A Novel Method for Measuring Serum Unbound Bilirubin Levels Using Glucose Oxidase–Peroxidase and Bilirubin-Inducible Fluorescent Protein (UnaG): No Influence of Direct Bilirubin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study A: Impact of Serum DB Levels on the Correlations between iDB/A Ratio and Serum UB Levels in Clinical Data
2.2. Study B: Impact of Serum DB Levels on Measuring Serum UB Levels Using the GOD–POD–UnaG Method
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study A
4.1.1. Setting and Study Design
4.1.2. Subjects
4.1.3. Measurement Methods
4.1.4. Study Methods
4.2. Study B
4.2.1. Setting
4.2.2. GOD–POD Method Protocol
4.2.3. GOD–POD–UnaG Method Protocol
4.2.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| iDB | Indirect bilirubin (serum unconjugated bilirubin) |
| UB | Unbound bilirubin (albumin free bilirubin) |
| GOD | Glucose oxidase |
| POD | Peroxidase |
| GOD–POD | Glucose oxidase–peroxidase |
| DB | Direct bilirubin (conjugated bilirubin) |
| NICU | Neonatal intensive care unit |
| UnaG | Bilirubin-inducible fluorescent protein from eel muscle |
| TB | Total serum bilirubin |
| iDB/A | Indirect bilirubin/albumin |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| TB/A | Total serum bilirubin/albumin |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
