Inhibition of Orbivirus Replication by Aurintricarboxylic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
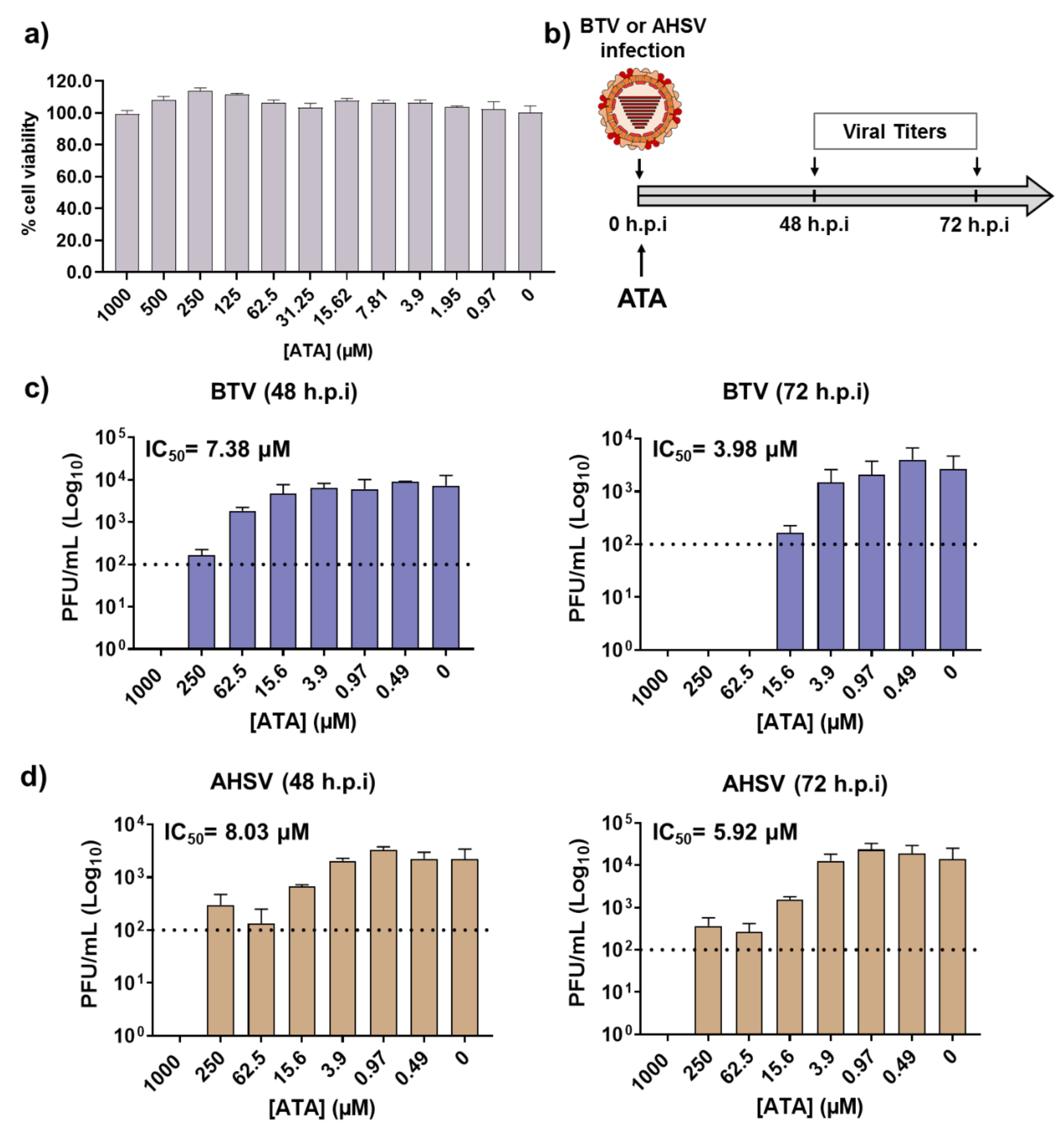
2.1. Inhibitory Effect of ATA on Viral Replication
2.2. ATA Testing in Mice
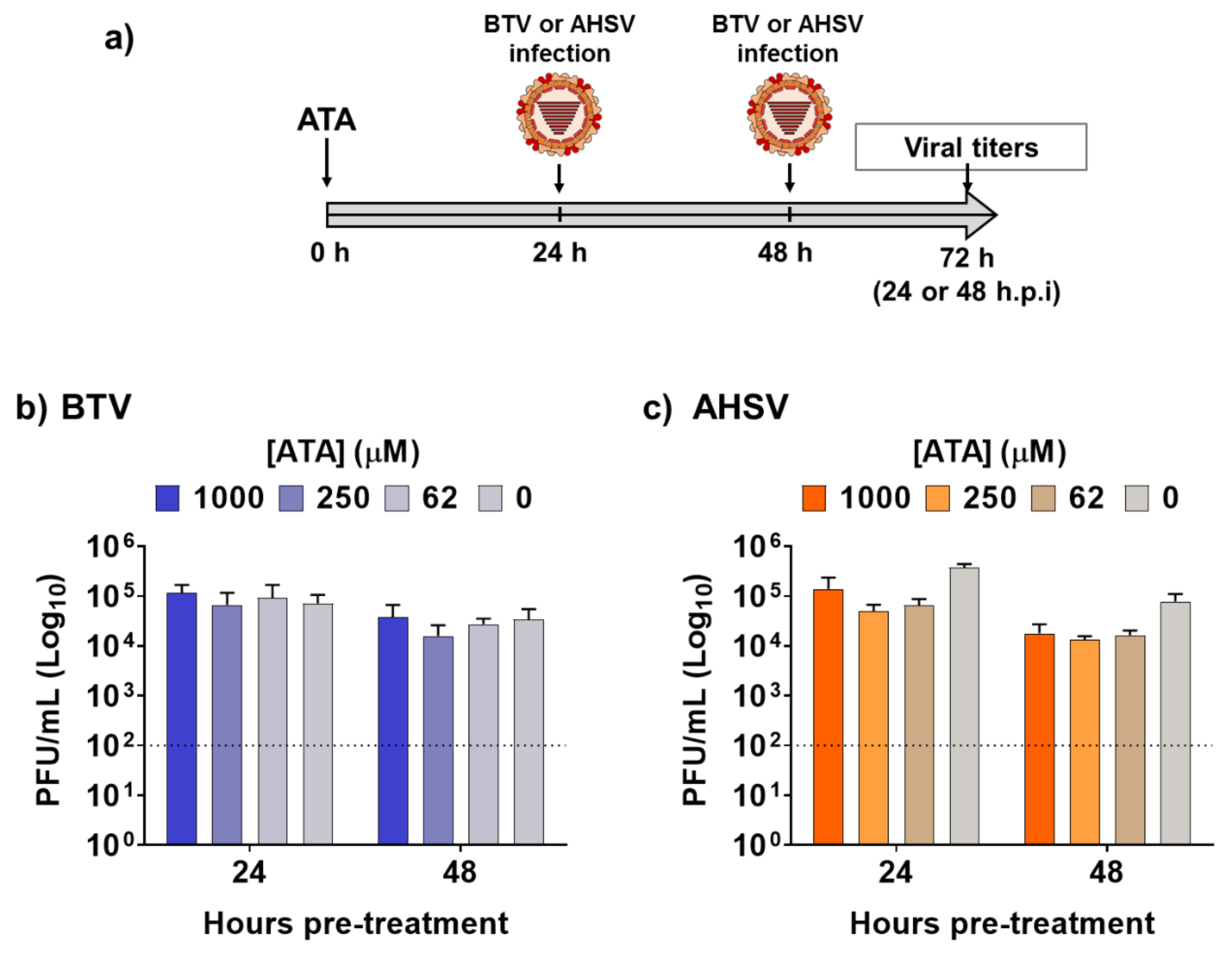
2.3. Therapeutic Activity of ATA in Insect Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Viruses
4.2. Compounds
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Antiviral Assays
4.4.1. Therapeutic Activity
4.4.2. Prophylactic Activity
4.5. Mouse Experiments
4.6. Analysis of the Effect of ATA In Vivo
4.7. Study of the Efficacy of ATA In Vivo
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, P. Bluetongue virus structure and assembly. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 24, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Roy, P. The molecular biology of Bluetongue virus replication. Virus Res. 2014, 182, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.; Hardy, A.; Barry, G.; Pinto, R.M.; Caporale, M.; Melzi, E.; Hughes, J.; Taggart, A.; Janowicz, A.; Varela, M.; et al. Characterization of a second open reading frame in genome segment 10 of bluetongue virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3280–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drolet, B.S.; van Rijn, P.; Howerth, E.W.; Beer, M.; Mertens, P.P. A Review of Knowledge Gaps and Tools for Orbivirus Research. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaganahalli, M.N.; Maan, S.; Maan, N.S.; Nomikou, K.; Pritchard, I.; Lunt, R.; Kirkland, P.D.; Attoui, H.; Brownlie, J.; Mertens, P.P.C. Full genome sequencing and genetic characterization of Eubenangee viruses identify Pata virus as a distinct species within the genus Orbivirus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagre, A.C.; Lee, J.S.; Kityo, R.M.; Bergren, N.A.; Mossel, E.C.; Nakayiki, T.; Nalikka, B.; Nyakarahuka, L.; Gilbert, A.T.; Peterhans, J.K.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of Bukakata orbivirus (Reoviridae:Orbivirus), a Novel Virus from a Ugandan Bat. Viruses 2019, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomazatos, A.; Marschang, R.E.; Maranda, I.; Baum, H.; Bialonski, A.; Spînu, M.; Lühken, R.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Cadar, D. Letea Virus: Comparative Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis of a Novel Reassortant Orbivirus Discovered in Grass Snakes (Natrix natrix). Viruses 2020, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coetzee, P.; van Vuuren, M.; Venter, E.H.; Stokstad, M. A review of experimental infections with bluetongue virus in the mammalian host. Virus Res. 2014, 182, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Guthrie, A.J. Re-emergence of bluetongue, African horse sickness, and other orbivirus diseases. Vet. Res. 2010, 41, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batten, C.A.; Henstock, M.R.; Steedman, H.M.; Waddington, S.; Edwards, L.; Oura, C.A.L. Bluetongue virus serotype 26: Infection kinetics, pathogenesis and possible contact transmission in goats. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréard, E.; Schulz, C.; Sailleau, C.; Bernelin-Cottet, C.; Viarouge, C.; Vitour, D.; Guillaume, B.; Caignard, G.; Gorlier, A.; Attoui, H.; et al. Bluetongue virus serotype 27: Experimental infection of goats, sheep and cattle with three BTV-27 variants reveal atypical characteristics and likely direct contact transmission BTV-27 between goats. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e251–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Castillo-Olivares, J.; Jabbar, T.; Ortego, J.; de la Poza, F.; Marín-López, A. Recombinant vaccines against bluetongue virus. Virus Res. 2014, 182, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nomikou, K.; Hughes, J.; Wash, R.; Kellam, P.; Breard, E.; Zientara, S.; Palmarini, M.; Biek, R.; Mertens, P. Widespread Reassortment Shapes the Evolution and Epidemiology of Bluetongue Virus following European Invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zientara, S.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Control of bluetongue in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouda, W.; Peperkamp, N.H.M.T.; Roumen, M.P.H.M.; Muskens, J.; van Rijn, A.; Vellema, P. Epizootic congenital hydranencephaly and abortion in cattle due to bluetongue virus serotype 8 in the Netherlands. Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd. 2009, 134, 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Vinomack, C.; Rivière, J.; Bréard, E.; Viarouge, C.; Postic, L.; Zientara, S.; Vitour, D.; Belbis, G.; Spony, V.; Pagneux, C.; et al. Clinical cases of Bluetongue serotype 8 in calves in France in the 2018-2019 winter. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, H.C.; Biswas, S.K.; Chand, K.; Rehman, W.; Das, B.; Dadawala, A.I.; Chandel, B.S.; Kher, H.N.; Mondal, B. Isolation of bluetongue virus serotype 1 from aborted goat fetuses. Rev. Off. Int. Epizoot. 2014, 33, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundlacz, C.; Caignard, G.; Sailleau, C.; Viarouge, C.; Postic, L.; Vitour, D.; Zientara, S.; Breard, E. Bluetongue Virus in France: An Illustration of the European and Mediterranean Context since the 2000s. Viruses 2019, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Guillamón, F.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Agüero, M.; Camacho-Sillero, L.; Risalde, M.A.; Zorrilla, I.; Villalba, R.; Rivero-Juárez, A.; García-Bocanegra, I. Re-emergence of bluetongue virus serotype 4 in Iberian ibex (Capra pyrenaica) and sympatric livestock in Spain, 2018-2019. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajko-Nenow, P.; Christodoulou, V.; Thurston, W.; Ropiak, H.M.; Savva, S.; Brown, H.; Qureshi, M.; Alvanitopoulos, K.; Gubbins, S.; Flannery, J.; et al. Origin of Bluetongue Virus Serotype 8 Outbreak in Cyprus, September 2016. Viruses 2020, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, A.J.; Mellor, P.S. Bluetongue in Europe: Past, present and future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulla, V.; Losada, A.; Lecollinet, S.; Kerviel, A.; Lilin, T.; Sailleau, C.; Beck, C.; Zientara, S.; Roy, P. Protective efficacy of multivalent replication-abortive vaccine strains in horses against African horse sickness virus challenge. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4262–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.; Mellor, P.S.; Fall, A.G.; Garros, C.; Venter, G.J. African Horse Sickness Virus: History, Transmission, and Current Status. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.; Venter, G.J.; Greyling, T.; Molini, U.; van Hamburg, H. Evidence of African horse sickness virus infection of Equus zebra hartmannae in the south-western Khomas Region, Namibia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, P.S.; Boned, J.; Hamblin, C.; Graham, S. Isolations of African horse sickness virus from vector insects made during the 1988 epizootic in Spain. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 105, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dennis, S.J.; Meyers, A.E.; Hitzeroth, I.I.; Rybicki, E.P. African Horse Sickness: A Review of Current Understanding and Vaccine Development. Viruses 2019, 11, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marín-López, A.; Otero-Romero, I.; de la Poza, F.; Menaya-Vargas, R.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Benavente, J.; Martínez-Costas, J.M.; Ortego, J. VP2, VP7, and NS1 proteins of bluetongue virus targeted in avian reovirus muNS-Mi microspheres elicit a protective immune response in IFNAR(−/−) mice. Antivir. Res. 2014, 110, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Rodríguez-Calvo, T.; Sevilla, N.; Ortego, J. Heterologous prime boost vaccination with DNA and recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara protects IFNAR(−/−) mice against lethal bluetongue infection. Vaccine 2009, 28, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Poza, F.; Marín-López, A.; Castillo-Olivares, J.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Ortego, J. Identification of CD8 T cell epitopes in VP2 and NS1 proteins of African horse sickness virus in IFNAR(−/−) mice. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Marín-López, A.; Utrilla-Trigo, S.; Jiménez-Cabello, L.; Ortego, J. Reverse genetics approaches: A novel strategy for African horse sickness virus vaccine design. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 44, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utrilla-Trigo, S.; Jiménez-Cabello, L.; Alonso-Ravelo, R.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Marín-López, A.; Moreno, S.; Lorenzo, G.; Benavides, J.; Gilbert, S.; Nogales, A.; et al. Heterologous Combination of ChAdOx1 and MVA Vectors Expressing Protein NS1 as Vaccination Strategy to Induce Durable and Cross-Protective CD8+ T Cell Immunity to Bluetongue Virus. Vaccines 2020, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, V.; Goffredo, M.; Mancini, G.; Quaglia, M.; Santilli, A.; Di Nicola, F.; De Ascentis, M.; Cabras, P.; Volpicelli, C.; De Liberato, C.; et al. Vector Competence of Italian Populations of Culicoides for Some Bluetongue Virus Strains Responsible for Recent Northern African and European Outbreaks. Viruses 2019, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.; Hägglund, S.; Bréard, E.; Riou, M.; Zohari, S.; Comtet, L.; Olofson, A.