Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Fragments Prevent Mouse Cone Photoreceptor Cell Loss Induced by Focal Phototoxicity In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
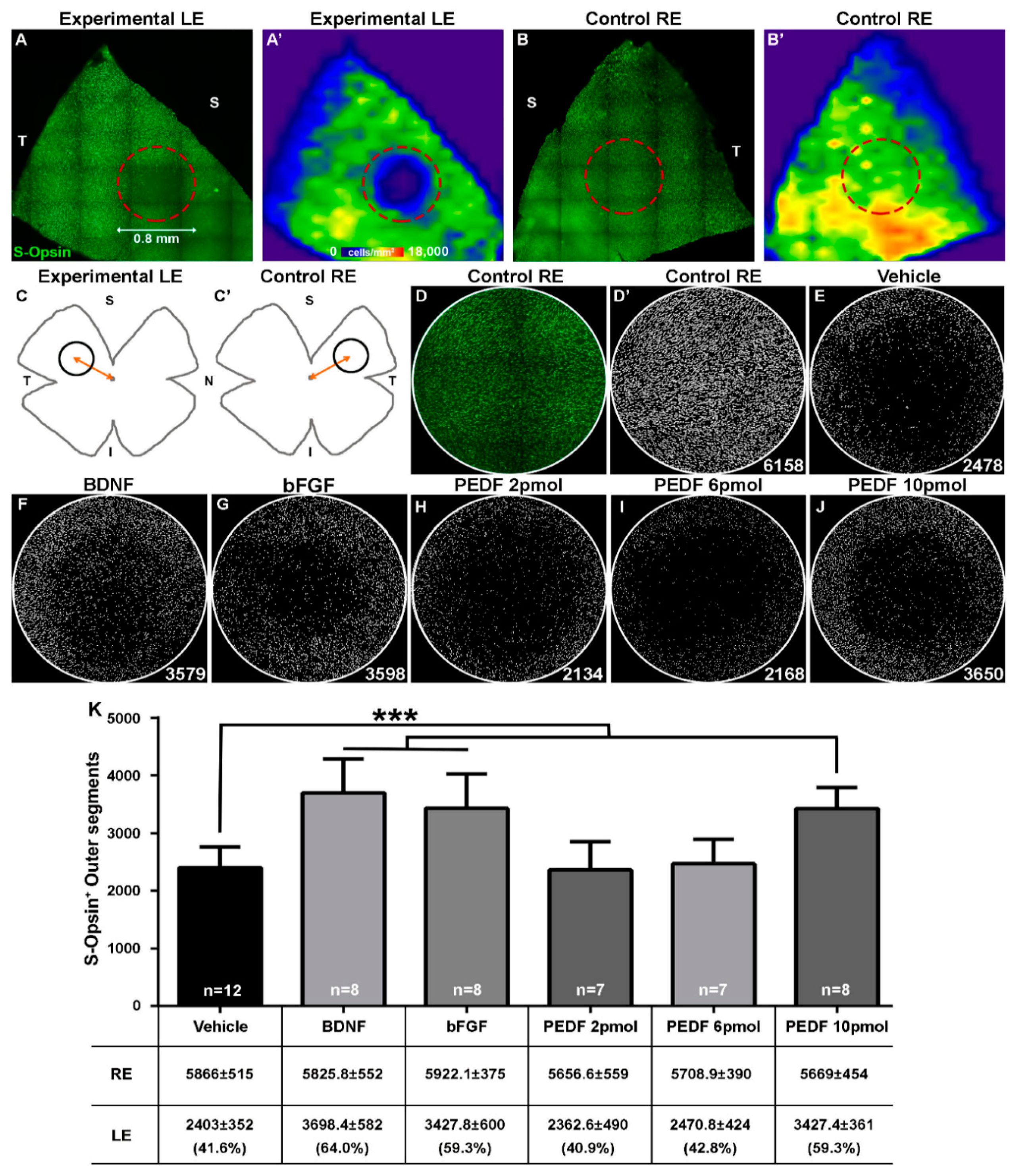
2.1. Light Emitting Diode Induced-Phototoxicity (LIP) Model Results in the Loss of S-Cones in the Damaged Region
2.2. Intravitreal Administration of PEDF, BDNF or bFGF Decreases LED-Induced Cone Loss
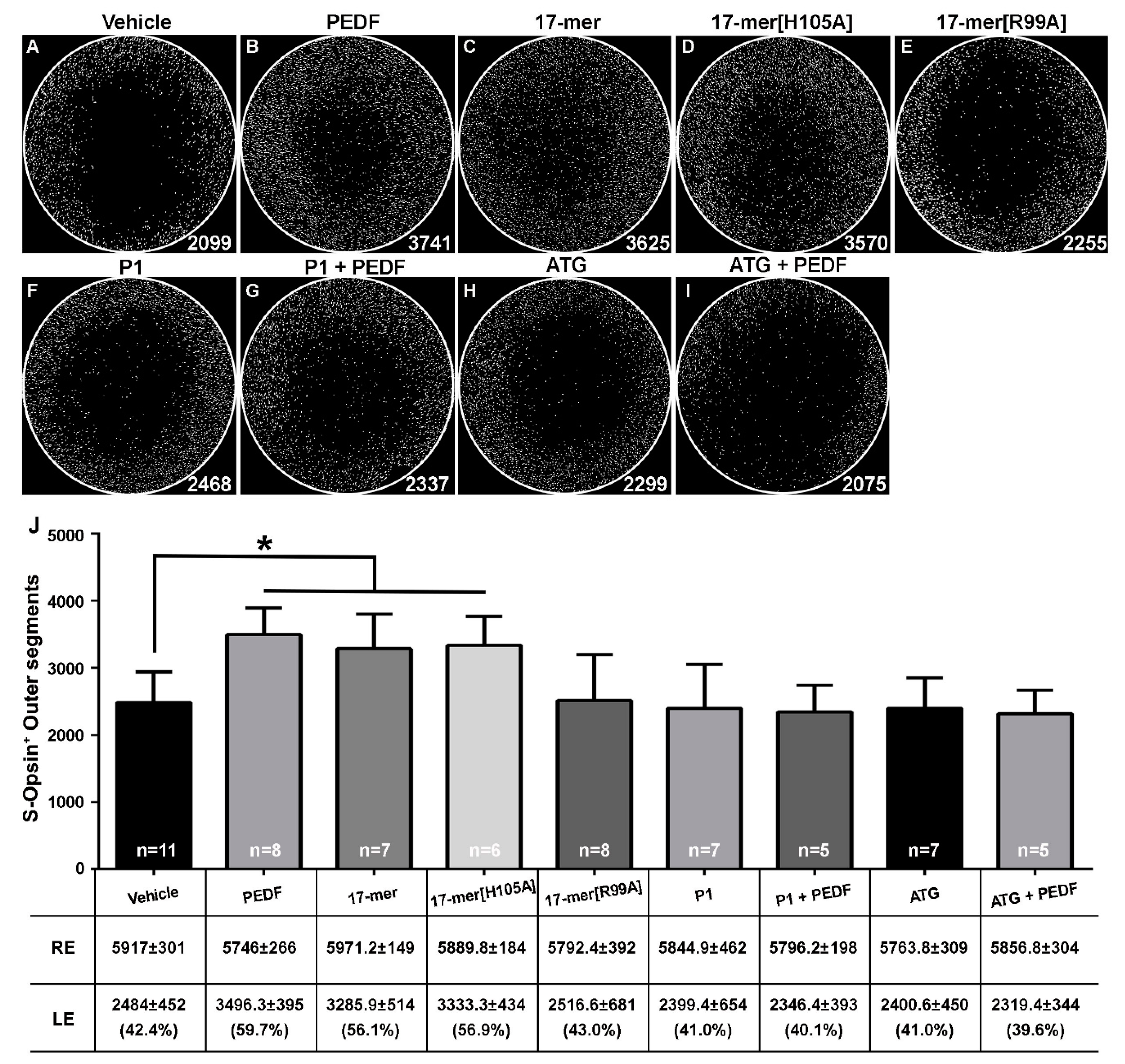
2.3. S-Cone-Protective Efficacy of PEDF Fragments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Handling
4.2. Light Emitting Diode-Induced Phototoxicity Model
4.3. Administration of the Neuroprotective Effectors
4.4. Tissue Processing and Retinal Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LIP | Light emitting diode-induced phototoxicity |
| OS | Outer Segments |
| PEDF | Pigment epithelium-derived factor |
| BDNF | Brain derived neurotrophic factor |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| P1 | PEDF-R blocker |
| ATG | Atglistatin |
| PFA | Pre-determined fixed-size circular area |
References
- Bourne, R.R.A.; Jonas, J.B.; Bron, A.M.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Friedman, D.S.; Keeffe, J.E.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J.; et al. Prevalence and causes of Vis. loss in high-income countries and in Eastern and Central Europe in 2015: Magnitude, temporal trends and projections. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Nash, S.D.; Krantz, E.M.; Nieto, F.J.; Huang, G.H.; Pankow, J.S.; Klein, B.E. The prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and associated risk factors. Arch. Ophthalmol 2010, 128, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, G.Y.; Liu, G.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Gao, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Tong, S.H.; Wang, L. Is sunlight exposure a risk factor for age-related macular degeneration? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pierdomenico, J.; Martinez-Vacas, A.; Hernandez-Munoz, D.; Gomez-Ramirez, A.M.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Garcia-Ayuso, D. Coordinated Intervention of Microglial and Muller Cells in Light-Induced Retinal Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Di Pierdomenico, J.; Hadj-Said, W.; Marie, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Picaud, S.; Villegas-Perez, M.P. Taurine Depletion Causes ipRGC Loss and Increases Light-Induced Photoreceptor Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1396–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Galindo-Romero, C.; Di Pierdomenico, J.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; Villegas Perez, M.P. Light-induced retinal degeneration causes a transient downregulation of melanopsin in the rat retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 161, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; Alarcon-Martinez, L.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P. Retinal ganglion cell axonal compression by retinal vessels in light-induced retinal degeneration. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 1716–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Marco-Gomariz, M.A.; Hurtado-Montalban, N.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Lund, R.D.; Villegas-Perez, M.P. Phototoxic-induced photoreceptor degeneration causes retinal ganglion cell degeneration in pigmented rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 498, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noell, W.K.; Walker, V.S.; Kang, B.S.; Berman, S. Retinal damage by light in rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. 1966, 5, 450–473. [Google Scholar]
