p38 MAPK Pathway in the Heart: New Insights in Health and Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cardiovascular Development
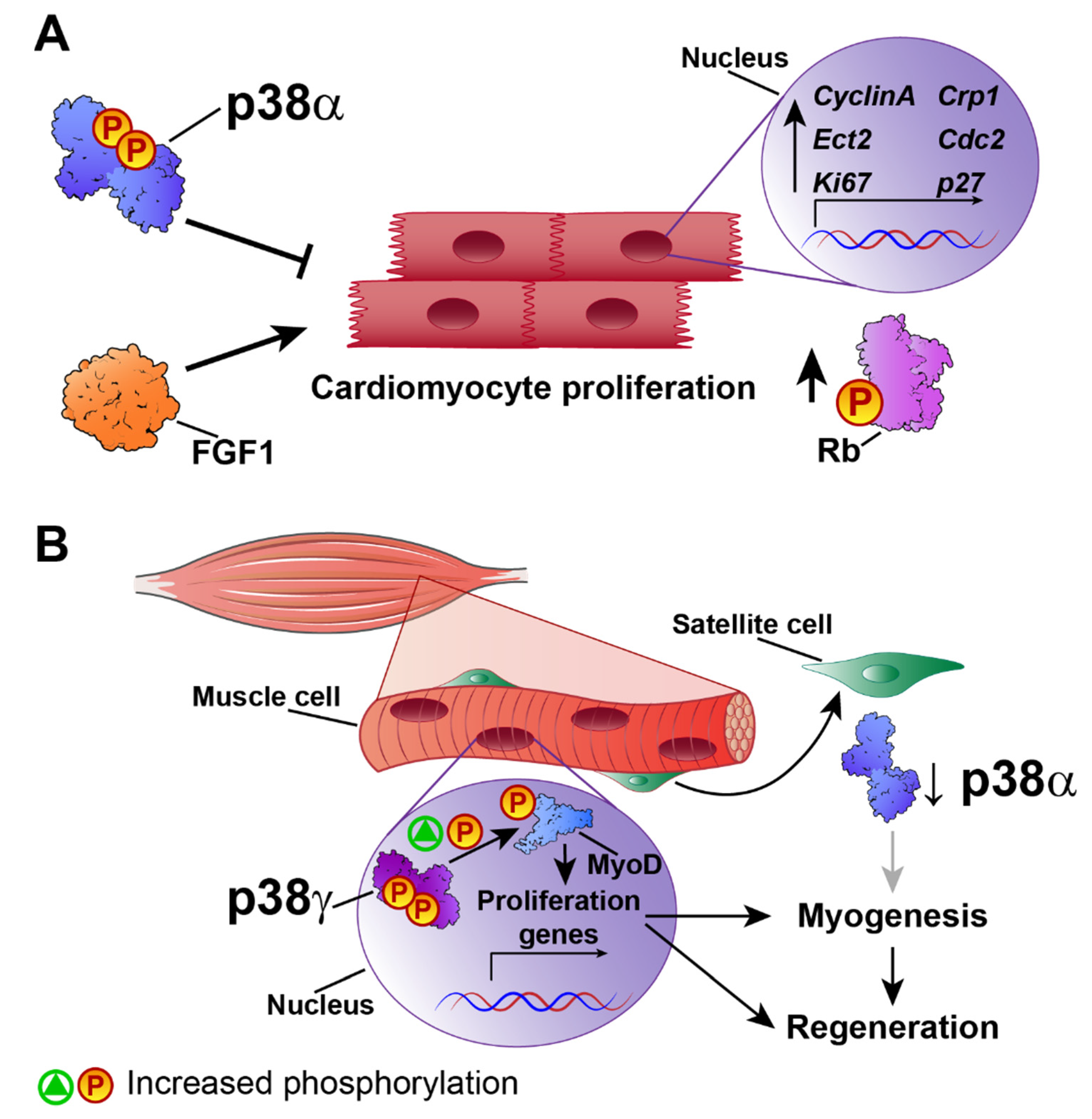
3. Cardiac Hypertrophy
4. Cardiac Regeneration
5. p38 in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury
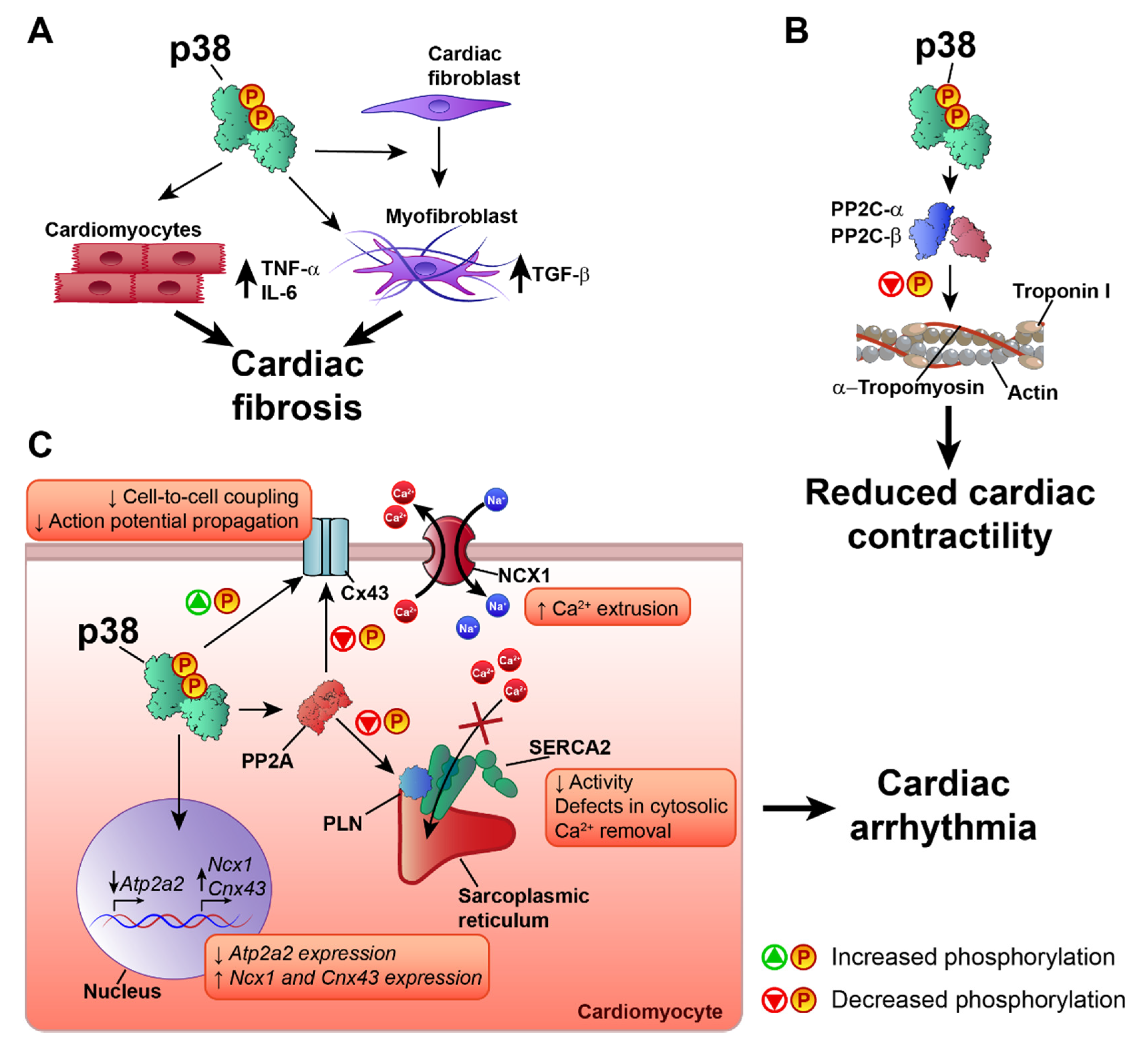
6. p38 in Heart Failure and Cardiac Arrhythmia
7. p38 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, J.; Lee, J.D.; Bibbs, L.; Ulevitch, R.J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science 1994, 265, 80888–80911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Laydon, J.T.; McDonnell, P.C.; Gallagher, T.F.; Kumar, S.; Green, D.; McNulty, D.; Blumenthal, M.J.; Keys, J.R.; Vatter, S.W.L.; et al. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 1994, 372, 73977–74046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, J.; Cohen, P.; Trigon, S.; Morange, M.; Alonso-Llamazares, A.; Zamanillo, D.; Hunt, T.; Nebreda, A.R. A novel kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates MAPKAP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell 1994, 78, 10271–11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, W.; A Gegner, J.; Lin, S.; Han, J. Characterization of the structure and function of a new mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38beta). J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17920–17926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Han, J. The primary structure of p38 gamma: A new member of p38 group of MAP kinases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 228, 3340–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gram, H.; Zhao, M.; New, L.; Gu, J.; Feng, L.; Di Padova, F.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Han, J. Characterization of the structure and function of the fourth member of p38 group mitogen-activated protein kinases, p38delta. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30122–30128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. Evolutionary history of the vertebrate mitogen activated protein kinases family. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Cuenda, A.; Spillantini, M.G.; Thomas, G.M.; Buée-Scherrer, V.; Cohen, P.; Goedert, M. Stress-activated protein kinase-3 interacts with the PDZ domain of alpha1-syntrophin. A mechanism for specific substrate recognition. J. Boil. Chem. 1999, 274, 12626–12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, G.; Arthur, J.S.C.; Kuma, Y.; Peggie, M.; Carr, J.; Murray-Tait, V.; Centeno, F.; Goedert, M.; A Morrice, N.; Cuenda, A. p38γ regulates the localisation of SAP97 in the cytoskeleton by modulating its interaction with GKAP. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, G.; Reuver, S.; Feijoo, C.; Hasegawa, M.; Thomas, G.M.; Centeno, F.; Kuhlendahl, S.; Leal-Ortiz, S.; Goedert, M.; Garner, C.; et al. Stress- and mitogen-induced phosphorylation of the synapse-associated protein SAP90/PSD-95 by activation of SAPK3/p38gamma and ERK1/ERK2. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado, A.; Nebreda, A.R. Mechanisms and functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.S.C.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabio, G.; Davis, R.J. TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, J.M.; Mittelstadt, P.R.; Guszczynski, T.; Copeland, T.D.; Yamaguchi, H.; Appella, E.; Fornace, A.J.; Ashwell, J.D. Alternative p38 activation pathway mediated by T cell receptor–proximal tyrosine kinases. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanna, A.; Henson, S.M.; Escors, D.; Akbar, A.N. The kinase p38 activated by the metabolic regulator AMPK and scaffold TAB1 drives the senescence of human T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matesanz, N.; Bernardo, E.; Acín-Pérez, R.; Manieri, E.; Pérez-Sieira, S.; Hernández-Cosido, L.; Montalvo-Romeral, V.; Mora, A.; Rodriguez, É.; Leiva-Vega, L.; et al. MKK6 controls T3-mediated browning of white adipose tissue. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittner, A.; Block, H.; Reichel, C.A.; Varjosalo, M.; Gehart, H.; Sumara, G.; Gstaiger, M.; Krombach, F.; Zarbock, A.; Ricci, R. Regulation of PTEN activity by p38δ-PKD1 signaling in neutrophils confers inflammatory responses in the lung. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2229–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Svensson, L.; Roach, M.; Hambor, J.; McNeish, J.; Gabel, C.A. Deficiency of the Stress Kinase P38α Results in Embryonic Lethality. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.H.; Porras, A.; Alonso, G.; Jones, M.; Vintersten, K.; Panelli, S.; Valladares, A.; Perez, L.; Klein, R.; Nebreda, A.R. Essential role of p38alpha MAP kinase in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgett, J.S.; Ding, J.; Guh-Siesel, L.; Chartrain, N.A.; Yang, L.; Gopal, S.; Shen, M.M. Essential role for p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase in placental angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10454–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keren, A.; Tamir, Y.; Bengal, E. The p38 MAPK signaling pathway: A major regulator of skeletal muscle development. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 252, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, M.; Leppä, S. Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases and Activator Protein 1 Are Required for Proliferation and Cardiomyocyte Differentiation of P19 Embryonal Carcinoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15992–16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouadi, M.; Bost, F.; Caron, L.; Laurent, K.; Brustel, Y.L.M.; Binétruy, B. p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activity Commits Embryonic Stem Cells to Either Neurogenesis or Cardiomyogenesis. STEM CELLS 2006, 24, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerits, N.; Kostenko, S.; Moens, U. In vivo functions of mitogen-activated protein kinases: Conclusions from knock-in and knock-out mice. Transgenic Res. 2007, 16, 281–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, F.B.; Schebesta, M.; Duong, M.T.; Lu, G.; Ren, S.; Madwed, J.B.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Keating, M.T. p38 MAP kinase inhibition enables proliferation of adult mammalian cardiomyocytes. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, F.B.; Hsieh, P.C.H.; Lee, R.T.; Keating, M.T. FGF1/p38 MAP kinase inhibitor therapy induces cardiomyocyte mitosis, reduces scarring, and rescues function after myocardial infarction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15546–15551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Torres, F.; Martínez-Fernández, S.; Zuluaga, S.; Nebreda, Á.; Porras, A.; Aránega, A.E.; Navarro, F. A role for p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase in embryonic cardiac differentiation. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kubota, J.; Hirayama, J.; Nagai, Y.; Nishina, S.; Yokoi, T.; Asaoka, Y.; Seo, J.; Shimizu, N.; Kajiho, H.; et al. p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Controls a Switch Between Cardiomyocyte and Neuronal Commitment of Murine Embryonic Stem Cells by Activating Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2C-Dependent Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 Transcription. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrantes, I.D.B.; Coya, J.M.; Maina, F.; Arthur, J.S.C.; Nebreda, A.R. Genetic analysis of specific and redundant roles for p38 and p38 MAPKs during mouse development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12764–12769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chan, T.W.; Ding, Y.; Rau, C.D.; Sung, K.; Ren, S.; et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates chamber specific perinatal growth in heart. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Terán, B.; López, J.A.; Rodríguez, E.; Leiva, L.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Bernal, J.A.; Jiménez-Borreguero, L.J.; Redondo, J.M.; Vazquez, J.; Sabio, G. p38γ and δ promote heart hypertrophy by targeting the mTOR-inhibitory protein DEPTOR for degradation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Sah, V.P.; Brown, J.H.; Han, J.; Chien, K.R. Cardiac Hypertrophy Induced by Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Kinase 7, a Specific Activator for c-Jun NH2-terminal Kinase in Ventricular Muscle Cells. J. Boil. Chem. 1998, 273, 5423–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zechner, D.; Thuerauf, D.J.; Hanford, D.S.; McDonough, P.M.; Glembotski, C.C. A Role for the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Myocardial Cell Growth, Sarcomeric Organization, and Cardiac-specific Gene Expression. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Sah, V.P.; Ross, J.; Brown, J.H.; Han, J.; Chien, K.R. Cardiac Muscle Cell Hypertrophy and Apoptosis Induced by Distinct Members of the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Family. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Yamaguchi, O.; Hirotani, S.; Hikoso, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Takeda, T.; Osuka, S.; Morita, T.; Kondoh, G.; et al. p38α Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Plays a Critical Role in Cardiomyocyte Survival but Not in Cardiac Hypertrophic Growth in Response to Pressure Overload. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 10611–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, J.C.; Bueno, O.F.; Liang, Q.; Wilkins, B.J.; Dai, Y.