Protective Effects of Evogliptin on Steatohepatitis in High-Fat-Fed Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Evogliptin on Body Weight, Epididymal Fat Pad Weight, Glucose Level, Food Intake, Serum Insulin, and Liver Enzyme in HFD Mice
2.2. Effect of Evogliptin on Hepatic Steatohepatitis in HFD Mice
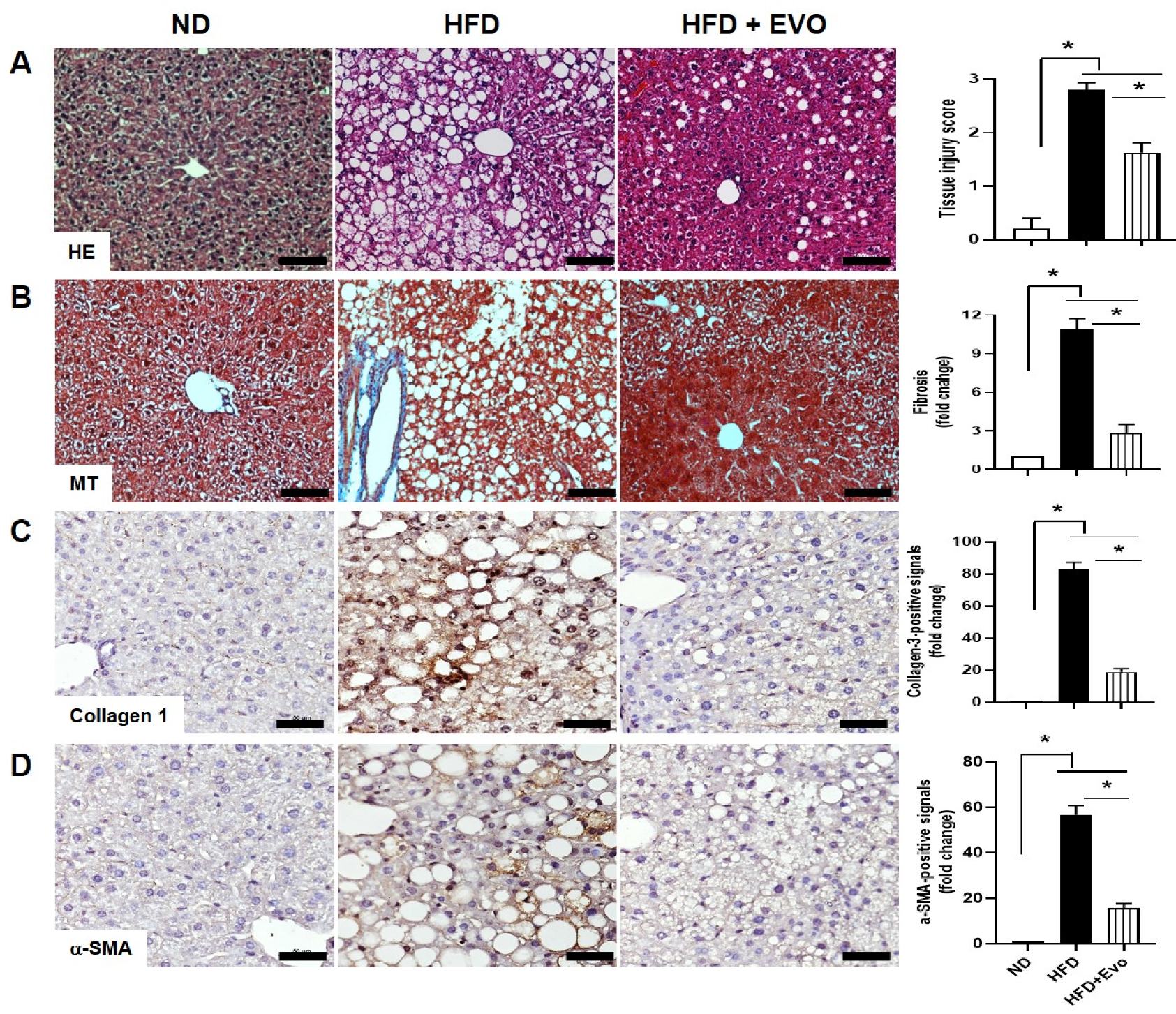
2.3. Effect of Evogliptin on Hepatic Morphological Changes and Fibrosis by HFD
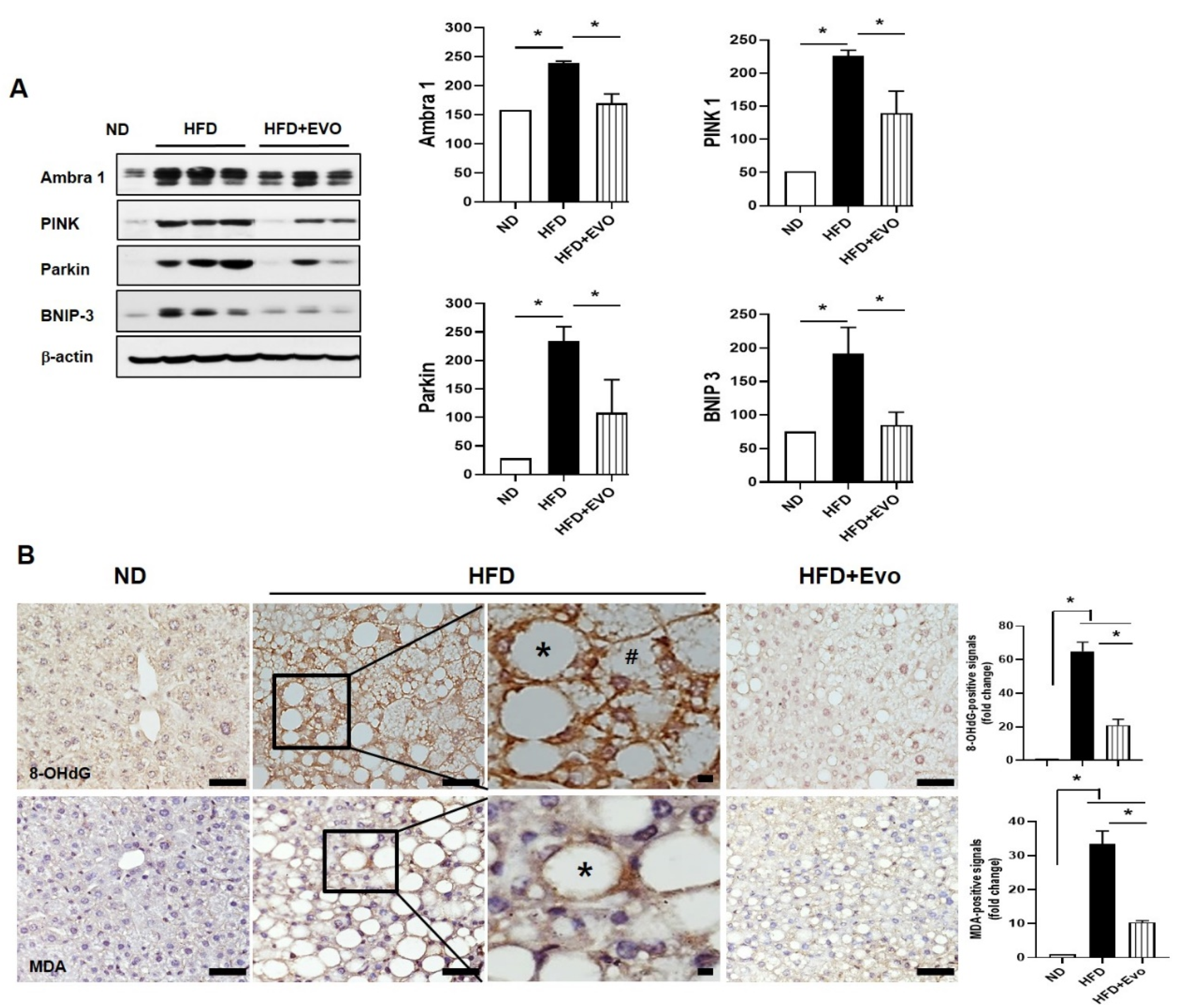
2.4. Effects of Evogliptin on Hepatic Autophagy in HFD Mice
2.5. Effects of Evogliptin on Hepatic Mitophagy and Oxidative Stress in HFD Mice
2.6. Effects of Evogliptin on Hepatic Cell Death by HFD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Animals and Treatment
4.3. Tissue Pathology
4.4. Oil Red O Staining and Masson’s Trichrome Staining
4.5. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End-Labeling Assay
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.7. Protein Preparation and Western Blotting
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| αSMA | A-smooth muscle actin |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferse |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| Dgat2 | Diglyceride acyltransferase 2 |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| MT | Masson trichrome |
| NAFLD | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| ND | Normal chow |
| 8-OHDG | 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine |
| PINK1 | PTEN-induced kinase 1 |
| Pnpla2 | Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing proteins 2 |
| pAkt | Phospho-Akt |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling |
References
- Krawczyk, M.; Bonfrate, L.; Portincasa, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.-S.; Roh, Y.S. Molecular Insights into the Role of Mitochondria in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Arch. Pharm Res. 2019, 42, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatiha, N.; Jamal, A.I. Role of Mitochondria in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8713–8742. [Google Scholar]
