; Nijs, J.; Pas, R.; Bilterys, T.; Vermeir, S.; Lahousse, A.; Beckwee, D. Chronic Pain in Breast Cancer Survivors: Nociceptive, Neuropathic, or Central Sensitization Pain? Pain Pract. 2019, 19, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broeke, E.N. Central sensitization and pain hypersensitivity: Some critical considerations. F1000Res. 2018, 7, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.X.; Cai, J.; Li, M.J.; Chi, Y.N.; Liao, F.F.; Liu, F.Y.; Wan, Y.; Han, J.S.; Xing, G.G. Role of the spinal cord NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the development of neuropathic pain. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 215, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygh, L.J.; Kontinen, V.K.; Suzuki, R.; Dickenson, A.H. Different increase in C-fibre evoked responses after nociceptive conditioning stimulation in sham-operated and neuropathic rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 288, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnion, B.P. Neuropathic pain: Current definition and review of drug treatment. Aust. Prescr. 2018, 41, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudt, M.D.; Clark, A.J.; Gordon, A.S.; Lynch, M.E.; Morley-Forster, P.K.; Nathan, H.; Smyth, C.; Stitt, L.W.; Toth, C.; Ware, M.A.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in the Management of Central Neuropathic Pain Syndromes: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 45, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canders, C.P.; Krishna, P.K.; Moheimani, R.S.; Weaver, C.M. Management of an Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Neuropathic Pain in the Emergency Department: A Case to Support Ultrasound-Guided Forearm Nerve Blocks. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 55, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Wu, F.; Gan, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, B.; Liu, L. The Involvement of Descending Pain Inhibitory System in Electroacupuncture-Induced Analgesia. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lao, L.; Ren, K.; Berman, B.M. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology 2014, 120, 482–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xia, Y.Y.; Huang, Z.H.; Huang, C. Involvement of alpha7nAChR in electroacupuncture relieving neuropathic pain in the spinal cord of rat with spared nerve injury. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 137, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.C.; Tang, N.Y.; Lin, Y.W.; Li, T.C.; Liu, H.J.; Hsieh, C.L. Effect of electroacupuncture on rats with chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 129875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Duanmu, C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Litscher, G. The Effect of Repeated Electroacupuncture Analgesia on Neurotrophic and Cytokine Factors in Neuropathic Pain Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 8403064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, W.Z.; Li, S.S.; Jiang, X.; Qian, X.R.; Yang, G.H.; Gu, P.P.; Lu, B.; Jiang, S.H. Effect of electro-acupuncture on the BDNF-TrκB pathway in the spinal cord of CCI rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3307–3315. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, G.G.; Liu, F.Y.; Qu, X.X.; Han, J.S.; Wan, Y. Long-term synaptic plasticity in the spinal dorsal horn and its modulation by electroacupuncture in rats with neuropathic pain. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 208, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, M.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Huang, C. Electroacupuncture treatment upregulates alpha7nAChR and inhibits JAK2/STAT3 in dorsal root ganglion of rat with spared nerve injury. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.Y.; Xue, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.H.; Huang, C. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Spared Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain and Modulates HMGB1/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway in The Spinal Cord. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2851–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moalem, G.; Tracey, D.J. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in neuropathic pain. Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 51, 240–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Interactions between the immune and nervous systems in pain. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, K.; Cengiz, G.; Erol, K.; Ozgocmen, S. Neuropathic Pain Component in Axial Spondyloarthritis and the Influence on Disease Burden. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 24, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.; Schaefer, C.; Sadosky, A.; Bergstrom, F.; Baik, R.; Parsons, B.; Nalamachu, S.; Stacey, B.R.; Tuchman, M.; Anschel, A.; et al. Burden of spinal cord injury-related neuropathic pain in the United States: Retrospective chart review and cross-sectional survey. Spinal Cord 2013, 51, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bannister, K.; Sachau, J.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H. Neuropathic Pain: Mechanism-Based Therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Y.; Qu, X.X.; Cai, J.; Wang, F.T.; Xing, G.G.; Wan, Y. Electrophysiological properties of spinal wide dynamic range neurons in neuropathic pain rats following spinal nerve ligation. Neurosci. Bull. 2011, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, M.; Xia, Y.Y.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, Z.H.; Huang, C. Electroacupuncture Treatment Suppresses Transcription Factor IRF8 in Spinal Cord of Rats with Spared Nerve Injury. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 1854363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, X.L.; Chen, H.M.; Wu, L.F. Effect of electroacupuncture on neurotrophin expression in cat spinal cord after partial dorsal rhizotomy. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Shao, X.; Liang, Y.; Du, J.; Fang, J.; et al. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Rats via Suppressing TLR4 Signaling and TRPV1 Upregulation in Sensory Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aloe, L.; Manni, L. Low-frequency electro-acupuncture reduces the nociceptive response and the pain mediator enhancement induced by nerve growth factor. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 449, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.F.; Wei, J.J.; Shou, S.Y.; Fang, J.Q.; Jiang, Y.L. Effects of electroacupuncture at 2 and 100 Hz on rat type 2 diabetic neuropathic pain and hyperalgesia-related protein expression in the dorsal root ganglion. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2017, 18, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, D.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W. Electroacupuncture analgesia with different frequencies is mediated via different opioid pathways in acute visceral hyperalgesia rats. Life Sci. 2016, 160, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Q.; Du, J.Y.; Fang, J.F.; Xiao, T.; Le, X.Q.; Pan, N.F.; Yu, J.; Liu, B.Y. Parameter-specific analgesic effects of electroacupuncture mediated by degree of regulation TRPV1 and P2X3 in inflammatory pain in rats. Life Sci. 2018, 200, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Qiao, L.N.; Zhang, J.L.; Duan-Mu, C.L.; Yan, Y.X.; Chen, S.P.; Liu, J.L. Repeated electroacupuncture treatment attenuated hyperalgesia through suppression of spinal glial activation in chronic neuropathic pain rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; You, Y.; Joseph, C.; Mirzaei, M.; Klistorner, A.; Graham, S.L.; Gupta, V. BDNF Polymorphism: A Review of Its Diagnostic and Clinical Relevance in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pezet, S. Neurotrophins and pain. Biol. Aujourdhui 2014, 208, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Nagappan, G.; Lu, B. Differential effects of transient and sustained activation of BDNF-TrκB signaling. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaalani, R.; Chen, H. Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), its tyrosine kinase receptor B (TrκB) and nicotine. Neurotoxicology 2018, 65, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowianski, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waskow, M.; Steliga, A.; Morys, J. BDNF: A Key Factor with Multipotent Impact on Brain Signaling and Synaptic Plasticity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Luo, H.; Sims, N.R.; Bobrovskaya, L.; Zhou, X.F. Investigation of Mature BDNF and proBDNF Signaling in a Rat Photothrombotic Ischemic Model. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, J.; Meeus, M.; Versijpt, J.; Moens, M.; Bos, I.; Knaepen, K.; Meeusen, R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a driving force behind neuroplasticity in neuropathic and central sensitization pain: A new therapeutic target? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, L.Y.; Xu, T.L. Reduced potassium-chloride co-transporter expression in spinal cord dorsal horn neurons contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity in rats. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richner, M.; Pallesen, L.T.; Ulrichsen, M.; Poulsen, E.T.; Holm, T.H.; Login, H.; Castonguay, A.; Lorenzo, L.E.; Goncalves, N.P.; Andersen, O.M.; et al. Sortilin gates neurotensin and BDNF signaling to control peripheral neuropathic pain. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lever, I.J.; Bradbury, E.J.; Cunningham, J.R.; Adelson, D.W.; Jones, M.G.; McMahon, S.B.; Marvizon, J.C.; Malcangio, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is released in the dorsal horn by distinctive patterns of afferent fiber stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 4469–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Cai, J.; Feng, Z.B.; Jin, Z.R.; Liu, B.H.; Zhao, H.Y.; Jing, H.B.; Wei, T.J.; Yang, G.N.; Liu, L.Y.; et al. BDNF Contributes to Spinal Long-Term Potentiation and Mechanical Hypersensitivity Via Fyn-Mediated Phosphorylation of NMDA Receptor GluN2B Subunit at Tyrosine 1472 in Rats Following Spinal Nerve Ligation. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 2712–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qi, J.G.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Meng, Q.S.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, T.H. Electro-acupuncture induced NGF, BDNF and NT-3 expression in spared L6 dorsal root ganglion in cats subjected to removal of adjacent ganglia. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 59, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, J.M.; Chaouch, A. Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception. Physiol. Rev. 1987, 67, 67–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, W.D., Jr. Is central sensitization of nociceptive transmission in the spinal cord a variety of long-term potentiation? Neuroreport 1997, 8, iii. [Google Scholar]
- Carlton, S.M.; Du, J.; Tan, H.Y.; Nesic, O.; Hargett, G.L.; Bopp, A.C.; Yamani, A.; Lin, Q.; Willis, W.D.; Hulsebosch, C.E. Peripheral and central sensitization in remote spinal cord regions contribute to central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Pain 2009, 147, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Cai, J.; Guo, X.Y.; Meng, X.L.; Xing, G.G. The antiallodynic action of pregabalin may depend on the suppression of spinal neuronal hyperexcitability in rats with spared nerve injury. Pain Res. Manag. 2014, 19, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berrocoso, E.; Mico, J.A.; Vitton, O.; Ladure, P.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Depoortere, R.; Bardin, L. Evaluation of milnacipran, in comparison with amitriptyline, on cold and mechanical allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 655, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M. Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genes | Sequences |
|---|---|
| GADPH-F | CAGCCGCATCTTCTTGTGC |
| BDNF-F | GGTAACCAGGCGTCCGATA |
| BDNF-R | CCAGATCCTCCCTGACTGGT |
| TrκB-F | TAAGGCTGAATGGTGTGCGT |
| TrκB-R | CTGCCTTCACAGATACCCAGTA |
| - | ACCTTAAACTCGGACCTCACC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, M.; Sun, Y.-L.; Xia, Y.-Y.; Huang, Z.-H.; Huang, C.; Xing, G.-G. Electroacupuncture Modulates Spinal BDNF/Tr?B Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates the Sensitization of Dorsal Horn WDR Neurons in Spared Nerve Injury Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186524
Xue M, Sun Y-L, Xia Y-Y, Huang Z-H, Huang C, Xing G-G. Electroacupuncture Modulates Spinal BDNF/Tr?B Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates the Sensitization of Dorsal Horn WDR Neurons in Spared Nerve Injury Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186524
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Meng, Ya-Lan Sun, Yang-Yang Xia, Zhi-Hua Huang, Cheng Huang, and Guo-Gang Xing. 2020. "Electroacupuncture Modulates Spinal BDNF/Tr?B Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates the Sensitization of Dorsal Horn WDR Neurons in Spared Nerve Injury Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186524
APA StyleXue, M., Sun, Y.-L., Xia, Y.-Y., Huang, Z.-H., Huang, C., & Xing, G.-G. (2020). Electroacupuncture Modulates Spinal BDNF/Tr?B Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates the Sensitization of Dorsal Horn WDR Neurons in Spared Nerve Injury Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186524






