Pathogenesis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Comprehensive Review of the Genetic and Molecular Aspects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition and Diagnosis of EoE
3. Genetics
3.1. Risk Genes
3.1.1. Common Risk Genes and Function
3.1.2. Rare Risk Genes and their Function
3.2. Associated Diseases of EoE
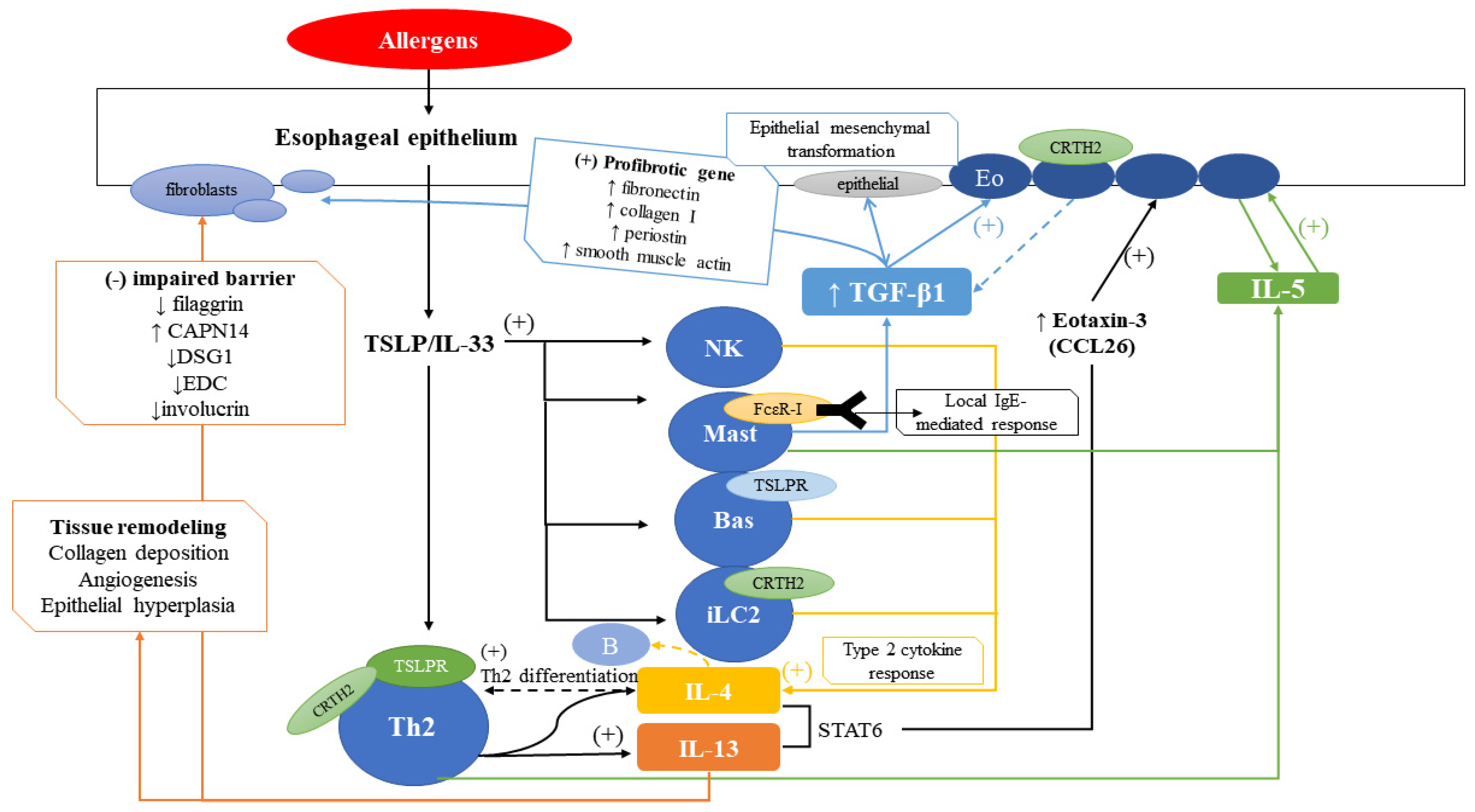
4. Pathophysiology
4.1. Role of Inflammatory Cells
4.1.1. Eosinophils
4.1.2. T Cells
4.1.3. Mast Cells
4.1.4. Basophils
4.1.5. Dendritic Cells
4.1.6. Innate Lymphoid Cells
4.1.7. Invariant Natural Killer T Cells (iNKT Cells)
4.1.8. B Cells
4.2. Role of Various Molecules
4.2.1. TSLP
4.2.2. TGF-β1
4.2.3. IL-4
4.2.4. IL-5
4.2.5. IL-13
4.2.6. IL-15
4.2.7. Eotaxin-3 (CCL26)
4.2.8. IgE and IgG4
4.2.9. Prostaglandins
4.2.10. Additional Cytokines
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clayton, F.; Peterson, K. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Pathophysiology and Definition. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinit, C.; Dieme, A.; Courbage, S.; Dehaine, C.; Dufeu, C.M.; Jacquemot, S.; Lajus, M.; Montigny, L.; Payen, E.; Yang, D.D.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Arch. Pediatr. 2019, 26, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landres, R.T.; Kuster, G.G.; Strum, W.B. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology 1978, 74, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Spichtin, H.P.; Bernoulli, R.; Loosli, J.; Vogtlin, J. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis: A frequently overlooked disease with typical clinical aspects and discrete endoscopic findings. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1994, 124, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lehman, H.K.; Lam, W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 66, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dellon, E.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I.; Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Katzka, D.A.; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 679–692, quiz 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, F.J.; Cheng, E.; Schoepfer, A.; Al-Haddad, S.; Bellizzi, A.M.; Dawson, H.; El-Zimaity, H.; Guindi, M.; Penagini, R.; Safrooneva, E.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Current perspectives from diagnosis to management. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1380, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, R.D.; Gupta, S.K. Emerging drugs for eosinophilic esophagitis. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2018, 23, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.P. Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Arias, A.; Arias-Gonzalez, L.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Ruiz-Ponce, M.; Lucendo, A.J. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The growing incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBrosse, C.W.; Collins, M.H.; Buckmeier Butz, B.K.; Allen, C.L.; King, E.C.; Assa’ad, A.H.; Abonia, J.P.; Putnam, P.E.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Franciosi, J.P. Identification, epidemiology, and chronicity of pediatric esophageal eosinophilia, 1982–1999. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurrell, J.M.; Genta, R.M.; Dellon, E.S. Prevalence of esophageal eosinophilia varies by climate zone in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spergel, J.M.; Book, W.M.; Mays, E.; Song, L.; Shah, S.S.; Talley, N.J.; Bonis, P.A. Variation in prevalence, diagnostic criteria, and initial management options for eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the United States. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kottyan, L.C.; Parameswaran, S.; Weirauch, M.T.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Martin, L.J. The genetic etiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furuta, G.T.; Katzka, D.A. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, E.T.; Kuhl, J.T.; Martin, L.J.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Dellon, E.S. Prenatal, intrapartum, and postnatal factors are associated with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandramouleeswaran, P.M.; Shen, D.; Lee, A.J.; Benitez, A.; Dods, K.; Gambanga, F.; Wilkins, B.J.; Merves, J.; Noah, Y.; Toltzis, S.; et al. Preferential Secretion of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP) by Terminally Differentiated Esophageal Epithelial Cells: Relevance to Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litosh, V.A.; Rochman, M.; Rymer, J.K.; Porollo, A.; Kottyan, L.C.; Rothenberg, M.E. Calpain-14 and its association with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1762–1771.e1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Liacouras, C.A.; Molina-Infante, J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Zevit, N.; Spechler, S.J.; Attwood, S.E.; Straumann, A.; Aceves, S.S.; et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1022–1033.