- Ueno, T.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy in the liver: Functions inhealth and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, N.; Ito, Y.; Otsuki, Y. Triggering of Parkin Mitochondrial Translocation in Mitophagy: Implications for Liver Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Furuya, N. Induction of PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1759, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Chang, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. Mst1 inhibition attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via reversing Parkin-related mitophagy. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Yu, X.Y.; Ma, X.F.; Wen-Jian, L.; Ming, H.; Hong-Yu, K. Exenatide Delays the Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in C57BL/6 Mice, Which May Involve Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome through the Mitophagy Pathway. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 1864307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijun, P.; Kai, L.; Daojie, L.; Fudong, L.; Yunjin, Z.; Fang, X.; Jiming, Y.; Ying, S.; Yanjun, W.; Dexi, C. Differential effects of reticulophagy and mitophagy on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Fukunishi, S.; Yokohama, K.; Hideko, O.; Yusuke, T.; Akira, A.; Yasuhiro, T.; Kazuhide, H. A long-lasting dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, teneligliptin, as a preventive drug for the development of hepatic steatosis in high-fructose diet-fed ob/ob mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuya, S.; Shinya, F.; Masaaki, I.; Ken, N.; Keisuke, Y.; Hideko, O.; Yusuke, T.; Akira, A.; Yasuhiro, T.; Kazuhide, H. Sitagliptin can inhibit the development of hepatic steatosis in high-fructose diet-fed ob/ob mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 57, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, M.; Klöting, N.; Niessen, H.G.; Leo, T.; Detlef, S.; Michael, M.; Thomas, K.; Matthias, B. Linagliptin improves insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohyama, T.; Sato, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Hiroaki, H.; Norio, H.; Satoru, K.; Masatomo, M.; Motoyasu, K.; Masanobu, Y. MK-0626, a selective DPP-4 inhibitor, attenuates hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16227–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi-Kyung, K.; Yu Na, C.; Gook-Jun, A.; Chang Yell, S.; Song-Hyen, C.; Eun Kyoung, Y.; Yong Sung, S.; Moon-Ho, S. Prevention and treatment effect of evogliptin on hepatic steatosis in high-fat-fed animal models. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 268–281. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Kaushik, S.; Wang, Y.; Ziang, Y.; Novak, I.; Komatesu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Cuervo, A.M.; Czaja, M.J. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 1131–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mentzel, S.; Dijkman, H.B.; Van Son, J.P.; Koene, R.A.; Assmann, K.J. Organ distribution of aminopeptidase A and dipeptidyl peptidase IV in normal mice. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1996, 44, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, H.-J.; Jung, T.W.; Kim, B.H.; Hong, H.C.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, K.M.; Choi, D.S.; Baik, S.H.; et al. A dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor improves hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by AMPK-dependent and JNK-dependent inhibition of LECT2 expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ma, C.; Gu, H.; Shi, L.; Tian, X.-T.; Xu, W.-Q. Sitagliptin improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction through activation of autophagy in streptozotocin induced diabetic mice. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8973–8983. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Zhou, J.; Song, S.; Kong, W.; Xia, W.; Chen, L.; Zeng, T. Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 Inhibitor Sitagliptin Ameliorates Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Modulating Inflammation and Autophagy in ob/ob Mice. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 8309723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, Y.; Ping, L.; Suneng, F.; Ediz, S.C.; Gökhan, S.H. Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 467–478. [Google Scholar]
- Inami, Y.; Yamashina, S.; Izumi, K.; Ueno, T.; Tanida, I.; Ikejima, K.; Watanabe, S. Hepatic steatosis inhibits autophagic proteolysis via impairment of autophagosomal acidification and cathepsin expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, E.; Cuervo, A.M. Chaperone-mediated autophagy in protein quality control. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.-M.; Codogno, P. Autophagic cell death: Loch Ness monster or endangered species? Autophagy 2011, 7, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.A.; Ni, H.-M.; Ding, Y.; Ding, W.-X. Parkin regulates mitophagy and mitochondrial function to protect against alcohol-induced liver injury and steatosis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.A.; Ding, W.