-S.; Parsons, S.; Braunwart, J.; Glascock, B.J.; Klevitsky, R.; Kimball, T.F.; et al. Targeted inhibition of p38 MAPK promotes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy through upregulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, I.P.; Cariolato, L.; Maric, D.; Gillet, L.; Abriel, H.; Diviani, D. A-kinase anchoring protein Lbc coordinates a p38 activating signaling complex controlling compensatory cardiac hypertrophy. Mol. Cell Biol 2013, 33, 2903–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingar, D.; Merlen, C.; A Grandy, S.; Gillis, M.-A.; Villeneuve, L.R.; Mamarbachi, A.M.; Fiset, C.; Allen, B.G. Effect of pressure overload-induced hypertrophy on the expression and localization of p38 MAP kinase isoforms in the mouse heart. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poss, K.D.; Wilson, L.G.; Keating, M.T. Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish. Science 2002, 298, 2188–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jopling, C.; Suñè, G.; Morera, C.; Belmonte, J.C.I. p38α MAPK regulates myocardial regeneration in zebrafish. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Bonilla, V.; Perdiguero, E.; Gresh, L.; Serrano, A.L.; Zamora, M.; Sousa-Victor, P.; Jardí, M.; Wagner, E.F.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Efficient adult skeletal muscle regeneration in mice deficient in p38β, p38γ and p38δ MAP kinases. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, M.A.; Le Grand, F.; Scimè, A.; Kuang, S.; Von Maltzahn, J.; Seale, V.; Cuenda, A.; Ranish, J.A.; Rudnicki, M.A. p38-γ–dependent gene silencing restricts entry into the myogenic differentiation program. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, L.; Ninfali, C.; Cortés, M.; Darling, D.S.; Postigo, A. ZEB1 protects skeletal muscle from damage and is required for its regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, P.; Pugazhendhi, D.; Woodhouse, S.; Oxley, D.; Pell, J.M. p38α MAPK Regulates Adult Muscle Stem Cell Fate by Restricting Progenitor Proliferation During Postnatal Growth and Repair. STEM CELLS 2013, 31, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa-Victor, P.; García-Prat, L.; Serrano, A.L.; Perdiguero, E.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Muscle stem cell aging: Regulation and rejuvenation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, J.D.; Doles, J.D.; Hall, J.K.; Tanaka, K.K.; Carter, T.A.; Olwin, B.B. p38 MAPK signaling underlies a cell-autonomous loss of stem cell self-renewal in skeletal muscle of aged mice. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Liu, K.; Niu, W.; Chen, M.; Wang, M.; Xue, Y.; Gao, C.; Ma, P.X.; Lei, B. Gold and gold-silver alloy nanoparticles enhance the myogenic differentiation of myoblasts through p38 MAPK signaling pathway and promote in vivo skeletal muscle regeneration. Biomater. 2018, 175, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-K.; Blackwood, E.A.; Azizi, K.M.; Thuerauf, N.J.; Fahem, A.G.; Hofmann, C.; Kaufman, R.J.; Doroudgar, S.; Glembotski, C.C. ATF6 Decreases Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Damage and Links ER Stress and Oxidative Stress Signaling Pathways in the Heart. Circ. Res. 2016, 120, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallert, M.; Ziegler, M.; Wang, X.; Maluenda, A.; Xu, X.; Yap, M.L.; Witt, R.; Giles, C.; Kluge, S.; Hortmann, M.; et al. α-Tocopherol preserves cardiac function by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibaut, M.; Mekis, D.; Petrovic, D. Pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction and Acute Management Strategies. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 14, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marais, E.; Genade, S.; Huisamen, B.; Strijdom, H.; Moolman, J.; Lochner, A. Activation of p38 MAPK Induced by a Multi-cycle Ischaemic Preconditioning Protocol is Associated with Attenuated p38 MAPK Activity During Sustained Ischaemia and Reperfusion. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard-Croft, C.; Kristo, G.; Yoshimura, Y.; Reid, E.; Keith, B.J.; Mentzer, R.M.; Lasley, R.D. Acute adenosine preconditioning is mediated by p38 MAPK activation in discrete subcellular compartments. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H1359–H1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, P.W.; Rust, R.T.; Han, J.; Millhorn, D.E.; Beitner-Johnson, D. Selective Activation of p38α and p38γ by Hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23570–23576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurin, A.T.; Martin, J.L.; Heads, R.; Foley, C.; Mockridge, J.W.; Wright, M.J.; Wang, Y.; Marber, M.S. The role of differential activation of p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase in preconditioned ventricular myocytes. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Kristo, G.; Keith, B.J.; Jahania, S.A.; Mentzer, R.M.; Lasley, R.D. The p38 MAPK Inhibitor SB203580 Blocks Adenosine A1 Receptor-Induced Attenuation of In Vivo Myocardial Stunning. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2004, 18, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.C.; Hines, D.S.; Kukreja, R.C. Adenosine-induced late preconditioning in mouse hearts: Role of p38 MAP kinase and mitochondrial KATP channels. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H1278–H1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, A.; Skarli, M.; Papakrivopoulou, J.; Yellon, D.M. Adenosine A1Receptor Induced Delayed Preconditioning in Rabbits. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerling, B.M.; Platanias, L.C.; Black, E.; Nebreda, A.R.; Davis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Activation of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Is Required for Hypoxia Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 4853–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas-Espinosa, A.; Basye, A.; Angelos, M.G.; Chen, C.-A. Modulation of p38 kinase by DUSP4 is important in regulating cardiovascular function under oxidative stress. Free. Radic. Boil. Med. 2015, 89, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurian, G.A.; Paddikkala, J. N-acetylcysteine and magnesium improve biochemical abnormalities associated with myocardial ischaemic reperfusion in South Indian patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: A comparative analysis. Singap. Med J. 2010, 51, 3813–3888. [Google Scholar]
- Kurian, G.A.; Paddikkala, J. Administration of aqueous extract of Desmodium gangeticum (L) root protects rat heart against ischemic reperfusion injury induced oxidative stress. Indian J. Exp. Boil. 2009, 47, 1291–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Kurian, G.A.; Suryanarayanan, S.; Raman, A.; Padikkala, J. Antioxidant effects of ethyl acetate extract of Desmodium gangeticum root on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rat hearts. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.I.; Ebner, M.; Wallner, C.; Haller, M.; Khalid, S.; Schwelberger, H.G.; Koziel, K.; Enthammer, M.; Hermann, M.; Sickinger, S.; et al. A p38MAPK/MK2 signaling pathway leading to redox stress, cell death and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.-T.; Sun, A.-J.; Fu, X.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Jing, L.-L.; Lu, A.-D.; Dong, Y.-F.; Jia, Z.-P. Protective Effect of Apigenin on Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury of the Isolated Rat Heart. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2014, 15, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Apigenin attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via the inactivation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 6873–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, M.; Xie, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, X. Prdx1 alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis through ROS-activated MAPK pathway during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, R.; Burgoyne, J.R.; DeNicola, G.F.; Rudyk, O.; DeSantis, V.; Charles, R.L.; Eaton, P.; Marber, M.S. Redox-dependent dimerization of p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase with mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16161–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säkkinen, H.; Aro, J.; Kaikkonen, L.; Ohukainen, P.; Näpänkangas, J.; Tokola, H.; Ruskoaho, H.; Rysä, J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 target regenerating islet-derived 3γ expression is upregulated in cardiac inflammatory response in the rat heart. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, D.; Aijie, H.; Bo, L.; Zhilin, M.; Long, Y. Gambogic acid exerts cardioprotective effects in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction through inhibition of inflammation, iNOS and NF-κB/p38 pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 15, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, F.; Tomar, D.; A C, S.A.; Elmoselhi, A.B.; Thomas, M.; Elrod, J.W.; Tilley, D.G.; Force, T. Nicotinamide riboside kinase-2 alleviates ischemia-induced heart failure through P38 signaling. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yates, C.C.; Lockyer, P.; Xie, L.; Bevilacqua, A.; He, J.; Lander, C.; Patterson, C.; Willis, M.S. MMI-0100 inhibits cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction by direct actions on cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts via MK2 inhibition. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 77, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molkentin, J.D.; Bugg, D.; Ghearing, N.; Dorn, L.E.; Kim, P.; Sargent, M.A.; Gunaje, J.; Otsu, K.; Davis, J. Fibroblast-Specific Genetic Manipulation of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase In Vivo Reveals Its Central Regulatory Role in Fibrosis. Circulation 2017, 136, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y. Rosuvastatin Attenuates Atrial Structural Remodelling in Rats with Myocardial Infarction through the Inhibition of the p38 MAPK Signalling Pathway. Hear. Lung Circ. 2015, 24, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, F.; Sang, M.; Sun, X.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Effects of atorvastatin on p38 phosphorylation and cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompunt, E.; Sanit, J.; Barrère-Lemaire, S.; Nargeot, J.; Noordali, H.; Madhani, M.; Kumphune, S. The cardioprotective effects of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 5231–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumphune, S.; Surinkaew, S.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Inhibition of p38 MAPK activation protects cardiac mitochondria from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Ma, J.; Meng, X.-W.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Song, S.-Y.; Chen, Q.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, K.; et al. Heat Shock Protein 70 Protects the Heart from Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inhibition of p38 MAPK Signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xu, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xuan, H.; Ma, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, N.; Zhu, H. Luteolin Enhances Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Activity through p38 MAPK Signaling thus Improving Rat Cardiac Function after Ischemia/Reperfusion. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-L.; Sulistyowati, E.; Hsu, J.-H.; Huang, B.-Y.; Dai, Z.-K.; Wu, B.-N.; Chao, Y.-Y.; Yeh, J.-L. KMUP-1 Ameliorates Ischemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis through the NO⁻cGMP⁻MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanit, J.; Prompunt, E.; Adulyaritthikul, P.; Nokkaew, N.; Mongkolpathumrat, P.; Kongpol, K.; Kijtawornrat, A.; Petchdee, S.; Kumphune, S. Combination of metformin and p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, reduced myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in non-obese type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surinkaew, S.; Kumphune, S.; Chattipakorn, S.; Chattipakorn, N. Inhibition of p38 MAPK During Ischemia, But Not Reperfusion, Effectively Attenuates Fatal Arrhythmia in Ischemia/Reperfusion Heart. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijles, D.N.; Cull, J.J.; Markou, T.; Cooper, S.T.; Haines, Z.H.; Fuller, S.J.; O’Gara, P.; Sheppard, M.; Harding, S.E.; Sugden, P.H.; et al. Redox Regulation of Cardiac ASK1 (Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1) Controls p38-MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) and Orchestrates Cardiac Remodeling to Hypertension. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaeian, B.; Fonarow, G.C. Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; Lund, L.H. Global Public Health Burden of Heart Failure. Card. Fail. Rev. 2017, 3, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardin, S.; Li, D.; Thorin-Trescases, N.; Leung, T.-K.; Thorin, E.; Nattel, S. Evolution of the atrial fibrillation substrate in experimental congestive heart failure: Angiotensin-dependent and -independent pathways. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 60, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shinagawa, K.; Pang, L.; Leung, T.K.; Cardin, S.; Wang, Z.; Nattel, S. Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on the development of the atrial fibrillation substrate in dogs with ventricular tachypacing-induced congestive heart failure. Circulation 2001, 104, 2608–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. p38 MAP Kinase Mediates Inflammatory Cytokine Induction in Cardiomyocytes and Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Heart. Circulation 2005, 111, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoi, S.; Otani, H.; Matsuhisa, S.; Akita, Y.; Tatsumi, K.; Enoki, C.; Fujiwara, H.; Imamura, H.; Kamihata, H.; Iwasaka, T. Opposing effect of p38 MAP kinase and JNK inhibitors on the development of heart failure in the cardiomyopathic hamster. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Sheppard, R.J.M.F. Fibrosis in heart disease: Understanding the role of transforming growth factor-β1 in cardiomyopathy, valvular disease and arrhythmia. Immunology 2006, 118, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.; Schelbert, E.B.; Díez, J.; Butler, J. Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis in Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, A.M.; Frazier, O.H.; Buja, L.M. Fibrosis and heart failure. Hear. Fail. Rev. 2012, 19, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Kovacs, A.; Zheng, M.; Lerner, D.; Pu, H.; Saffitz, J.; Chien, K.; Xiao, R.-P.; Kass, D.A.; et al. The in vivo role of p38 MAP kinases in cardiac remodeling and restrictive cardiomyopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12283–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi, L.F.; Bissett, J.; Romeo, F.; Mehta, J.L. Role of Inflammation in Heart Failure. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, K.E.; Turner, N.A. Cardiac fibroblasts: At the heart of myocardial remodeling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lau, W.B.; Ma, X.L.; Du, J. Cardiac Fibroblast–Specific Activating Transcription Factor 3 Protects Against Heart Failure by Suppressing MAP2K3-p38 Signaling. Circulation 2017, 135, 2041–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujak, M.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The role of TGF-β signaling in myocardial infarction and cardiac remodeling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 74, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijnen, P.; Petrov, V.; Fagard, R. Induction of Cardiac Fibrosis by Transforming Growth Factor-β1. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2000, 71, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, G.W.; Molkentin, J.D. Manipulating Cardiac Contractility in Heart Failure. Circulation 2004, 109, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rajashree, R.; Liu, Q.; Hofmann, P. Acute p38 MAPK activation decreases force development in ventricular myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2003, 285, H2578–H2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liao, P.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wang, S.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, S.-J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, R.-P. p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Mediates a Negative Inotropic Effect in Cardiac Myocytes. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szokodi, I.; Kerkelä, R.; Kubin, A.-M.; Sármán, B.; Pikkarainen, S.; Kónyi, A.; Horváth, I.G.; Papp, L.; Tóth, M.; Skoumal, R.; et al. Functionally Opposing Roles of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 and p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in the Regulation of Cardiac Contractility. Circulation 2008, 118, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, S.-J.; Zhu, W.-Z.; Ziman, B.; Kobilka, B.K.; Xiao, R.-P. β2-Adrenergic Receptor-induced p38 MAPK Activation Is Mediated by Protein Kinase A Rather than by Gior Gβγ in Adult Mouse Cardiomyocytes. J. Boil. Chem. 2000, 275, 40635–40640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomeque, J.; Sapia, L.; Hajjar, R.J.; Mattiazzi, A.; Petroff, M.V. Angiotensin II-induced negative inotropy in rat ventricular myocytes: Role of reactive oxygen species and p38 MAPK. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H96–H106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahebi, S.; Ota, A.; Li, M.; Warren, C.M.; De Tombe, P.P.; Wang, Y.; Solaro, R.J. p38-MAPK Induced Dephosphorylation of α-Tropomyosin Is Associated With Depression of Myocardial Sarcomeric Tension and ATPase Activity. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo, M.S.; Aiello, E.A.; Sepúlveda, M.; Petroff, M.G.V.; Aiello, E.A.; De Giusti, V.C. The reduced myofilament responsiveness to calcium contributes to the negative force-frequency relationship in rat cardiomyocytes: Role of reactive oxygen species and p-38 map kinase. Pflügers Archiv. Eur. J. Physiol. 2017, 469, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikkonen, L.; Magga, J.; Ronkainen, V.-P.; Koivisto, E.; Perjés, Á.; Chuprun, J.K.; Vinge, L.E.; Kilpiö, T.; Aro, J.; Ulvila, J.; et al. p38α regulates SERCA2a function. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2014, 67, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, D.M. Calcium fluxes involved in control of cardiac myocyte contraction. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Anderson, M.E. Mechanisms of altered Ca²⁺ handling in heart failure. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 690–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidkamp, M.C.; Scully, B.T.; Vijayan, K.; Engman, S.J.; Szotek, E.L.; Samarel, A.M. PYK2 regulates SERCA2 gene expression in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2005, 289, C471–C482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Andrews, C.; Ho, P.D.; Dillmann, W.H.; Glembotski, C.C.; McDonough, P.M. The MKK6-p38 MAPK pathway prolongs the cardiac contractile calcium transient, downregulates SERCA2, and activates NF-AT. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 59, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, M.; Neef, S.; Freund, R.; Geers-Knörr, C.; Franz-Wachtel, M.; Brandis, A.; Krone, D.; Schneider, H.; Groos, S.; Menon, M.B.; et al. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Activated Protein Kinases 2 and 3 Regulate SERCA2a Expression and Fiber Type Composition To Modulate Skeletal Muscle and Cardiomyocyte Function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2586–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerk, A.; Michael, A.; Sugden, P.H. Stimulation of the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Neonatal Rat Ventricular Myocytes by the G Protein–coupled Receptor Agonists, Endothelin-1 and Phenylephrine: A Role in Cardiac Myocyte Hypertrophy? J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranias, E.G.; Hajjar, R.J. Modulation of Cardiac Contractility by the Phopholamban/SERCA2a Regulatome. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1646–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, T.; Du, N.; Lu, G.; Minamisawa, S.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, H. A Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Localized Protein Phosphatase Regulates Phospholamban Phosphorylation and Promotes Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in the Heart. JACC. Basic Transl. Sci. 2017, 2, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Wang, X.; Ke, Y.; Solaro, R.J. Regulation of Ca2+ transient by PP2A in normal and failing heart. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hofmann, P.A. Modulation of protein phosphatase 2a by adenosine A1 receptors in cardiomyocytes: Role for p38 MAPK. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2003, 285, H97–H103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kappler, C.; Menick, D. The role of p38 in the regulation of Na?Ca exchanger expression in adult cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2005, 38, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menick, D.R.; Renaud, L.; Buchholz, A.; Müller, J.G.; Zhou, H.; Kappler, C.S.; Kubalak, S.W.; Conway, S.J.; Xu, L. Regulation of Ncx1 gene expression in the normal and hypertrophic heart. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2007, 1099, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kappler, C.S.; Mani, S.K.; Shepherd, N.R.; Renaud, L.; Snider, P.; Conway, S.J.; Menick, D.R. Chronic Administration of KB-R7943 Induces Up-regulation of Cardiac NCX1. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27265–27272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogwizd, S.M.; Schlotthauer, K.; Li, L.; Yuan, W.; Bers, D.M. Arrhythmogenesis and Contractile Dysfunction in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kao, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-A.; Chen, Y.-J. Extracellular matrix of collagen modulates arrhythmogenic activity of pulmonary veins through p38 MAPK activation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 59, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H. The MAPK pathway is involved in the regulation of rapid pacing-induced ionic channel remodeling in rat atrial myocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2677–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mollenhauer, M.; Friedrichs, K.; Lange, M.; Gesenberg, J.; Remane, L.; Kerkenpaß, C.; Krause, J.; Schneider, J.; Ravekes, T.; Maass, M.; et al. Myeloperoxidase Mediates Postischemic Arrhythmogenic Ventricular Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desplantez, T. Cardiac Cx43, Cx40 and Cx45 co-assembling: Involvement of connexins epitopes in formation of hemichannels and Gap junction channels. BMC Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, A.J.; Asatryan, B.; Wehrens, X.H. Genetic basis and molecular biology of cardiac arrhythmias in cardiomyopathies. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, J.L.; Lampe, P.D. Connexin43 phosphorylation: Structural changes and biological effects. Biochem. J. 2009, 419, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polontchouk, L.; Ebelt, B.; Jackels, M.; Dhein, S. Chronic effects of endothelin-1 and angiotensin-II on gap junctions and intercellular communication in cardiac cells. FASEB J. 2001, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, A.; Schneider, P.; Mühlberg, K.; Hagendorff, A.; Dhein, S.; Pfeiffer, D. Chronic regulation of the expression of gap junction proteins connexin40, connexin43, and connexin45 in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 503, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Ohkusa, T.; Nao, T.; Lee, J.