- Organisciak, D.T.; Darrow, R.M.; Noell, W.K.; Blanks, J.C. Hyperthermia accelerates retinal light damage in rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1995, 36, 997–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Tejedor, J.; Marchena, M.; Ramirez, L.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Gomez-Vicente, V.; Sanchez-Ramos, C.; de la Villa, P.; Germain, F. Removal of the blue component of light significantly decreases retinal damage after high intensity exposure. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, H.I.; Paik, S.S.; Jung, S.W.; Kang, S.; Kim, I.B. Functional and morphological evaluation of blue light-emitting diode-induced retinal degeneration in mice. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch. Fur Klin. Und Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuse, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Damage of photoreceptor-derived cells in culture induced by light emitting diode-derived blue light. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Kuse, Y.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. The Involvement of the Oxidative Stress in Murine Blue LED Light-Induced Retinal Damage Model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yako, T.; Kuse, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Nishinaka, A.; Nakamura, S.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Exposure to excessive blue LED light damages retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptors of pigmented mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 177, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortin-Martinez, A.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Alarcon-Martinez, L.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Bernal-Garro, J.M.; Nieto-Lopez, L.; Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Wheeler, L.A.; et al. A novel in vivo model of focal light emitting diode-induced cone-photoreceptor phototoxicity: Neuroprotection afforded by brimonidine, BDNF, PEDF or bFGF. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, J.R.; Nakanishi, K.; Parish, C.A. The lipofuscin fluorophore A2E mediates blue light-induced damage to retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Ortin-Martinez, A.; Di Pierdomenico, J.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Gallego-Ortega, A.; Miralles de Imperial-Ollero, J.A.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Wheeler, L.A.; Vidal-Sanz, M. Topical Brimonidine or Intravitreal BDNF, CNTF, or bFGF Protect Cones Against Phototoxicity. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortin-Martinez, A.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Alarcon-Martinez, L.; Sauve, Y.