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J.; Arias, A.; von Arnim, U.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Bussmann, C.; Amil Dias, J.; Bove, M.; Gonzalez-Cervera, J.; Larsson, H.; et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singla, M.B.; Moawad, F.J. An Overview of the Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, K.M.; Aceves, S.S.; Dellon, E.S.; Gupta, S.K.; Spergel, J.M.; Furuta, G.T.; Rothenberg, M.E. Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.K.; Fang, R.; Wagner, B.D.; Choe, H.N.; Kelly, C.J.; Schroeder, S.; Moore, W.; Stevens, M.J.; Yeckes, A.; Amsden, K.; et al. Esophageal microbiome in eosinophilic esophagitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Rothenberg, M.E. Genetic dissection of eosinophilic esophagitis provides insight into disease pathogenesis and treatment strategies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 23–32, quiz 33-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, C.; Mingler, M.K.; Vicario, M.; Abonia, J.P.; Wu, Y.Y.; Lu, T.X.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Wells, S.I.; Rothenberg, M.E. IL-13 involvement in eosinophilic esophagitis: Transcriptome analysis and reversibility with glucocorticoids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Wang, N.; Stringer, K.F.; Mishra, A.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Abonia, J.P.; Jameson, S.C.; Kirby, C.; Konikoff, M.R.; Collins, M.H.; et al. Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rochman, M.; Travers, J.; Miracle, C.E.; Bedard, M.C.; Wen, T.; Azouz, N.P.; Caldwell, J.M.; Kc, K.; Sherrill, J.D.; Davis, B.P.; et al. Profound loss of esophageal tissue differentiation in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 738–749.e733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Kc, K.; Wu, D.; Djukic, Z.; Caldwell, J.M.; Stucke, E.M.; Kemme, K.A.; Costello, M.S.; Mingler, M.K.; Blanchard, C.; et al. Desmoglein-1 regulates esophageal epithelial barrier function and immune responses in eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Yagi, M.; Yaoita, T.; Nishise, S.; Ueno, Y. Diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in clinical practice. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, M.R.; Ziegler, S.F. The influence of TSLP on the allergic response. Mucosal Immunol. 2010, 3, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitajima, M.; Lee, H.C.; Nakayama, T.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP enhances the function of helper type 2 cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hui, C.C.; Rusta-Sallehy, S.; Asher, I.; Heroux, D.; Denburg, J.A. The effects of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and IL-3 on human eosinophil-basophil lineage commitment: Relevance to atopic sensitization. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2014, 2, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J.M.; Paul, M.; Rothenberg, M.E. Novel immunologic mechanisms in eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 48, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.E. Molecular, genetic, and cellular bases for treating eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, C.; Wang, N.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Pathogenesis, genetics, and therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Stucke, E.M.; Burwinkel, K.; Caldwell, J.M.; Collins, M.H.; Ahrens, A.; Buckmeier, B.K.; Jameson, S.C.; Greenberg, A.; Kaul, A.; et al. Coordinate interaction between IL-13 and epithelial differentiation cluster genes in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.E.; Forney, C.; Rochman, M.; Cranert, S.; Habel, J.; Rymer, J.; Lynch, A.; Schroeder, C.; Lee, J.; Sauder, A.; et al. Genetic, Inflammatory, and Epithelial Cell Differentiation Factors Control Expression of Human Calpain-14. G3 (Bethesda) 2019, 9, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottyan, L.C.; Rothenberg, M.E. Genetics of eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, D.; Radonjic-Hosli, S.; Straumann, A.