-S.; Gélineau, R.; Martin, G.; Elvander, M.; et al. Strong protection induced by an experimental DIVA subunit vaccine against bluetongue virus serotype 8 in cattle. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6614–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, E.; Celma, C.C.P.; Boyce, M.; Viarouge, C.; Sailleau, C.; Dubois, E.; Bréard, E.; Thiéry, R.; Zientara, S.; Roy, P. Generation of replication-defective virus-based vaccines that confer full protection in sheep against virulent bluetongue virus challenge. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10213–10221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-G.; Ávila-Pérez, G.; Madere, F.; Hilimire, T.A.; Nogales, A.; Almazán, F.; Martínez-Sobrido, L. Potent Inhibition of Zika Virus Replication by Aurintricarboxylic Acid. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beery, R.; Haimsohn, M.; Wertheim, N.; Hemi, R.; Nir, U.; Karasik, A.; Kanety, H.; Geier, A. Activation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling pathway by the antiapoptotic agents aurintricarboxylic acid and evans blue. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimsohn, M.; Beery, R.; Karasik, A.; Kanety, H.; Geier, A. Aurintricarboxylic acid induces a distinct activation of the IGF-I receptor signaling within MDA-231 cells. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchokroun, Y.; Couprie, J.; Larsen, A.K. Aurintricarboxylic acid, a putative inhibitor of apoptosis, is a potent inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase II in vitro and in Chinese hamster fibrosarcoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catchpoole, D.R.; Stewart, B.W. Inhibition of topoisomerase II by aurintricarboxylic acid: Implications for mechanisms of apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 1994, 14, 853–856. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, A.; Dhruv, H.D.; Mathews, I.T.; Inge, L.J.; Tuncali, S.; Hartman, L.K.; Chow, D.; Millard, N.; Yin, H.H.; Kloss, J.; et al. Identification of aurintricarboxylic acid as a selective inhibitor of the TWEAK-Fn14 signaling pathway in glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12234–12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, W.; Chai, H.; Xie, X. Aurintricarboxylic acid ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by blocking chemokine-mediated pathogenic cell migration and infiltration. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, D.-G.; Park, Y.-H.; Kim, S.-E.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, C.-S.; Kim, S.-C.; Park, C.-G.; Han, D.-J. Aurintricarboxylic acid promotes the conversion of naive CD4+CD25- T cells into Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, H.; Wei, G.; Wang, D.; Yung, P.; Ying, W. Posttreatment with the Ca(2+)-Mg(2+)-dependent endonuclease inhibitor aurintricarboxylic acid abolishes genotoxic agent-induced nuclear condensation and DNA fragmentation and decreases death of astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, S.; Tang, S.