References
- Morioka, I.; Iwatani, S.; Koda, T.; Iijima, K.; Nakamura, H. Disorders of bilirubin binding to albumin and bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 20, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watchko, J.F.; Tiribelli, C. Bilirubin-induced neurologic damage—Mechanisms and management approaches. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2021–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitai, Y.; Hirai, S.; Okuyama, N.; Hirotsune, M.; Nishimoto, S.; Mizutani, S.; Okumura, A.; Kumada, S.; Arai, H. A questionnaire survey on the efficacy of various treatments for dyskinetic cerebral palsy due to preterm bilirubin encephalopathy. Brain Dev. 2020, 42, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitai, Y.; Hirai, S.; Okuyama, N.; Hirotsune, M.; Mizutani, S.; Ogura, K.; Ohmura, K.; Okumura, A.; Arai, H. Diagnosis of bilirubin encephalopathy in preterm infants with dyskinetic cerebral palsy. Neonatology 2020, 117, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morioka, I.; Nakamura, H.; Koda, T.; Yokota, T.; Okada, H.; Katayama, Y.; Kunikata, T.; Kondo, M.; Nakamura, M.; Hosono, S.; et al. Current incidence of clinical kernicterus in preterm infants in Japan. Pediatr. Int. 2015, 57, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Lee, Y. Microdetermination of unbound bilirubin in icteric newborn sera: An enzymatic method employing peroxidase and glucose oxidase. Clin. Chim. Acta 1977, 79, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimabuku, R.; Nakamura, H. Total and unbound bilirubin determination using an automated peroxidase micromethod. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 1982, 28, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwatani, S.; Kataoka, D.; Tamaki, S.; Yokota, T.; Yoshimoto, S. High prevalence of cholestasis at a tertiary neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, A.; Ando, R.; Miyatake, H.; Greimel, P.; Kobayashi, T.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Shimogori, T.; Miyawaki, A. A bilirubin-inducible fluorescent protein from eel muscle. Cell 2013, 153, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwatani, S.; Nakamura, H.; Kurokawa, D.; Yamana, K.; Nishida, K.; Fukushima, S.; Koda, T.; Nishimura, N.; Nishio, H.; Iijima, K.; et al. Fluorescent protein-based detection of unconjugated bilirubin in newborn serum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Morioka, I.; Miwa, A.; Yokota, T.; Matsuo, K.; Koda, T.; Fujioka, K.; Morikawa, S.; Shibata, A.; Yokoyama, N.; et al. Is