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.U. Active eosinophilic esophagitis is characterized by epithelial barrier defects and eosinophil extracellular trap formation. Allergy 2015, 70, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Ohbayashi, N.; Ishibashi, K.; Fukuda, M. Structure-function analysis of VPS9-ankyrin-repeat protein (Varp) in the trafficking of tyrosinase-related protein 1 in melanocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7507–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, M. Multiple Roles of VARP in Endosomal Trafficking: Rabs, Retromer Components and R-SNARE VAMP7 Meet on VARP. Traffic 2016, 17, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, D.; Chen, Y. Cellular functions of programmed cell death 5. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Wensel, T.G. R9AP, a membrane anchor for the photoreceptor GTPase accelerating protein, RGS9-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9755–9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundermeier, T.R.; Vinberg, F.; Mustafi, D.; Bai, X.; Kefalov, V.J.; Palczewski, K. R9AP overexpression alters phototransduction kinetics in iCre75 mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kottyan, L.C.; Maddox, A.; Braxton, J.R.; Stucke, E.M.; Mukkada, V.; Putnam, P.E.; Abonia, J.P.; Chehade, M.; Wood, R.A.; Pesek, R.D.; et al. Genetic variants at the 16p13 locus confer risk for eosinophilic esophagitis. Genes Immun. 2019, 20, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothenberg, M.E.; Spergel, J.M.; Sherrill, J.D.; Annaiah, K.; Martin, L.J.; Cianferoni, A.; Gober, L.; Kim, C.; Glessner, J.; Frackelton, E.; et al. Common variants at 5q22 associate with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, P.M.; Wang, M.L.; Cianferoni, A.; Aceves, S.; Gonsalves, N.; Nadeau, K.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Hakonarson, H. GWAS identifies four novel eosinophilic esophagitis loci. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottyan, L.C.; Davis, B.P.; Sherrill, J.D.; Liu, K.; Rochman, M.; Kaufman, K.; Weirauch, M.T.; Vaughn, S.; Lazaro, S.; Rupert, A.M.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of eosinophilic esophagitis provides insight into the tissue specificity of this allergic disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Kc, K.; Wang, X.; Wen, T.; Chamberlin, A.; Stucke, E.M.; Collins, M.H.; Abonia, J.P.; Peng, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing uncovers oxidoreductases DHTKD1 and OGDHL as linkers between mitochondrial dysfunction and eosinophilic esophagitis. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abonia, J.P.; Wen, T.; Stucke, E.M.; Grotjan, T.; Griffith, M.S.; Kemme, K.A.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Franciosi, J.P.; von Tiehl, K.F.; et al. High prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with inherited connective tissue disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frischmeyer-Guerrerio, P.A.; Guerrerio, A.L.; Oswald, G.; Chichester, K.; Myers, L.; Halushka, M.K.; Oliva-Hemker, M.; Wood, R.A.; Dietz, H.C. TGFbeta receptor mutations impose a strong predisposition for human allergic disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 195ra194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beppu, L.Y.; Anilkumar, A.A.; Newbury, R.O.; Dohil, R.; Broide, D.H.; Aceves, S.S. TGF-beta1-induced phospholamban expression alters esophageal smooth muscle cell contraction in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1100–1107.e1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aceves, S.S.; Chen, D.; Newbury, R.O.; Dohil, R.; Bastian, J.F.; Broide, D.H. Mast cells infiltrate the esophageal smooth muscle in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis, express TGF-beta1, and increase esophageal smooth muscle contraction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1198–1204.e1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobey, G. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: How to diagnose and when to perform genetic tests. Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syx, D.; Van Damme, T.; Symoens, S.; Maiburg, M.C.; van de Laar, I.; Morton, J.; Suri, M.; Del Campo, M.; Hausser, I.; Hermanns-Le, T.; et al. Genetic heterogeneity and clinical variability in musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by impaired dermatan sulfate biosynthesis. Hum. Mutat. 2015, 36, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, H. Marfan Syndrome. In GeneReviews; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1335/ (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Paluel-Marmont, C.; Bellon, N.; Barbet, P.; Leclerc-Mercier, S.; Hadj-Rabia, S.; Dupont, C.; Bodemer, C. Eosinophilic esophagitis and colonic mucosal eosinophilia in Netherton syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 2003–2005.e2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.J.; McLean, W.H. Eczema genetics: Current state of knowledge and future goals. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furio, L.; Pampalakis, G.; Michael, I.P.; Nagy, A.; Sotiropoulou, G.; Hovnanian, A. KLK5 Inactivation Reverses Cutaneous Hallmarks of Netherton Syndrome. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, M.J.; Shaffer, E.; Urbanski, S.J.; Beck, P.L.; Storr, M.A. The association between celiac disease and eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milella, M.; Falcone, I.; Conciatori, F.; Cesta Incani, U.; Del Curatolo, A.; Inzerilli, N.; Nuzzo, C.M.; Vaccaro, V.; Vari, S.; Cognetti, F.; et al. PTEN: Multiple Functions in Human Malignant Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, J.J.; Sun, G.; Stone, K.D.; Nelson, C.; Wisch, L.; O’Brien, M.; Jones, N.; Lindsley, A.; Komarow, H.D.; Bai, Y.; et al. Mendelian inheritance of elevated serum tryptase associated with atopy and connective tissue abnormalities. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Randall, K.L.; Lambe, T.; Johnson, A.L.; Treanor, B.; Kucharska, E.; Domaschenz, H.; Whittle, B.; Tze, L.E.; Enders, A.; Crockford, T.L.; et al. Dock8 mutations cripple B cell immunological synapses, germinal centers and long-lived antibody production. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Dove, C.G.; Hor, J.L.; Murdock, H.M.; Strauss-Albee, D.M.; Garcia, J.A.; Mandl, J.N.; Grodick, R.A.; Jing, H.; Chandler-Brown, D.B.; et al. DOCK8 regulates lymphocyte shape integrity for skin antiviral immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2549–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyons, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C.A.; Yu, X.; O’Connell, M.P.; Lawrence, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Karpe, K.; Zhao, M.; Siegel, A.M.; et al. ERBIN deficiency links STAT3 and TGF-beta pathway defects with atopy in humans. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffle, M.E.; Polydorides, A.D.; Niakan, J.; Chehade, M. Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Esophageal Granular Cell Tumor: An Unexpected Association. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, T.; Matsuda, A.; Nomura, I.; Okada, N.; Orihara, K.; Mikami, H.; Ishimura, N.; Ishihara, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Kinoshita, Y. Eosinophilic esophagitis versus proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: Transcriptome analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 2010–2013.e2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aceves, S.S. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, P.; Rajavelu, P.; Rayapudi, M.; Paul, R.J.; Mishra, A. Esophageal functional impairments in experimental eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G1347–G1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Wang, M.; Pemmaraju, V.R.; Collins, M.H.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Abonia, J.P.; Blanchard, C.; Putnam, P.E.; Rothenberg, M.E. Esophageal remodeling develops as a consequence of tissue specific IL-5-induced eosinophilia. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, L.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Finkelman, F.D.; Mingler, M.; Fischetti, C.A.; Blanchard, C.; Rothenberg, M.E. IL-13 induces esophageal remodeling and gene expression by an eosinophil-independent, IL-13R alpha 2-inhibited pathway. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rieder, F.; Nonevski, I.; Ma, J.; Ouyang, Z.; West, G.; Protheroe, C.; DePetris, G.; Schirbel, A.; Lapinski, J.; Goldblum, J.; et al. T-helper 2 cytokines, transforming growth factor beta1, and eosinophil products induce fibrogenesis and alter muscle motility in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1266–1277.e1261–e1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, B.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. Antigen presentation by eosinophils in eosinophilic esophagitis? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, E.; Cho, J.Y.; Rosenthal, P.; Chao, J.; Miller, M.; Pham, A.; Aceves, S.S.; Varki, A.; Broide, D.H. Siglec-F inhibition reduces esophageal eosinophilia and angiogenesis in a mouse model of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Navarro, M.; Comas, C.; Pascual, J.M.; Burgos, E.; Santamaria, L.; Larrauri, J. Immunophenotypic characterization and quantification of the epithelial inflammatory infiltrate in eosinophilic esophagitis through stereology: An analysis of the cellular mechanisms of the disease and the immunologic capacity of the esophagus. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitelbaum, J.E.; Fox, V.L.; Twarog, F.J.; Nurko, S.; Antonioli, D.; Gleich, G.; Badizadegan, K.; Furuta, G.T. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children: Immunopathological analysis and response to fluticasone propionate. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Wang, Y.H. Hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase: Linking pathogenic effector CD4+ TH2 cells to proeosinophilic inflammation in patients with gastrointestinal allergic disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitson-Salazar, A.; Yin, Y.; Wansley, D.L.; Young, M.; Bolan, H.; Arceo, S.; Ho, N.; Koh, C.; Milner, J.D.; Stone, K.D.; et al. Hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase defines a proeosinophilic pathogenic effector human T(H)2 cell subpopulation with enhanced function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 907–918.e909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Schlotman, J.; Wang, M.; Rothenberg, M.E. Critical role for adaptive T cell immunity in experimental eosinophilic esophagitis in mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonia, J.P.; Blanchard, C.; Butz, B.B.; Rainey, H.F.; Collins, M.H.; Stringer, K.; Putnam, P.E.; Rothenberg, M.E. Involvement of mast cells in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niranjan, R.; Mavi, P.; Rayapudi, M.; Dynda, S.; Mishra, A. Pathogenic role of mast cells in experimental eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G1087–G1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggadottir, S.M.; Hill, D.A.; Ruymann, K.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.F.; Cianferoni, A.; Shuker, M.; Wang, M.L.; Chikwava, K.; Verma, R.; Liacouras, C.A.; et al. Resolution of acute IgE-mediated allergy with development of eosinophilic esophagitis triggered by the same food. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1487–1489.e1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Hogan, S.P.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Abonia, J.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. Expanding the paradigm of eosinophilic esophagitis: Mast cells and IL-9. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1583–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otani, I.M.; Anilkumar, A.A.; Newbury, R.O.; Bhagat, M.; Beppu, L.Y.; Dohil, R.; Broide, D.H.; Aceves, S.S. Anti-IL-5 therapy reduces mast cell and IL-9 cell numbers in pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen-Brady, K.; Firszt, R.; Fang, J.C.; Wong, J.; Smith, K.R.; Peterson, K.A. Population-based familial aggregation of eosinophilic esophagitis suggests a genetic contribution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siracusa, M.C.; Saenz, S.A.; Hill, D.A.; Kim, B.S.; Headley, M.B.; Doering, T.A.; Wherry, E.J.; Jessup, H.K.; Siegel, L.A.; Kambayashi, T.; et al. TSLP promotes interleukin-3-independent basophil haematopoiesis and type 2 inflammation. Nature 2011, 477, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voehringer, D. Protective and pathological roles of mast cells and basophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. Mechanisms of Disease of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 365–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inage, E.; Furuta, G.T.; Menard-Katcher, C.; Masterson, J.C. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Pathophysiology and its clinical implications. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G879–G886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noti, M.; Wojno, E.D.; Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Giacomin, P.R.; Nair, M.G.; Benitez, A.J.; Ruymann, K.R.; Muir, A.B.; Hill, D.A.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-elicited basophil responses promote eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturelli, N.; Lexmond, W.S.; Ohsaki, A.; Nurko, S.; Karasuyama, H.; Fiebiger, E.; Oyoshi, M.K. Allergic skin sensitization promotes eosinophilic esophagitis through the IL-33-basophil axis in mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1367–1380.e1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tantibhaedhyangkul, U.; Tatevian, N.; Gilger, M.A.; Major, A.M.; Davis, C.M. Increased esophageal regulatory T cells and eosinophil characteristics in children with eosinophilic esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 39, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Straumann, A.; Bauer, M.; Fischer, B.; Blaser, K.; Simon, H.U. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis is associated with a T(H)2-type allergic inflammatory response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fraissinette, A.; Schmitt, D.; Thivolet, J. Langerhans cells of human mucosa. J. Dermatol. 1989, 16, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiwegger, T.; Akdis, C.A. IL-33 links tissue cells, dendritic cells and Th2 cell development in a mouse model of asthma. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, H.; Chieppa, M.; Perros, F.; Willart, M.A.; Germain, R.N.; Lambrecht, B.N. House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christianson, C.A.; Goplen, N.P.; Zafar, I.; Irvin, C.; Good, J.T., Jr.; Rollins, D.R.; Gorentla, B.; Liu, W.; Gorska, M.M.; Chu, H.; et al. Persistence of asthma requires multiple feedback circuits involving type 2 innate lymphoid cells and IL-33. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 59–68.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mjosberg, J.M.; Trifari, S.; Crellin, N.K.; Peters, C.P.; van Drunen, C.M.; Piet, B.; Fokkens, W.J.; Cupedo, T.; Spits, H. Human IL-25- and IL-33-responsive type 2 innate lymphoid cells are defined by expression of CRTH2 and CD161. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.A.; Baum, R.; Newbury, R.O.; Yang, T.; Dohil, R.; Aquino, M.; Doshi, A.; Walford, H.H.; Kurten, R.C.; Broide, D.H.; et al. Group 2 innate lymphocytes (ILC2) are enriched in active eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 792–794.e793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berin, M.C.; Shreffler, W.G. T(H)2 adjuvants: Implications for food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1311–1320, quiz 1321-1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvillo, E.; Garrote, J.A.; Bernardo, D.; Arranz, E. Innate lymphoid cells and natural killer T cells in the gastrointestinal tract immune system. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2014, 106, 334–345. [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac, A.; Savage, P.B.; Teyton, L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olszak, T.; An, D.; Zeissig, S.; Vera, M.P.; Richter, J.; Franke, A.; Glickman, J.N.; Siebert, R.; Baron, R.M.; Kasper, D.L.; et al. Microbial exposure during early life has persistent effects on natural killer T cell function. Science 2012, 336, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajavelu, P.; Rayapudi, M.; Moffitt, M.; Mishra, A.; Mishra, A. Significance of para-esophageal lymph nodes in food or aeroallergen-induced iNKT cell-mediated experimental eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G645–G654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rayapudi, M.; Rajavelu, P.; Zhu, X.; Kaul, A.; Niranjan, R.; Dynda, S.; Mishra, A.; Mattner, J.; Zaidi, A.; Dutt, P.; et al. Invariant natural killer T-cell neutralization is a possible novel therapy for human eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2014, 3, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyonouchi, S.; Smith, C.L.; Saretta, F.; Abraham, V.; Ruymann, K.R.; Modayur-Chandramouleeswaran, P.; Wang, M.L.; Spergel, J.M.; Cianferoni, A. Invariant natural killer T cells in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aceves, S.S.; Newbury, R.O.; Dohil, R.; Bastian, J.F.; Broide, D.H. Esophageal remodeling in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Degen, L.; Felder, S.; Kummer, M.; Engel, H.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.; Simon, H.U. Budesonide is effective in adolescent and adult patients with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1526–1537.e1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Grzonka, P.; Kita, H.; Kephart, G.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Smith, D.A.; Patel, J.; Byrne, M.; et al. Anti-interleukin-5 antibody treatment (mepolizumab) in active eosinophilic oesophagitis: A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Gut 2010, 59, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.Y.; Doshi, A.; Rosenthal, P.; Beppu, A.; Miller, M.; Aceves, S.; Broide, D. Smad3-deficient mice have reduced esophageal fibrosis and angiogenesis in a model of egg-induced eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kagalwalla, A.F.; Akhtar, N.; Woodruff, S.A.; Rea, B.A.; Masterson, J.C.; Mukkada, V.; Parashette, K.R.; Du, J.; Fillon, S.; Protheroe, C.A.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Epithelial mesenchymal transition contributes to esophageal remodeling and reverses with treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1387–1396.e1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; Inman, M.D.; Parameswaran, K. The trials and tribulations of IL-5, eosinophils, and allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straumann, A.; Kristl, J.; Conus, S.; Vassina, E.; Spichtin, H.P.; Beglinger, C.; Simon, H.U. Cytokine expression in healthy and inflamed mucosa: Probing the role of eosinophils in the digestive tract. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2005, 11, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Murray, J.A.; Arora, A.S.; Alexander, J.A.; Smyrk, T.C.; Butterfield, J.H.; Kita, H. Allergen-specific in vitro cytokine production in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2006, 51, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, C.; Mishra, A.; Saito-Akei, H.; Monk, P.; Anderson, I.; Rothenberg, M.E. Inhibition of human interleukin-13-induced respiratory and oesophageal inflammation by anti-human-interleukin-13 antibody (CAT-354). Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 35, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.E.; Wen, T.; Greenberg, A.; Alpan, O.; Enav, B.; Hirano, I.; Nadeau, K.; Kaiser, S.; Peters, T.; Perez, A.; et al. Intravenous anti-IL-13 mAb QAX576 for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niranjan, R.; Rayapudi, M.; Mishra, A.; Dutt, P.; Dynda, S.; Mishra, A. Pathogenesis of allergen-induced eosinophilic esophagitis is independent of interleukin (IL)-13. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2013, 91, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, M.; Mavi, P.; Rayapudi, M.; Pandey, A.K.; Kaul, A.; Putnam, P.E.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Mishra, A. Interleukin-15 expression is increased in human eosinophilic esophagitis and mediates pathogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 182–193.e187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Kiran, K.C.; Blanchard, C.; Stucke, E.M.; Kemme, K.A.; Collins, M.H.; Abonia, J.P.; Putnam, P.E.; Mukkada, V.A.; Kaul, A.; et al. Analysis and expansion of the eosinophilic esophagitis transcriptome by RNA sequencing. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, F.; Fang, J.C.; Gleich, G.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Olalla, J.M.; Vinson, L.A.; Lowichik, A.; Chen, X.; Emerson, L.; Cox, K.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults is associated with IgG4 and not mediated by IgE. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuyler, A.J.; Wilson, J.M.; Tripathi, A.; Commins, S.P.; Ogbogu, P.U.; Kruzsewski, P.G.; Barnes, B.H.; McGowan, E.C.; Workman, L.J.; Lidholm, J.; et al. Specific IgG4 antibodies to cow’s milk proteins in pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 139–148.e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Yu, S. Prostaglandin D2 receptor D-type prostanoid receptor 2 mediates eosinophil trafficking into the esophagus. Dis. Esophagus 2014, 27, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettipher, R.; Hansel, T.T.; Armer, R. Antagonism of the prostaglandin D2 receptors DP1 and CRTH2 as an approach to treat allergic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collison, A.M.; Sokulsky, L.A.; Sherrill, J.D.; Nightingale, S.; Hatchwell, L.; Talley, N.J.; Walker, M.M.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Mattes, J. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) regulates midline-1, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, inflammation, and remodeling in experimental eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Souza, H.S.; Tortori, C.A.; Lintomen, L.; Figueiredo, R.T.; Bernardazzi, C.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Madi, K.; Buongusto, F.; Elia, C.C.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes eosinophil accumulation and tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutt, P.; Shukla, J.S.; Ventateshaiah, S.U.; Mariswamy, S.J.; Mattner, J.; Shukla, A.; Mishra, A. Allergen-induced interleukin-18 promotes experimental eosinophilic oesophagitis in mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genetic Risk Loci | Gene at and Near Risk Variants | p-Value in Case of GWAS Approach (or the Approach Used) | Known Function/Possible Pathogenic Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2p23.1 | CAPN14 | 5 × 10−10 | Encodes a proteolytic enzyme specific to the esophagus that is induced by IL-13 and involved in epithelial homeostasis and repair |
| CCL26 (/eotaxin-3) | (candidate gene) | A potent eosinophil chemoattractant and activating factor induced by IL-13 | |
| CRLF2 | (candidate gene) | TSLP receptor | |
| FLG | (candidate gene) | Esophageal barrier function | |
| IL-5/IL-13 | (PheWAS) | Th2 signaling | |
| 11q13.5 | LRRC32 C11orf30 (EMSY) CAPN5 | 4 × 10−11 | LRRC32 is a TGF-β binding protein. Possibly TFG-β signaling/epithelial protease function/barrier function EMSY is involved in transcriptional regulation |
| 12q13 | STAT6 | 2 × 10−6 | IL-13 responsive transcription factor, Th2 development |
| TGFβ1 | (candidate gene) | Th2 skewing and fibrosis | |
| 5q22.1 | TSLP WDR36 | 3 × 10−9 | Potent Th2 skewing Induces Th2 cell development and activates eosinophils and basophils |
| 19q13.11 | ANKRD27 PDCD5 RGS9BP | 2 × 10−9 | ANKRD27 inhibits the SNARE complex PDCD5 is involved in apoptotic pathways RGS9BP is not expressed in the esophagus or by immune cells |