-C.; Buja, L.M.; Trump, B.F.; Liepins, A.; Weerasinghe, P. Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits protein synthesis independent, sanguinarine-induced apoptosis and oncosis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fong, K.; Smith, T.J. Citrate-mediated release of aurintricarboxylic acid from a calcium alginate complex: Implications for intravaginal HIV chemoprophylaxis and related applications. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 14, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, H.-C.; Chen, T.-C.; Fang, M.-Y.; Yen, K.-J.; Shih, S.-R.; Hsu, J.T.-A.; Tseng, C.-P. Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication and the viral 3D polymerase by aurintricarboxylic acid. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yap, Y.; Zhang, X.; Andonov, A.; He, R. Structural analysis of inhibition mechanisms of aurintricarboxylic acid on SARS-CoV polymerase and other proteins. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2005, 29, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Adonov, A.; Traykova-Adonova, M.; Cao, J.; Cutts, T.; Grudesky, E.; Deschambaul, Y.; Berry, J.; Drebot, M.; Li, X. Potent and selective inhibition of SARS coronavirus replication by aurintricarboxylic acid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.M.; Flaman, A.S.; Farnsworth, A.; Brown, E.G.; Van Domselaar, G.; He, R.; Li, X. Aurintricarboxylic acid is a potent inhibitor of influenza A and B virus neuraminidases. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.-C.; Tseng, C.-P.; Yang, J.-M.; Ju, Y.-W.; Tseng, S.-N.; Chen, Y.-F.; Chao, Y.-S.; Hsieh, H.-P.; Shih, S.-R.; Hsu, J.T.-A. Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits influenza virus neuraminidase. Antivir. Res. 2009, 81, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, K.; Sallamand, C.; Petzold, C.; Coutard, B.; Collet, A.; Thillier, Y.; Zimmermann, J.; Vasseur, J.-J.; Canard, B.; Rohayem, J.; et al. Development of specific dengue virus 2′-O- and N7-methyltransferase assays for antiviral drug screening. Antivir. Res. 2013, 99, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, S.P.; Weisblum, B. Aptamer Displacement Screen for Flaviviral RNA Methyltransferase Inhibitors. J. Biomol. Screen. 2014, 19, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Bopda-Waffo, A.; Basu, A.; Krishnan, R.; Silberstein, E.; Taylor, D.R.; Talele, T.T.; Arora, P.; Kaushik-Basu, N. Characterization of aurintricarboxylic acid as a potent hepatitis C virus replicase inhibitor. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2009, 20, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Hanson, A.M.; Shadrick, W.R.; Ndjomou, J.; Sweeney, N.L.; Hernandez, J.J.; Bartczak, D.; Li, K.; Frankowski, K.J.; Heck, J.A.; et al. Identification and analysis of hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase inhibitors using nucleic acid binding assays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 8607–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadrick, W.