-K.; Matsumoto, T.; Hisamatsu, Y.; Satoh, T.; Yano, M.; Yasui, K.; Kodama, I.; et al. Rapid electrical stimulation of contraction modulates gap junction protein in neonatal rat cultured cardiomyocytes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yao, J.; Ke, J.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, G.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, W. Combination of HGF and IGF-1 promotes connexin 43 expression and improves ventricular arrhythmia after myocardial infarction through activating the MAPK/ERK and MAPK/p38 signaling pathways in a rat model. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 9, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, A.; Krautblatter, S.; Baeβler, S.; Karl, S.; Gomez, D.R.; Dhein, S.; Pfeiffer, D.; Baessler, S. Signal Transduction and Transcriptional Control of Cardiac Connexin43 Up-Regulation after α1-Adrenoceptor Stimulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liu, H.-J.; Chen, H.-J.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wang, H.-H.; Hung, T.-C.; Yeh, H.-I. AGE-BSA down-regulates endothelial connexin43 gap junctions. BMC Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, R.; Gres, P.; Skyschally, A.; Duschin, A.; Belosjorow, S.; Konietzka, I.; Heusch, G. Ischemic preconditioning preserves connexin 43 phosphorylation during sustained ischemia in pig hearts in vivo. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yan, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, L.; Gou, Z.; Sun, Z.; Talabieke, S.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, D. Connexin 43 dephosphorylation contributes to arrhythmias and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion hearts. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2019, 114, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Hayashi, T.; Kyoizumi, S.; Kusunoki, Y.; Nakachi, K.; Macphee, D.G.; Trosko, J.E.; Kataoka, K.; Yorioka, N. Anisomycin downregulates gap-junctional intercellular communication via the p38 MAP-kinase pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Chang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, P.; Qi, Z.; Zou, J. Up-regulated Cx43 phosphorylation at Ser368 prolongs QRS duration in myocarditis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3537–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newby, L.K.; Marber, M.S.; Melloni, C.; Sarov-Blat, L.; Aberle, L.H.; E Aylward, P.; Cai, G.; De Winter, R.J.; Hamm, C.W.; Heitner, J.F.; et al. Losmapimod, a novel p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, in non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: A randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Glaser, R.; Cavender, M.A.; Aylward, P.E.; Bonaca, M.P.; Budaj, A.; Davies, R.Y.; Dellborg, M.; Fox, K.A.A.; Gutierrez, J.A.T.; et al. Effect of Losmapimod on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Acute Myocardial Infarction. JAMA 2016, 315, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulos, J.; Wijnands, F.P.G.; Alebeek, J.A.J.V.D.H.-V.; Van Vugt, M.J.H.; Rullmann, J.A.C.; Schot, J.-J.G.; De Groot, M.W.G.D.M.; Wagenaars, J.L.; Os, R.V.R.-V.; Smets, R.L.; et al. p38 inhibition and not MK2 inhibition enhances the secretion of chemokines from TNF-? activated rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shiroto, K.; Otani, H.; Yamamoto, F.; Huang, C.-K.; Maulik, N.; Das, D.K. MK2 gene knockout mouse hearts carry anti-apoptotic signal and are resistant to ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2005, 38, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Becerra, R.; Santamans, A.M.; Folgueira, C.; Sabio, G. p38 MAPK Pathway in the Heart: New Insights in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197412
Romero-Becerra R, Santamans AM, Folgueira C, Sabio G. p38 MAPK Pathway in the Heart: New Insights in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197412
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Becerra, Rafael, Ayelén M. Santamans, Cintia Folgueira, and Guadalupe Sabio. 2020. "p38 MAPK Pathway in the Heart: New Insights in Health and Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197412
APA StyleRomero-Becerra, R., Santamans, A. M., Folgueira, C., & Sabio, G. (2020). p38 MAPK Pathway in the Heart: New Insights in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197412




