The Novel Synthetic Peptide AESIS-1 Exerts a Preventive Effect on Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model via STAT3 Suppression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Novel Synthetic Peptide AESIS-1 Exerted Preventive Effects on Collagen-Induced Arthritis In Vivo
2.2. AESIS-1 Suppressed Synovial Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation In Vivo
2.3. AESIS-1 Significantly Upregulated Negative Regulator of STAT3 Signaling (SOCS3), Resulting in Decreased STAT3 Phosphorylation
2.4. AESIS-1 Suppressed IL-17 Production and Th17 Cell Populations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Novel Synthetic Peptide AESIS-1
4.2. Ethics Statement
4.3. Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model
4.4. Evaluation of Arthritic Severity
4.5. Measurement of Collagen-Specific Ig Titers
4.6. Evaluation of Synovial Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation
4.7. JAK/STAT Gene Expression Array
4.8. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.11. Cytokine Array
4.12. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.13. Flow Cytometry
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Steiner, G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommel, C.; Camps, M.; Ji, H. Pi3k delta and pi3k gamma: Partners in crime in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and beyond? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefevre, S.; Knedla, A.; Tennie, C.; Kampmann, A.; Wunrau, C.; Dinser, R.; Korb, A.; Schnaker, E.M.; Tarner, I.H.; Robbins, P.D.; et al. Synovial fibroblasts spread rheumatoid arthritis to unaffected joints. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pope, R.M. Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, A.A.; Reichert, J.M. Future directions for peptide therapeutics development. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Gianturco, L.; Talotta, R.; Varisco, V.; Ditto, M.C.; Turiel, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Investigating the potential side effects of anti-tnf therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: Cause for concern? Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiserman, M.; Codreanu, C.; Handa, R.; Xibille-Friedmann, D.; Mysler, E.; Briceno, F.; Akar, S. The effect of antidrug antibodies on the sustainable efficacy of biologic therapies in rheumatoid arthritis: Practical consequences. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Schoels, M.M.; Nishimoto, N.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Ferraccioli, G.; Gabay, C.; Gibofsky, A.; et al. Consensus statement on blocking the effects of interleukin-6 and in particular by interleukin-6 receptor inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kremer, J.M.; Bloom, B.J.; Breedveld, F.C.; Coombs, J.H.; Fletcher, M.P.; Gruben, D.; Krishnaswami, S.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Wilkinson, B.; Zerbini, C.A.; et al. The safety and efficacy of a jak inhibitor in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase iia trial of three dosage levels of cp-690,550 versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winthrop, K.L. The emerging safety profile of jak inhibitors in rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosgerau, K.; Hoffmann, T. Peptide therapeutics: Current status and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Hu, X. The jak/stat pathway in rheumatoid arthritis: Pathogenic or protective? Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Zhou, S.F. Inflammation, cytokines, the il-17/il-6/stat3/nf-kappab axis, and tumorigenesis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2941–2946. [Google Scholar]