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Hanson, A.M.; Sweeney, N.L.; Frick, D.N. Aurintricarboxylic acid modulates the affinity of hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase for both nucleic acid and ATP. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 6151–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bossart, W.; Paoletti, E.; Nuss, D.L. Cell-free translation of purified virion-associated high-molecular-weight RNA synthesized in vitro by vaccinia virus. J. Virol. 1978, 28, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myskiw, C.; Deschambault, Y.; Jefferies, K.; He, R.; Cao, J. Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits the early stage of vaccinia virus replication by targeting both cellular and viral factors. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smee, D.F.; Hurst, B.L.; Wong, M.-H. Lack of efficacy of aurintricarboxylic acid and ethacrynic acid against vaccinia virus respiratory infections in mice. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2010, 20, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, P.; Cirioni, O.; Giacometti, A.; Scalise, G. In vitro and in vivo activity of aurintricarboxylic acid preparations against Cryptosporidium parvum. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, F.; Huang, Z.; Lee, S.-Y.; Liang, J.; Ivanov, M.I.; Alonso, A.; Bliska, J.B.; Lawrence, D.S.; Mustelin, T.; Zhang, Z.-Y. Aurintricarboxylic acid blocks in vitro and in vivo activity of YopH, an essential virulent factor of Yersinia pestis, the agent of plague. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41734–41741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marín-López, A.; Bermúdez, R.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Moreno, S.; Brun, A.; Ortego, J. Pathological Characterization Of IFNAR(−/−) Mice Infected With Bluetongue Virus Serotype 4. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marín-Lopez, A.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Moreno, S.; Utrilla-Trigo, S.; Nogales, A.; Brun, A.; Fikrig, E.; Ortego, J. Modeling Arboviral Infection in Mice Lacking the Interferon Alpha/Beta Receptor. Viruses 2019, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mellor, P.S.; Boorman, J.; Baylis, M. Culicoides Biting Midges: Their Role as Arbovirus Vectors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 307–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leta, S.; Fetene, E.; Mulatu, T.; Amenu, K.; Jaleta, M.B.; Beyene, T.J.; Negussie, H.; Kriticos, D.; Revie, C.W. Updating the global occurrence of Culicoides imicola, a vector for emerging viral diseases. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Maddox, C.; Rasmussen, L.; Hobrath, J.V.; White, L.E. Assay development and high-throughput antiviral drug screening against Bluetongue virus. Antivir. Res. 2009, 83, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Sekhar, K.; Venkataramaiah, C.; Raju, C.N. In silico, in ovo and in vitro antiviral efficacy of phosphorylated derivatives of abacavir: An experimental approach. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darpel, K.E.; Langner, K.F.A.; Nimtz, M.; Anthony, S.J.; Brownlie, J.; Takamatsu, H.