bilirubin/albumin ratio correlated with unbound bilirubin concentration? Pediatr. Int. 2012, 54, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlfors, C.E.; Vreman, H.J.; Wong, R.J.; Bender, G.J.; Oh, W.; Morris, B.H.; Stevenson, D.K. Effects of sample dilution, peroxidase concentration, and chloride ion on the measurement of unbound bilirubin in premature newborns. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morioka, I. Hyperbilirubinemia in preterm infants in Japan: New treatment criteria. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Yonetani, M.; Uetani, Y.; Funato, M.; Lee, Y. Determination of serum unbound bilirubin for prediction of kernicterus in low birthweight infants. Acta Paediatr. Jpn. 1992, 34, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, A.H.; Zhu, B.; Kwan, T.; Kampf, J.P.; Hegyi, T.; Kleinfeld, A.M. Fluorescence sensor for the quantification of unbound bilirubin concentrations. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bell, J.G.; Mousavi, M.P.S.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Tan, E.K.W.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-based potentiometric sensing of free bilirubin in blood serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
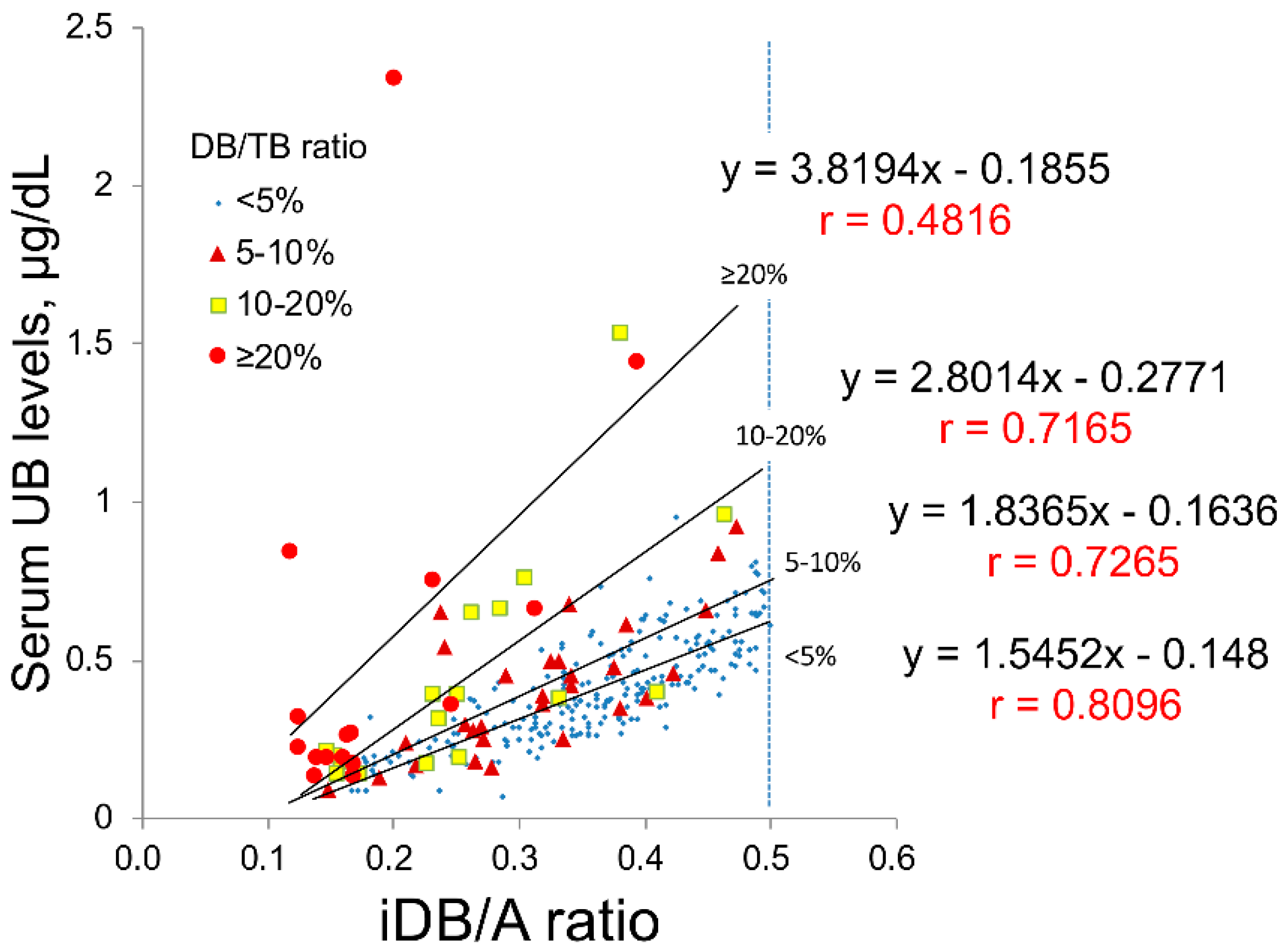