| 18q12.1 | DSG1 DCC | (mapping/sequencing/phenotype association) 7 × 10−6 | Regulates esophageal epithelial barrier function |
| TGFβR1/TGFβR2/PBN | (phenotype association) | Th2 skewing and fibrosis | |
| PTEN | (phenotype association) | Regulation of eosinophil response | |
| STAT3 | (phenotype association) | Engagement in signal pathway of growth factors, hormones and multiple cytokines | |
| SPINK5 | (phenotype association) | Esophageal barrier function | |
| DOCK8 | (phenotype association) | Potent role in T-cell homeostasis |
| Genetic Risk Locus | Tag Genetic Variant | Genes at and Near Risk Variants | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1p13.3 | rs2000260 | SLC25A24 | 7 × 10−7 |
| 1p36.13 | rs28530674 | KIF17 | 3 × 10−7 |
| rs2296225 | 1 × 10−7 | ||
| 1p32.2 | rs11206830 | AC119674.2 | 8 × 10−8 |
| rs77569859 | 3 × 10−10 | ||
| 3q26.32 | rs6799767 | 4 × 10−7 | |
| 4q21.1 | rs13106227 | SHROOM3 | 4 × 10−6 |
| rs1986734 | 1 × 10−6 | ||
| rs3806933 | 2 × 10−8 | ||
| rs252716 | 4 × 10−14 | ||
| 5q23.1 | rs2055376 | SEMA6A | 7 × 10−8 |
| 5q14.2 | rs1032757 | 2 × 10−6 | |
| 6p11.2 | rs9500256 | AL445250.1 | 5 × 10−6 |
| 8p23.1 | rs2898261 | XKR6 | 5 × 10−8 |
| 8q24.12 | rs11989782 | SNTB1 | 7 × 10−6 |
| 8q22.2 | rs13278732 | ERICH5 | 6 × 10−6 |
| 10p12.31 | rs11819199 | MIR4675 | 3 × 10−7 |
| 10q23.1 | rs2224865 | MARK2P15-LINC02650 | 9 × 10−6 |
| rs2155219 | 4 × 10−7 | ||
| rs77301713 | 1 × 10−7 | ||
| 11q14.2 | rs118086209 | CCDC81 | 2 × 10−7 |
| 11q21 | rs1939875 | NR | 3 × 10−6 |
| 14q12 | rs8008716 | NOVA1 | 7 × 10−8 |
| 15q13.3 | rs8041227 | LOC283710, KLF13 | 6 × 10−10 |
| 16p13 | rs12924112 | CLEC16A | 2 × 10−9 |
| 16q24.1 | rs371915 | MEAK7 | 2 × 10−8 |
| 17q24.3 | rs6501384 | CALM2P1-AC011990.1 | 6 × 10−6 |
| 17q25.3 | rs3744790 | TIMP2, CEP295NL | 8 × 10−7 |
| rs9956738 | 4 × 10−7 | ||
| 21q22.3 | rs17004598 | HSF2BP | 1 × 10−7 |
| 22q11.21 | rs2075277 | P2RX6 | 9 × 10−7 |
| Mendelian Disease Associated with EoE | Genetic Mutation | Plausible Etiologic Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) | Mutations in TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 | Enhanced TGF-β signaling |
| Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, hypermobility type | Unknown; other subtypes of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are caused by mutations in collagen genes | Disrupted joint and skin development; increased activity of TGF-β due to altered binding by extracellular matrix |
| Severe atopy syndrome associated with metabolic wasting (SAM syndrome) | Homozygous mutations in DSG1 | Disrupted epithelial barrier |
| Neherton syndrome | Loss-of-function mutations in SPINK5 | Unrestricted protease activity of KLK5 and KLK7 |
| PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) | Mutations in PTEN | Inhibited regulation of the phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway |
| Autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome | Deleterious mutations in STAT3 | Dysregulated response to IL-6 and possibly IL-5 |
| Autosomal recessive hyper-IgE syndrome | Loss-of-function mutations in DOCK8 | Loss of T-cell homeostasis; lack of durable secondary antibody response against specific antigens |
| ERBIN deficiency | Loss-of-function mutation in ERBIN | Increased TGF-β pathway activation in T cells with increased Th2 responses |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, S.; Lee, K.H.; Tizaoui, K.; Terrazzino, S.; Cargnin, S.; Effenberger, M.; Shin, J.I.; Kronbichler, A. Pathogenesis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Comprehensive Review of the Genetic and Molecular Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197253
Ryu S, Lee KH, Tizaoui K, Terrazzino S, Cargnin S, Effenberger M, Shin JI, Kronbichler A. Pathogenesis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Comprehensive Review of the Genetic and Molecular Aspects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197253
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Seohyun, Keum Hwa Lee, Kalthoum Tizaoui, Salvatore Terrazzino, Sarah Cargnin, Maria Effenberger, Jae Il Shin, and Andreas Kronbichler. 2020. "Pathogenesis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Comprehensive Review of the Genetic and Molecular Aspects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197253
APA StyleRyu, S., Lee, K. H., Tizaoui, K., Terrazzino, S., Cargnin, S., Effenberger, M., Shin, J. I., & Kronbichler, A. (2020). Pathogenesis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Comprehensive Review of the Genetic and Molecular Aspects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197253