-H.; Mellor, P.S.; Mertens, P.P.C. Saliva proteins of vector Culicoides modify structure and infectivity of bluetongue virus particles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howerth, E.W.; Greene, C.E.; Prestwood, A.K. Experimentally induced bluetongue virus infection in white-tailed deer: Coagulation, clinical pathologic, and gross pathologic changes. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar]
- McColl, K.A.; Gould, A.R. Bluetongue virus infection in sheep: Haematological changes and detection by polymerase chain reaction. Aust. Vet. J. 1994, 71, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Poza, F.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; López-Gil, E.; Marín-López, A.; Mateos, F.; Castillo-Olivares, J.; Lorenzo, G.; Ortego, J. Ns1 is a key protein in the vaccine composition to protect Ifnar(−/−) mice against infection with multiple serotypes of African horse sickness virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marín-López, A.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Barriales, D.; Lorenzo, G.; Brun, A.; Anguita, J.; Ortego, J. CD8 T Cell Responses to an Immunodominant Epitope within the Nonstructural Protein NS1 Provide Wide Immunoprotection against Bluetongue Virus in IFNAR −/− Mice. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Rodríguez-Calvo, T.; Anguita, J.; Sevilla, N.; Ortego, J. Establishment of a Bluetongue Virus Infection Model in Mice that Are Deficient in the Alpha/Beta Interferon Receptor. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toussaint, J.F.; Sailleau, C.; Breard, E.; Zientara, S.; De Clercq, K. Bluetongue virus detection by two real-time RT-qPCRs targeting two different genomic segments. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 140, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agüero, M.; Gómez-Tejedor, C.; Angeles Cubillo, M.; Rubio, C.; Romero, E.; Jiménez-Clavero, A. Real-time fluorogenic reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of African horse sickness virus. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alonso, C.; Utrilla-Trigo, S.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Jiménez-Cabello, L.; Ortego, J.; Nogales, A. Inhibition of Orbivirus Replication by Aurintricarboxylic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197294
Alonso C, Utrilla-Trigo S, Calvo-Pinilla E, Jiménez-Cabello L, Ortego J, Nogales A. Inhibition of Orbivirus Replication by Aurintricarboxylic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197294
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlonso, Celia, Sergio Utrilla-Trigo, Eva Calvo-Pinilla, Luis Jiménez-Cabello, Javier Ortego, and Aitor Nogales. 2020. "Inhibition of Orbivirus Replication by Aurintricarboxylic Acid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197294
APA StyleAlonso, C., Utrilla-Trigo, S., Calvo-Pinilla, E., Jiménez-Cabello, L., Ortego, J., & Nogales, A. (2020). Inhibition of Orbivirus Replication by Aurintricarboxylic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197294




