First Evidence of Kv3.1b Potassium Channel Subtype Expression during Neuronal Serotonergic 1C11 Cell Line Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation of Kv3.1b Gene Expression in a 1C11 Cell Line
2.1.1. Kv3.1b Gene Expression in 1C11
2.1.2. Quantification of Kv3.1 Besides Kv1.1, Kv1.2, Kv1.3, Kv1.4 and Kv2.1 mRNA Expression in 1C11
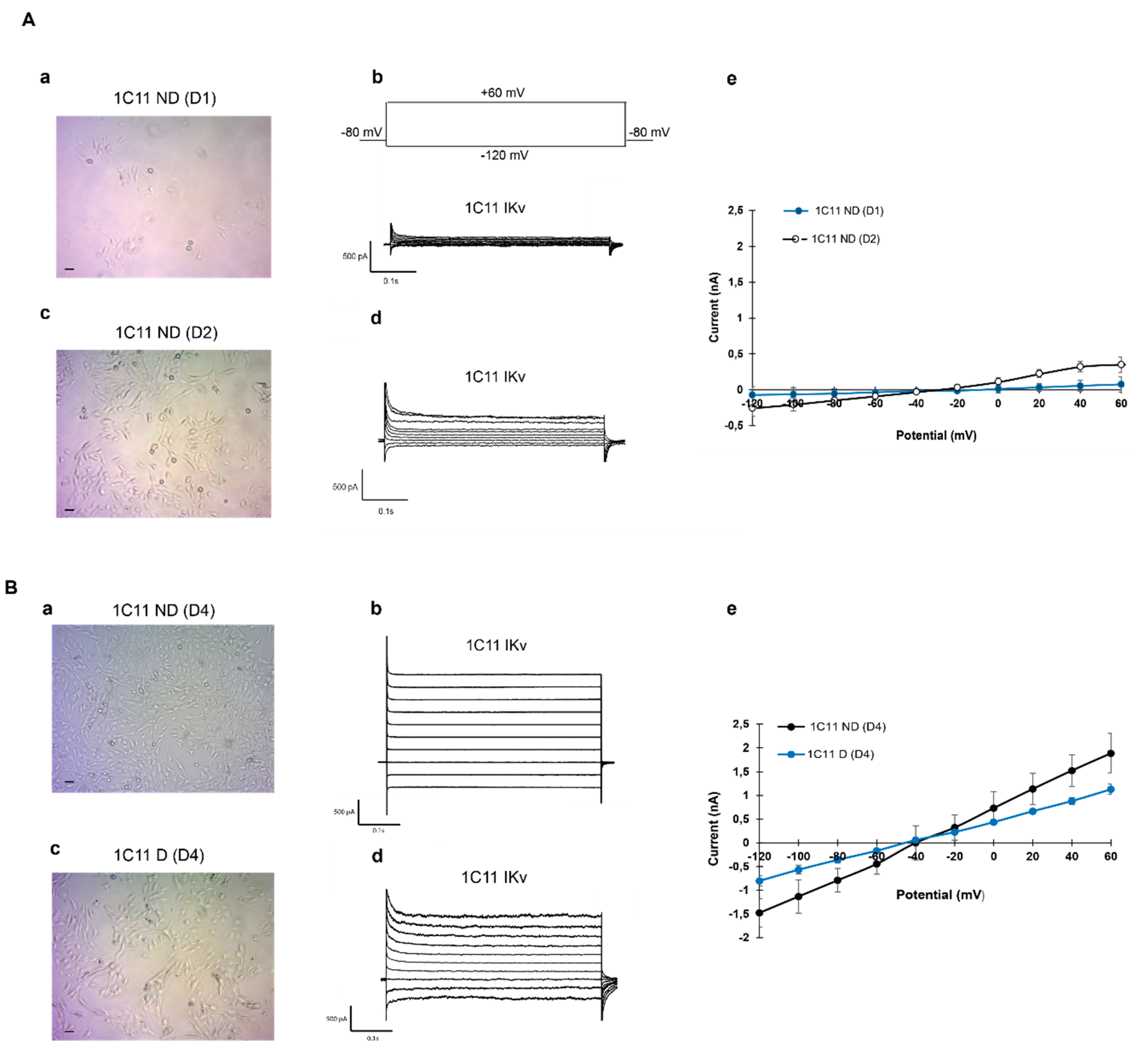
2.2. Potassium Channel Expression During 1C11 Development in the Culture
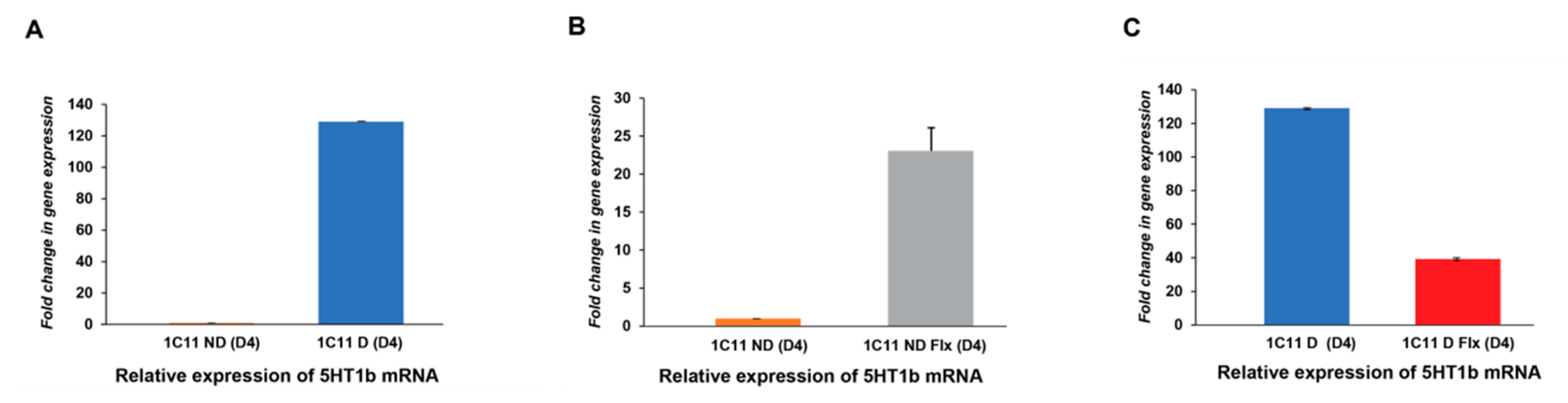
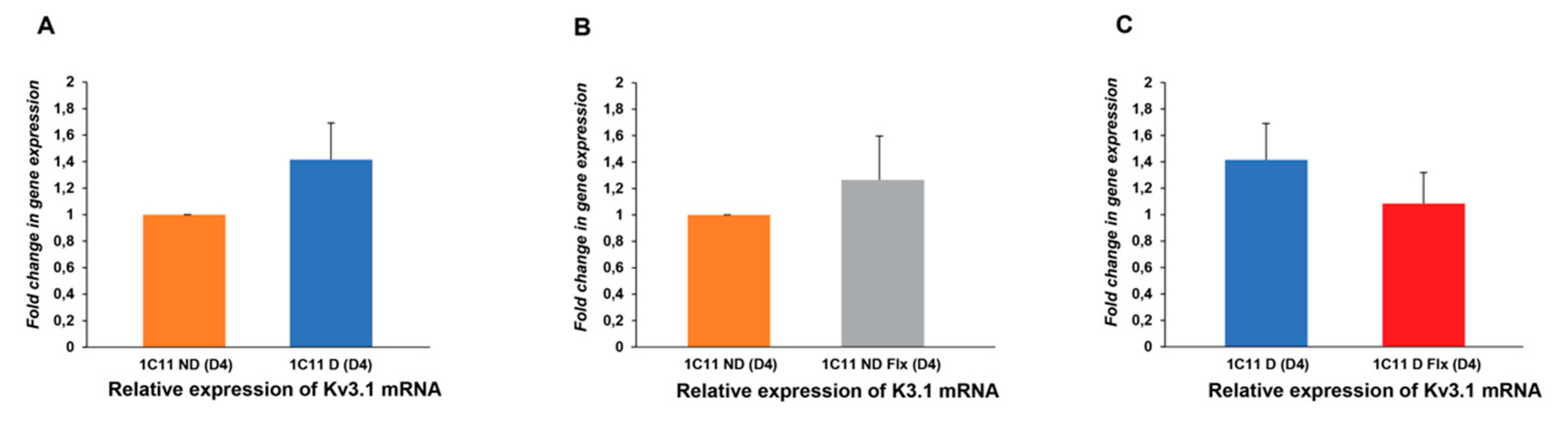
2.3. Variation of Kv3.1b and 5HT1b mRNA Expression in the 1C11 Cell Culture In Vitro And As A Function of Fluoxetine
2.3.1. Analysis of the Fluoxetine Effect on 5HT1b Expression In the 1C11 Cell Line
2.3.2. Analysis of the Fluoxetine Effect on Kv3.1b Expression in the 1C11 Cell Line
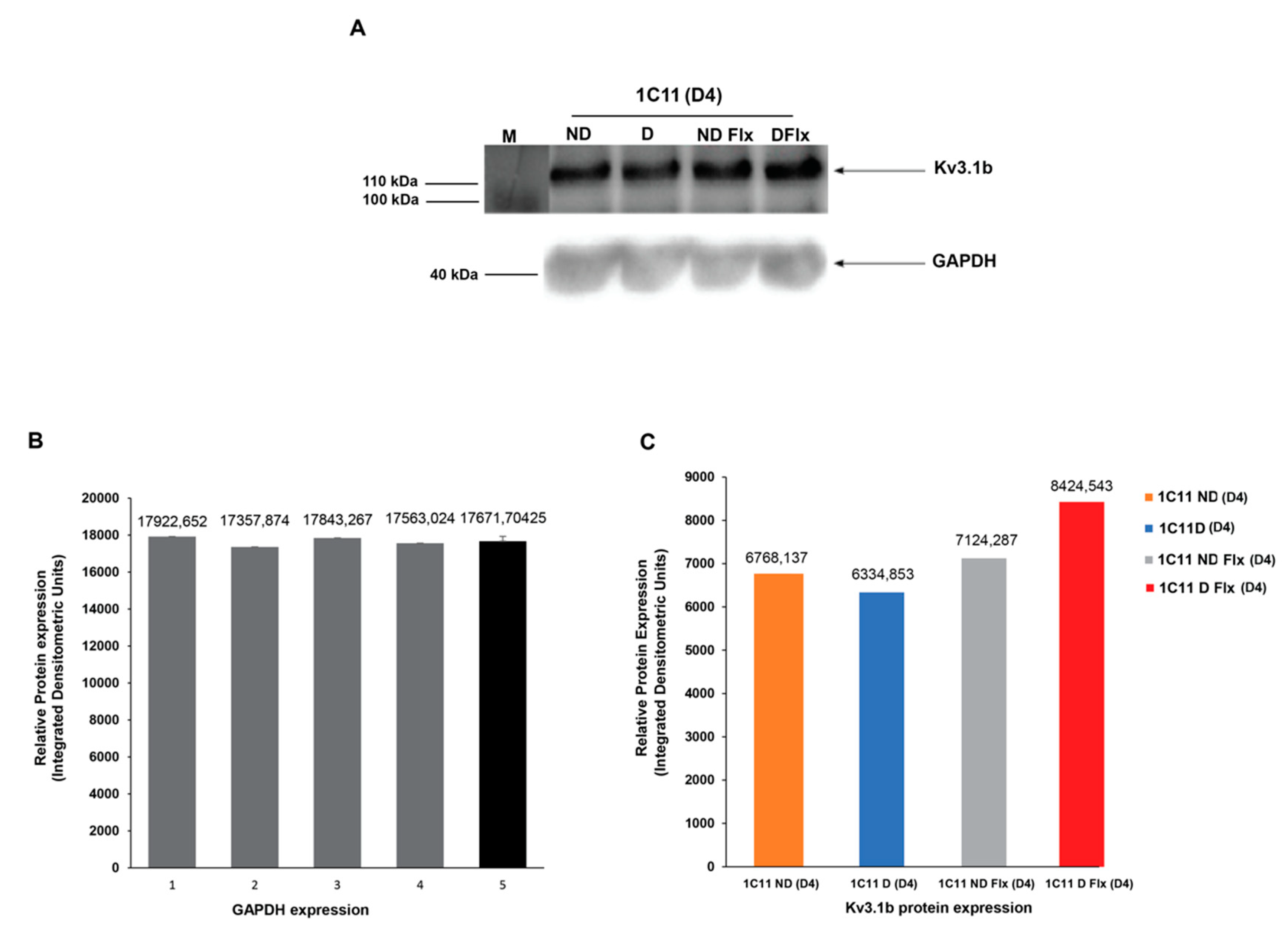
2.4. Evaluation of Kv3.1b Channel Protein Expression in Cultured 1C11
2.5. Evaluation of the Fluoxetine Effect on the Serotoninergic Activity of 1C11 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
3.1.1. C11 Cell Line
3.1.2. Cell Treatment
3.1.3. CHO Cell Culture and Transfection
3.2. Molecular Biology
3.2.1. RNA Extraction, RT-PCR and Real-Time PCR
RNAs Extraction
Reverse Transcription and PCR Amplification
Quantitative-PCR
3.2.2. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
3.3. Serotonin Quantification
3.3.1. Electrophysiological Analysis
3.3.2. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tournois, C.; Mutel, V.; Manivet, P.; Launay, J.-M.; Kellermann, O. Cross-talk between 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptors in a Serotonergic Cell Line. J. Boil. Chem. 1998, 273, 17498–17503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hibino, H.; Inanobe, A.; Furutani, K.; Murakami, S.; Findlay, I.; Kurachi, Y. Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Their Structure, Function, and Physiological Roles. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 291–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-gated sodium channels at 60: Structure, function and pathophysiology. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perney, T.M.; Kaczmarek, L.K. The molecular biology of K+ channels. Curr. Opin. Cell Boil. 1991, 3, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luneau, C.J.; Williams, J.B.; Marshall, J.; Levitan, E.S.; Oliva, C.; Smith, J.S.; Antanavage, J.; Folander, K.; Stein, R.B.; Swanson, R. Alternative splicing contributes to K+ channel diversity in the mammalian central nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3932–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Critz, S.D.; Wible, B.A.; Lopez, H.S.; Brown, A.M. Stable Expression and Regulation of a Rat Brain K+Channel. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grissmer, S.; Nguyen, A.N.; Aiyar, J.; Hanson, D.C.; Mather, R.J.; Gutman, G.A.; Karmilowicz, M.J.; Auperin, D.D.; Chandy, K.G. Pharmacological characterization of five cloned voltage-gated K+ channels, types Kv1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.5, and 3.1, stably expressed in mammalian cell lines. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 45, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Kanemasa, T.; Gan, L.; Perney, T.M.; Wang, L.Y.; Kaczmarek, L.K. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of a mammalian Shaw channel expressed in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 74, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, W.A.; Amarillo, Y.; Chiu, J.; Chow, A.; Lau, D.; McCormack, T.; Morena, H.; Nadal, M.S.; Ozaita, A.; Pountney, D.; et al. Molecular Diversity of K+ Channels. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 868, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.J.; Ahn, H.S.; Hahn, S.J.; Choi, B.H. Open channel block of Kv3.1 currents by fluoxetine. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 106, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perney, T.M.; Marshall, J.; Martin, K.A.; Hockfield, S.; Kaczmarek, L.K. Expression of the mRNAs for the Kv3.1 potassium channel gene in the adult and developing rat brain. J. Neurophysiol. 1992, 68, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.; Vega-Saenz de Miera, E.; Kentros, C.; Moreno, H.; Franzen, L.; Hillman, D.; Baker, H.; Rudu, B. Differential expression of Shaw-related K+ channels in the rat central nervous system. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 949–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lenz, S.; Perney, T.M.; Qin, Y.; Robbins, E.; Chesselet, M.-F. GABA-Ergic interneurons of the striatum express the shaw-like potassium channel KvS3.1. Synapse 1994, 18, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boda, E.; Hoxha, E.; Pini, A.; Montarolo, F.; Tempia, F. Brain Expression of Kv3 Subunits During Development, Adulthood and Aging and in a Murine Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 46, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.; Chen, L.Q. Heterologous expression of specific K+ channels in T lymphocytes: Functional consequences for volume regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10036–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muona, M.; Berkovic, S.; Dibbens, L.M.; Oliver, K.L.; Maljevic, S.; Bayly, M.A.; Joensuu, T.; Canafoglia, L.; Franceschetti, S.; Michelucci, R.; et al. A recurrent de novo mutation in KCNC1 causes progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Nat. Genet. 2014, 47, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukkola, P.; Gu, Y.; Lovett-Racke, A.E.; Gu, C. Suppression of Inflammatory Demyelinaton and Axon Degeneration through Inhibiting Kv3 Channels. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, M.S.; Park, S.M.; Park, J.S.; Byun, J.H.; Jin, H.J.; Seo, S.H.; Ryu, P.D.; Lee, S.Y. Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, Are Involved in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parekh, P.K.; Sidor, M.M.; Gillman, A.; Becker-Krail, D.; Bettelini, L.; Arban, R.; Alvaro, G.S.; Zambello, E.; Mutinelli, C.; Huang, Y.; et al. Antimanic Efficacy of a Novel Kv3 Potassium Channel Modulator. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 43, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, M.; Joho, R.H.; Southcott, S.A.; Shukla, A.A.; Ghose, S.; Tamminga, C.A. Kv3.1-containing K+ channels are reduced in untreated schizophrenia and normalized with antipsychotic drugs. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 19, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joho, R.H.; Street, C.; Matsushita, S.; Knöpfel, T. Behavioral motor dysfunction in Kv3-type potassium channel-deficient mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2006, 5, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, F.; Marks, G.; Heintz, N.; Joho, R.H. Increased motor drive and sleep loss in mice lacking Kv3-type potassium channels. Genes Brain Behav. 2004, 3, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Rong, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.-L. Effects of fluoxetine on protein expression of potassium ion channels in the brain of chronic mild stress rats. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 5, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meltzer, H.Y.; Massey, B. The role of serotonin receptors in the action of atypical antipsychotic drugs. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, M.H.; Fava, M.