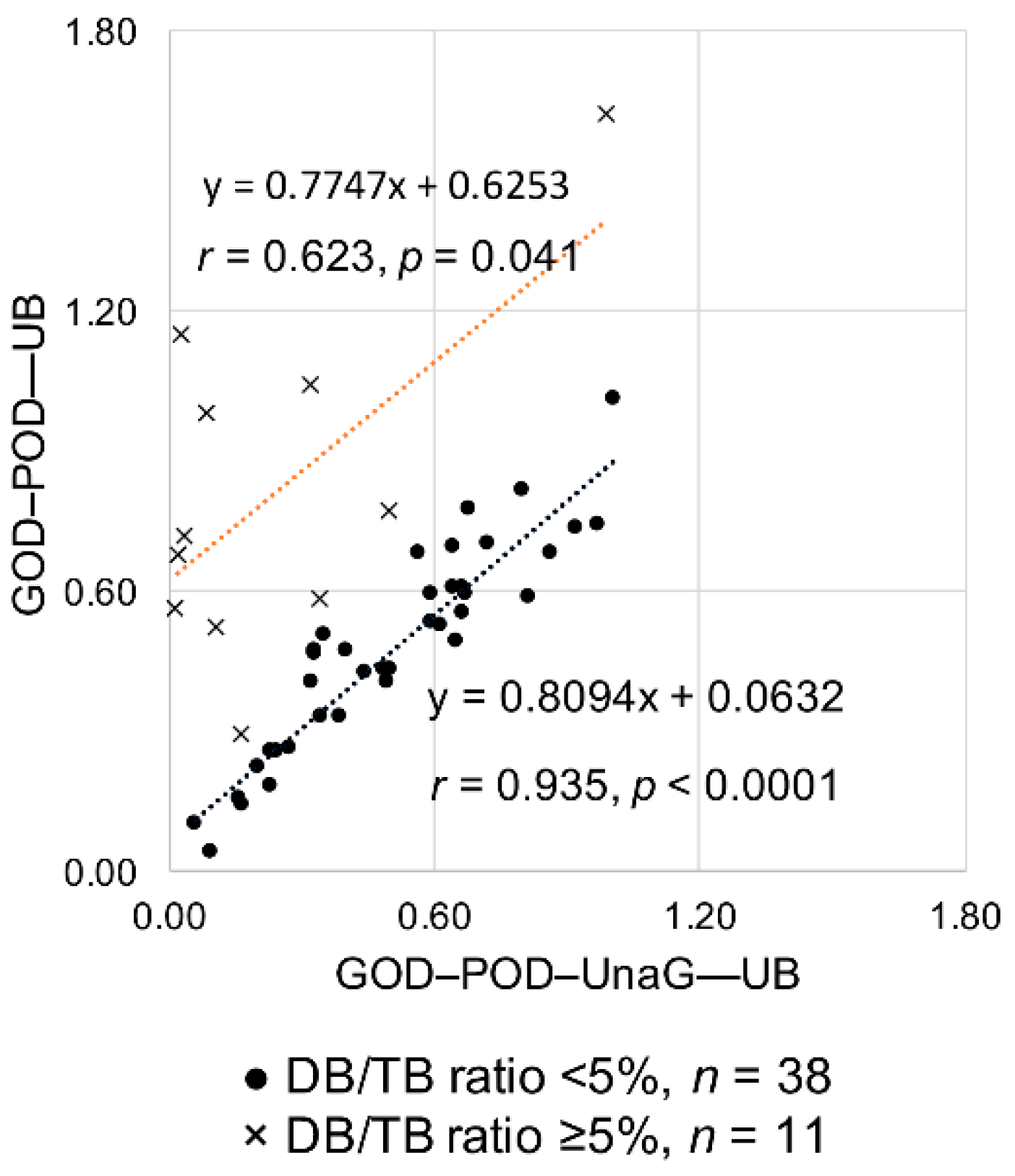
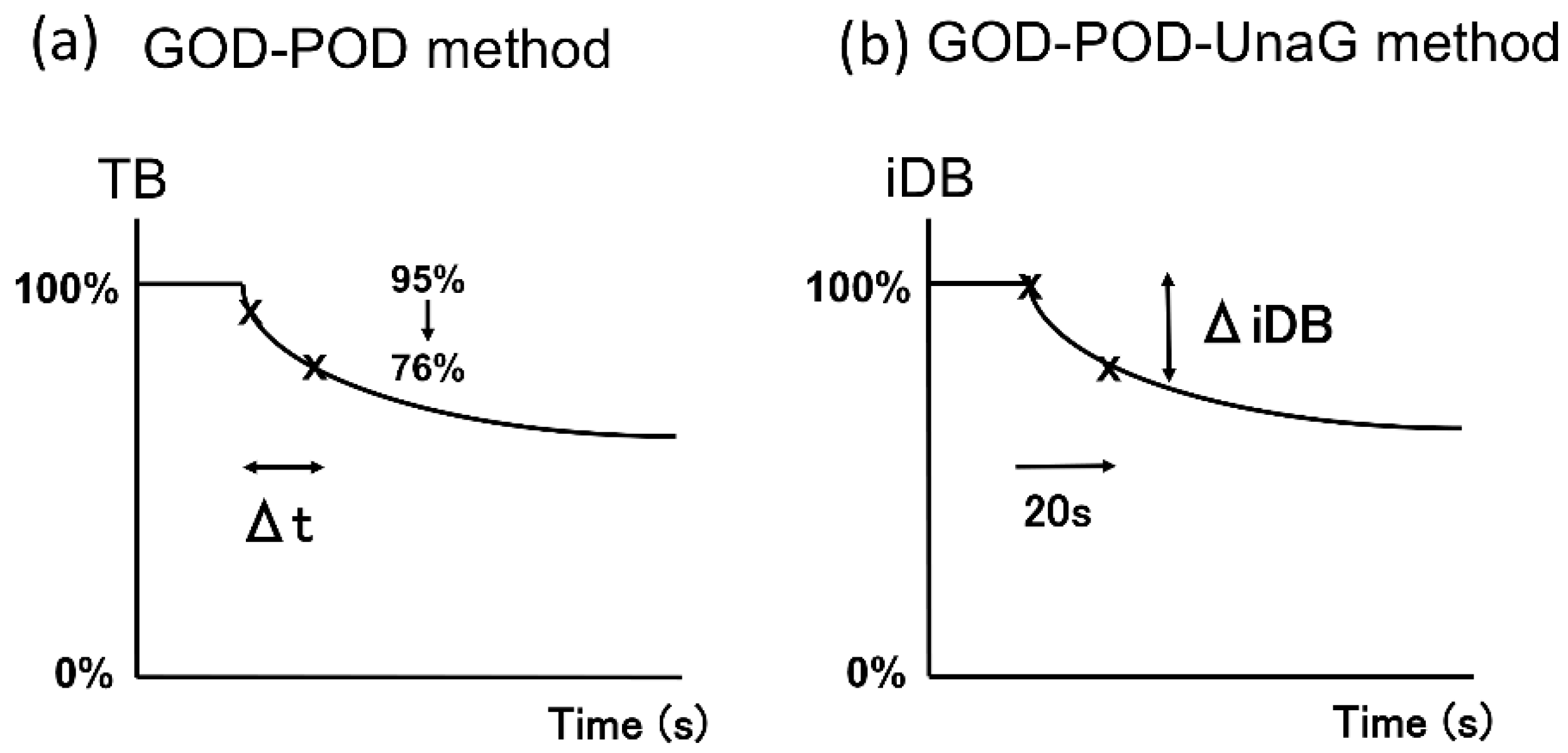
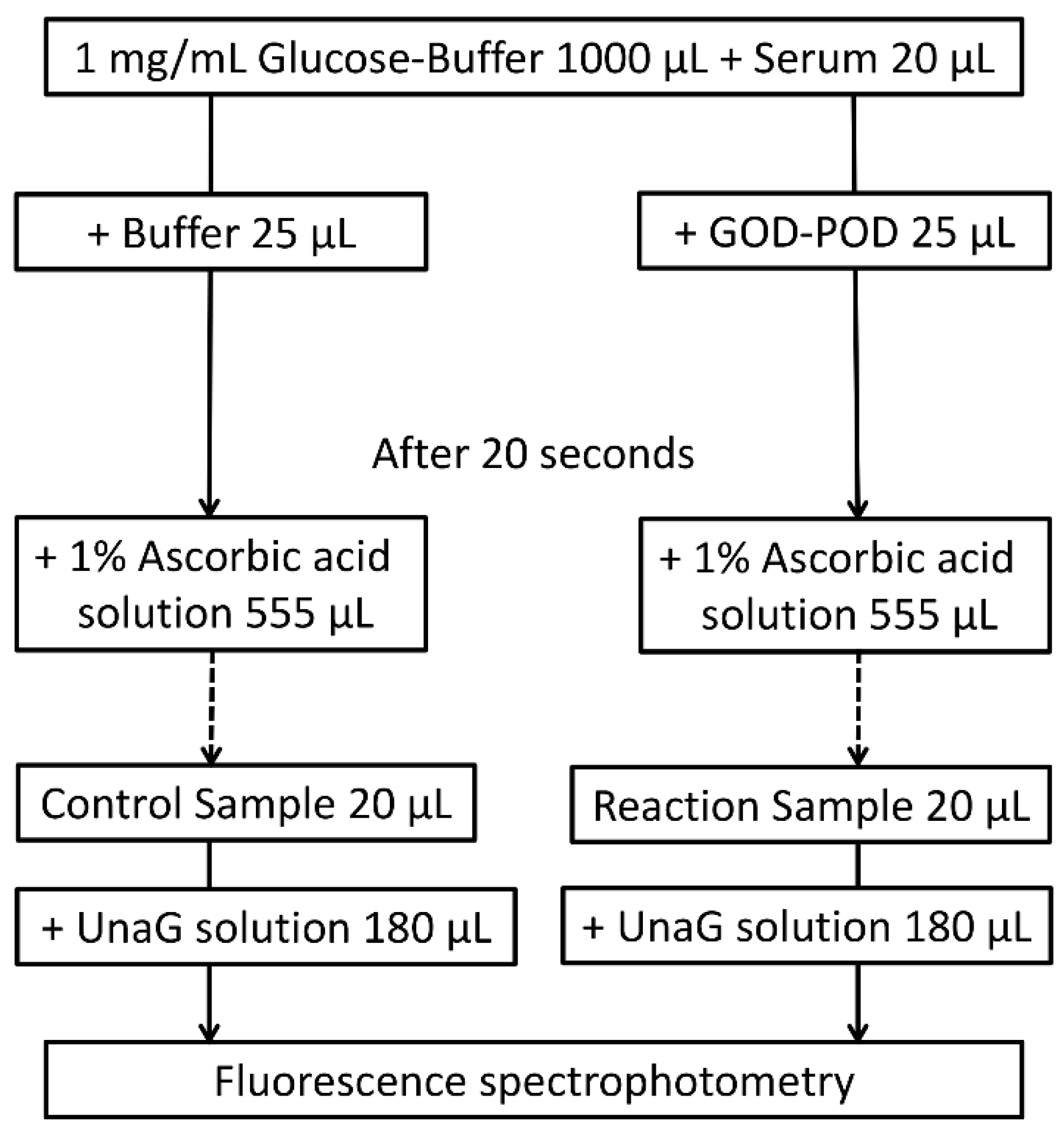
| Sample Number | Case Number | TB (mg/dL) | DB (mg/dL) | iDB (mg/dL) | DB/TB (%) | Alb (g/dL) | UB (µg/dL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GOD–POD | GOD–POD–UnaG | |||||||
| #1 | a | 14.7 | 1.2 | 13.5 | 8.2 | 4.1 | 1.62 | 0.99 |
| #2 | a | 9.1 | 1.0 | 8.1 | 11.0 | 2.6 | 0.77 | 0.50 |
| #3 | a | 9.6 | 1.5 | 8.1 | 15.6 | 3.1 | 0.58 | 0.34 |
| #4 | a | 9.1 | 2.1 | 7.0 | 23.1 | 2.7 | 1.04 | 0.32 |
| #5 | b | 5 | 1.3 | 3.7 | 26.0 | 1.9 | 0.29 | 0.16 |
| #6 | c | 7.2 | 5.0 | 2.2 | 69.4 | 3.1 | 0.68 | 0.02 |
| #7 | c | 7.9 | 5.5 | 2.4 | 69.6 | 3.1 | 0.72 | 0.04 |
| #8 | c | 8.6 | 6.0 | 2.6 | 69.8 | 3.3 | 0.98 | 0.09 |
| #9 | c | 8.7 | 6.1 | 2.6 | 70.1 | 3.4 | 0.52 | 0.11 |
| #10 | b | 4.9 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 71.4 | 2.8 | 0.56 | 0.02 |
| #11 | d | 8.0 | 6.0 | 2.0 | 75.0 | 3.2 | 1.15 | 0.03 |
| Median | 8.60 | 3.50 | 2.60 | 69.44 | 3.10 | 0.72 | 0.11 | |
| p = 0.0011 | ||||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwatani, S.; Yamana, K.; Nakamura, H.; Nishida, K.; Morisawa, T.; Mizobuchi, M.; Osawa, K.; Iijima, K.; Morioka, I. A Novel Method for Measuring Serum Unbound Bilirubin Levels Using Glucose Oxidase–Peroxidase and Bilirubin-Inducible Fluorescent Protein (UnaG): No Influence of Direct Bilirubin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186778
Iwatani S, Yamana K, Nakamura H, Nishida K, Morisawa T, Mizobuchi M, Osawa K, Iijima K, Morioka I. A Novel Method for Measuring Serum Unbound Bilirubin Levels Using Glucose Oxidase–Peroxidase and Bilirubin-Inducible Fluorescent Protein (UnaG): No Influence of Direct Bilirubin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186778
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwatani, Sota, Keiji Yamana, Hajime Nakamura, Kosuke Nishida, Takeshi Morisawa, Masami Mizobuchi, Kayo Osawa, Kazumoto Iijima, and Ichiro Morioka. 2020. "A Novel Method for Measuring Serum Unbound Bilirubin Levels Using Glucose Oxidase–Peroxidase and Bilirubin-Inducible Fluorescent Protein (UnaG): No Influence of Direct Bilirubin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186778
APA StyleIwatani, S., Yamana, K., Nakamura, H., Nishida, K., Morisawa, T., Mizobuchi, M., Osawa, K., Iijima, K., & Morioka, I. (2020). A Novel Method for Measuring Serum Unbound Bilirubin Levels Using Glucose Oxidase–Peroxidase and Bilirubin-Inducible Fluorescent Protein (UnaG): No Influence of Direct Bilirubin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186778