- Oike, T.; Sato, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakamura, S.; Kaneko, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Harato, K.; Saya, H.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. Stat3 as a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isomaki, P.; Junttila, I.; Vidqvist, K.L.; Korpela, M.; Silvennoinen, O. The activity of jak-stat pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: Constitutive activation of stat3 correlates with interleukin 6 levels. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodge, D.R.; Hurt, E.M.; Farrar, W.L. The role of il-6 and stat3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.H.; Rose-John, S. Il-6 biology: Implications for clinical targeting in rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Signal transduction pathways and transcriptional regulation in the control of th17 differentiation. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brand, D.D.; Latham, K.A.; Rosloniec, E.F. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Jia, K.; Jin, Y.; He, B.; Qiu, W.W.; Du, C.; Siwko, S.; Chen, H.; et al. A betulinic acid derivative sh479 inhibits collagen-induced arthritis by modulating t cell differentiation and cytokine balance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 126, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hamburg, J.P.; Tas, S.W. Molecular mechanisms underpinning t helper 17 cell heterogeneity and functions in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 87, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Chiricozzi, A. The immunologic role of il-17 in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van den Berg, W.B.; Miossec, P. Il-17 as a future therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2009, 5, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofani, M.; Madar, A.; Galan, C.; Sellars, M.; Mace, K.; Pauli, F.; Agarwal, A.; Huang, W.; Parkhurst, C.N.; Muratet, M.; et al. A validated regulatory network for th17 cell specification. Cell 2012, 151, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, W.; Dai, Y. Socs3 and its role in associated diseases. Hum. Immunol. 2015, 76, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hanada, T.; Wakioka, T.; Oishi, M.; Miyoshi, K.; Komiya, S.; Kosai, K.; Hanakawa, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; et al. Induction of the cytokine signal regulator socs3/cis3 as a therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.K.; Egan, P.J.; Croker, B.A.; O’Donnell, K.; Sims, N.A.; Drake, S.; Kiu, H.; McManus, E.J.; Alexander, W.S.; Roberts, A.W.; et al. Socs-3 negatively regulates innate and adaptive immune mechanisms in acute il-1-dependent inflammatory arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, K.; Liu, B. Regulation of jak-stat signalling in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto-Konomi, A.; Miyauchi, K.; Ozaki, N.; Motomura, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Suzuki, S.; Cua, D.; Kubo, M. Dysregulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in keratinocytes causes skin inflammation mediated by interleukin-20 receptor-related cytokines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewe, R.; Bijlsma, J.; Burmester, G.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Dougados, M.; Nam, J.; Ramiro, S.; Voshaar, M.; van Vollenhoven, R.; et al. Eular recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 960–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazici, H.; Ozguler, Y.; Hatemi, G.; Yazici, Y. Recommendations in the american college of rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis related to the use of biologic agents in patients with a history of cancer need reconsideration: Comment on the article by singh et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Dell, J.R.; Curtis, J.R.; Mikuls, T.R.; Cofield, S.S.; Bridges, S.L., Jr.; Ranganath, V.K.; Moreland, L.W.; Investigators, T.T. Validation of the methotrexate-first strategy in patients with early, poor-prognosis rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a two-year randomized, double-blind trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klareskog, L.; van der Heijde, D.; de Jager, J.P.; Gough, A.; Kalden, J.; Malaise, M.; Martin Mola, E.; Pavelka, K.; Sany, J.; Settas, L.; et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Koeller, M.; Weisman, M.H.; Emery, P. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2007, 370, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K.; Kawase, I.; Tanaka, T.; Kishimoto, T. Tocilizumab ameliorates clinical symptoms in polymyalgia rheumatica. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1075–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Xu, S. Tnf inhibitor therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norman, P. Selective jak inhibitors in development for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2014, 23, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.C.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Pacheco-Tena, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kinnman, N. Vx-509 (decernotinib), an oral selective jak-3 inhibitor, in combination with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalec, P.; Mikrut, A.; Wisniewska, N.; Pilc, A. The effectiveness of tofacitinib, a novel janus kinase inhibitor, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Bak-Jensen, K.S.; Chen, Y.; Tato, C.M.; Blumenschein, W.; McClanahan, T.; Cua, D.J. Tgf-beta and il-6 drive the production of il-17 and il-10 by t cells and restrain t(h)-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.T.; Kanno, Y.; Cannons, J.L.; Handon, R.; Bible, P.; Elkahloun, A.G.; Anderson, S.M.; Wei, L.; Sun, H.; O’Shea, J.J.; et al. Functional and epigenetic studies reveal multistep differentiation and plasticity of in vitro-generated and in vivo-derived follicular t helper cells. Immunity 2011, 35, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, A.; Naka, T.; Kishimoto, T. Il-6-dependent and -independent pathways in the development of interleukin 17-producing t helper cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12099–12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Su, W.; Lin, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Brand, D.; Ryffel, B.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Adoptive transfer of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis via suppression of th1 and th17 cells and enhancement of regulatory t cell differentiation. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, M.J.; Moon, S.J.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, E.K.; Baek, J.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, K.A.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.S.; et al. Daurinol attenuates autoimmune arthritis via stabilization of nrp1-pten-foxp3 signaling in regulatory t cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


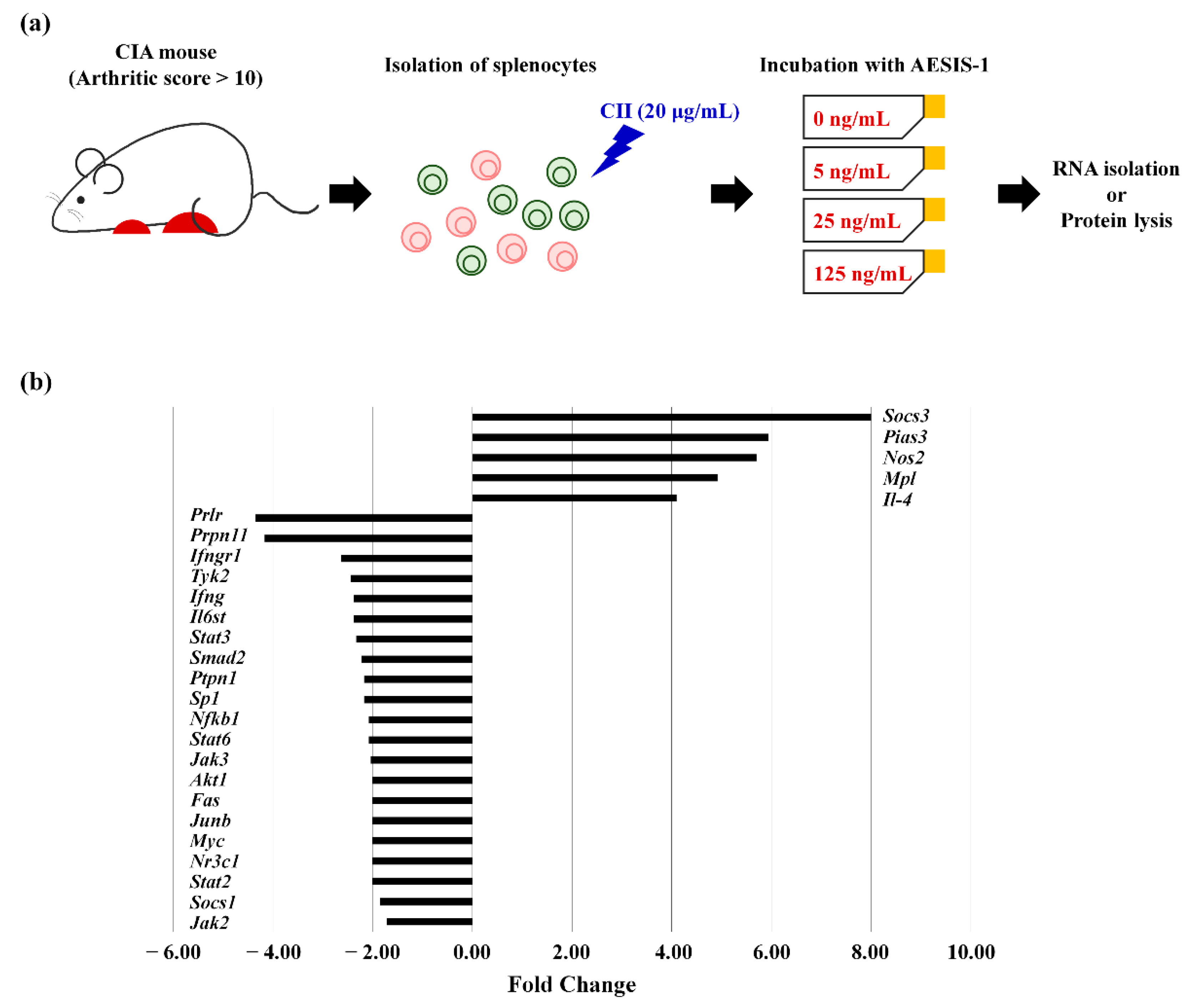



| Gene Name (Gene Symbol) | Fold Change | Function in JAK/STAT-Mediated Signaling |
|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | ||
| Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (Socs3) | 8.00 | Negative regulator of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 |
| Protein inhibitor of activated STAT 3 (Pias3) | 5.94 | Negative regulator of STAT3 |
| Nitric oxide synthase 2 (Nos2) | 6.70 | Genes induced by STAT proteins; Inflammatory response |
| Myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene (Mpl) | 4.92 | Receptor that binds and activates JAK proteins |
| Interleukin-4 (Il-4) | 4.10 | Lymphocyte activation |
| Downregulated | ||
| Prolactin receptor (Prlr) | 0.23 | Receptor that binds and activates JAK proteins |
| Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (Ptpn11) | 0.24 | Involved in the immune response |
| Interferon (alpha and beta) receptor 1 (Ifngr1) | 0.38 | Receptor that binds and activates JAK proteins |
| Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2) | 0.41 | One of the JAKs members |
| Interferon γ (IFNγ) | 0.42 | Transcription factor or regulator that interacts with STAT proteins |
| Interleukin 6 signal transducer (Il-6st) | 0.42 | Receptor that binds and activates JAK proteins |
| Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) | 0.43 | STAT family |
| MAD homolog 2 (Drosophila) (Smad2) | 0.45 | Transcription factor or regulator that interacts with STAT proteins |
| Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 1 (Ptpn1) | 0.46 | Regulator of JAK/ STAT pathway |
| Trans-acting transcription factor 1 (Sp1) | 0.46 | Other transcription factor and regulator |
| Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1, p105 (Nfkb1) | 0.48 | Transcription factor or regulator that interacts with STAT proteins |
| Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (Stat6) | 0.48 | STAT family |
| Janus kinase 3 (Jak3) | 0.49 | Janus kinase activity |
| Thymoma viral proto-oncogene 1 (Akt1) | 0.5 | Apoptosis |
| Fas (TNF receptor superfamily member 6) (Fas) | 0.5 | Apoptosis |
| Jun-B oncogene (Junb) | 0.5 | Genes induced by STAT3 proteins |
| Myelocytomatosis oncogene (Myc) | 0.5 | Genes induced by STAT3 proteins |
| Nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 1 (Nr3c1) | 0.5 | Receptor that binds and activates JAK proteins |
| Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 (Stat2) | 0.5 | STAT family |
| Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (Socs1) | 0.54 | Regulator of JAK/STAT pathway |
| Janus kinase 2 (Jak2) | 0.58 | Janus kinase activity |
| Name | AESIS-1 |
|---|---|
| Sequence | MSLPSPRDGRTDGRTDCTR |
| Number of Residues | 19 |
| Chemical Formula | C82H141N31O31S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 2121.4 g/mol |
| Isoelectric Point | 8.55 |
| Extinction Coefficient | 120·M−1cm−1 |
| Hydrophilicity Analysis | Basic 2 |
| Solubility | Water |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.E.; Jeon, S.; Song, J.; Kim, T.S.; Jung, M.K.; Kim, M.S.; Park, S.; Park, S.B.; Park, J.M.; Park, H.J.; et al. The Novel Synthetic Peptide AESIS-1 Exerts a Preventive Effect on Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model via STAT3 Suppression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020378
Kim KE, Jeon S, Song J, Kim TS, Jung MK, Kim MS, Park S, Park SB, Park JM, Park HJ, et al. The Novel Synthetic Peptide AESIS-1 Exerts a Preventive Effect on Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model via STAT3 Suppression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(2):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020378
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyung Eun, Suwon Jeon, Jisun Song, Tae Sung Kim, Min Kyung Jung, Myun Soo Kim, Sunyoung Park, Seung Beom Park, Jeong Min Park, Hyun Jeong Park, and et al. 2020. "The Novel Synthetic Peptide AESIS-1 Exerts a Preventive Effect on Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model via STAT3 Suppression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 2: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020378
APA StyleKim, K. E., Jeon, S., Song, J., Kim, T. S., Jung, M. K., Kim, M. S., Park, S., Park, S. B., Park, J. M., Park, H. J., & Cho, D. (2020). The Novel Synthetic Peptide AESIS-1 Exerts a Preventive Effect on Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model via STAT3 Suppression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(2), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020378