-X. Mechanistic Review of Mitophagy and Its Role in Protection against Alcoholic Liver Disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2619–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Toro, J.A.; Go, K.L.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Kim, J.-S. Autophagy in the Liver: Cell’s Cannibalism and Beyond. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Lou, J.; Wen, T.; Yin, J.; Xu, B.; Ding, W.; Wang, A.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Chen, D.; et al. Depending on the Stage of Hepatosteatosis, p53 Causes Apoptosis Primarily Through Either DRAM-induced Autophagy or BAX. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeon, B.T.; Jeong, E.A.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Roh, G.S. Resveratrol attenuates obesty-associated peripheral and central inflammation and improves memory deficit in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, B.T.; Heo, R.W.; Shin, H.J.; Yi, C.-O.; Lee, Y.H.; Joung, H.-N.; Jung, J.H.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.K.; Hahm, J.R.; et al. Attenuation by a Vigna nakashimae extract of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet-fed mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.E.; Jung, Y.; Min, S.; Nam, M.; Heo, R.W.; Jeon, B.T.; Song, D.H.; Yi, C.-O.; Jeong, E.A.; Kim, H.; et al. Caloric restriction of db/db mice prevents hepatic steatosis amd body weight with divergent hepatic metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.J.; Roh, G.S.; Cho, H.S.; Kang, H.; Kim, S.K. Protective Effects of Evogliptin on Steatohepatitis in High-Fat-Fed Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186743
Kim JH, Jang SJ, Roh GS, Cho HS, Kang H, Kim SK. Protective Effects of Evogliptin on Steatohepatitis in High-Fat-Fed Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186743
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jin Hyun, Si Jung Jang, Gu Seob Roh, Hyun Seop Cho, Heeyoung Kang, and Soo Kyoung Kim. 2020. "Protective Effects of Evogliptin on Steatohepatitis in High-Fat-Fed Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186743
APA StyleKim, J. H., Jang, S. J., Roh, G. S., Cho, H. S., Kang, H., & Kim, S. K. (2020). Protective Effects of Evogliptin on Steatohepatitis in High-Fat-Fed Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186743