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M. Automated quantification and topographical distribution of the whole population of S-and L-cones in adult albino and pigmented rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3171–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Kunze, V.P.; Ball, J.M.; Peng, B.T.; Krishnan, A.; Zhou, G.; Dong, L.; Li, W. True S-cones are concentrated in the ventral mouse retina and wired for color detection in the upper visual field. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comitato, A.; Subramanian, P.; Turchiano, G.; Montanari, M.; Becerra, S.P.; Marigo, V. Pigment epithelium-derived factor hinders photoreceptor cell death by reducing intracellular calcium in the degenerating retina. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pierdomenico, J.; Scholz, R.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Sanchez-Migallon, M.C.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Langmann, T.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Villegas-Perez, M.P. Neuroprotective Effects of FGF2 and Minocycline in Two Animal Models of Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 4392–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Pinto, A.; Polato, F.; Subramanian, P.; Rocha-Munoz, A.; Vitale, S.; de la Rosa, E.J.; Becerra, S.P. PEDF peptides promote photoreceptor survival in rd10 retina models. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 184, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolomeyer, A.M.; Zarbin, M.A. Trophic factors in the pathogenesis and therapy for retinal degenerative diseases. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2014, 59, 134–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaVail, M.M.; Yasumura, D.; Matthes, M.T.; Lau-Villacorta, C.; Unoki, K.; Sung, C.H.; Steinberg, R.H. Protection of mouse photoreceptors by survival factors in retinal degenerations. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 592–602. [Google Scholar]
- Polato, F.; Becerra, S.P. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor, a Protective Factor for Photoreceptors in Vivo. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 854, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.; Locatelli-Hoops, S.; Kenealey, J.; DesJardin, J.; Notari, L.; Becerra, S.P. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) prevents retinal cell death via PEDF Receptor (PEDF-R): Identification of a functional ligand binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23928–23942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, S.P. Focus on Molecules: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF). Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 739–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notari, L.; Baladron, V.; Aroca-Aguilar, J.D.; Balko, N.; Heredia, R.; Meyer, C.; Notario, P.M.; Saravanamuthu, S.; Nueda, M.L.; Sanchez-Sanchez, F.; et al. Identification of a lipase-linked cell membrane receptor for pigment epithelium-derived factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 38022–38037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Polato, F.; Samardzija, M.; Abu-Asab, M.; Grimm, C.; Crawford, S.E.; Becerra, S.P. PEDF deficiency increases the susceptibility of rd10 mice to retinal degeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 198, 108121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenealey, J.; Subramanian, P.; Comitato, A.; Bullock, J.; Keehan, L.; Polato, F.; Hoover, D.; Marigo, V.; Becerra, S.P. Small Retinoprotective Peptides Reveal a Receptor-binding Region on Pigment Epithelium-derived Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25241–25253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Geng, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, B.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Hou, L. Photoreceptor degeneration in microphthalmia (Mitf) mice: Partial rescue by pigment epithelium-derived factor. Dis. Models Mech. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp, M.; Woo, G.; Al-Ubaidi, M.R.; Becerra, S.P.; Subramanian, P. Pigment epithelium-derived factor protects cone photoreceptor-derived 661W cells from light damage through Akt activation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, J.; Pagan-Mercado, G.; Becerra, S.P. Cell-based assays to identify novel retinoprotective agents. MethodsX 2020, 7, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortin-Martinez, A.; Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Alburquerque-Bejar, J.J.; Nieto-Lopez, L.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M. Number and distribution of mouse retinal cone photoreceptors: Differences between an albino (Swiss) and a pigmented (C57/BL6) strain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoz, R.; Ramirez, A.I.; Gonzalez-Martin, R.; Ajoy, D.; Rojas, B.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Aviles-Trigueros, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; et al. Bilateral early activation of retinal microglial cells in a mouse model of unilateral laser-induced experimental ocular hypertension. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 171, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierdomenico, J.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P. Different Ipsi- and Contralateral Glial Responses to Anti-VEGF and Triamcinolone Intravitreal Injections in Rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 3533–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Ruiz, F.; Galindo-Romero, C.; Rodriguez-Ramirez, K.T.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M. Neuronal Death in the Contralateral Un-Injured Retina after Unilateral Axotomy: Role of Microglial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodeutsch, N.; Siebert, H.; Dermon, C.; Thanos, S. Unilateral injury to the adult rat optic nerve causes multiple cellular responses in the contralateral site. J. Neurobiol. 1999, 38, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonngren, U.; Napankangas, U.; Lafuente, M.; Mayor, S.; Lindqvist, N.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Hallbook, F. The growth factor response in ischemic rat retina and superior colliculus after brimonidine pre-treatment. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 71, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Sunagawa, G.A.; Kondo, M.; Takahashi, M.; Mandai, M. Evaluation of micro Electroretinograms Recorded with Multiple Electrode Array to Assess Focal Retinal Function. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organisciak, D.T.; Vaughan, D.K. Retinal light damage: Mechanisms and protection. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2010, 29, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, D.K.; Nemke, J.L.; Fliesler, S.J.; Darrow, R.M.; Organisciak, D.T. Evidence for a circadian rhythm of susceptibility to retinal light damage. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 75, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratikos, E.; Alberdi, E.; Gettins, P.G.; Becerra, S.P. Recombinant human pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF): Characterization of PEDF overexpressed and secreted by eukaryotic cells. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 1996, 5, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Sanz, M.; Galindo-Romero, C.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Ortin-Martinez, A.; Rovere, G.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Lucas-Ruiz, F.; Sanchez-Migallon, M.C.; Sobrado-Calvo, P.; et al. Shared and Differential Retinal Responses against Optic Nerve Injury and Ocular Hypertension. Front. Neuro Sci. 2017, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Sanz, M.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Ortin-Martinez, A.; Nadal-Nicolas, F.M.; Jimenez-Lopez, M.; Salinas-Navarro, M.; Alarcon-Martinez, L.; Garcia-Ayuso, D.; Aviles-Trigueros, M.; Agudo-Barriuso, M.; et al. Retinal neurodegeneration in experimental glaucoma. Prog. Brain Res. 2015, 220, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Di Pierdomenico, J.; García-Ayuso, D.; Ortín-Martínez, A.; Miralles de Imperial-Ollero, J.A.; Gallego-Ortega, A.; Jiménez-López, M.; Villegas-Pérez, M.P.; Becerra, S.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Fragments Prevent Mouse Cone Photoreceptor Cell Loss Induced by Focal Phototoxicity In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197242
Valiente-Soriano FJ, Di Pierdomenico J, García-Ayuso D, Ortín-Martínez A, Miralles de Imperial-Ollero JA, Gallego-Ortega A, Jiménez-López M, Villegas-Pérez MP, Becerra SP, Vidal-Sanz M. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Fragments Prevent Mouse Cone Photoreceptor Cell Loss Induced by Focal Phototoxicity In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197242
Chicago/Turabian StyleValiente-Soriano, Francisco J., Johnny Di Pierdomenico, Diego García-Ayuso, Arturo Ortín-Martínez, Juan A. Miralles de Imperial-Ollero, Alejandro Gallego-Ortega, Manuel Jiménez-López, M. Paz Villegas-Pérez, S. Patricia Becerra, and Manuel Vidal-Sanz. 2020. "Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Fragments Prevent Mouse Cone Photoreceptor Cell Loss Induced by Focal Phototoxicity In Vivo" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197242
APA StyleValiente-Soriano, F. J., Di Pierdomenico, J., García-Ayuso, D., Ortín-Martínez, A., Miralles de Imperial-Ollero, J. A., Gallego-Ortega, A., Jiménez-López, M., Villegas-Pérez, M. P., Becerra, S. P., & Vidal-Sanz, M. (2020). Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Fragments Prevent Mouse Cone Photoreceptor Cell Loss Induced by Focal Phototoxicity In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197242