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Thase, M.E.; Quitkin, F.; Warden, D.; Ritz, L.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Lebowitz, B.D.; Biggs, M.M.; et al. Medication Augmentation after the Failure of SSRIs for Depression. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, L.E.; Chumbley, J.R.; Ranatunga, K.M.; Armstrong, S.J.; Veale, E.L.; Mathie, A. Inhibition of the human two-pore domain potassium channel, TREK-1, by fluoxetine and its metabolite norfluoxetine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 144, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wooltorton, J.R.; Mathie, A. Block of potassium currents in rat isolated sympathetic neurones by tricyclic antidepressants and structurally related compounds. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tytgat, J.; Maertens, C.; Daenens, P. Effect of fluoxetine on a neuronal, voltage-dependent potassium channel (Kv1.1). Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.; Choi, J.-S.; Hahn, S.J. Effects of fluoxetine on cloned Kv4.3 potassium channels. Brain Res. 2013, 1500, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, A.; Benkhalifa, R.; Landoulsi, Z.; Chatti, I.; El Ayeb, M. Inhibition of human Kv3.1 current expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the toxic venom fraction of Androctonus australis hector. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013, 37, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrihan, L.; Umschweif, G.; Sinha, A.; Reed, S.; Lee, J.; Gindinova, K.; Sinha, S.C.; Greengard, P.; Sagi, Y. Reduced Kv3.1 Activity in Dentate Gyrus Parvalbumin Cells Induces Vulnerability to Depression. Boil. Psychiatry 2020, 88, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mouillet-Richard, S.; Mutel, V.; Loric, S.; Tournois, C.; Launay, J.-M.; Kellermann, O. Regulation by Neurotransmitter Receptors of Serotonergic or Catecholaminergic Neuronal Cell Differentiation. J. Boil. Chem. 2000, 275, 9186–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loric, S.; Maroteaux, L.; Kellermann, O.; Launay, J. Functional serotonin-2B receptors are expressed by a teratocarcinoma-derived cell line during serotoninergic differentiation. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Kenneth, J. Livak and Thomas, D. Schmittgen. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real- Time Quantitative PCR and the 2_ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buc-Caron, M.; Launay, J.; Marie, P.; Kellermann, O. Une stratégie pour immortaliser des lignées orientées vers l’endoderme, le neuroectoderme ou le mésoderme à partir du tératocarcinome de la souris. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 1990, 30, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermann, O.; Kelly, F. Immortalization of early embryonic cell derivatives after the transfer of the early region of simian virus 40 into F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Differentiation 1986, 32, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermann, O.; Buc-Caron, M.-H.; Gaillard, J. Immortalization of precursors of endodermal, neuroectodermal and mesodermal lineages, following the introduction of the simian virus (SV40) early region into F9 cells. Differentiation 1987, 35, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermann, O.; Buc-Caron, M.H.; Marie, P.J.; Lamblin, D.; Jacob, F. An immortalized osteogenic cell line derived from mouse teratocarcinoma is able to mineralize in vivo and in vitro. J. Cell Boil. 1990, 110, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cusack, B.; Nelson, A.; Richelson, E. Binding of antidepressants to human brain receptors: Focus on newer generation compounds. Psychopharmacology 1994, 114, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.T.; Bymaster, F.P.; Engleman, E.A. Prozac (fluoxetine, lilly 110140), the first selective serotonin uptake inhibitor and an antidepressant drug: Twenty years since its first publication. Life Sci. 1995, 57, 411–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaarschmidt, G.; Wegner, F.; Schwarz, S.C.; Schmidt, H.; Schwarz, J. Characterization of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Human Neural Progenitor Cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, T.; Bartlett, P.F.; Adams, D.J. K(ir) and K(v) channels regulate electrical properties and proliferation of adult neural precursor cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 37, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari-Woodruff, S.; Beltrán-Parrazal, L.; Charles, A.; Keck, T.M.; Vu, T.; Bronstein, J. K+ channel KV3.1 associates with OSP/claudin-11 and regulates oligodendrocyte development. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2006, 291, C687–C698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blier, P.; El Mansari, M. Serotonin and beyond: Therapeutics for major depression. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschfeld, R.M.A. Antidepressants in the United States: Current status and future needs. Treat. Depress. Bridging 21st Century Am. Psychiatr. Press 2001, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Adell, A.; Castro, E.; Celada, P.; Bortolozzi, A.; Pazos, A.; Artigas, F.; Pedrosa, M.P.C. Strategies for producing faster acting antidepressants. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, L.E.; Ring, R.H.; Beyer, C.E.; Hughes, Z.A.; Khawaja, X.; Malberg, J.E.; Rosenzweig-Lipson, S. Innovative Approaches for the Development of Antidepressant Drugs: Current and Future Strategies. NeuroRX 2005, 2, 590–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.; Valdizán, E.M.; Mostany, R.; Pazos, A.; Castro, E. Long-term treatment with fluoxetine induces desensitization of 5-HT4receptor-dependent signalling and functionality in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riksen, E.A.; Stunes, A.K.; Kalvik, A.; Gustafsson, B.I.; Snead, M.L.; Syversen, U.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Reseland, J.E. Serotonin and fluoxetine receptors are expressed in enamel organs and LS8 cells and modulate gene expression in LS8 cells. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 118, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.G.; Miledi, R. Blockage of 5HT2C serotonin receptors by fluoxetine (Prozac). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2036–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malberg, J.E.; Eisch, A.J.; Nestler, E.J.; Duman, R.S. Chronic Antidepressant Treatment Increases Neurogenesis in Adult Rat Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 9104–9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, P. Validity, reliability and utility of the chronic mild stress model of depression: A 10-year review and evaluation. Psychopharmacology 1997, 134, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, N.M.; Sharp, T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 1999, 38, 1083–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, A.M.; Sheng, Z.-H. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by the second messenger-activated protein kinases: Implications for presynaptic plasticity. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 105, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middlemiss, D.; Hutson, P. The 5-HT1B Receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 600, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, C.E.; McDevitt, R.A.; Liu, Y.; Furay, A.R.; Neumaier, J.F. 5-HT1Bautoreceptor regulation of serotonin transporter activity in synaptosomes. Synapse 2012, 66, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montañez, S.; Munn, J.L.; Owens, W.A.; Horton, R.E.; Daws, L.C. 5-HT1B receptor modulation of the serotonin transporter in vivo: Studies using KO mice. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 73, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| DMEN + SVF 10% | dbcAMP | CCA | Fluoxetine 10 nM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1C11 ND (D4) | + | − | − | − |
| 1C11 D (D4) | + | + | + | − |
| 1C11 ND Flx (D4) | + | − | − | + |
| 1C11 D Flx (D4) | + | + | + | + |
| Primer’s Name | Primer’s Sequence |
|---|---|
| F-hGAPDH | 5′CGCTCTCTGCTCCTCCTGTT |
| R-hGAPDH | 3′CCATGGTGTCTGAGCGATGT |
| Kv3.1-F | 5′CTTTGCCTCCCTCTTCTTCATC |
| Kv3.1-R | 3′TTCGGTCTTGTTCACGATGG |
| 5HT1b-F | 5′GGAGATGCTGGACTGCTTTG |
| 5HT1b-R | 3′GAGGAGCAGGGTGGGTAAAT |
| Kv1.1-F | GAAGAAGCTGAGTCGCACTTCTCCAG |
| Kv1.1-R | TTAAACATCGGTCAGGAGCTTGCTC |
| Kv1.2-F | GTCATCCGGTTGGTAAGAGTCTTTAG |
| Kv1.2-R | GTGTTAGCCAAGGTACAGTTGGCTG |
| Kv1.3-F | ATCTTCAAGCTCTCCCGACCA |
| Kv1.3-R | CGAATCACCATATACTCCGAC |
| Kv1.4-F | GCTCACTCCAGGGCAGCTGCAGCTGCTGCT |
| Kv1.4-R | TCACGCATGCTGGCTCTTAGGGTGTGGCCC |
| Kv2.1-F | CTCCACCATTGCCCTGTC |
| Kv2.1-R | TCCGCTTGATTGCTTTCTC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabka, H.; Cheikh, A.; Maatoug, S.; Ayeb, M.E.; Bendahhou, S.; Benkhalifa, R. First Evidence of Kv3.1b Potassium Channel Subtype Expression during Neuronal Serotonergic 1C11 Cell Line Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197175
Tabka H, Cheikh A, Maatoug S, Ayeb ME, Bendahhou S, Benkhalifa R. First Evidence of Kv3.1b Potassium Channel Subtype Expression during Neuronal Serotonergic 1C11 Cell Line Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197175
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabka, Hager, Amani Cheikh, Sonia Maatoug, Mohamed El Ayeb, Saïd Bendahhou, and Rym Benkhalifa. 2020. "First Evidence of Kv3.1b Potassium Channel Subtype Expression during Neuronal Serotonergic 1C11 Cell Line Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197175
APA StyleTabka, H., Cheikh, A., Maatoug, S., Ayeb, M. E., Bendahhou, S., & Benkhalifa, R. (2020). First Evidence of Kv3.1b Potassium Channel Subtype Expression during Neuronal Serotonergic 1C11 Cell Line Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197175





